mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2024-12-19 17:43:07 +00:00
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> # Objective Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps. Fixes #3629 Before 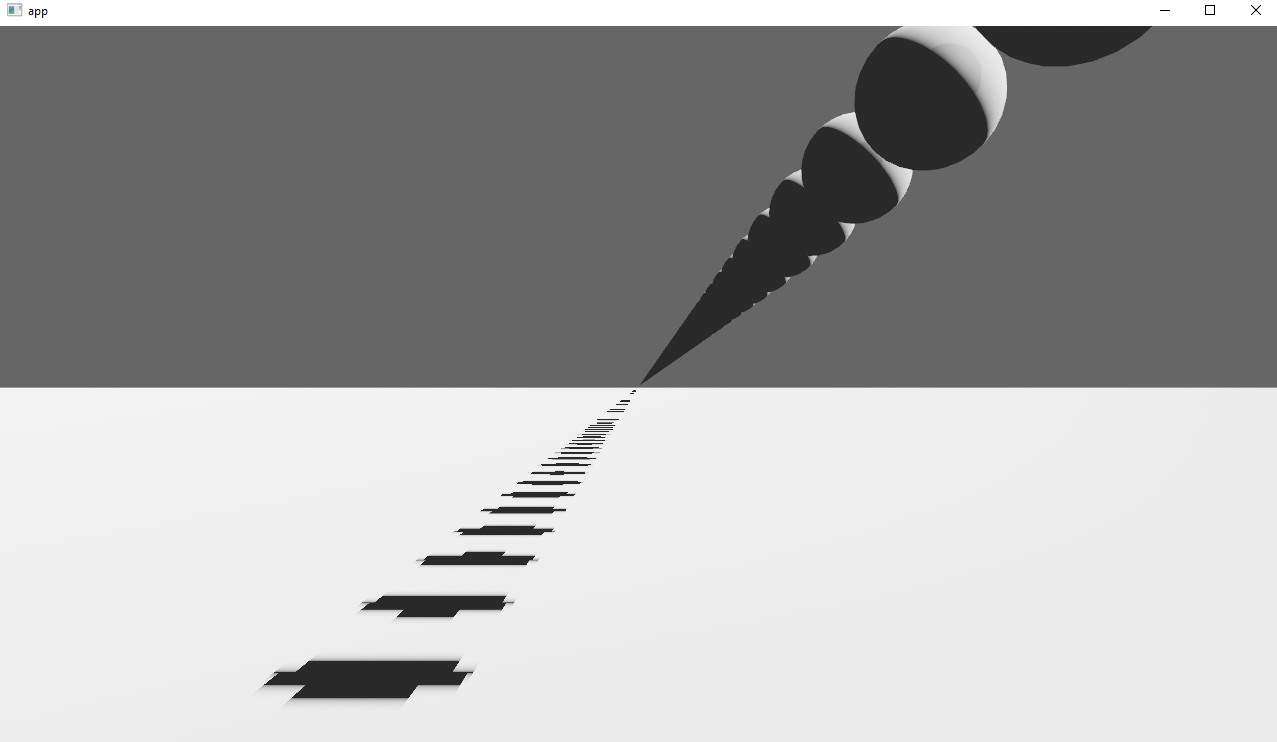 After 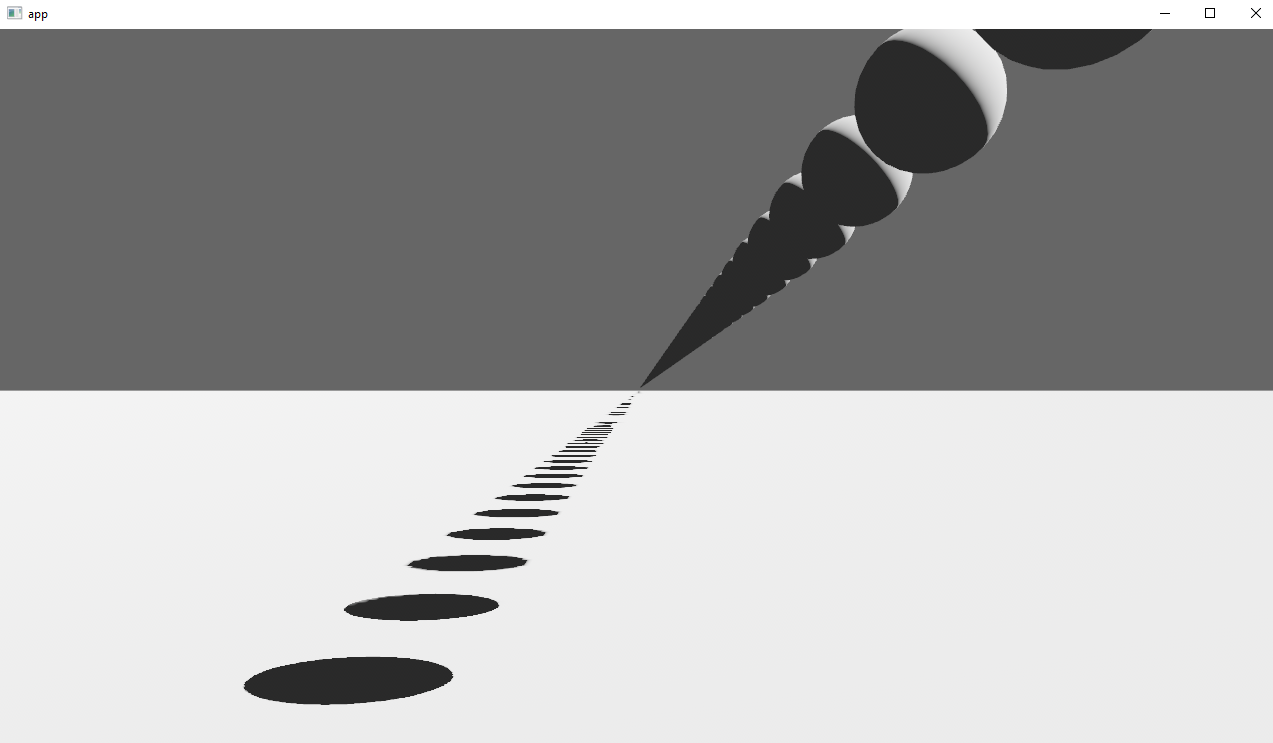 ## Solution Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination. --- ## Changelog Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality. ## Migration Guide You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
2123 lines
84 KiB
Rust
2123 lines
84 KiB
Rust
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||
|
||
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
|
||
use bevy_math::{Mat4, UVec2, UVec3, Vec2, Vec3, Vec3A, Vec3Swizzles, Vec4, Vec4Swizzles};
|
||
use bevy_reflect::prelude::*;
|
||
use bevy_render::{
|
||
camera::Camera,
|
||
color::Color,
|
||
extract_resource::ExtractResource,
|
||
prelude::Projection,
|
||
primitives::{Aabb, CascadesFrusta, CubemapFrusta, Frustum, Plane, Sphere},
|
||
render_resource::BufferBindingType,
|
||
renderer::RenderDevice,
|
||
view::{ComputedVisibility, RenderLayers, VisibleEntities},
|
||
};
|
||
use bevy_transform::{components::GlobalTransform, prelude::Transform};
|
||
use bevy_utils::{tracing::warn, HashMap};
|
||
|
||
use crate::{
|
||
calculate_cluster_factors, spot_light_projection_matrix, spot_light_view_matrix,
|
||
CascadesVisibleEntities, CubeMapFace, CubemapVisibleEntities, ViewClusterBindings,
|
||
CLUSTERED_FORWARD_STORAGE_BUFFER_COUNT, CUBE_MAP_FACES, MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS,
|
||
POINT_LIGHT_NEAR_Z,
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/// A light that emits light in all directions from a central point.
|
||
///
|
||
/// Real-world values for `intensity` (luminous power in lumens) based on the electrical power
|
||
/// consumption of the type of real-world light are:
|
||
///
|
||
/// | Luminous Power (lumen) (i.e. the intensity member) | Incandescent non-halogen (Watts) | Incandescent halogen (Watts) | Compact fluorescent (Watts) | LED (Watts |
|
||
/// |------|-----|----|--------|-------|
|
||
/// | 200 | 25 | | 3-5 | 3 |
|
||
/// | 450 | 40 | 29 | 9-11 | 5-8 |
|
||
/// | 800 | 60 | | 13-15 | 8-12 |
|
||
/// | 1100 | 75 | 53 | 18-20 | 10-16 |
|
||
/// | 1600 | 100 | 72 | 24-28 | 14-17 |
|
||
/// | 2400 | 150 | | 30-52 | 24-30 |
|
||
/// | 3100 | 200 | | 49-75 | 32 |
|
||
/// | 4000 | 300 | | 75-100 | 40.5 |
|
||
///
|
||
/// Source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lumen_(unit)#Lighting)
|
||
#[derive(Component, Debug, Clone, Copy, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component, Default)]
|
||
pub struct PointLight {
|
||
pub color: Color,
|
||
pub intensity: f32,
|
||
pub range: f32,
|
||
pub radius: f32,
|
||
pub shadows_enabled: bool,
|
||
pub shadow_depth_bias: f32,
|
||
/// A bias applied along the direction of the fragment's surface normal. It is scaled to the
|
||
/// shadow map's texel size so that it can be small close to the camera and gets larger further
|
||
/// away.
|
||
pub shadow_normal_bias: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for PointLight {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
PointLight {
|
||
color: Color::rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
|
||
/// Luminous power in lumens
|
||
intensity: 800.0, // Roughly a 60W non-halogen incandescent bulb
|
||
range: 20.0,
|
||
radius: 0.0,
|
||
shadows_enabled: false,
|
||
shadow_depth_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS,
|
||
shadow_normal_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl PointLight {
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS: f32 = 0.02;
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS: f32 = 0.6;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Resource, Clone, Debug, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Resource)]
|
||
pub struct PointLightShadowMap {
|
||
pub size: usize,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for PointLightShadowMap {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
Self { size: 1024 }
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// A light that emits light in a given direction from a central point.
|
||
/// Behaves like a point light in a perfectly absorbant housing that
|
||
/// shines light only in a given direction. The direction is taken from
|
||
/// the transform, and can be specified with [`Transform::looking_at`](bevy_transform::components::Transform::looking_at).
|
||
#[derive(Component, Debug, Clone, Copy, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component, Default)]
|
||
pub struct SpotLight {
|
||
pub color: Color,
|
||
pub intensity: f32,
|
||
pub range: f32,
|
||
pub radius: f32,
|
||
pub shadows_enabled: bool,
|
||
pub shadow_depth_bias: f32,
|
||
/// A bias applied along the direction of the fragment's surface normal. It is scaled to the
|
||
/// shadow map's texel size so that it can be small close to the camera and gets larger further
|
||
/// away.
|
||
pub shadow_normal_bias: f32,
|
||
/// Angle defining the distance from the spot light direction to the outer limit
|
||
/// of the light's cone of effect.
|
||
/// `outer_angle` should be < `PI / 2.0`.
|
||
/// `PI / 2.0` defines a hemispherical spot light, but shadows become very blocky as the angle
|
||
/// approaches this limit.
|
||
pub outer_angle: f32,
|
||
/// Angle defining the distance from the spot light direction to the inner limit
|
||
/// of the light's cone of effect.
|
||
/// Light is attenuated from `inner_angle` to `outer_angle` to give a smooth falloff.
|
||
/// `inner_angle` should be <= `outer_angle`
|
||
pub inner_angle: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl SpotLight {
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS: f32 = 0.02;
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS: f32 = 0.6;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for SpotLight {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
// a quarter arc attenuating from the centre
|
||
Self {
|
||
color: Color::rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
|
||
/// Luminous power in lumens
|
||
intensity: 800.0, // Roughly a 60W non-halogen incandescent bulb
|
||
range: 20.0,
|
||
radius: 0.0,
|
||
shadows_enabled: false,
|
||
shadow_depth_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS,
|
||
shadow_normal_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS,
|
||
inner_angle: 0.0,
|
||
outer_angle: std::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_4,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// A Directional light.
|
||
///
|
||
/// Directional lights don't exist in reality but they are a good
|
||
/// approximation for light sources VERY far away, like the sun or
|
||
/// the moon.
|
||
///
|
||
/// The light shines along the forward direction of the entity's transform. With a default transform
|
||
/// this would be along the negative-Z axis.
|
||
///
|
||
/// Valid values for `illuminance` are:
|
||
///
|
||
/// | Illuminance (lux) | Surfaces illuminated by |
|
||
/// |-------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||
/// | 0.0001 | Moonless, overcast night sky (starlight) |
|
||
/// | 0.002 | Moonless clear night sky with airglow |
|
||
/// | 0.05–0.3 | Full moon on a clear night |
|
||
/// | 3.4 | Dark limit of civil twilight under a clear sky |
|
||
/// | 20–50 | Public areas with dark surroundings |
|
||
/// | 50 | Family living room lights |
|
||
/// | 80 | Office building hallway/toilet lighting |
|
||
/// | 100 | Very dark overcast day |
|
||
/// | 150 | Train station platforms |
|
||
/// | 320–500 | Office lighting |
|
||
/// | 400 | Sunrise or sunset on a clear day. |
|
||
/// | 1000 | Overcast day; typical TV studio lighting |
|
||
/// | 10,000–25,000 | Full daylight (not direct sun) |
|
||
/// | 32,000–100,000 | Direct sunlight |
|
||
///
|
||
/// Source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lux)
|
||
///
|
||
/// ## Shadows
|
||
///
|
||
/// To enable shadows, set the `shadows_enabled` property to `true`.
|
||
///
|
||
/// Shadows are produced via [cascaded shadow maps](https://developer.download.nvidia.com/SDK/10.5/opengl/src/cascaded_shadow_maps/doc/cascaded_shadow_maps.pdf).
|
||
///
|
||
/// To modify the cascade set up, such as the number of cascades or the maximum shadow distance,
|
||
/// change the [`CascadeShadowConfig`] component of the [`crate::bundle::DirectionalLightBundle`].
|
||
///
|
||
/// To control the resolution of the shadow maps, use the [`DirectionalLightShadowMap`] resource:
|
||
///
|
||
/// ```
|
||
/// # use bevy_app::prelude::*;
|
||
/// # use bevy_pbr::DirectionalLightShadowMap;
|
||
/// App::new()
|
||
/// .insert_resource(DirectionalLightShadowMap { size: 2048 });
|
||
/// ```
|
||
#[derive(Component, Debug, Clone, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component, Default)]
|
||
pub struct DirectionalLight {
|
||
pub color: Color,
|
||
/// Illuminance in lux
|
||
pub illuminance: f32,
|
||
pub shadows_enabled: bool,
|
||
pub shadow_depth_bias: f32,
|
||
/// A bias applied along the direction of the fragment's surface normal. It is scaled to the
|
||
/// shadow map's texel size so that it is automatically adjusted to the orthographic projection.
|
||
pub shadow_normal_bias: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for DirectionalLight {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
DirectionalLight {
|
||
color: Color::rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
|
||
illuminance: 100000.0,
|
||
shadows_enabled: false,
|
||
shadow_depth_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS,
|
||
shadow_normal_bias: Self::DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl DirectionalLight {
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_DEPTH_BIAS: f32 = 0.02;
|
||
pub const DEFAULT_SHADOW_NORMAL_BIAS: f32 = 0.6;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// Controls the resolution of [`DirectionalLight`] shadow maps.
|
||
#[derive(Resource, Clone, Debug, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Resource)]
|
||
pub struct DirectionalLightShadowMap {
|
||
pub size: usize,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for DirectionalLightShadowMap {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
#[cfg(feature = "webgl")]
|
||
return Self { size: 1024 };
|
||
#[cfg(not(feature = "webgl"))]
|
||
return Self { size: 2048 };
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// Controls how cascaded shadow mapping works.
|
||
#[derive(Component, Clone, Debug, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component)]
|
||
pub struct CascadeShadowConfig {
|
||
/// The (positive) distance to the far boundary of each cascade.
|
||
pub bounds: Vec<f32>,
|
||
/// The proportion of overlap each cascade has with the previous cascade.
|
||
pub overlap_proportion: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for CascadeShadowConfig {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
if cfg!(feature = "webgl") {
|
||
// Currently only support one cascade in webgl.
|
||
Self::new(1, 5.0, 100.0, 0.2)
|
||
} else {
|
||
Self::new(4, 5.0, 1000.0, 0.2)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn calculate_cascade_bounds(
|
||
num_cascades: usize,
|
||
nearest_bound: f32,
|
||
shadow_maximum_distance: f32,
|
||
) -> Vec<f32> {
|
||
if num_cascades == 1 {
|
||
return vec![shadow_maximum_distance];
|
||
}
|
||
let base = (shadow_maximum_distance / nearest_bound).powf(1.0 / (num_cascades - 1) as f32);
|
||
(0..num_cascades)
|
||
.map(|i| nearest_bound * base.powf(i as f32))
|
||
.collect()
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl CascadeShadowConfig {
|
||
/// Returns a cascade config for `num_cascades` cascades, with the first cascade
|
||
/// having far bound `nearest_bound` and the last cascade having far bound `shadow_maximum_distance`.
|
||
/// In-between cascades will be exponentially spaced.
|
||
pub fn new(
|
||
num_cascades: usize,
|
||
nearest_bound: f32,
|
||
shadow_maximum_distance: f32,
|
||
overlap_proportion: f32,
|
||
) -> Self {
|
||
assert!(
|
||
num_cascades > 0,
|
||
"num_cascades must be positive, but was {}",
|
||
num_cascades
|
||
);
|
||
assert!(
|
||
(0.0..1.0).contains(&overlap_proportion),
|
||
"overlap_proportion must be in [0.0, 1.0) but was {}",
|
||
overlap_proportion
|
||
);
|
||
Self {
|
||
bounds: calculate_cascade_bounds(num_cascades, nearest_bound, shadow_maximum_distance),
|
||
overlap_proportion,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Component, Clone, Debug, Default, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component)]
|
||
pub struct Cascades {
|
||
/// Map from a view to the configuration of each of its [`Cascade`]s.
|
||
pub(crate) cascades: HashMap<Entity, Vec<Cascade>>,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Clone, Debug, Default, Reflect, FromReflect)]
|
||
pub struct Cascade {
|
||
/// The transform of the light, i.e. the view to world matrix.
|
||
pub(crate) view_transform: Mat4,
|
||
/// The orthographic projection for this cascade.
|
||
pub(crate) projection: Mat4,
|
||
/// The view-projection matrix for this cacade, converting world space into light clip space.
|
||
/// Importantly, this is derived and stored separately from `view_transform` and `projection` to
|
||
/// ensure shadow stability.
|
||
pub(crate) view_projection: Mat4,
|
||
/// Size of each shadow map texel in world units.
|
||
pub(crate) texel_size: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn update_directional_light_cascades(
|
||
directional_light_shadow_map: Res<DirectionalLightShadowMap>,
|
||
views: Query<(Entity, &GlobalTransform, &Projection, &Camera)>,
|
||
mut lights: Query<(
|
||
&GlobalTransform,
|
||
&DirectionalLight,
|
||
&CascadeShadowConfig,
|
||
&mut Cascades,
|
||
)>,
|
||
) {
|
||
let views = views
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.filter_map(|view| match view {
|
||
// TODO: orthographic camera projection support.
|
||
(entity, transform, Projection::Perspective(projection), camera)
|
||
if camera.is_active =>
|
||
{
|
||
Some((
|
||
entity,
|
||
projection.aspect_ratio,
|
||
(0.5 * projection.fov).tan(),
|
||
transform.compute_matrix(),
|
||
))
|
||
}
|
||
_ => None,
|
||
})
|
||
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
|
||
|
||
for (transform, directional_light, cascades_config, mut cascades) in lights.iter_mut() {
|
||
if !directional_light.shadows_enabled {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// It is very important to the numerical and thus visual stability of shadows that
|
||
// light_to_world has orthogonal upper-left 3x3 and zero translation.
|
||
// Even though only the direction (i.e. rotation) of the light matters, we don't constrain
|
||
// users to not change any other aspects of the transform - there's no guarantee
|
||
// `transform.compute_matrix()` will give us a matrix with our desired properties.
|
||
// Instead, we directly create a good matrix from just the rotation.
|
||
let light_to_world = Mat4::from_quat(transform.compute_transform().rotation);
|
||
let light_to_world_inverse = light_to_world.inverse();
|
||
|
||
cascades.cascades.clear();
|
||
for (view_entity, aspect_ratio, tan_half_fov, view_to_world) in views.iter().copied() {
|
||
let camera_to_light_view = light_to_world_inverse * view_to_world;
|
||
let view_cascades = cascades_config
|
||
.bounds
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.enumerate()
|
||
.map(|(idx, far_bound)| {
|
||
calculate_cascade(
|
||
aspect_ratio,
|
||
tan_half_fov,
|
||
directional_light_shadow_map.size as f32,
|
||
light_to_world,
|
||
camera_to_light_view,
|
||
// Negate bounds as -z is camera forward direction.
|
||
if idx > 0 {
|
||
(1.0 - cascades_config.overlap_proportion)
|
||
* -cascades_config.bounds[idx - 1]
|
||
} else {
|
||
0.0
|
||
},
|
||
-far_bound,
|
||
)
|
||
})
|
||
.collect();
|
||
cascades.cascades.insert(view_entity, view_cascades);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn calculate_cascade(
|
||
aspect_ratio: f32,
|
||
tan_half_fov: f32,
|
||
cascade_texture_size: f32,
|
||
light_to_world: Mat4,
|
||
camera_to_light: Mat4,
|
||
z_near: f32,
|
||
z_far: f32,
|
||
) -> Cascade {
|
||
debug_assert!(z_near <= 0.0, "z_near {} must be <= 0.0", z_near);
|
||
debug_assert!(z_far <= 0.0, "z_far {} must be <= 0.0", z_far);
|
||
// NOTE: This whole function is very sensitive to floating point precision and instability and
|
||
// has followed instructions to avoid view dependence from the section on cascade shadow maps in
|
||
// Eric Lengyel's Foundations of Game Engine Development 2: Rendering. Be very careful when
|
||
// modifying this code!
|
||
|
||
let a = z_near.abs() * tan_half_fov;
|
||
let b = z_far.abs() * tan_half_fov;
|
||
// NOTE: These vertices are in a specific order: bottom right, top right, top left, bottom left
|
||
// for near then for far
|
||
let frustum_corners = [
|
||
Vec3A::new(a * aspect_ratio, -a, z_near),
|
||
Vec3A::new(a * aspect_ratio, a, z_near),
|
||
Vec3A::new(-a * aspect_ratio, a, z_near),
|
||
Vec3A::new(-a * aspect_ratio, -a, z_near),
|
||
Vec3A::new(b * aspect_ratio, -b, z_far),
|
||
Vec3A::new(b * aspect_ratio, b, z_far),
|
||
Vec3A::new(-b * aspect_ratio, b, z_far),
|
||
Vec3A::new(-b * aspect_ratio, -b, z_far),
|
||
];
|
||
|
||
let mut min = Vec3A::splat(f32::MAX);
|
||
let mut max = Vec3A::splat(f32::MIN);
|
||
for corner_camera_view in frustum_corners {
|
||
let corner_light_view = camera_to_light.transform_point3a(corner_camera_view);
|
||
min = min.min(corner_light_view);
|
||
max = max.max(corner_light_view);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Use the larger of the frustum slice far plane diagonal and body diagonal lengths as this
|
||
// will be the maximum possible projection size. Use the ceiling to get an integer which is
|
||
// very important for floating point stability later. It is also important that these are
|
||
// calculated using the original camera space corner positions for floating point precision
|
||
// as even though the lengths using corner_light_view above should be the same, precision can
|
||
// introduce small but significant differences.
|
||
// NOTE: The size remains the same unless the view frustum or cascade configuration is modified.
|
||
let cascade_diameter = (frustum_corners[0] - frustum_corners[6])
|
||
.length()
|
||
.max((frustum_corners[4] - frustum_corners[6]).length())
|
||
.ceil();
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: If we ensure that cascade_texture_size is a power of 2, then as we made cascade_diameter an
|
||
// integer, cascade_texel_size is then an integer multiple of a power of 2 and can be
|
||
// exactly represented in a floating point value.
|
||
let cascade_texel_size = cascade_diameter / cascade_texture_size;
|
||
// NOTE: For shadow stability it is very important that the near_plane_center is at integer
|
||
// multiples of the texel size to be exactly representable in a floating point value.
|
||
let near_plane_center = Vec3A::new(
|
||
(0.5 * (min.x + max.x) / cascade_texel_size).floor() * cascade_texel_size,
|
||
(0.5 * (min.y + max.y) / cascade_texel_size).floor() * cascade_texel_size,
|
||
// NOTE: max.z is the near plane for right-handed y-up
|
||
max.z,
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// It is critical for `world_to_cascade` to be stable. So rather than forming `cascade_to_world`
|
||
// and inverting it, which risks instability due to numerical precision, we directly form
|
||
// `world_to_cascde` as the reference material suggests.
|
||
let light_to_world_transpose = light_to_world.transpose();
|
||
let world_to_cascade = Mat4::from_cols(
|
||
light_to_world_transpose.x_axis,
|
||
light_to_world_transpose.y_axis,
|
||
light_to_world_transpose.z_axis,
|
||
(-near_plane_center).extend(1.0),
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// Right-handed orthographic projection, centered at `near_plane_center`.
|
||
// NOTE: This is different from the reference material, as we use reverse Z.
|
||
let r = (max.z - min.z).recip();
|
||
let cascade_projection = Mat4::from_cols(
|
||
Vec4::new(2.0 / cascade_diameter, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
|
||
Vec4::new(0.0, 2.0 / cascade_diameter, 0.0, 0.0),
|
||
Vec4::new(0.0, 0.0, r, 0.0),
|
||
Vec4::new(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0),
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let cascade_view_projection = cascade_projection * world_to_cascade;
|
||
Cascade {
|
||
view_transform: world_to_cascade.inverse(),
|
||
projection: cascade_projection,
|
||
view_projection: cascade_view_projection,
|
||
texel_size: cascade_texel_size,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// An ambient light, which lights the entire scene equally.
|
||
#[derive(Resource, Clone, Debug, ExtractResource, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Resource)]
|
||
pub struct AmbientLight {
|
||
pub color: Color,
|
||
/// A direct scale factor multiplied with `color` before being passed to the shader.
|
||
pub brightness: f32,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for AmbientLight {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
Self {
|
||
color: Color::rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
|
||
brightness: 0.05,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// Add this component to make a [`Mesh`](bevy_render::mesh::Mesh) not cast shadows.
|
||
#[derive(Component, Reflect, Default)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component, Default)]
|
||
pub struct NotShadowCaster;
|
||
/// Add this component to make a [`Mesh`](bevy_render::mesh::Mesh) not receive shadows.
|
||
#[derive(Component, Reflect, Default)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component, Default)]
|
||
pub struct NotShadowReceiver;
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Debug, Hash, PartialEq, Eq, Clone, SystemLabel)]
|
||
pub enum SimulationLightSystems {
|
||
AddClusters,
|
||
AssignLightsToClusters,
|
||
UpdateDirectionalLightCascades,
|
||
UpdateLightFrusta,
|
||
CheckLightVisibility,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Clustered-forward rendering notes
|
||
// The main initial reference material used was this rather accessible article:
|
||
// http://www.aortiz.me/2018/12/21/CG.html
|
||
// Some inspiration was taken from “Practical Clustered Shading” which is part 2 of:
|
||
// https://efficientshading.com/2015/01/01/real-time-many-light-management-and-shadows-with-clustered-shading/
|
||
// (Also note that Part 3 of the above shows how we could support the shadow mapping for many lights.)
|
||
// The z-slicing method mentioned in the aortiz article is originally from Tiago Sousa's Siggraph 2016 talk about Doom 2016:
|
||
// http://advances.realtimerendering.com/s2016/Siggraph2016_idTech6.pdf
|
||
|
||
/// Configure the far z-plane mode used for the furthest depth slice for clustered forward
|
||
/// rendering
|
||
#[derive(Debug, Copy, Clone, Reflect, FromReflect)]
|
||
pub enum ClusterFarZMode {
|
||
/// Calculate the required maximum z-depth based on currently visible lights.
|
||
/// Makes better use of available clusters, speeding up GPU lighting operations
|
||
/// at the expense of some CPU time and using more indices in the cluster light
|
||
/// index lists.
|
||
MaxLightRange,
|
||
/// Constant max z-depth
|
||
Constant(f32),
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// Configure the depth-slicing strategy for clustered forward rendering
|
||
#[derive(Debug, Copy, Clone, Reflect, FromReflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Default)]
|
||
pub struct ClusterZConfig {
|
||
/// Far `Z` plane of the first depth slice
|
||
pub first_slice_depth: f32,
|
||
/// Strategy for how to evaluate the far `Z` plane of the furthest depth slice
|
||
pub far_z_mode: ClusterFarZMode,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for ClusterZConfig {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
Self {
|
||
first_slice_depth: 5.0,
|
||
far_z_mode: ClusterFarZMode::MaxLightRange,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/// Configuration of the clustering strategy for clustered forward rendering
|
||
#[derive(Debug, Copy, Clone, Component, Reflect)]
|
||
#[reflect(Component)]
|
||
pub enum ClusterConfig {
|
||
/// Disable light cluster calculations for this view
|
||
None,
|
||
/// One single cluster. Optimal for low-light complexity scenes or scenes where
|
||
/// most lights affect the entire scene.
|
||
Single,
|
||
/// Explicit `X`, `Y` and `Z` counts (may yield non-square `X/Y` clusters depending on the aspect ratio)
|
||
XYZ {
|
||
dimensions: UVec3,
|
||
z_config: ClusterZConfig,
|
||
/// Specify if clusters should automatically resize in `X/Y` if there is a risk of exceeding
|
||
/// the available cluster-light index limit
|
||
dynamic_resizing: bool,
|
||
},
|
||
/// Fixed number of `Z` slices, `X` and `Y` calculated to give square clusters
|
||
/// with at most total clusters. For top-down games where lights will generally always be within a
|
||
/// short depth range, it may be useful to use this configuration with 1 or few `Z` slices. This
|
||
/// would reduce the number of lights per cluster by distributing more clusters in screen space
|
||
/// `X/Y` which matches how lights are distributed in the scene.
|
||
FixedZ {
|
||
total: u32,
|
||
z_slices: u32,
|
||
z_config: ClusterZConfig,
|
||
/// Specify if clusters should automatically resize in `X/Y` if there is a risk of exceeding
|
||
/// the available cluster-light index limit
|
||
dynamic_resizing: bool,
|
||
},
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Default for ClusterConfig {
|
||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||
// 24 depth slices, square clusters with at most 4096 total clusters
|
||
// use max light distance as clusters max `Z`-depth, first slice extends to 5.0
|
||
Self::FixedZ {
|
||
total: 4096,
|
||
z_slices: 24,
|
||
z_config: ClusterZConfig::default(),
|
||
dynamic_resizing: true,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl ClusterConfig {
|
||
fn dimensions_for_screen_size(&self, screen_size: UVec2) -> UVec3 {
|
||
match &self {
|
||
ClusterConfig::None => UVec3::ZERO,
|
||
ClusterConfig::Single => UVec3::ONE,
|
||
ClusterConfig::XYZ { dimensions, .. } => *dimensions,
|
||
ClusterConfig::FixedZ {
|
||
total, z_slices, ..
|
||
} => {
|
||
let aspect_ratio = screen_size.x as f32 / screen_size.y as f32;
|
||
let mut z_slices = *z_slices;
|
||
if *total < z_slices {
|
||
warn!("ClusterConfig has more z-slices than total clusters!");
|
||
z_slices = *total;
|
||
}
|
||
let per_layer = *total as f32 / z_slices as f32;
|
||
|
||
let y = f32::sqrt(per_layer / aspect_ratio);
|
||
|
||
let mut x = (y * aspect_ratio) as u32;
|
||
let mut y = y as u32;
|
||
|
||
// check extremes
|
||
if x == 0 {
|
||
x = 1;
|
||
y = per_layer as u32;
|
||
}
|
||
if y == 0 {
|
||
x = per_layer as u32;
|
||
y = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
UVec3::new(x, y, z_slices)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn first_slice_depth(&self) -> f32 {
|
||
match self {
|
||
ClusterConfig::None | ClusterConfig::Single => 0.0,
|
||
ClusterConfig::XYZ { z_config, .. } | ClusterConfig::FixedZ { z_config, .. } => {
|
||
z_config.first_slice_depth
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn far_z_mode(&self) -> ClusterFarZMode {
|
||
match self {
|
||
ClusterConfig::None => ClusterFarZMode::Constant(0.0),
|
||
ClusterConfig::Single => ClusterFarZMode::MaxLightRange,
|
||
ClusterConfig::XYZ { z_config, .. } | ClusterConfig::FixedZ { z_config, .. } => {
|
||
z_config.far_z_mode
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn dynamic_resizing(&self) -> bool {
|
||
match self {
|
||
ClusterConfig::None | ClusterConfig::Single => false,
|
||
ClusterConfig::XYZ {
|
||
dynamic_resizing, ..
|
||
}
|
||
| ClusterConfig::FixedZ {
|
||
dynamic_resizing, ..
|
||
} => *dynamic_resizing,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Component, Debug, Default)]
|
||
pub struct Clusters {
|
||
/// Tile size
|
||
pub(crate) tile_size: UVec2,
|
||
/// Number of clusters in `X` / `Y` / `Z` in the view frustum
|
||
pub(crate) dimensions: UVec3,
|
||
/// Distance to the far plane of the first depth slice. The first depth slice is special
|
||
/// and explicitly-configured to avoid having unnecessarily many slices close to the camera.
|
||
pub(crate) near: f32,
|
||
pub(crate) far: f32,
|
||
pub(crate) lights: Vec<VisiblePointLights>,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl Clusters {
|
||
fn update(&mut self, screen_size: UVec2, requested_dimensions: UVec3) {
|
||
debug_assert!(
|
||
requested_dimensions.x > 0 && requested_dimensions.y > 0 && requested_dimensions.z > 0
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let tile_size = (screen_size.as_vec2() / requested_dimensions.xy().as_vec2())
|
||
.ceil()
|
||
.as_uvec2()
|
||
.max(UVec2::ONE);
|
||
self.tile_size = tile_size;
|
||
self.dimensions = (screen_size.as_vec2() / tile_size.as_vec2())
|
||
.ceil()
|
||
.as_uvec2()
|
||
.extend(requested_dimensions.z)
|
||
.max(UVec3::ONE);
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Maximum 4096 clusters due to uniform buffer size constraints
|
||
debug_assert!(self.dimensions.x * self.dimensions.y * self.dimensions.z <= 4096);
|
||
}
|
||
fn clear(&mut self) {
|
||
self.tile_size = UVec2::ONE;
|
||
self.dimensions = UVec3::ZERO;
|
||
self.near = 0.0;
|
||
self.far = 0.0;
|
||
self.lights.clear();
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn clip_to_view(inverse_projection: Mat4, clip: Vec4) -> Vec4 {
|
||
let view = inverse_projection * clip;
|
||
view / view.w
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn add_clusters(
|
||
mut commands: Commands,
|
||
cameras: Query<(Entity, Option<&ClusterConfig>), (With<Camera>, Without<Clusters>)>,
|
||
) {
|
||
for (entity, config) in &cameras {
|
||
let config = config.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
// actual settings here don't matter - they will be overwritten in assign_lights_to_clusters
|
||
commands
|
||
.entity(entity)
|
||
.insert((Clusters::default(), config));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Clone, Component, Debug, Default)]
|
||
pub struct VisiblePointLights {
|
||
pub(crate) entities: Vec<Entity>,
|
||
pub point_light_count: usize,
|
||
pub spot_light_count: usize,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl VisiblePointLights {
|
||
#[inline]
|
||
pub fn iter(&self) -> impl DoubleEndedIterator<Item = &Entity> {
|
||
self.entities.iter()
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[inline]
|
||
pub fn len(&self) -> usize {
|
||
self.entities.len()
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[inline]
|
||
pub fn is_empty(&self) -> bool {
|
||
self.entities.is_empty()
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Keep in sync with bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl
|
||
fn view_z_to_z_slice(
|
||
cluster_factors: Vec2,
|
||
z_slices: u32,
|
||
view_z: f32,
|
||
is_orthographic: bool,
|
||
) -> u32 {
|
||
let z_slice = if is_orthographic {
|
||
// NOTE: view_z is correct in the orthographic case
|
||
((view_z - cluster_factors.x) * cluster_factors.y).floor() as u32
|
||
} else {
|
||
// NOTE: had to use -view_z to make it positive else log(negative) is nan
|
||
((-view_z).ln() * cluster_factors.x - cluster_factors.y + 1.0) as u32
|
||
};
|
||
// NOTE: We use min as we may limit the far z plane used for clustering to be closer than
|
||
// the furthest thing being drawn. This means that we need to limit to the maximum cluster.
|
||
z_slice.min(z_slices - 1)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Keep in sync as the inverse of view_z_to_z_slice above
|
||
fn z_slice_to_view_z(
|
||
near: f32,
|
||
far: f32,
|
||
z_slices: u32,
|
||
z_slice: u32,
|
||
is_orthographic: bool,
|
||
) -> f32 {
|
||
if is_orthographic {
|
||
return -near - (far - near) * z_slice as f32 / z_slices as f32;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Perspective
|
||
if z_slice == 0 {
|
||
0.0
|
||
} else {
|
||
-near * (far / near).powf((z_slice - 1) as f32 / (z_slices - 1) as f32)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn ndc_position_to_cluster(
|
||
cluster_dimensions: UVec3,
|
||
cluster_factors: Vec2,
|
||
is_orthographic: bool,
|
||
ndc_p: Vec3,
|
||
view_z: f32,
|
||
) -> UVec3 {
|
||
let cluster_dimensions_f32 = cluster_dimensions.as_vec3();
|
||
let frag_coord = (ndc_p.xy() * VEC2_HALF_NEGATIVE_Y + VEC2_HALF).clamp(Vec2::ZERO, Vec2::ONE);
|
||
let xy = (frag_coord * cluster_dimensions_f32.xy()).floor();
|
||
let z_slice = view_z_to_z_slice(
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
cluster_dimensions.z,
|
||
view_z,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
);
|
||
xy.as_uvec2()
|
||
.extend(z_slice)
|
||
.clamp(UVec3::ZERO, cluster_dimensions - UVec3::ONE)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
const VEC2_HALF: Vec2 = Vec2::splat(0.5);
|
||
const VEC2_HALF_NEGATIVE_Y: Vec2 = Vec2::new(0.5, -0.5);
|
||
|
||
/// Calculate bounds for the light using a view space aabb.
|
||
/// Returns a `(Vec3, Vec3)` containing minimum and maximum with
|
||
/// `X` and `Y` in normalized device coordinates with range `[-1, 1]`
|
||
/// `Z` in view space, with range `[-inf, -f32::MIN_POSITIVE]`
|
||
fn cluster_space_light_aabb(
|
||
inverse_view_transform: Mat4,
|
||
projection_matrix: Mat4,
|
||
light_sphere: &Sphere,
|
||
) -> (Vec3, Vec3) {
|
||
let light_aabb_view = Aabb {
|
||
center: Vec3A::from(inverse_view_transform * light_sphere.center.extend(1.0)),
|
||
half_extents: Vec3A::splat(light_sphere.radius),
|
||
};
|
||
let (mut light_aabb_view_min, mut light_aabb_view_max) =
|
||
(light_aabb_view.min(), light_aabb_view.max());
|
||
|
||
// Constrain view z to be negative - i.e. in front of the camera
|
||
// When view z is >= 0.0 and we're using a perspective projection, bad things happen.
|
||
// At view z == 0.0, ndc x,y are mathematically undefined. At view z > 0.0, i.e. behind the camera,
|
||
// the perspective projection flips the directions of the axes. This breaks assumptions about
|
||
// use of min/max operations as something that was to the left in view space is now returning a
|
||
// coordinate that for view z in front of the camera would be on the right, but at view z behind the
|
||
// camera is on the left. So, we just constrain view z to be < 0.0 and necessarily in front of the camera.
|
||
light_aabb_view_min.z = light_aabb_view_min.z.min(-f32::MIN_POSITIVE);
|
||
light_aabb_view_max.z = light_aabb_view_max.z.min(-f32::MIN_POSITIVE);
|
||
|
||
// Is there a cheaper way to do this? The problem is that because of perspective
|
||
// the point at max z but min xy may be less xy in screenspace, and similar. As
|
||
// such, projecting the min and max xy at both the closer and further z and taking
|
||
// the min and max of those projected points addresses this.
|
||
let (
|
||
light_aabb_view_xymin_near,
|
||
light_aabb_view_xymin_far,
|
||
light_aabb_view_xymax_near,
|
||
light_aabb_view_xymax_far,
|
||
) = (
|
||
light_aabb_view_min,
|
||
light_aabb_view_min.xy().extend(light_aabb_view_max.z),
|
||
light_aabb_view_max.xy().extend(light_aabb_view_min.z),
|
||
light_aabb_view_max,
|
||
);
|
||
let (
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymin_near,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymin_far,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymax_near,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymax_far,
|
||
) = (
|
||
projection_matrix * light_aabb_view_xymin_near.extend(1.0),
|
||
projection_matrix * light_aabb_view_xymin_far.extend(1.0),
|
||
projection_matrix * light_aabb_view_xymax_near.extend(1.0),
|
||
projection_matrix * light_aabb_view_xymax_far.extend(1.0),
|
||
);
|
||
let (
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymin_near,
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymin_far,
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymax_near,
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymax_far,
|
||
) = (
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymin_near.xyz() / light_aabb_clip_xymin_near.w,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymin_far.xyz() / light_aabb_clip_xymin_far.w,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymax_near.xyz() / light_aabb_clip_xymax_near.w,
|
||
light_aabb_clip_xymax_far.xyz() / light_aabb_clip_xymax_far.w,
|
||
);
|
||
let (light_aabb_ndc_min, light_aabb_ndc_max) = (
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymin_near
|
||
.min(light_aabb_ndc_xymin_far)
|
||
.min(light_aabb_ndc_xymax_near)
|
||
.min(light_aabb_ndc_xymax_far),
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_xymin_near
|
||
.max(light_aabb_ndc_xymin_far)
|
||
.max(light_aabb_ndc_xymax_near)
|
||
.max(light_aabb_ndc_xymax_far),
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// clamp to ndc coords without depth
|
||
let (aabb_min_ndc, aabb_max_ndc) = (
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_min.xy().clamp(NDC_MIN, NDC_MAX),
|
||
light_aabb_ndc_max.xy().clamp(NDC_MIN, NDC_MAX),
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// pack unadjusted z depth into the vecs
|
||
(
|
||
aabb_min_ndc.extend(light_aabb_view_min.z),
|
||
aabb_max_ndc.extend(light_aabb_view_max.z),
|
||
)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
fn screen_to_view(screen_size: Vec2, inverse_projection: Mat4, screen: Vec2, ndc_z: f32) -> Vec4 {
|
||
let tex_coord = screen / screen_size;
|
||
let clip = Vec4::new(
|
||
tex_coord.x * 2.0 - 1.0,
|
||
(1.0 - tex_coord.y) * 2.0 - 1.0,
|
||
ndc_z,
|
||
1.0,
|
||
);
|
||
clip_to_view(inverse_projection, clip)
|
||
}
|
||
const NDC_MIN: Vec2 = Vec2::NEG_ONE;
|
||
const NDC_MAX: Vec2 = Vec2::ONE;
|
||
|
||
// Calculate the intersection of a ray from the eye through the view space position to a z plane
|
||
fn line_intersection_to_z_plane(origin: Vec3, p: Vec3, z: f32) -> Vec3 {
|
||
let v = p - origin;
|
||
let t = (z - Vec3::Z.dot(origin)) / Vec3::Z.dot(v);
|
||
origin + t * v
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[allow(clippy::too_many_arguments)]
|
||
fn compute_aabb_for_cluster(
|
||
z_near: f32,
|
||
z_far: f32,
|
||
tile_size: Vec2,
|
||
screen_size: Vec2,
|
||
inverse_projection: Mat4,
|
||
is_orthographic: bool,
|
||
cluster_dimensions: UVec3,
|
||
ijk: UVec3,
|
||
) -> Aabb {
|
||
let ijk = ijk.as_vec3();
|
||
|
||
// Calculate the minimum and maximum points in screen space
|
||
let p_min = ijk.xy() * tile_size;
|
||
let p_max = p_min + tile_size;
|
||
|
||
let cluster_min;
|
||
let cluster_max;
|
||
if is_orthographic {
|
||
// Use linear depth slicing for orthographic
|
||
|
||
// Convert to view space at the cluster near and far planes
|
||
// NOTE: 1.0 is the near plane due to using reverse z projections
|
||
let p_min = screen_to_view(
|
||
screen_size,
|
||
inverse_projection,
|
||
p_min,
|
||
1.0 - (ijk.z / cluster_dimensions.z as f32),
|
||
)
|
||
.xyz();
|
||
let p_max = screen_to_view(
|
||
screen_size,
|
||
inverse_projection,
|
||
p_max,
|
||
1.0 - ((ijk.z + 1.0) / cluster_dimensions.z as f32),
|
||
)
|
||
.xyz();
|
||
|
||
cluster_min = p_min.min(p_max);
|
||
cluster_max = p_min.max(p_max);
|
||
} else {
|
||
// Convert to view space at the near plane
|
||
// NOTE: 1.0 is the near plane due to using reverse z projections
|
||
let p_min = screen_to_view(screen_size, inverse_projection, p_min, 1.0);
|
||
let p_max = screen_to_view(screen_size, inverse_projection, p_max, 1.0);
|
||
|
||
let z_far_over_z_near = -z_far / -z_near;
|
||
let cluster_near = if ijk.z == 0.0 {
|
||
0.0
|
||
} else {
|
||
-z_near * z_far_over_z_near.powf((ijk.z - 1.0) / (cluster_dimensions.z - 1) as f32)
|
||
};
|
||
// NOTE: This could be simplified to:
|
||
// cluster_far = cluster_near * z_far_over_z_near;
|
||
let cluster_far = if cluster_dimensions.z == 1 {
|
||
-z_far
|
||
} else {
|
||
-z_near * z_far_over_z_near.powf(ijk.z / (cluster_dimensions.z - 1) as f32)
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// Calculate the four intersection points of the min and max points with the cluster near and far planes
|
||
let p_min_near = line_intersection_to_z_plane(Vec3::ZERO, p_min.xyz(), cluster_near);
|
||
let p_min_far = line_intersection_to_z_plane(Vec3::ZERO, p_min.xyz(), cluster_far);
|
||
let p_max_near = line_intersection_to_z_plane(Vec3::ZERO, p_max.xyz(), cluster_near);
|
||
let p_max_far = line_intersection_to_z_plane(Vec3::ZERO, p_max.xyz(), cluster_far);
|
||
|
||
cluster_min = p_min_near.min(p_min_far).min(p_max_near.min(p_max_far));
|
||
cluster_max = p_min_near.max(p_min_far).max(p_max_near.max(p_max_far));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
Aabb::from_min_max(cluster_min, cluster_max)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Sort lights by
|
||
// - point-light vs spot-light, so that we can iterate point lights and spot lights in contiguous blocks in the fragment shader,
|
||
// - then those with shadows enabled first, so that the index can be used to render at most `point_light_shadow_maps_count`
|
||
// point light shadows and `spot_light_shadow_maps_count` spot light shadow maps,
|
||
// - then by entity as a stable key to ensure that a consistent set of lights are chosen if the light count limit is exceeded.
|
||
pub(crate) fn point_light_order(
|
||
(entity_1, shadows_enabled_1, is_spot_light_1): (&Entity, &bool, &bool),
|
||
(entity_2, shadows_enabled_2, is_spot_light_2): (&Entity, &bool, &bool),
|
||
) -> std::cmp::Ordering {
|
||
is_spot_light_1
|
||
.cmp(is_spot_light_2) // pointlights before spot lights
|
||
.then_with(|| shadows_enabled_2.cmp(shadows_enabled_1)) // shadow casters before non-casters
|
||
.then_with(|| entity_1.cmp(entity_2)) // stable
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Sort lights by
|
||
// - those with shadows enabled first, so that the index can be used to render at most `directional_light_shadow_maps_count`
|
||
// directional light shadows
|
||
// - then by entity as a stable key to ensure that a consistent set of lights are chosen if the light count limit is exceeded.
|
||
pub(crate) fn directional_light_order(
|
||
(entity_1, shadows_enabled_1): (&Entity, &bool),
|
||
(entity_2, shadows_enabled_2): (&Entity, &bool),
|
||
) -> std::cmp::Ordering {
|
||
shadows_enabled_2
|
||
.cmp(shadows_enabled_1) // shadow casters before non-casters
|
||
.then_with(|| entity_1.cmp(entity_2)) // stable
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Clone, Copy)]
|
||
// data required for assigning lights to clusters
|
||
pub(crate) struct PointLightAssignmentData {
|
||
entity: Entity,
|
||
transform: GlobalTransform,
|
||
range: f32,
|
||
shadows_enabled: bool,
|
||
spot_light_angle: Option<f32>,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl PointLightAssignmentData {
|
||
pub fn sphere(&self) -> Sphere {
|
||
Sphere {
|
||
center: self.transform.translation_vec3a(),
|
||
radius: self.range,
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[derive(Resource, Default)]
|
||
pub struct GlobalVisiblePointLights {
|
||
entities: HashSet<Entity>,
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
impl GlobalVisiblePointLights {
|
||
#[inline]
|
||
pub fn iter(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = &Entity> {
|
||
self.entities.iter()
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[inline]
|
||
pub fn contains(&self, entity: Entity) -> bool {
|
||
self.entities.contains(&entity)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Run this before update_point_light_frusta!
|
||
#[allow(clippy::too_many_arguments)]
|
||
pub(crate) fn assign_lights_to_clusters(
|
||
mut commands: Commands,
|
||
mut global_lights: ResMut<GlobalVisiblePointLights>,
|
||
mut views: Query<(
|
||
Entity,
|
||
&GlobalTransform,
|
||
&Camera,
|
||
&Frustum,
|
||
&ClusterConfig,
|
||
&mut Clusters,
|
||
Option<&mut VisiblePointLights>,
|
||
)>,
|
||
point_lights_query: Query<(Entity, &GlobalTransform, &PointLight, &ComputedVisibility)>,
|
||
spot_lights_query: Query<(Entity, &GlobalTransform, &SpotLight, &ComputedVisibility)>,
|
||
mut lights: Local<Vec<PointLightAssignmentData>>,
|
||
mut cluster_aabb_spheres: Local<Vec<Option<Sphere>>>,
|
||
mut max_point_lights_warning_emitted: Local<bool>,
|
||
render_device: Option<Res<RenderDevice>>,
|
||
) {
|
||
let render_device = match render_device {
|
||
Some(render_device) => render_device,
|
||
None => return,
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
global_lights.entities.clear();
|
||
lights.clear();
|
||
// collect just the relevant light query data into a persisted vec to avoid reallocating each frame
|
||
lights.extend(
|
||
point_lights_query
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.filter(|(.., visibility)| visibility.is_visible())
|
||
.map(
|
||
|(entity, transform, point_light, _visibility)| PointLightAssignmentData {
|
||
entity,
|
||
transform: GlobalTransform::from_translation(transform.translation()),
|
||
shadows_enabled: point_light.shadows_enabled,
|
||
range: point_light.range,
|
||
spot_light_angle: None,
|
||
},
|
||
),
|
||
);
|
||
lights.extend(
|
||
spot_lights_query
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.filter(|(.., visibility)| visibility.is_visible())
|
||
.map(
|
||
|(entity, transform, spot_light, _visibility)| PointLightAssignmentData {
|
||
entity,
|
||
transform: *transform,
|
||
shadows_enabled: spot_light.shadows_enabled,
|
||
range: spot_light.range,
|
||
spot_light_angle: Some(spot_light.outer_angle),
|
||
},
|
||
),
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let clustered_forward_buffer_binding_type =
|
||
render_device.get_supported_read_only_binding_type(CLUSTERED_FORWARD_STORAGE_BUFFER_COUNT);
|
||
let supports_storage_buffers = matches!(
|
||
clustered_forward_buffer_binding_type,
|
||
BufferBindingType::Storage { .. }
|
||
);
|
||
if lights.len() > MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS && !supports_storage_buffers {
|
||
lights.sort_by(|light_1, light_2| {
|
||
point_light_order(
|
||
(
|
||
&light_1.entity,
|
||
&light_1.shadows_enabled,
|
||
&light_1.spot_light_angle.is_some(),
|
||
),
|
||
(
|
||
&light_2.entity,
|
||
&light_2.shadows_enabled,
|
||
&light_2.spot_light_angle.is_some(),
|
||
),
|
||
)
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
// check each light against each view's frustum, keep only those that affect at least one of our views
|
||
let frusta: Vec<_> = views
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.map(|(_, _, _, frustum, _, _, _)| *frustum)
|
||
.collect();
|
||
let mut lights_in_view_count = 0;
|
||
lights.retain(|light| {
|
||
// take one extra light to check if we should emit the warning
|
||
if lights_in_view_count == MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS + 1 {
|
||
false
|
||
} else {
|
||
let light_sphere = light.sphere();
|
||
let light_in_view = frusta
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.any(|frustum| frustum.intersects_sphere(&light_sphere, true));
|
||
|
||
if light_in_view {
|
||
lights_in_view_count += 1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
light_in_view
|
||
}
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
if lights.len() > MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS && !*max_point_lights_warning_emitted {
|
||
warn!(
|
||
"MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS ({}) exceeded",
|
||
MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS
|
||
);
|
||
*max_point_lights_warning_emitted = true;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
lights.truncate(MAX_UNIFORM_BUFFER_POINT_LIGHTS);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for (view_entity, camera_transform, camera, frustum, config, clusters, mut visible_lights) in
|
||
&mut views
|
||
{
|
||
let clusters = clusters.into_inner();
|
||
|
||
if matches!(config, ClusterConfig::None) {
|
||
if visible_lights.is_some() {
|
||
commands.entity(view_entity).remove::<VisiblePointLights>();
|
||
}
|
||
clusters.clear();
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let Some(screen_size) = camera.physical_viewport_size() else {
|
||
clusters.clear();
|
||
continue;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
let mut requested_cluster_dimensions = config.dimensions_for_screen_size(screen_size);
|
||
|
||
let view_transform = camera_transform.compute_matrix();
|
||
let inverse_view_transform = view_transform.inverse();
|
||
let is_orthographic = camera.projection_matrix().w_axis.w == 1.0;
|
||
|
||
let far_z = match config.far_z_mode() {
|
||
ClusterFarZMode::MaxLightRange => {
|
||
let inverse_view_row_2 = inverse_view_transform.row(2);
|
||
lights
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.map(|light| {
|
||
-inverse_view_row_2.dot(light.transform.translation().extend(1.0))
|
||
+ light.range
|
||
})
|
||
.reduce(f32::max)
|
||
.unwrap_or(0.0)
|
||
}
|
||
ClusterFarZMode::Constant(far) => far,
|
||
};
|
||
let first_slice_depth = match (is_orthographic, requested_cluster_dimensions.z) {
|
||
(true, _) => {
|
||
// NOTE: Based on glam's Mat4::orthographic_rh(), as used to calculate the orthographic projection
|
||
// matrix, we can calculate the projection's view-space near plane as follows:
|
||
// component 3,2 = r * near and 2,2 = r where r = 1.0 / (near - far)
|
||
// There is a caveat here that when calculating the projection matrix, near and far were swapped to give
|
||
// reversed z, consistent with the perspective projection. So,
|
||
// 3,2 = r * far and 2,2 = r where r = 1.0 / (far - near)
|
||
// rearranging r = 1.0 / (far - near), r * (far - near) = 1.0, r * far - 1.0 = r * near, near = (r * far - 1.0) / r
|
||
// = (3,2 - 1.0) / 2,2
|
||
(camera.projection_matrix().w_axis.z - 1.0) / camera.projection_matrix().z_axis.z
|
||
}
|
||
(false, 1) => config.first_slice_depth().max(far_z),
|
||
_ => config.first_slice_depth(),
|
||
};
|
||
// NOTE: Ensure the far_z is at least as far as the first_depth_slice to avoid clustering problems.
|
||
let far_z = far_z.max(first_slice_depth);
|
||
let cluster_factors = calculate_cluster_factors(
|
||
first_slice_depth,
|
||
far_z,
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.z as f32,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
if config.dynamic_resizing() {
|
||
let mut cluster_index_estimate = 0.0;
|
||
for light in &lights {
|
||
let light_sphere = light.sphere();
|
||
|
||
// Check if the light is within the view frustum
|
||
if !frustum.intersects_sphere(&light_sphere, true) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// calculate a conservative aabb estimate of number of clusters affected by this light
|
||
// this overestimates index counts by at most 50% (and typically much less) when the whole light range is in view
|
||
// it can overestimate more significantly when light ranges are only partially in view
|
||
let (light_aabb_min, light_aabb_max) = cluster_space_light_aabb(
|
||
inverse_view_transform,
|
||
camera.projection_matrix(),
|
||
&light_sphere,
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// since we won't adjust z slices we can calculate exact number of slices required in z dimension
|
||
let z_cluster_min = view_z_to_z_slice(
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.z,
|
||
light_aabb_min.z,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
);
|
||
let z_cluster_max = view_z_to_z_slice(
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.z,
|
||
light_aabb_max.z,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
);
|
||
let z_count =
|
||
z_cluster_min.max(z_cluster_max) - z_cluster_min.min(z_cluster_max) + 1;
|
||
|
||
// calculate x/y count using floats to avoid overestimating counts due to large initial tile sizes
|
||
let xy_min = light_aabb_min.xy();
|
||
let xy_max = light_aabb_max.xy();
|
||
// multiply by 0.5 to move from [-1,1] to [-0.5, 0.5], max extent of 1 in each dimension
|
||
let xy_count = (xy_max - xy_min)
|
||
* 0.5
|
||
* Vec2::new(
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.x as f32,
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.y as f32,
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
// add up to 2 to each axis to account for overlap
|
||
let x_overlap = if xy_min.x <= -1.0 { 0.0 } else { 1.0 }
|
||
+ if xy_max.x >= 1.0 { 0.0 } else { 1.0 };
|
||
let y_overlap = if xy_min.y <= -1.0 { 0.0 } else { 1.0 }
|
||
+ if xy_max.y >= 1.0 { 0.0 } else { 1.0 };
|
||
cluster_index_estimate +=
|
||
(xy_count.x + x_overlap) * (xy_count.y + y_overlap) * z_count as f32;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if cluster_index_estimate > ViewClusterBindings::MAX_INDICES as f32 {
|
||
// scale x and y cluster count to be able to fit all our indices
|
||
|
||
// we take the ratio of the actual indices over the index estimate.
|
||
// this not not guaranteed to be small enough due to overlapped tiles, but
|
||
// the conservative estimate is more than sufficient to cover the
|
||
// difference
|
||
let index_ratio = ViewClusterBindings::MAX_INDICES as f32 / cluster_index_estimate;
|
||
let xy_ratio = index_ratio.sqrt();
|
||
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.x =
|
||
((requested_cluster_dimensions.x as f32 * xy_ratio).floor() as u32).max(1);
|
||
requested_cluster_dimensions.y =
|
||
((requested_cluster_dimensions.y as f32 * xy_ratio).floor() as u32).max(1);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
clusters.update(screen_size, requested_cluster_dimensions);
|
||
clusters.near = first_slice_depth;
|
||
clusters.far = far_z;
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Maximum 4096 clusters due to uniform buffer size constraints
|
||
debug_assert!(
|
||
clusters.dimensions.x * clusters.dimensions.y * clusters.dimensions.z <= 4096
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let inverse_projection = camera.projection_matrix().inverse();
|
||
|
||
for lights in &mut clusters.lights {
|
||
lights.entities.clear();
|
||
lights.point_light_count = 0;
|
||
lights.spot_light_count = 0;
|
||
}
|
||
let cluster_count =
|
||
(clusters.dimensions.x * clusters.dimensions.y * clusters.dimensions.z) as usize;
|
||
clusters
|
||
.lights
|
||
.resize_with(cluster_count, VisiblePointLights::default);
|
||
|
||
// initialize empty cluster bounding spheres
|
||
cluster_aabb_spheres.clear();
|
||
cluster_aabb_spheres.extend(std::iter::repeat(None).take(cluster_count));
|
||
|
||
// Calculate the x/y/z cluster frustum planes in view space
|
||
let mut x_planes = Vec::with_capacity(clusters.dimensions.x as usize + 1);
|
||
let mut y_planes = Vec::with_capacity(clusters.dimensions.y as usize + 1);
|
||
let mut z_planes = Vec::with_capacity(clusters.dimensions.z as usize + 1);
|
||
|
||
if is_orthographic {
|
||
let x_slices = clusters.dimensions.x as f32;
|
||
for x in 0..=clusters.dimensions.x {
|
||
let x_proportion = x as f32 / x_slices;
|
||
let x_pos = x_proportion * 2.0 - 1.0;
|
||
let view_x = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(x_pos, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)).x;
|
||
let normal = Vec3::X;
|
||
let d = view_x * normal.x;
|
||
x_planes.push(Plane::new(normal.extend(d)));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let y_slices = clusters.dimensions.y as f32;
|
||
for y in 0..=clusters.dimensions.y {
|
||
let y_proportion = 1.0 - y as f32 / y_slices;
|
||
let y_pos = y_proportion * 2.0 - 1.0;
|
||
let view_y = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(0.0, y_pos, 1.0, 1.0)).y;
|
||
let normal = Vec3::Y;
|
||
let d = view_y * normal.y;
|
||
y_planes.push(Plane::new(normal.extend(d)));
|
||
}
|
||
} else {
|
||
let x_slices = clusters.dimensions.x as f32;
|
||
for x in 0..=clusters.dimensions.x {
|
||
let x_proportion = x as f32 / x_slices;
|
||
let x_pos = x_proportion * 2.0 - 1.0;
|
||
let nb = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(x_pos, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0)).xyz();
|
||
let nt = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(x_pos, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)).xyz();
|
||
let normal = nb.cross(nt);
|
||
let d = nb.dot(normal);
|
||
x_planes.push(Plane::new(normal.extend(d)));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let y_slices = clusters.dimensions.y as f32;
|
||
for y in 0..=clusters.dimensions.y {
|
||
let y_proportion = 1.0 - y as f32 / y_slices;
|
||
let y_pos = y_proportion * 2.0 - 1.0;
|
||
let nl = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(-1.0, y_pos, 1.0, 1.0)).xyz();
|
||
let nr = clip_to_view(inverse_projection, Vec4::new(1.0, y_pos, 1.0, 1.0)).xyz();
|
||
let normal = nr.cross(nl);
|
||
let d = nr.dot(normal);
|
||
y_planes.push(Plane::new(normal.extend(d)));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let z_slices = clusters.dimensions.z;
|
||
for z in 0..=z_slices {
|
||
let view_z = z_slice_to_view_z(first_slice_depth, far_z, z_slices, z, is_orthographic);
|
||
let normal = -Vec3::Z;
|
||
let d = view_z * normal.z;
|
||
z_planes.push(Plane::new(normal.extend(d)));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let mut update_from_light_intersections = |visible_lights: &mut Vec<Entity>| {
|
||
for light in &lights {
|
||
let light_sphere = light.sphere();
|
||
|
||
// Check if the light is within the view frustum
|
||
if !frustum.intersects_sphere(&light_sphere, true) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: The light intersects the frustum so it must be visible and part of the global set
|
||
global_lights.entities.insert(light.entity);
|
||
visible_lights.push(light.entity);
|
||
|
||
// note: caching seems to be slower than calling twice for this aabb calculation
|
||
let (light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_min, light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_max) =
|
||
cluster_space_light_aabb(
|
||
inverse_view_transform,
|
||
camera.projection_matrix(),
|
||
&light_sphere,
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let min_cluster = ndc_position_to_cluster(
|
||
clusters.dimensions,
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_min,
|
||
light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_min.z,
|
||
);
|
||
let max_cluster = ndc_position_to_cluster(
|
||
clusters.dimensions,
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_max,
|
||
light_aabb_xy_ndc_z_view_max.z,
|
||
);
|
||
let (min_cluster, max_cluster) =
|
||
(min_cluster.min(max_cluster), min_cluster.max(max_cluster));
|
||
|
||
// What follows is the Iterative Sphere Refinement algorithm from Just Cause 3
|
||
// Persson et al, Practical Clustered Shading
|
||
// http://newq.net/dl/pub/s2015_practical.pdf
|
||
// NOTE: A sphere under perspective projection is no longer a sphere. It gets
|
||
// stretched and warped, which prevents simpler algorithms from being correct
|
||
// as they often assume that the widest part of the sphere under projection is the
|
||
// center point on the axis of interest plus the radius, and that is not true!
|
||
let view_light_sphere = Sphere {
|
||
center: Vec3A::from(inverse_view_transform * light_sphere.center.extend(1.0)),
|
||
radius: light_sphere.radius,
|
||
};
|
||
let spot_light_dir_sin_cos = light.spot_light_angle.map(|angle| {
|
||
let (angle_sin, angle_cos) = angle.sin_cos();
|
||
(
|
||
(inverse_view_transform * light.transform.back().extend(0.0)).truncate(),
|
||
angle_sin,
|
||
angle_cos,
|
||
)
|
||
});
|
||
let light_center_clip =
|
||
camera.projection_matrix() * view_light_sphere.center.extend(1.0);
|
||
let light_center_ndc = light_center_clip.xyz() / light_center_clip.w;
|
||
let cluster_coordinates = ndc_position_to_cluster(
|
||
clusters.dimensions,
|
||
cluster_factors,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
light_center_ndc,
|
||
view_light_sphere.center.z,
|
||
);
|
||
let z_center = if light_center_ndc.z <= 1.0 {
|
||
Some(cluster_coordinates.z)
|
||
} else {
|
||
None
|
||
};
|
||
let y_center = if light_center_ndc.y > 1.0 {
|
||
None
|
||
} else if light_center_ndc.y < -1.0 {
|
||
Some(clusters.dimensions.y + 1)
|
||
} else {
|
||
Some(cluster_coordinates.y)
|
||
};
|
||
for z in min_cluster.z..=max_cluster.z {
|
||
let mut z_light = view_light_sphere.clone();
|
||
if z_center.is_none() || z != z_center.unwrap() {
|
||
// The z plane closer to the light has the larger radius circle where the
|
||
// light sphere intersects the z plane.
|
||
let z_plane = if z_center.is_some() && z < z_center.unwrap() {
|
||
z_planes[(z + 1) as usize]
|
||
} else {
|
||
z_planes[z as usize]
|
||
};
|
||
// Project the sphere to this z plane and use its radius as the radius of a
|
||
// new, refined sphere.
|
||
if let Some(projected) = project_to_plane_z(z_light, z_plane) {
|
||
z_light = projected;
|
||
} else {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
for y in min_cluster.y..=max_cluster.y {
|
||
let mut y_light = z_light.clone();
|
||
if y_center.is_none() || y != y_center.unwrap() {
|
||
// The y plane closer to the light has the larger radius circle where the
|
||
// light sphere intersects the y plane.
|
||
let y_plane = if y_center.is_some() && y < y_center.unwrap() {
|
||
y_planes[(y + 1) as usize]
|
||
} else {
|
||
y_planes[y as usize]
|
||
};
|
||
// Project the refined sphere to this y plane and use its radius as the
|
||
// radius of a new, even more refined sphere.
|
||
if let Some(projected) =
|
||
project_to_plane_y(y_light, y_plane, is_orthographic)
|
||
{
|
||
y_light = projected;
|
||
} else {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// Loop from the left to find the first affected cluster
|
||
let mut min_x = min_cluster.x;
|
||
loop {
|
||
if min_x >= max_cluster.x
|
||
|| -get_distance_x(
|
||
x_planes[(min_x + 1) as usize],
|
||
y_light.center,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
) + y_light.radius
|
||
> 0.0
|
||
{
|
||
break;
|
||
}
|
||
min_x += 1;
|
||
}
|
||
// Loop from the right to find the last affected cluster
|
||
let mut max_x = max_cluster.x;
|
||
loop {
|
||
if max_x <= min_x
|
||
|| get_distance_x(
|
||
x_planes[max_x as usize],
|
||
y_light.center,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
) + y_light.radius
|
||
> 0.0
|
||
{
|
||
break;
|
||
}
|
||
max_x -= 1;
|
||
}
|
||
let mut cluster_index = ((y * clusters.dimensions.x + min_x)
|
||
* clusters.dimensions.z
|
||
+ z) as usize;
|
||
|
||
if let Some((view_light_direction, angle_sin, angle_cos)) =
|
||
spot_light_dir_sin_cos
|
||
{
|
||
for x in min_x..=max_x {
|
||
// further culling for spot lights
|
||
// get or initialize cluster bounding sphere
|
||
let cluster_aabb_sphere = &mut cluster_aabb_spheres[cluster_index];
|
||
let cluster_aabb_sphere = if let Some(sphere) = cluster_aabb_sphere
|
||
{
|
||
&*sphere
|
||
} else {
|
||
let aabb = compute_aabb_for_cluster(
|
||
first_slice_depth,
|
||
far_z,
|
||
clusters.tile_size.as_vec2(),
|
||
screen_size.as_vec2(),
|
||
inverse_projection,
|
||
is_orthographic,
|
||
clusters.dimensions,
|
||
UVec3::new(x, y, z),
|
||
);
|
||
let sphere = Sphere {
|
||
center: aabb.center,
|
||
radius: aabb.half_extents.length(),
|
||
};
|
||
*cluster_aabb_sphere = Some(sphere);
|
||
cluster_aabb_sphere.as_ref().unwrap()
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// test -- based on https://bartwronski.com/2017/04/13/cull-that-cone/
|
||
let spot_light_offset = Vec3::from(
|
||
view_light_sphere.center - cluster_aabb_sphere.center,
|
||
);
|
||
let spot_light_dist_sq = spot_light_offset.length_squared();
|
||
let v1_len = spot_light_offset.dot(view_light_direction);
|
||
|
||
let distance_closest_point = (angle_cos
|
||
* (spot_light_dist_sq - v1_len * v1_len).sqrt())
|
||
- v1_len * angle_sin;
|
||
let angle_cull =
|
||
distance_closest_point > cluster_aabb_sphere.radius;
|
||
|
||
let front_cull = v1_len > cluster_aabb_sphere.radius + light.range;
|
||
let back_cull = v1_len < -cluster_aabb_sphere.radius;
|
||
|
||
if !angle_cull && !front_cull && !back_cull {
|
||
// this cluster is affected by the spot light
|
||
clusters.lights[cluster_index].entities.push(light.entity);
|
||
clusters.lights[cluster_index].spot_light_count += 1;
|
||
}
|
||
cluster_index += clusters.dimensions.z as usize;
|
||
}
|
||
} else {
|
||
for _ in min_x..=max_x {
|
||
// all clusters within range are affected by point lights
|
||
clusters.lights[cluster_index].entities.push(light.entity);
|
||
clusters.lights[cluster_index].point_light_count += 1;
|
||
cluster_index += clusters.dimensions.z as usize;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// reuse existing visible lights Vec, if it exists
|
||
if let Some(visible_lights) = visible_lights.as_mut() {
|
||
visible_lights.entities.clear();
|
||
update_from_light_intersections(&mut visible_lights.entities);
|
||
} else {
|
||
let mut entities = Vec::new();
|
||
update_from_light_intersections(&mut entities);
|
||
commands.entity(view_entity).insert(VisiblePointLights {
|
||
entities,
|
||
..Default::default()
|
||
});
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: This exploits the fact that a x-plane normal has only x and z components
|
||
fn get_distance_x(plane: Plane, point: Vec3A, is_orthographic: bool) -> f32 {
|
||
if is_orthographic {
|
||
point.x - plane.d()
|
||
} else {
|
||
// Distance from a point to a plane:
|
||
// signed distance to plane = (nx * px + ny * py + nz * pz + d) / n.length()
|
||
// NOTE: For a x-plane, ny and d are 0 and we have a unit normal
|
||
// = nx * px + nz * pz
|
||
plane.normal_d().xz().dot(point.xz())
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: This exploits the fact that a z-plane normal has only a z component
|
||
fn project_to_plane_z(z_light: Sphere, z_plane: Plane) -> Option<Sphere> {
|
||
// p = sphere center
|
||
// n = plane normal
|
||
// d = n.p if p is in the plane
|
||
// NOTE: For a z-plane, nx and ny are both 0
|
||
// d = px * nx + py * ny + pz * nz
|
||
// = pz * nz
|
||
// => pz = d / nz
|
||
let z = z_plane.d() / z_plane.normal_d().z;
|
||
let distance_to_plane = z - z_light.center.z;
|
||
if distance_to_plane.abs() > z_light.radius {
|
||
return None;
|
||
}
|
||
Some(Sphere {
|
||
center: Vec3A::from(z_light.center.xy().extend(z)),
|
||
// hypotenuse length = radius
|
||
// pythagoras = (distance to plane)^2 + b^2 = radius^2
|
||
radius: (z_light.radius * z_light.radius - distance_to_plane * distance_to_plane).sqrt(),
|
||
})
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: This exploits the fact that a y-plane normal has only y and z components
|
||
fn project_to_plane_y(y_light: Sphere, y_plane: Plane, is_orthographic: bool) -> Option<Sphere> {
|
||
let distance_to_plane = if is_orthographic {
|
||
y_plane.d() - y_light.center.y
|
||
} else {
|
||
-y_light.center.yz().dot(y_plane.normal_d().yz())
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
if distance_to_plane.abs() > y_light.radius {
|
||
return None;
|
||
}
|
||
Some(Sphere {
|
||
center: y_light.center + distance_to_plane * y_plane.normal(),
|
||
radius: (y_light.radius * y_light.radius - distance_to_plane * distance_to_plane).sqrt(),
|
||
})
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn update_directional_light_frusta(
|
||
mut views: Query<
|
||
(
|
||
&Cascades,
|
||
&DirectionalLight,
|
||
&ComputedVisibility,
|
||
&mut CascadesFrusta,
|
||
),
|
||
(
|
||
// Prevents this query from conflicting with camera queries.
|
||
Without<Camera>,
|
||
),
|
||
>,
|
||
) {
|
||
for (cascades, directional_light, visibility, mut frusta) in &mut views {
|
||
// The frustum is used for culling meshes to the light for shadow mapping
|
||
// so if shadow mapping is disabled for this light, then the frustum is
|
||
// not needed.
|
||
if !directional_light.shadows_enabled || !visibility.is_visible() {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
frusta.frusta = cascades
|
||
.cascades
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.map(|(view, cascades)| {
|
||
(
|
||
*view,
|
||
cascades
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.map(|c| Frustum::from_view_projection(&c.view_projection))
|
||
.collect::<Vec<_>>(),
|
||
)
|
||
})
|
||
.collect();
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: Run this after assign_lights_to_clusters!
|
||
pub fn update_point_light_frusta(
|
||
global_lights: Res<GlobalVisiblePointLights>,
|
||
mut views: Query<
|
||
(Entity, &GlobalTransform, &PointLight, &mut CubemapFrusta),
|
||
Or<(Changed<GlobalTransform>, Changed<PointLight>)>,
|
||
>,
|
||
) {
|
||
let projection =
|
||
Mat4::perspective_infinite_reverse_rh(std::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_2, 1.0, POINT_LIGHT_NEAR_Z);
|
||
let view_rotations = CUBE_MAP_FACES
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.map(|CubeMapFace { target, up }| Transform::IDENTITY.looking_at(*target, *up))
|
||
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
|
||
|
||
for (entity, transform, point_light, mut cubemap_frusta) in &mut views {
|
||
// The frusta are used for culling meshes to the light for shadow mapping
|
||
// so if shadow mapping is disabled for this light, then the frusta are
|
||
// not needed.
|
||
// Also, if the light is not relevant for any cluster, it will not be in the
|
||
// global lights set and so there is no need to update its frusta.
|
||
if !point_light.shadows_enabled || !global_lights.entities.contains(&entity) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// ignore scale because we don't want to effectively scale light radius and range
|
||
// by applying those as a view transform to shadow map rendering of objects
|
||
// and ignore rotation because we want the shadow map projections to align with the axes
|
||
let view_translation = Transform::from_translation(transform.translation());
|
||
let view_backward = transform.back();
|
||
|
||
for (view_rotation, frustum) in view_rotations.iter().zip(cubemap_frusta.iter_mut()) {
|
||
let view = view_translation * *view_rotation;
|
||
let view_projection = projection * view.compute_matrix().inverse();
|
||
|
||
*frustum = Frustum::from_view_projection_custom_far(
|
||
&view_projection,
|
||
&transform.translation(),
|
||
&view_backward,
|
||
point_light.range,
|
||
);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn update_spot_light_frusta(
|
||
global_lights: Res<GlobalVisiblePointLights>,
|
||
mut views: Query<
|
||
(Entity, &GlobalTransform, &SpotLight, &mut Frustum),
|
||
Or<(Changed<GlobalTransform>, Changed<SpotLight>)>,
|
||
>,
|
||
) {
|
||
for (entity, transform, spot_light, mut frustum) in views.iter_mut() {
|
||
// The frusta are used for culling meshes to the light for shadow mapping
|
||
// so if shadow mapping is disabled for this light, then the frusta are
|
||
// not needed.
|
||
// Also, if the light is not relevant for any cluster, it will not be in the
|
||
// global lights set and so there is no need to update its frusta.
|
||
if !spot_light.shadows_enabled || !global_lights.entities.contains(&entity) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// ignore scale because we don't want to effectively scale light radius and range
|
||
// by applying those as a view transform to shadow map rendering of objects
|
||
let view_backward = transform.back();
|
||
|
||
let spot_view = spot_light_view_matrix(transform);
|
||
let spot_projection = spot_light_projection_matrix(spot_light.outer_angle);
|
||
let view_projection = spot_projection * spot_view.inverse();
|
||
|
||
*frustum = Frustum::from_view_projection_custom_far(
|
||
&view_projection,
|
||
&transform.translation(),
|
||
&view_backward,
|
||
spot_light.range,
|
||
);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn check_light_mesh_visibility(
|
||
visible_point_lights: Query<&VisiblePointLights>,
|
||
mut point_lights: Query<(
|
||
&PointLight,
|
||
&GlobalTransform,
|
||
&CubemapFrusta,
|
||
&mut CubemapVisibleEntities,
|
||
Option<&RenderLayers>,
|
||
)>,
|
||
mut spot_lights: Query<(
|
||
&SpotLight,
|
||
&GlobalTransform,
|
||
&Frustum,
|
||
&mut VisibleEntities,
|
||
Option<&RenderLayers>,
|
||
)>,
|
||
mut directional_lights: Query<
|
||
(
|
||
&DirectionalLight,
|
||
&CascadesFrusta,
|
||
&mut CascadesVisibleEntities,
|
||
Option<&RenderLayers>,
|
||
&mut ComputedVisibility,
|
||
),
|
||
Without<SpotLight>,
|
||
>,
|
||
mut visible_entity_query: Query<
|
||
(
|
||
Entity,
|
||
&mut ComputedVisibility,
|
||
Option<&RenderLayers>,
|
||
Option<&Aabb>,
|
||
Option<&GlobalTransform>,
|
||
),
|
||
(Without<NotShadowCaster>, Without<DirectionalLight>),
|
||
>,
|
||
) {
|
||
fn shrink_entities(visible_entities: &mut VisibleEntities) {
|
||
// Check that visible entities capacity() is no more than two times greater than len()
|
||
let capacity = visible_entities.entities.capacity();
|
||
let reserved = capacity
|
||
.checked_div(visible_entities.entities.len())
|
||
.map_or(0, |reserve| {
|
||
if reserve > 2 {
|
||
capacity / (reserve / 2)
|
||
} else {
|
||
capacity
|
||
}
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
visible_entities.entities.shrink_to(reserved);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Directional lights
|
||
for (
|
||
directional_light,
|
||
frusta,
|
||
mut visible_entities,
|
||
maybe_view_mask,
|
||
light_computed_visibility,
|
||
) in &mut directional_lights
|
||
{
|
||
// Re-use already allocated entries where possible.
|
||
let mut views_to_remove = Vec::new();
|
||
for (view, cascade_view_entities) in visible_entities.entities.iter_mut() {
|
||
match frusta.frusta.get(view) {
|
||
Some(view_frusta) => {
|
||
cascade_view_entities.resize(view_frusta.len(), Default::default());
|
||
cascade_view_entities
|
||
.iter_mut()
|
||
.for_each(|x| x.entities.clear());
|
||
}
|
||
None => views_to_remove.push(*view),
|
||
};
|
||
}
|
||
for (view, frusta) in frusta.frusta.iter() {
|
||
visible_entities
|
||
.entities
|
||
.entry(*view)
|
||
.or_insert_with(|| vec![VisibleEntities::default(); frusta.len()]);
|
||
}
|
||
for v in views_to_remove {
|
||
visible_entities.entities.remove(&v);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: If shadow mapping is disabled for the light then it must have no visible entities
|
||
if !directional_light.shadows_enabled || !light_computed_visibility.is_visible() {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let view_mask = maybe_view_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
|
||
for (entity, mut computed_visibility, maybe_entity_mask, maybe_aabb, maybe_transform) in
|
||
&mut visible_entity_query
|
||
{
|
||
if !computed_visibility.is_visible_in_hierarchy() {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let entity_mask = maybe_entity_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
if !view_mask.intersects(&entity_mask) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// If we have an aabb and transform, do frustum culling
|
||
if let (Some(aabb), Some(transform)) = (maybe_aabb, maybe_transform) {
|
||
for (view, view_frusta) in frusta.frusta.iter() {
|
||
let view_visible_entities = visible_entities
|
||
.entities
|
||
.get_mut(view)
|
||
.expect("Per-view visible entities should have been inserted already");
|
||
|
||
for (frustum, frustum_visible_entities) in
|
||
view_frusta.iter().zip(view_visible_entities)
|
||
{
|
||
// Disable near-plane culling, as a shadow caster could lie before the near plane.
|
||
if !frustum.intersects_obb(aabb, &transform.compute_matrix(), false, true) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
computed_visibility.set_visible_in_view();
|
||
frustum_visible_entities.entities.push(entity);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for (_, cascade_view_entities) in visible_entities.entities.iter_mut() {
|
||
cascade_view_entities.iter_mut().for_each(shrink_entities);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for visible_lights in &visible_point_lights {
|
||
for light_entity in visible_lights.entities.iter().copied() {
|
||
// Point lights
|
||
if let Ok((
|
||
point_light,
|
||
transform,
|
||
cubemap_frusta,
|
||
mut cubemap_visible_entities,
|
||
maybe_view_mask,
|
||
)) = point_lights.get_mut(light_entity)
|
||
{
|
||
for visible_entities in cubemap_visible_entities.iter_mut() {
|
||
visible_entities.entities.clear();
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: If shadow mapping is disabled for the light then it must have no visible entities
|
||
if !point_light.shadows_enabled {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let view_mask = maybe_view_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
let light_sphere = Sphere {
|
||
center: Vec3A::from(transform.translation()),
|
||
radius: point_light.range,
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
for (
|
||
entity,
|
||
mut computed_visibility,
|
||
maybe_entity_mask,
|
||
maybe_aabb,
|
||
maybe_transform,
|
||
) in &mut visible_entity_query
|
||
{
|
||
if !computed_visibility.is_visible_in_hierarchy() {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let entity_mask = maybe_entity_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
if !view_mask.intersects(&entity_mask) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// If we have an aabb and transform, do frustum culling
|
||
if let (Some(aabb), Some(transform)) = (maybe_aabb, maybe_transform) {
|
||
let model_to_world = transform.compute_matrix();
|
||
// Do a cheap sphere vs obb test to prune out most meshes outside the sphere of the light
|
||
if !light_sphere.intersects_obb(aabb, &model_to_world) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for (frustum, visible_entities) in cubemap_frusta
|
||
.iter()
|
||
.zip(cubemap_visible_entities.iter_mut())
|
||
{
|
||
if frustum.intersects_obb(aabb, &model_to_world, true, true) {
|
||
computed_visibility.set_visible_in_view();
|
||
visible_entities.entities.push(entity);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
} else {
|
||
computed_visibility.set_visible_in_view();
|
||
for visible_entities in cubemap_visible_entities.iter_mut() {
|
||
visible_entities.entities.push(entity);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for visible_entities in cubemap_visible_entities.iter_mut() {
|
||
shrink_entities(visible_entities);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Spot lights
|
||
if let Ok((point_light, transform, frustum, mut visible_entities, maybe_view_mask)) =
|
||
spot_lights.get_mut(light_entity)
|
||
{
|
||
visible_entities.entities.clear();
|
||
|
||
// NOTE: If shadow mapping is disabled for the light then it must have no visible entities
|
||
if !point_light.shadows_enabled {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let view_mask = maybe_view_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
let light_sphere = Sphere {
|
||
center: Vec3A::from(transform.translation()),
|
||
radius: point_light.range,
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
for (
|
||
entity,
|
||
mut computed_visibility,
|
||
maybe_entity_mask,
|
||
maybe_aabb,
|
||
maybe_transform,
|
||
) in visible_entity_query.iter_mut()
|
||
{
|
||
if !computed_visibility.is_visible_in_hierarchy() {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let entity_mask = maybe_entity_mask.copied().unwrap_or_default();
|
||
if !view_mask.intersects(&entity_mask) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// If we have an aabb and transform, do frustum culling
|
||
if let (Some(aabb), Some(transform)) = (maybe_aabb, maybe_transform) {
|
||
let model_to_world = transform.compute_matrix();
|
||
// Do a cheap sphere vs obb test to prune out most meshes outside the sphere of the light
|
||
if !light_sphere.intersects_obb(aabb, &model_to_world) {
|
||
continue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if frustum.intersects_obb(aabb, &model_to_world, true, true) {
|
||
computed_visibility.set_visible_in_view();
|
||
visible_entities.entities.push(entity);
|
||
}
|
||
} else {
|
||
computed_visibility.set_visible_in_view();
|
||
visible_entities.entities.push(entity);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
shrink_entities(&mut visible_entities);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[cfg(test)]
|
||
mod test {
|
||
use super::*;
|
||
|
||
fn test_cluster_tiling(config: ClusterConfig, screen_size: UVec2) -> Clusters {
|
||
let dims = config.dimensions_for_screen_size(screen_size);
|
||
|
||
// note: near & far do not affect tiling
|
||
let mut clusters = Clusters::default();
|
||
clusters.update(screen_size, dims);
|
||
|
||
// check we cover the screen
|
||
assert!(clusters.tile_size.x * clusters.dimensions.x >= screen_size.x);
|
||
assert!(clusters.tile_size.y * clusters.dimensions.y >= screen_size.y);
|
||
// check a smaller number of clusters would not cover the screen
|
||
assert!(clusters.tile_size.x * (clusters.dimensions.x - 1) < screen_size.x);
|
||
assert!(clusters.tile_size.y * (clusters.dimensions.y - 1) < screen_size.y);
|
||
// check a smaller tilesize would not cover the screen
|
||
assert!((clusters.tile_size.x - 1) * clusters.dimensions.x < screen_size.x);
|
||
assert!((clusters.tile_size.y - 1) * clusters.dimensions.y < screen_size.y);
|
||
// check we don't have more clusters than pixels
|
||
assert!(clusters.dimensions.x <= screen_size.x);
|
||
assert!(clusters.dimensions.y <= screen_size.y);
|
||
|
||
clusters
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[test]
|
||
// check tiling for small screen sizes
|
||
fn test_default_cluster_setup_small_screensizes() {
|
||
for x in 1..100 {
|
||
for y in 1..100 {
|
||
let screen_size = UVec2::new(x, y);
|
||
let clusters = test_cluster_tiling(ClusterConfig::default(), screen_size);
|
||
assert!(
|
||
clusters.dimensions.x * clusters.dimensions.y * clusters.dimensions.z <= 4096
|
||
);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
#[test]
|
||
// check tiling for long thin screen sizes
|
||
fn test_default_cluster_setup_small_x() {
|
||
for x in 1..10 {
|
||
for y in 1..5000 {
|
||
let screen_size = UVec2::new(x, y);
|
||
let clusters = test_cluster_tiling(ClusterConfig::default(), screen_size);
|
||
assert!(
|
||
clusters.dimensions.x * clusters.dimensions.y * clusters.dimensions.z <= 4096
|
||
);
|
||
|
||
let screen_size = UVec2::new(y, x);
|
||
let clusters = test_cluster_tiling(ClusterConfig::default(), screen_size);
|
||
assert!(
|
||
clusters.dimensions.x * clusters.dimensions.y * clusters.dimensions.z <= 4096
|
||
);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|