mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2024-12-25 20:43:07 +00:00
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> # Objective Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps. Fixes #3629 Before 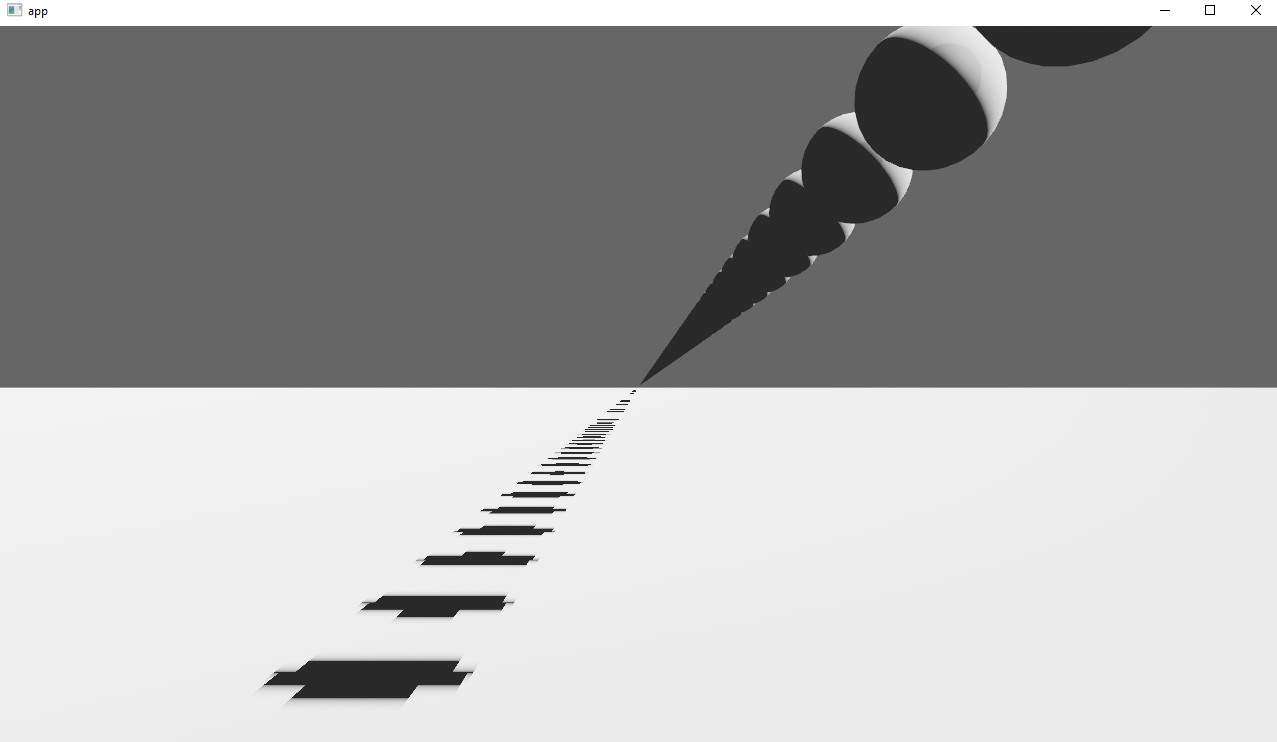 After 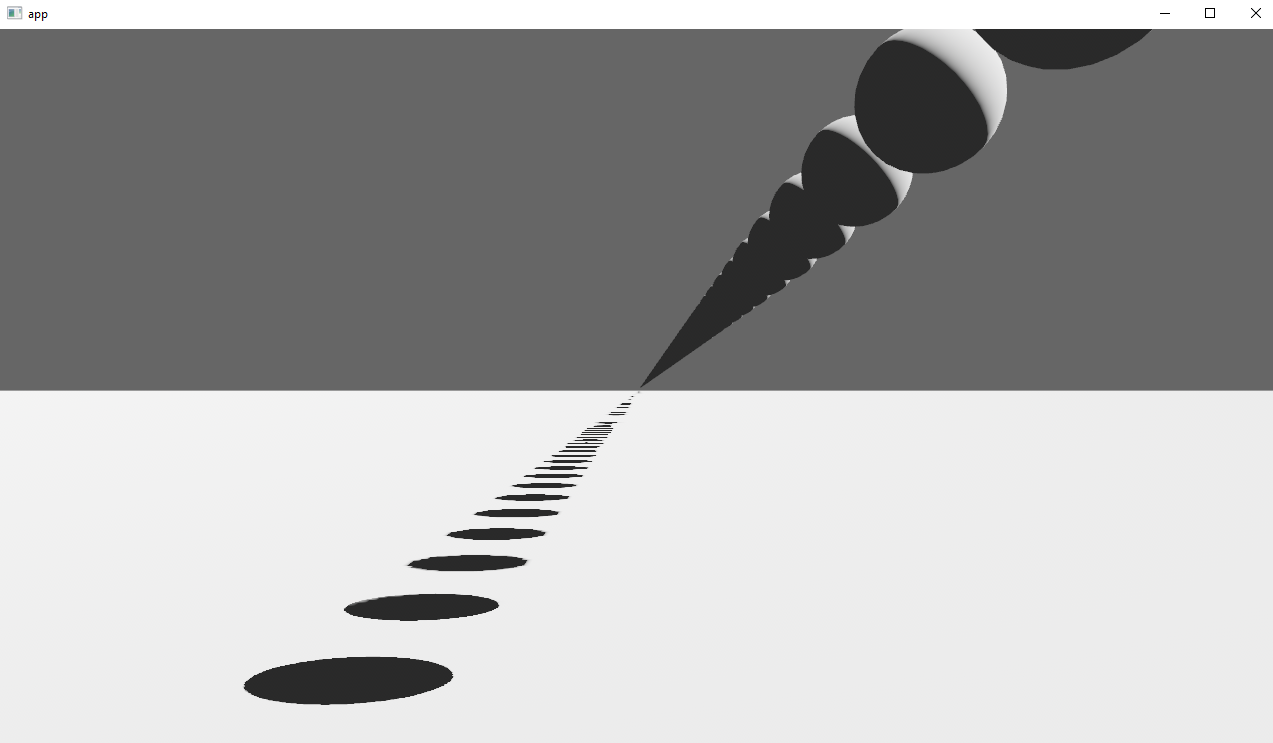 ## Solution Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination. --- ## Changelog Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality. ## Migration Guide You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
180 lines
8.3 KiB
WebGPU Shading Language
180 lines
8.3 KiB
WebGPU Shading Language
#define_import_path bevy_pbr::shadows
|
|
|
|
fn fetch_point_shadow(light_id: u32, frag_position: vec4<f32>, surface_normal: vec3<f32>) -> f32 {
|
|
let light = &point_lights.data[light_id];
|
|
|
|
// because the shadow maps align with the axes and the frustum planes are at 45 degrees
|
|
// we can get the worldspace depth by taking the largest absolute axis
|
|
let surface_to_light = (*light).position_radius.xyz - frag_position.xyz;
|
|
let surface_to_light_abs = abs(surface_to_light);
|
|
let distance_to_light = max(surface_to_light_abs.x, max(surface_to_light_abs.y, surface_to_light_abs.z));
|
|
|
|
// The normal bias here is already scaled by the texel size at 1 world unit from the light.
|
|
// The texel size increases proportionally with distance from the light so multiplying by
|
|
// distance to light scales the normal bias to the texel size at the fragment distance.
|
|
let normal_offset = (*light).shadow_normal_bias * distance_to_light * surface_normal.xyz;
|
|
let depth_offset = (*light).shadow_depth_bias * normalize(surface_to_light.xyz);
|
|
let offset_position = frag_position.xyz + normal_offset + depth_offset;
|
|
|
|
// similar largest-absolute-axis trick as above, but now with the offset fragment position
|
|
let frag_ls = (*light).position_radius.xyz - offset_position.xyz;
|
|
let abs_position_ls = abs(frag_ls);
|
|
let major_axis_magnitude = max(abs_position_ls.x, max(abs_position_ls.y, abs_position_ls.z));
|
|
|
|
// NOTE: These simplifications come from multiplying:
|
|
// projection * vec4(0, 0, -major_axis_magnitude, 1.0)
|
|
// and keeping only the terms that have any impact on the depth.
|
|
// Projection-agnostic approach:
|
|
let zw = -major_axis_magnitude * (*light).light_custom_data.xy + (*light).light_custom_data.zw;
|
|
let depth = zw.x / zw.y;
|
|
|
|
// do the lookup, using HW PCF and comparison
|
|
// NOTE: Due to the non-uniform control flow above, we must use the Level variant of
|
|
// textureSampleCompare to avoid undefined behaviour due to some of the fragments in
|
|
// a quad (2x2 fragments) being processed not being sampled, and this messing with
|
|
// mip-mapping functionality. The shadow maps have no mipmaps so Level just samples
|
|
// from LOD 0.
|
|
#ifdef NO_ARRAY_TEXTURES_SUPPORT
|
|
return textureSampleCompare(point_shadow_textures, point_shadow_textures_sampler, frag_ls, depth);
|
|
#else
|
|
return textureSampleCompareLevel(point_shadow_textures, point_shadow_textures_sampler, frag_ls, i32(light_id), depth);
|
|
#endif
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
fn fetch_spot_shadow(light_id: u32, frag_position: vec4<f32>, surface_normal: vec3<f32>) -> f32 {
|
|
let light = &point_lights.data[light_id];
|
|
|
|
let surface_to_light = (*light).position_radius.xyz - frag_position.xyz;
|
|
|
|
// construct the light view matrix
|
|
var spot_dir = vec3<f32>((*light).light_custom_data.x, 0.0, (*light).light_custom_data.y);
|
|
// reconstruct spot dir from x/z and y-direction flag
|
|
spot_dir.y = sqrt(max(0.0, 1.0 - spot_dir.x * spot_dir.x - spot_dir.z * spot_dir.z));
|
|
if (((*light).flags & POINT_LIGHT_FLAGS_SPOT_LIGHT_Y_NEGATIVE) != 0u) {
|
|
spot_dir.y = -spot_dir.y;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// view matrix z_axis is the reverse of transform.forward()
|
|
let fwd = -spot_dir;
|
|
let distance_to_light = dot(fwd, surface_to_light);
|
|
let offset_position =
|
|
-surface_to_light
|
|
+ ((*light).shadow_depth_bias * normalize(surface_to_light))
|
|
+ (surface_normal.xyz * (*light).shadow_normal_bias) * distance_to_light;
|
|
|
|
// the construction of the up and right vectors needs to precisely mirror the code
|
|
// in render/light.rs:spot_light_view_matrix
|
|
var sign = -1.0;
|
|
if (fwd.z >= 0.0) {
|
|
sign = 1.0;
|
|
}
|
|
let a = -1.0 / (fwd.z + sign);
|
|
let b = fwd.x * fwd.y * a;
|
|
let up_dir = vec3<f32>(1.0 + sign * fwd.x * fwd.x * a, sign * b, -sign * fwd.x);
|
|
let right_dir = vec3<f32>(-b, -sign - fwd.y * fwd.y * a, fwd.y);
|
|
let light_inv_rot = mat3x3<f32>(right_dir, up_dir, fwd);
|
|
|
|
// because the matrix is a pure rotation matrix, the inverse is just the transpose, and to calculate
|
|
// the product of the transpose with a vector we can just post-multiply instead of pre-multplying.
|
|
// this allows us to keep the matrix construction code identical between CPU and GPU.
|
|
let projected_position = offset_position * light_inv_rot;
|
|
|
|
// divide xy by perspective matrix "f" and by -projected.z (projected.z is -projection matrix's w)
|
|
// to get ndc coordinates
|
|
let f_div_minus_z = 1.0 / ((*light).spot_light_tan_angle * -projected_position.z);
|
|
let shadow_xy_ndc = projected_position.xy * f_div_minus_z;
|
|
// convert to uv coordinates
|
|
let shadow_uv = shadow_xy_ndc * vec2<f32>(0.5, -0.5) + vec2<f32>(0.5, 0.5);
|
|
|
|
// 0.1 must match POINT_LIGHT_NEAR_Z
|
|
let depth = 0.1 / -projected_position.z;
|
|
|
|
#ifdef NO_ARRAY_TEXTURES_SUPPORT
|
|
return textureSampleCompare(directional_shadow_textures, directional_shadow_textures_sampler,
|
|
shadow_uv, depth);
|
|
#else
|
|
return textureSampleCompareLevel(directional_shadow_textures, directional_shadow_textures_sampler,
|
|
shadow_uv, i32(light_id) + lights.spot_light_shadowmap_offset, depth);
|
|
#endif
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
fn get_cascade_index(light_id: u32, view_z: f32) -> u32 {
|
|
let light = &lights.directional_lights[light_id];
|
|
|
|
for (var i: u32 = 0u; i < (*light).num_cascades; i = i + 1u) {
|
|
if (-view_z < (*light).cascades[i].far_bound) {
|
|
return i;
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
return (*light).num_cascades;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
fn sample_cascade(light_id: u32, cascade_index: u32, frag_position: vec4<f32>, surface_normal: vec3<f32>) -> f32 {
|
|
let light = &lights.directional_lights[light_id];
|
|
let cascade = &(*light).cascades[cascade_index];
|
|
|
|
// The normal bias is scaled to the texel size.
|
|
let normal_offset = (*light).shadow_normal_bias * (*cascade).texel_size * surface_normal.xyz;
|
|
let depth_offset = (*light).shadow_depth_bias * (*light).direction_to_light.xyz;
|
|
let offset_position = vec4<f32>(frag_position.xyz + normal_offset + depth_offset, frag_position.w);
|
|
|
|
let offset_position_clip = (*cascade).view_projection * offset_position;
|
|
if (offset_position_clip.w <= 0.0) {
|
|
return 1.0;
|
|
}
|
|
let offset_position_ndc = offset_position_clip.xyz / offset_position_clip.w;
|
|
// No shadow outside the orthographic projection volume
|
|
if (any(offset_position_ndc.xy < vec2<f32>(-1.0)) || offset_position_ndc.z < 0.0
|
|
|| any(offset_position_ndc > vec3<f32>(1.0))) {
|
|
return 1.0;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// compute texture coordinates for shadow lookup, compensating for the Y-flip difference
|
|
// between the NDC and texture coordinates
|
|
let flip_correction = vec2<f32>(0.5, -0.5);
|
|
let light_local = offset_position_ndc.xy * flip_correction + vec2<f32>(0.5, 0.5);
|
|
|
|
let depth = offset_position_ndc.z;
|
|
// do the lookup, using HW PCF and comparison
|
|
// NOTE: Due to non-uniform control flow above, we must use the level variant of the texture
|
|
// sampler to avoid use of implicit derivatives causing possible undefined behavior.
|
|
#ifdef NO_ARRAY_TEXTURES_SUPPORT
|
|
return textureSampleCompareLevel(
|
|
directional_shadow_textures,
|
|
directional_shadow_textures_sampler,
|
|
light_local,
|
|
depth
|
|
);
|
|
#else
|
|
return textureSampleCompareLevel(
|
|
directional_shadow_textures,
|
|
directional_shadow_textures_sampler,
|
|
light_local,
|
|
i32((*light).depth_texture_base_index + cascade_index),
|
|
depth
|
|
);
|
|
#endif
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
fn fetch_directional_shadow(light_id: u32, frag_position: vec4<f32>, surface_normal: vec3<f32>, view_z: f32) -> f32 {
|
|
let light = &lights.directional_lights[light_id];
|
|
let cascade_index = get_cascade_index(light_id, view_z);
|
|
|
|
if (cascade_index >= (*light).num_cascades) {
|
|
return 1.0;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
var shadow = sample_cascade(light_id, cascade_index, frag_position, surface_normal);
|
|
|
|
// Blend with the next cascade, if there is one.
|
|
let next_cascade_index = cascade_index + 1u;
|
|
if (next_cascade_index < (*light).num_cascades) {
|
|
let this_far_bound = (*light).cascades[cascade_index].far_bound;
|
|
let next_near_bound = (1.0 - (*light).cascades_overlap_proportion) * this_far_bound;
|
|
if (-view_z >= next_near_bound) {
|
|
let next_shadow = sample_cascade(light_id, next_cascade_index, frag_position, surface_normal);
|
|
shadow = mix(shadow, next_shadow, (-view_z - next_near_bound) / (this_far_bound - next_near_bound));
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
return shadow;
|
|
}
|