# Objective
- Part of #11590
- Fix `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn` for trivial cases in bevy_ecs
## Solution
Fix `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn` in bevy_ecs for trivial cases, i.e., add an
`unsafe` block when the safety comment already exists or add a comment
like "The invariants are uphold by the caller".
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
## Objective
Always have `some_system.into_system().type_id() ==
some_system.into_system_set().system_type().unwrap()`.
System sets have a `fn system_type() -> Option<TypeId>` that is
implemented by `SystemTypeSet` to returning the TypeId of the system's
function type. This was implemented in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7715 and is used in
`bevy_mod_debugdump` to handle `.after(function)` constraints.
Back then, `System::type_id` always also returned the type id of the
function item, not of `FunctionSystem<M, F>`.
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/11728 changes the behaviour of
`System::type_id` so that it returns the id of the
`FunctionSystem`/`ExclusiveFunctionSystem` wrapper, but it did not
change `SystemTypeSet::system_type`, so doing the lookup breaks in
`bevy_mod_debugdump`.
## Solution
Change `IntoSystemSet` for functions to return a
`SystemTypeSet<FunctionSystem>` /
`SystemTypeSet<ExclusiveFunctionSystem>` instead of `SystemTypeSet<F>`.
# Objective
We deprecated quite a few APIs in 0.13. 0.13 has shipped already. It
should be OK to remove them in 0.14's release. Fixes#4059. Fixes#9011.
## Solution
Remove them.
# Objective
There's a repeating pattern of `ThreadLocal<Cell<Vec<T>>>` which is very
useful for low overhead, low contention multithreaded queues that have
cropped up in a few places in the engine. This pattern is surprisingly
useful when building deferred mutation across multiple threads, as noted
by it's use in `ParallelCommands`.
However, `ThreadLocal<Cell<Vec<T>>>` is not only a mouthful, it's also
hard to ensure the thread-local queue is replaced after it's been
temporarily removed from the `Cell`.
## Solution
Wrap the pattern into `bevy_utils::Parallel<T>` which codifies the
entire pattern and ensures the user follows the contract. Instead of
fetching indivdual cells, removing the value, mutating it, and replacing
it, `Parallel::get` returns a `ParRef<'a, T>` which contains the
temporarily removed value and a reference back to the cell, and will
write the mutated value back to the cell upon being dropped.
I would like to use this to simplify the remaining part of #4899 that
has not been adopted/merged.
---
## Changelog
TODO
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
When applying a command, we currently use double indirection for the
world reference `&mut Option<&mut World>`. Since this is used across a
`fn` pointer boundary, this can't get optimized away.
## Solution
Reborrow the world reference and pass `Option<&mut World>` instead.
# Objective
Bevy's change detection functionality is invaluable for writing robust
apps, but it only works in the context of systems and exclusive systems.
Oftentimes it is necessary to detect changes made in earlier code
without having to place the code in separate systems, but it is not
currently possible to do so since there is no way to set the value of
`World::last_change_tick`.
`World::clear_trackers` allows you to update the change tick, but this
has unintended side effects, since it irreversibly affects the behavior
of change and removal detection for the entire app.
## Solution
Add a method `World::last_change_tick_scope`. This allows you to set
`last_change_tick` to a specific value for a region of code. To ensure
that misuse doesn't break unrelated functions, we restore the world's
original change tick at the end of the provided scope.
### Example
A function that uses this to run an update loop repeatedly, allowing
each iteration of the loop to react to changes made in the previous loop
iteration.
```rust
fn update_loop(
world: &mut World,
mut update_fn: impl FnMut(&mut World) -> std::ops::ControlFlow<()>,
) {
let mut last_change_tick = world.last_change_tick();
// Repeatedly run the update function until it requests a break.
loop {
// Update once.
let control_flow = world.last_change_tick_scope(last_change_tick, |world| {
update_fn(world)
});
// End the loop when the closure returns `ControlFlow::Break`.
if control_flow.is_break() {
break;
}
// Increment the change tick so the next update can detect changes from this update.
last_change_tick = world.change_tick();
world.increment_change_tick();
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
+ Added `World::last_change_tick_scope`, which allows you to specify the
reference for change detection within a certain scope.
# Objective
- Fixes#11679
## Solution
- Added `IntoSystem::system_type_id` which returns the equivalent of
`system.into_system().type_id()` without construction. This allows for
getting the `TypeId` of functions (a function is an unnamed type and
therefore you cannot call `TypeId::of::<apply_deferred::System>()`)
- Added default implementation of `System::type_id` to ensure
consistency between implementations. Some returned `Self`, while others
were returning an inner value instead. This ensures consistency with
`IntoSystem::system_type_id`.
## Migration Guide
If you use `System::type_id()` on function systems (exclusive or not),
ensure you are comparing its value to other `System::type_id()` calls,
or `IntoSystem::system_type_id()`.
This code wont require any changes, because `IntoSystem`'s are directly
compared to each other.
```rust
fn test_system() {}
let type_id = test_system.type_id();
// ...
// No change required
assert_eq!(test_system.type_id(), type_id);
```
Likewise, this code wont, because `System`'s are directly compared.
```rust
fn test_system() {}
let type_id = IntoSystem::into_system(test_system).type_id();
// ...
// No change required
assert_eq!(IntoSystem::into_system(test_system).type_id(), type_id);
```
The below _does_ require a change, since you're comparing a `System`
type to a `IntoSystem` type.
```rust
fn test_system() {}
// Before
assert_eq!(test_system.type_id(), IntoSystem::into_system(test_system).type_id());
// After
assert_eq!(test_system.system_type_id(), IntoSystem::into_system(test_system).type_id());
```
# Objective
- (Partially) Fixes#9904
- Acts on #9910
## Solution
- Deprecated the relevant methods from `Query`, cascading changes as
required across Bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Deprecated `QueryState::get_component_unchecked_mut` method
- Deprecated `Query::get_component` method
- Deprecated `Query::get_component_mut` method
- Deprecated `Query::component` method
- Deprecated `Query::component_mut` method
- Deprecated `Query::get_component_unchecked_mut` method
## Migration Guide
### `QueryState::get_component_unchecked_mut`
Use `QueryState::get_unchecked_manual` and select for the exact
component based on the structure of the exact query as required.
### `Query::(get_)component(_unchecked)(_mut)`
Use `Query::get` and select for the exact component based on the
structure of the exact query as required.
- For mutable access (`_mut`), use `Query::get_mut`
- For unchecked access (`_unchecked`), use `Query::get_unchecked`
- For panic variants (non-`get_`), add `.unwrap()`
## Notes
- `QueryComponentError` can be removed once these deprecated methods are
also removed. Due to an interaction with `thiserror`'s derive macro, it
is not marked as deprecated.
# Objective
Fixes#11311
## Solution
Adds an example to the documentation for `par_iter_mut`. I didn't add
any examples to `par_iter`, because I couldn't think of a good example
and I figure users can infer that `par_iter` and `par_iter_mut` are
similar.
# Objective
It would be convenient to be able to call functions with `Commands` as a
parameter without having to move your own instance of `Commands`. Since
this struct is composed entirely of references, we can easily get an
owned instance of `Commands` by shortening the lifetime.
## Solution
Add `Commands::reborrow`, `EntiyCommands::reborrow`, and
`Deferred::reborrow`, which returns an owned version of themselves with
a shorter lifetime.
Remove unnecessary lifetimes from `EntityCommands`. The `'w` and `'s`
lifetimes only have to be separate for `Commands` because it's used as a
`SystemParam` -- this is not the case for `EntityCommands`.
---
## Changelog
Added `Commands::reborrow`. This is useful if you have `&mut Commands`
but need `Commands`. Also added `EntityCommands::reborrow` and
`Deferred:reborrow` which serve the same purpose.
## Migration Guide
The lifetimes for `EntityCommands` have been simplified.
```rust
// Before (Bevy 0.12)
struct MyStruct<'w, 's, 'a> {
commands: EntityCommands<'w, 's, 'a>,
}
// After (Bevy 0.13)
struct MyStruct<'a> {
commands: EntityCommands<'a>,
}
```
The method `EntityCommands::commands` now returns `Commands` rather than
`&mut Commands`.
```rust
// Before (Bevy 0.12)
let commands = entity_commands.commands();
commands.spawn(...);
// After (Bevy 0.13)
let mut commands = entity_commands.commands();
commands.spawn(...);
```
# Objective
Document a few common cases of which lifetime is required when using
SystemParam Derive
## Solution
Added a table in the doc comment
---------
Co-authored-by: laund <me@laund.moe>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Expand the existing `Query` API to support more dynamic use cases i.e.
scripting.
## Prior Art
- #6390
- #8308
- #10037
## Solution
- Create a `QueryBuilder` with runtime methods to define the set of
component accesses for a built query.
- Create new `WorldQueryData` implementations `FilteredEntityMut` and
`FilteredEntityRef` as variants of `EntityMut` and `EntityRef` that
provide run time checked access to the components included in a given
query.
- Add new methods to `Query` to create "query lens" with a subset of the
access of the initial query.
### Query Builder
The `QueryBuilder` API allows you to define a query at runtime. At it's
most basic use it will simply create a query with the corresponding type
signature:
```rust
let query = QueryBuilder::<Entity, With<A>>::new(&mut world).build();
// is equivalent to
let query = QueryState::<Entity, With<A>>::new(&mut world);
```
Before calling `.build()` you also have the opportunity to add
additional accesses and filters. Here is a simple example where we add
additional filter terms:
```rust
let entity_a = world.spawn((A(0), B(0))).id();
let entity_b = world.spawn((A(0), C(0))).id();
let mut query_a = QueryBuilder::<Entity>::new(&mut world)
.with::<A>()
.without::<C>()
.build();
assert_eq!(entity_a, query_a.single(&world));
```
This alone is useful in that allows you to decide which archetypes your
query will match at runtime. However it is also very limited, consider a
case like the following:
```rust
let query_a = QueryBuilder::<&A>::new(&mut world)
// Add an additional access
.data::<&B>()
.build();
```
This will grant the query an additional read access to component B
however we have no way of accessing the data while iterating as the type
signature still only includes &A. For an even more concrete example of
this consider dynamic components:
```rust
let query_a = QueryBuilder::<Entity>::new(&mut world)
// Adding a filter is easy since it doesn't need be read later
.with_id(component_id_a)
// How do I access the data of this component?
.ref_id(component_id_b)
.build();
```
With this in mind the `QueryBuilder` API seems somewhat incomplete by
itself, we need some way method of accessing the components dynamically.
So here's one:
### Query Transmutation
If the problem is not having the component in the type signature why not
just add it? This PR also adds transmute methods to `QueryBuilder` and
`QueryState`. Here's a simple example:
```rust
world.spawn(A(0));
world.spawn((A(1), B(0)));
let mut query = QueryBuilder::<()>::new(&mut world)
.with::<B>()
.transmute::<&A>()
.build();
query.iter(&world).for_each(|a| assert_eq!(a.0, 1));
```
The `QueryState` and `QueryBuilder` transmute methods look quite similar
but are different in one respect. Transmuting a builder will always
succeed as it will just add the additional accesses needed for the new
terms if they weren't already included. Transmuting a `QueryState` will
panic in the case that the new type signature would give it access it
didn't already have, for example:
```rust
let query = QueryState::<&A, Option<&B>>::new(&mut world);
/// This is fine, the access for Option<&A> is less restrictive than &A
query.transmute::<Option<&A>>(&world);
/// Oh no, this would allow access to &B on entities that might not have it, so it panics
query.transmute::<&B>(&world);
/// This is right out
query.transmute::<&C>(&world);
```
This is quite an appealing API to also have available on `Query` however
it does pose one additional wrinkle: In order to to change the iterator
we need to create a new `QueryState` to back it. `Query` doesn't own
it's own state though, it just borrows it, so we need a place to borrow
it from. This is why `QueryLens` exists, it is a place to store the new
state so it can be borrowed when you call `.query()` leaving you with an
API like this:
```rust
fn function_that_takes_a_query(query: &Query<&A>) {
// ...
}
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &B)>) {
let lens = query.transmute_lens::<&A>();
let q = lens.query();
function_that_takes_a_query(&q);
}
```
Now you may be thinking: Hey, wait a second, you introduced the problem
with dynamic components and then described a solution that only works
for static components! Ok, you got me, I guess we need a bit more:
### Filtered Entity References
Currently the only way you can access dynamic components on entities
through a query is with either `EntityMut` or `EntityRef`, however these
can access all components and so conflict with all other accesses. This
PR introduces `FilteredEntityMut` and `FilteredEntityRef` as
alternatives that have additional runtime checking to prevent accessing
components that you shouldn't. This way you can build a query with a
`QueryBuilder` and actually access the components you asked for:
```rust
let mut query = QueryBuilder::<FilteredEntityRef>::new(&mut world)
.ref_id(component_id_a)
.with(component_id_b)
.build();
let entity_ref = query.single(&world);
// Returns Some(Ptr) as we have that component and are allowed to read it
let a = entity_ref.get_by_id(component_id_a);
// Will return None even though the entity does have the component, as we are not allowed to read it
let b = entity_ref.get_by_id(component_id_b);
```
For the most part these new structs have the exact same methods as their
non-filtered equivalents.
Putting all of this together we can do some truly dynamic ECS queries,
check out the `dynamic` example to see it in action:
```
Commands:
comp, c Create new components
spawn, s Spawn entities
query, q Query for entities
Enter a command with no parameters for usage.
> c A, B, C, Data 4
Component A created with id: 0
Component B created with id: 1
Component C created with id: 2
Component Data created with id: 3
> s A, B, Data 1
Entity spawned with id: 0v0
> s A, C, Data 0
Entity spawned with id: 1v0
> q &Data
0v0: Data: [1, 0, 0, 0]
1v0: Data: [0, 0, 0, 0]
> q B, &mut Data
0v0: Data: [2, 1, 1, 1]
> q B || C, &Data
0v0: Data: [2, 1, 1, 1]
1v0: Data: [0, 0, 0, 0]
```
## Changelog
- Add new `transmute_lens` methods to `Query`.
- Add new types `QueryBuilder`, `FilteredEntityMut`, `FilteredEntityRef`
and `QueryLens`
- `update_archetype_component_access` has been removed, archetype
component accesses are now determined by the accesses set in
`update_component_access`
- Added method `set_access` to `WorldQuery`, this is called before
`update_component_access` for queries that have a restricted set of
accesses, such as those built by `QueryBuilder` or `QueryLens`. This is
primarily used by the `FilteredEntity*` variants and has an empty trait
implementation.
- Added method `get_state` to `WorldQuery` as a fallible version of
`init_state` when you don't have `&mut World` access.
## Future Work
Improve performance of `FilteredEntityMut` and `FilteredEntityRef`,
currently they have to determine the accesses a query has in a given
archetype during iteration which is far from ideal, especially since we
already did the work when matching the archetype in the first place. To
avoid making more internal API changes I have left it out of this PR.
---------
Co-authored-by: Mike Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
# Objective
In #9604 we removed the ability to define an `EntityCommand` as
`fn(Entity, &mut World)`. However I have since realized that `fn(Entity,
&mut World)` is an incredibly expressive and powerful way to define a
command for an entity that may or may not exist (`fn(EntityWorldMut)`
only works on entities that are alive).
## Solution
Support `EntityCommand`s in the style of `fn(Entity, &mut World)`, as
well as `fn(EntityWorldMut)`. Use a marker generic on the
`EntityCommand` trait to allow multiple impls.
The second commit in this PR replaces all of the internal command
definitions with ones using `fn` definitions. This is mostly just to
show off how expressive this style of command is -- we can revert this
commit if we'd rather avoid breaking changes.
---
## Changelog
Re-added support for expressively defining an `EntityCommand` as a
function that takes `Entity, &mut World`.
## Migration Guide
All `Command` types in `bevy_ecs`, such as `Spawn`, `SpawnBatch`,
`Insert`, etc., have been made private. Use the equivalent methods on
`Commands` or `EntityCommands` instead.
# Objective
`SystemName` might be useful in systems which accept `&mut World`.
## Solution
- `impl ExclusiveSystemParam for SystemName`
- move `SystemName` into a separate file, because it no longer belongs
to a file which defines `SystemParam`
- add a test for new impl, and for existing impl
## Changelog
- `impl ExclusiveSystemParam for SystemName`
# Objective
There are a lot of doctests that are `ignore`d for no documented reason.
And that should be fixed.
## Solution
I searched the bevy repo with the regex ` ```[a-z,]*ignore ` in order to
find all `ignore`d doctests. For each one of the `ignore`d doctests, I
did the following steps:
1. Attempt to remove the `ignored` attribute while still passing the
test. I did this by adding hidden dummy structs and imports.
2. If step 1 doesn't work, attempt to replace the `ignored` attribute
with the `no_run` attribute while still passing the test.
3. If step 2 doesn't work, keep the `ignored` attribute but add
documentation for why the `ignored` attribute was added.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implement `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `PhantomData`.
For the same reason `SystemParam` impl exists: to simplify writing
generic code.
786abbf3f5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/system/system_param.rs (L1557)
Also for consistency.
## Solution
`impl ExclusiveSystemParam for PhantomData`.
## Changelog
Added: PhantomData<T> now implements ExclusiveSystemParam.
# Objective
- Users are often confused when their command effects are not visible in
the next system. This PR auto inserts sync points if there are deferred
buffers on a system and there are dependents on that system (systems
with after relationships).
- Manual sync points can lead to users adding more than needed and it's
hard for the user to have a global understanding of their system graph
to know which sync points can be merged. However we can easily calculate
which sync points can be merged automatically.
## Solution
1. Add new edge types to allow opting out of new behavior
2. Insert an sync point for each edge whose initial node has deferred
system params.
3. Reuse nodes if they're at the number of sync points away.
* add opt outs for specific edges with `after_ignore_deferred`,
`before_ignore_deferred` and `chain_ignore_deferred`. The
`auto_insert_apply_deferred` boolean on `ScheduleBuildSettings` can be
set to false to opt out for the whole schedule.
## Perf
This has a small negative effect on schedule build times.
```text
group auto-sync main-for-auto-sync
----- ----------- ------------------
build_schedule/1000_schedule 1.06 2.8±0.15s ? ?/sec 1.00 2.7±0.06s ? ?/sec
build_schedule/1000_schedule_noconstraints 1.01 26.2±0.88ms ? ?/sec 1.00 25.8±0.36ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/100_schedule 1.02 13.1±0.33ms ? ?/sec 1.00 12.9±0.28ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/100_schedule_noconstraints 1.08 505.3±29.30µs ? ?/sec 1.00 469.4±12.48µs ? ?/sec
build_schedule/500_schedule 1.00 485.5±6.29ms ? ?/sec 1.00 485.5±9.80ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/500_schedule_noconstraints 1.00 6.8±0.10ms ? ?/sec 1.02 6.9±0.16ms ? ?/sec
```
---
## Changelog
- Auto insert sync points and added `after_ignore_deferred`,
`before_ignore_deferred`, `chain_no_deferred` and
`auto_insert_apply_deferred` APIs to opt out of this behavior
## Migration Guide
- `apply_deferred` points are added automatically when there is ordering
relationship with a system that has deferred parameters like `Commands`.
If you want to opt out of this you can switch from `after`, `before`,
and `chain` to the corresponding `ignore_deferred` API,
`after_ignore_deferred`, `before_ignore_deferred` or
`chain_ignore_deferred` for your system/set ordering.
- You can also set `ScheduleBuildSettings::auto_insert_sync_points` to
`false` if you want to do it for the whole schedule. Note that in this
mode you can still add `apply_deferred` points manually.
- For most manual insertions of `apply_deferred` you should remove them
as they cannot be merged with the automatically inserted points and
might reduce parallelizability of the system graph.
## TODO
- [x] remove any apply_deferred used in the engine
- [x] ~~decide if we should deprecate manually using apply_deferred.~~
We'll still allow inserting manual sync points for now for whatever edge
cases users might have.
- [x] Update migration guide
- [x] rerun schedule build benchmarks
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Make the implementation order consistent between all sources to fit
the order in the trait.
## Solution
- Change the implementation order.
# Objective
Since #10776 split `WorldQuery` to `WorldQueryData` and
`WorldQueryFilter`, it should be clear that the query is actually
composed of two parts. It is not factually correct to call "query" only
the data part. Therefore I suggest to rename the `Q` parameter to `D` in
`Query` and related items.
As far as I know, there shouldn't be breaking changes from renaming
generic type parameters.
## Solution
I used a combination of rust-analyzer go to reference and `Ctrl-F`ing
various patterns to catch as many cases as possible. Hopefully I got
them all. Feel free to check if you're concerned of me having missed
some.
## Notes
This and #10779 have many lines in common, so merging one will cause a
lot of merge conflicts to the other.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
The `Despawn` command breaks the hierarchy whenever you use it if the
despawned entity has a parent or any children. This is a serious footgun
because the `Despawn` command has the shortest name, the behavior is
unexpected and not likely to be what you want, and the crash that it
causes can be very difficult to track down.
## Solution
Until this can be fixed by relations, add a note mentioning the footgun
in the documentation.
## Solution
`Commands.remove` and `.retain` (because I copied `remove`s doc)
referenced `EntityWorldMut.remove` and `retain` for more detail but the
`Commands` docs are much more detailed (which makes sense because it is
the most common api), so I have instead inverted this so that
`EntityWorldMut` docs link to `Commands`.
I also made `EntityWorldMut.despawn` reference `World.despawn` for more
details, like `Commands.despawn` does.
# Objective
Test more complex function signatures for exclusive systems, and test
that `StaticSystemParam` is indeed a `SystemParam`.
I mean, it currently works, but might as well add a test for it.
# Objective
Adds `EntityCommands.retain` and `EntityWorldMut.retain` to remove all
components except the given bundle from the entity.
Fixes#10865.
## Solution
I added a private unsafe function in `EntityWorldMut` called
`remove_bundle_info` which performs the shared behaviour of `remove` and
`retain`, namely taking a `BundleInfo` of components to remove, and
removing them from the given entity. Then `retain` simply gets all the
components on the entity and filters them by whether they are in the
bundle it was passed, before passing this `BundleInfo` into
`remove_bundle_info`.
`EntityCommands.retain` just creates a new type `Retain` which runs
`EntityWorldMut.retain` when run.
---
## Changelog
Added `EntityCommands.retain` and `EntityWorldMut.retain`, which remove
all components except the given bundle from the entity, they can also be
used to remove all components by passing `()` as the bundle.
# Objective
After #6547, `Query::for_each` has been capable of automatic
vectorization on certain queries, which is seeing a notable (>50% CPU
time improvements) for iteration. However, `Query::for_each` isn't
idiomatic Rust, and lacks the flexibility of iterator combinators.
Ideally, `Query::iter` and friends should be able to achieve the same
results. However, this does seem to blocked upstream
(rust-lang/rust#104914) by Rust's loop optimizations.
## Solution
This is an intermediate solution and refactor. This moves the
`Query::for_each` implementation onto the `Iterator::fold`
implementation for `QueryIter` instead. This should result in the same
automatic vectorization optimization on all `Iterator` functions that
internally use fold, including `Iterator::for_each`, `Iterator::count`,
etc.
With this, it should close the gap between the two completely.
Internally, this PR changes `Query::for_each` to use
`query.iter().for_each(..)` instead of the duplicated implementation.
Separately, the duplicate implementations of internal iteration (i.e.
`Query::par_for_each`) now use portions of the current `Query::for_each`
implementation factored out into their own functions.
This also massively cleans up our internal fragmentation of internal
iteration options, deduplicating the iteration code used in `for_each`
and `par_iter().for_each()`.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Query::for_each`, `Query::for_each_mut`, `Query::for_each`,
and `Query::for_each_mut` have been moved to `QueryIter`'s
`Iterator::for_each` implementation, and still retains their performance
improvements over normal iteration. These APIs are deprecated in 0.13
and will be removed in 0.14.
---------
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Shorten paths by removing unnecessary prefixes
## Solution
- Remove the prefixes from many paths which do not need them. Finding
the paths was done automatically using built-in refactoring tools in
Jetbrains RustRover.
# Objective
- Fixes#7680
- This is an updated for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8899
which had the same objective but fell a long way behind the latest
changes
## Solution
The traits `WorldQueryData : WorldQuery` and `WorldQueryFilter :
WorldQuery` have been added and some of the types and functions from
`WorldQuery` has been moved into them.
`ReadOnlyWorldQuery` has been replaced with `ReadOnlyWorldQueryData`.
`WorldQueryFilter` is safe (as long as `WorldQuery` is implemented
safely).
`WorldQueryData` is unsafe - safely implementing it requires that
`Self::ReadOnly` is a readonly version of `Self` (this used to be a
safety requirement of `WorldQuery`)
The type parameters `Q` and `F` of `Query` must now implement
`WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter` respectively.
This makes it impossible to accidentally use a filter in the data
position or vice versa which was something that could lead to bugs.
~~Compile failure tests have been added to check this.~~
It was previously sometimes useful to use `Option<With<T>>` in the data
position. Use `Has<T>` instead in these cases.
The `WorldQuery` derive macro has been split into separate derive macros
for `WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter`.
Previously it was possible to derive both `WorldQuery` for a struct that
had a mixture of data and filter items. This would not work correctly in
some cases but could be a useful pattern in others. *This is no longer
possible.*
---
## Notes
- The changes outside of `bevy_ecs` are all changing type parameters to
the new types, updating the macro use, or replacing `Option<With<T>>`
with `Has<T>`.
- All `WorldQueryData` types always returned `true` for `IS_ARCHETYPAL`
so I moved it to `WorldQueryFilter` and
replaced all calls to it with `true`. That should be the only logic
change outside of the macro generation code.
- `Changed<T>` and `Added<T>` were being generated by a macro that I
have expanded. Happy to revert that if desired.
- The two derive macros share some functions for implementing
`WorldQuery` but the tidiest way I could find to implement them was to
give them a ton of arguments and ask clippy to ignore that.
## Changelog
### Changed
- Split `WorldQuery` into `WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter` which
now have separate derive macros. It is not possible to derive both for
the same type.
- `Query` now requires that the first type argument implements
`WorldQueryData` and the second implements `WorldQueryFilter`
## Migration Guide
- Update derives
```rust
// old
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct CustomQuery {
entity: Entity,
a: &'static mut ComponentA
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
struct QueryFilter {
_c: With<ComponentC>
}
// new
#[derive(WorldQueryData)]
#[world_query_data(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct CustomQuery {
entity: Entity,
a: &'static mut ComponentA,
}
#[derive(WorldQueryFilter)]
struct QueryFilter {
_c: With<ComponentC>
}
```
- Replace `Option<With<T>>` with `Has<T>`
```rust
/// old
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, Option<With<ComponentA>>)>)
{
for (entity, has_a_option) in query.iter(){
let has_a:bool = has_a_option.is_some();
//todo!()
}
}
/// new
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, Has<ComponentA>)>)
{
for (entity, has_a) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
```
- Fix queries which had filters in the data position or vice versa.
```rust
// old
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, With<ComponentA>)>)
{
for (entity, _) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// new
fn my_system(query: Query<Entity, With<ComponentA>>)
{
for entity in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// old
fn my_system(query: Query<AnyOf<(&ComponentA, With<ComponentB>)>>)
{
for (entity, _) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// new
fn my_system(query: Query<Option<&ComponentA>, Or<(With<ComponentA>, With<ComponentB>)>>)
{
for entity in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#10676, preventing a possible memory leak for commands which
owned resources.
## Solution
Implemented `Drop` for `CommandQueue`. This has been done entirely in
the private API of `CommandQueue`, ensuring no breaking changes. Also
added a unit test, `test_command_queue_inner_drop_early`, based on the
reproduction steps as outlined in #10676.
## Notes
I believe this can be applied to `0.12.1` as well, but I am uncertain of
the process to make that kind of change. Please let me know if there's
anything I can do to help with the back-porting of this change.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- I've been experimenting with different patterns to try and make async
tasks more convenient. One of the better ones I've found is to return a
command queue to allow for deferred &mut World access. It can be
convenient to check for task completion in a normal system, but it is
hard to do something with the command queue after getting it back. This
pr adds a `append` to Commands. This allows appending the returned
command queue onto the system's commands.
## Solution
- I edited the async compute example to use the new `append`, but not
sure if I should keep the example changed as this might be too
opinionated.
## Future Work
- It would be very easy to pull the pattern used in the example out into
a plugin or a external crate, so users wouldn't have to add the checking
system.
---
## Changelog
- add `append` to `Commands` and `CommandQueue`
# Objective
Make the impl block for RemovedSystem generic so that the methods can be
called for systems that have inputs or outputs.
## Solution
Simply adding generics to the impl block.
# Objective
Allows chained systems taking an `In<_>` input parameter to be run as
one-shot systems. This API was mentioned in #8963.
In addition, `run_system(_with_input)` returns the system output, for
any `'static` output type.
## Solution
A new function, `World::run_system_with_input` allows a `SystemId<I, O>`
to be run by providing an `I` value as input and producing `O` as an
output.
`SystemId<I, O>` is now generic over the input type `I` and output type
`O`, along with the related functions and types `RegisteredSystem`,
`RemovedSystem`, `register_system`, `remove_system`, and
`RegisteredSystemError`. These default to `()`, preserving the existing
API, for all of the public types.
---
## Changelog
- Added `World::run_system_with_input` function to allow one-shot
systems that take `In<_>` input parameters
- Changed `World::run_system` and `World::register_system` to support
systems with return types beyond `()`
- Added `Commands::run_system_with_input` command that schedules a
one-shot system with an `In<_>` input parameter
# Objective
- `CommandQueue::apply` calculates the address of the end of the
internal buffer as a `usize` rather than as a pointer, requiring two
casts of `cursor` to `usize`. Casting pointers to integers is generally
discouraged and may also prevent optimizations. It's also unnecessary
here.
## Solution
- Calculate the end address as a pointer rather than a `usize`.
Small note:
A trivial translation of the old code to use pointers would have
computed `end_addr` as `cursor.add(self.bytes.len())`, which is not
wrong but is an additional `unsafe` operation that also needs to be
properly documented and proven correct. However this operation is
already implemented in the form of the safe `as_mut_ptr_range`, so I
just used that.
# Objective
- Allow registration of one-shot systems when those systems have already
been `Box`ed.
- Needed for `bevy_eventlisteners` which allows adding event listeners
with callbacks in normal systems. The current one shot system
implementation requires systems be registered from an exclusive system,
and that those systems be passed in as types that implement
`IntoSystem`. However, the eventlistener callback crate allows users to
define their callbacks in normal systems, by boxing the system and
deferring initialization to an exclusive system.
## Solution
- Separate the registration of the system from the boxing of the system.
This is non-breaking, and adds a new method.
---
## Changelog
- Added `World::register_boxed_system` to allow registration of
already-boxed one shot systems.
# Objective
Align all error-like types to implement `Error`.
Fixes #10176
## Solution
- Derive `Error` on more types
- Refactor instances of manual implementations that could be derived
This adds thiserror as a dependency to bevy_transform, which might
increase compilation time -- but I don't know of any situation where you
might only use that but not any other crate that pulls in bevy_utils.
The `contributors` example has a `LoadContributorsError` type, but as
it's an example I have not updated it. Doing that would mean either
having a `use bevy_internal::utils::thiserror::Error;` in an example
file, or adding `thiserror` as a dev-dependency to the main `bevy`
crate.
---
## Changelog
- All `…Error` types now implement the `Error` trait
# Objective
First of all, this PR took heavy inspiration from #7760 and #5715. It
intends to also fix#5569, but with a slightly different approach.
This also fixes#9335 by reexporting `DynEq`.
## Solution
The advantage of this API is that we can intern a value without
allocating for zero-sized-types and for enum variants that have no
fields. This PR does this automatically in the `SystemSet` and
`ScheduleLabel` derive macros for unit structs and fieldless enum
variants. So this should cover many internal and external use cases of
`SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel`. In these optimal use cases, no memory
will be allocated.
- The interning returns a `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`, which is just a
wrapper around a `&'static dyn SystemSet`.
- `Hash` and `Eq` are implemented in terms of the pointer value of the
reference, similar to my first approach of anonymous system sets in
#7676.
- Therefore, `Interned<T>` does not implement `Borrow<T>`, only `Deref`.
- The debug output of `Interned<T>` is the same as the interned value.
Edit:
- `AppLabel` is now also interned and the old
`derive_label`/`define_label` macros were replaced with the new
interning implementation.
- Anonymous set ids are reused for different `Schedule`s, reducing the
amount of leaked memory.
### Pros
- `InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel` behave very similar to
the current `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel`, but can be copied
without an allocation.
- Many use cases don't allocate at all.
- Very fast lookups and comparisons when using `InternedSystemSet` and
`InternedScheduleLabel`.
- The `intern` module might be usable in other areas.
- `Interned{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}` does implement
`{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}`, increasing ergonomics.
### Cons
- Implementors of `SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel` still need to
implement `Hash` and `Eq` (and `Clone`) for it to work.
## Changelog
### Added
- Added `intern` module to `bevy_utils`.
- Added reexports of `DynEq` to `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_app`.
### Changed
- Replaced `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel` with
`InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel`.
- Replaced `impl AsRef<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with `impl ScheduleLabel`.
- Replaced `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel`.
- Changed `AppLabel` to use `Debug` for error messages.
- Changed `AppLabel` to use interning.
- Changed `define_label`/`derive_label` to use interning.
- Replaced `define_boxed_label`/`derive_boxed_label` with
`define_label`/`derive_label`.
- Changed anonymous set ids to be only unique inside a schedule, not
globally.
- Made interned label types implement their label trait.
### Removed
- Removed `define_boxed_label` and `derive_boxed_label`.
## Migration guide
- Replace `BoxedScheduleLabel` and `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with
`InternedScheduleLabel` or `Interned<dyn ScheduleLabel>`.
- Replace `BoxedSystemSet` and `Box<dyn SystemSet>` with
`InternedSystemSet` or `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`.
- Replace `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel` or `Interned<dyn
AppLabel>`.
- Types manually implementing `ScheduleLabel`, `AppLabel` or `SystemSet`
need to implement:
- `dyn_hash` directly instead of implementing `DynHash`
- `as_dyn_eq`
- Pass labels to `World::try_schedule_scope`, `World::schedule_scope`,
`World::try_run_schedule`. `World::run_schedule`, `Schedules::remove`,
`Schedules::remove_entry`, `Schedules::contains`, `Schedules::get` and
`Schedules::get_mut` by value instead of by reference.
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Updates for rust 1.73
## Solution
- new doc check for `redundant_explicit_links`
- updated to text for compile fail tests
---
## Changelog
- updates for rust 1.73
Objective
---------
- Since #6742, It is not possible to build an `ArchetypeId` from a
`ArchetypeGeneration`
- This was useful to 3rd party crate extending the base bevy ECS
capabilities, such as [`bevy_ecs_dynamic`] and now
[`bevy_mod_dynamic_query`]
- Making `ArchetypeGeneration` opaque this way made it completely
useless, and removed the ability to limit archetype updates to a subset
of archetypes.
- Making the `index` method on `ArchetypeId` private prevented the use
of bitfields and other optimized data structure to store sets of
archetype ids. (without `transmute`)
This PR is not a simple reversal of the change. It exposes a different
API, rethought to keep the private stuff private and the public stuff
less error-prone.
- Add a `StartRange<ArchetypeGeneration>` `Index` implementation to
`Archetypes`
- Instead of converting the generation into an index, then creating a
ArchetypeId from that index, and indexing `Archetypes` with it, use
directly the old `ArchetypeGeneration` to get the range of new
archetypes.
From careful benchmarking, it seems to also be a performance improvement
(~0-5%) on add_archetypes.
---
Changelog
---------
- Added `impl Index<RangeFrom<ArchetypeGeneration>> for Archetypes` this
allows you to get a slice of newly added archetypes since the last
recorded generation.
- Added `ArchetypeId::index` and `ArchetypeId::new` methods. It should
enable 3rd party crates to use the `Archetypes` API in a meaningful way.
[`bevy_ecs_dynamic`]:
https://github.com/jakobhellermann/bevy_ecs_dynamic/tree/main
[`bevy_mod_dynamic_query`]:
https://github.com/nicopap/bevy_mod_dynamic_query/
---------
Co-authored-by: vero <email@atlasdostal.com>
# Objective
We've done a lot of work to remove the pattern of a `&World` with
interior mutability (#6404, #8833). However, this pattern still persists
within `bevy_ecs` via the `unsafe_world` method.
## Solution
* Make `unsafe_world` private. Adjust any callsites to use
`UnsafeWorldCell` for interior mutability.
* Add `UnsafeWorldCell::removed_components`, since it is always safe to
access the removed components collection through `UnsafeWorldCell`.
## Future Work
Remove/hide `UnsafeWorldCell::world_metadata`, once we have provided
safe ways of accessing all world metadata.
---
## Changelog
+ Added `UnsafeWorldCell::removed_components`, which provides read-only
access to a world's collection of removed components.
# Objective
- There were a few typos in the project.
- This PR fixes these typos.
## Solution
- Fixing the typos.
Signed-off-by: SADIK KUZU <sadikkuzu@hotmail.com>
# Objective
Improve code-gen for `QueryState::validate_world` and
`SystemState::validate_world`.
## Solution
* Move panics into separate, non-inlined functions, to reduce the code
size of the outer methods.
* Mark the panicking functions with `#[cold]` to help the compiler
optimize for the happy path.
* Mark the functions with `#[track_caller]` to make debugging easier.
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
- I spoke with some users in the ECS channel of bevy discord today and
they suggested that I implement a fallible form of .insert for
components.
- In my opinion, it would be nice to have a fallible .insert like
.try_insert (or to just make insert be fallible!) because it was causing
a lot of panics in my game. In my game, I am spawning terrain chunks and
despawning them in the Update loop. However, this was causing bevy_xpbd
to panic because it was trying to .insert some physics components on my
chunks and a race condition meant that its check to see if the entity
exists would pass but then the next execution step it would not exist
and would do an .insert and then panic. This means that there is no way
to avoid a panic with conditionals.
Luckily, bevy_xpbd does not care about inserting these components if the
entity is being deleted and so if there were a .try_insert, like this PR
provides it could use that instead in order to NOT panic.
( My interim solution for my own game has been to run the entity despawn
events in the Last schedule but really this is just a hack and I should
not be expected to manage the scheduling of despawns like this - it
should just be easy and simple. IF it just so happened that bevy_xpbd
ran .inserts in the Last schedule also, this would be an untenable soln
overall )
## Solution
- Describe the solution used to achieve the objective above.
Add a new command named TryInsert (entitycommands.try_insert) which
functions exactly like .insert except if the entity does not exist it
will not panic. Instead, it will log to info. This way, crates that are
attaching components in ways which they do not mind that the entity no
longer exists can just use try_insert instead of insert.
---
## Changelog
## Additional Thoughts
In my opinion, NOT panicing should really be the default and having an
.insert that does panic should be the odd edgecase but removing the
panic! from .insert seems a bit above my paygrade -- although i would
love to see it. My other thought is it would be good for .insert to
return an Option AND not panic but it seems it uses an event bus right
now so that seems to be impossible w the current architecture.
I'm adopting this ~~child~~ PR.
# Objective
- Working with exclusive world access is not always easy: in many cases,
a standard system or three is more ergonomic to write, and more
modularly maintainable.
- For small, one-off tasks (commonly handled with scripting), running an
event-reader system incurs a small but flat overhead cost and muddies
the schedule.
- Certain forms of logic (e.g. turn-based games) want very fine-grained
linear and/or branching control over logic.
- SystemState is not automatically cached, and so performance can suffer
and change detection breaks.
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2192.
- Partial workaround for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/279.
## Solution
- Adds a SystemRegistry resource to the World, which stores initialized
systems keyed by their SystemSet.
- Allows users to call world.run_system(my_system) and
commands.run_system(my_system), without re-initializing or losing state
(essential for change detection).
- Add a Callback type to enable convenient use of dynamic one shot
systems and reduce the mental overhead of working with Box<dyn
SystemSet>.
- Allow users to run systems based on their SystemSet, enabling more
complex user-made abstractions.
## Future work
- Parameterized one-shot systems would improve reusability and bring
them closer to events and commands. The API could be something like
run_system_with_input(my_system, my_input) and use the In SystemParam.
- We should evaluate the unification of commands and one-shot systems
since they are two different ways to run logic on demand over a World.
### Prior attempts
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2234
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2417
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4090
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7999
This PR continues the work done in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7999.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Federico Rinaldi <gisquerin@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alejandro Pascual Pozo <alejandro.pascual.pozo@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Dmytro Banin <banind@cs.washington.edu>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Rename RemovedComponents::iter/iter_with_id to read/read_with_id to make
it clear that it consume the data
Fixes#9755.
(It's my first pull request, if i've made any mistake, please let me
know)
## Solution
Refactor RemovedComponents::iter/iter_with_id to read/read_with_id
## Changelog
Refactor RemovedComponents::iter/iter_with_id to read/read_with_id
Deprecate RemovedComponents::iter/iter_with_id
Remove IntoIterator implementation
Update removal_detection example accordingly
---
## Migration Guide
Rename calls of RemovedComponents::iter/iter_with_id to
read/read_with_id
Replace IntoIterator iteration (&mut <RemovedComponents>) with .read()
---------
Co-authored-by: denshi_ika <mojang2824@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#9683
## Solution
- Moved `get_component` from `Query` to `QueryState`.
- Moved `get_component_unchecked_mut` from `Query` to `QueryState`.
- Moved `QueryComponentError` from `bevy_ecs::system` to
`bevy_ecs::query`. Minor Breaking Change.
- Narrowed scope of `unsafe` blocks in `Query` methods.
---
## Migration Guide
- `use bevy_ecs::system::QueryComponentError;` -> `use
bevy_ecs::query::QueryComponentError;`
## Notes
I am not very familiar with unsafe Rust nor its use within Bevy, so I
may have committed a Rust faux pas during the migration.
---------
Co-authored-by: Zac Harrold <zharrold@c5prosolutions.com>
Co-authored-by: Tristan Guichaoua <33934311+tguichaoua@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#9244.
## Solution
- Changed the `(Into)SystemSetConfigs` traits and structs be more like
the `(Into)SystemConfigs` traits and structs.
- Replaced uses of `IntoSystemSetConfig` with `IntoSystemSetConfigs`
- Added generic `ItemConfig` and `ItemConfigs` types.
- Changed `SystemConfig(s)` and `SystemSetConfig(s)` to be type aliases
to `ItemConfig(s)`.
- Added generic `process_configs` to `ScheduleGraph`.
- Changed `configure_sets_inner` and `add_systems_inner` to reuse
`process_configs`.
---
## Changelog
- Added `run_if` to `IntoSystemSetConfigs`
- Deprecated `Schedule::configure_set` and `App::configure_set`
- Removed `IntoSystemSetConfig`
## Migration Guide
- Use `App::configure_sets` instead of `App::configure_set`
- Use `Schedule::configure_sets` instead of `Schedule::configure_set`
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Currently we don't have panicking alternative for getting components
from `Query` like for resources. Partially addresses #9443.
## Solution
- Add these functions.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `Query::component` and `Query::component_mut` to get specific
component from query and panic on error.
# Objective
`QueryState::is_empty` is unsound, as it does not validate the world. If
a mismatched world is passed in, then the query filter may cast a
component to an incorrect type, causing undefined behavior.
## Solution
Add world validation. To prevent a performance regression in `Query`
(whose world does not need to be validated), the unchecked function
`is_empty_unsafe_world_cell` has been added. This also allows us to
remove one of the last usages of the private function
`UnsafeWorldCell::unsafe_world`, which takes us a step towards being
able to remove that method entirely.
# Objective
Fix#4278Fix#5504Fix#9422
Provide safe ways to borrow an entire entity, while allowing disjoint
mutable access. `EntityRef` and `EntityMut` are not suitable for this,
since they provide access to the entire world -- they are just helper
types for working with `&World`/`&mut World`.
This has potential uses for reflection and serialization
## Solution
Remove `EntityRef::world`, which allows it to soundly be used within
queries.
`EntityMut` no longer supports structural world mutations, which allows
multiple instances of it to exist for different entities at once.
Structural world mutations are performed using the new type
`EntityWorldMut`.
```rust
fn disjoint_system(
q2: Query<&mut A>,
q1: Query<EntityMut, Without<A>>,
) { ... }
let [entity1, entity2] = world.many_entities_mut([id1, id2]);
*entity1.get_mut::<T>().unwrap() = *entity2.get().unwrap();
for entity in world.iter_entities_mut() {
...
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Removed `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with queries.
+ Removed the ability to structurally mutate the world using
`EntityMut`, which allows it to be used in queries.
+ Added `EntityWorldMut`, which is used to perform structural mutations
that are no longer allowed using `EntityMut`.
## Migration Guide
**Note for maintainers: ensure that the guide for #9604 is updated
accordingly.**
Removed the method `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with
queries. If you need access to `&World` while using an `EntityRef`,
consider passing the world as a separate parameter.
`EntityMut` can no longer perform 'structural' world mutations, such as
adding or removing components, or despawning the entity. Additionally,
`EntityMut::world`, `EntityMut::world_mut` , and
`EntityMut::world_scope` have been removed.
Instead, use the newly-added type `EntityWorldMut`, which is a helper
type for working with `&mut World`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Move schedule name into `Schedule` to allow the schedule name to be
used for errors and tracing in Schedule methods
- Fixes#9510
## Solution
- Move label onto `Schedule` and adjust api's on `World` and `Schedule`
to not pass explicit label where it makes sense to.
- add name to errors and tracing.
- `Schedule::new` now takes a label so either add the label or use
`Schedule::default` which uses a default label. `default` is mostly used
in doc examples and tests.
---
## Changelog
- move label onto `Schedule` to improve error message and logging for
schedules.
## Migration Guide
`Schedule::new` and `App::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
app.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
app.add_schedule(schedule);
```
if you aren't using a label and are using the schedule struct directly
you can use the default constructor.
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedule.run(world);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::default();
schedule.run(world);
```
`Schedules:insert`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedules.insert(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
schedules.insert(schedule);
```
`World::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
world.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
world.add_schedule(schedule);
```
# Objective
To enable non exclusive system usage of reflected components and make
reflection more ergonomic to use by making it more in line with standard
entity commands.
## Solution
- Implements a new `EntityCommands` extension trait for reflection
related functions in the reflect module of bevy_ecs.
- Implements 4 new commands, `insert_reflect`,
`insert_reflect_with_registry`, `remove_reflect`, and
`remove_reflect_with_registry`. Both insert commands take a `Box<dyn
Reflect>` component while the remove commands take the component type
name.
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module. (Might be worth making these just public to enable user end
custom entity commands in a different pr)
- Added basic tests to ensure the commands are actually working.
- Documentation of functions.
---
## Changelog
Added:
- Implements 4 new commands on the new entity commands extension.
- `insert_reflect`
- `remove_reflect`
- `insert_reflect_with_registry`
- `remove_reflect_with_registry`
The commands operate the same except the with_registry commands take a
generic parameter for a resource that implements `AsRef<TypeRegistry>`.
Otherwise the default commands use the `AppTypeRegistry` for reflection
data.
Changed:
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module.
> Hopefully this time it works. Please don't make me rebase again ☹
# Objective
- Fixes#4917
- Replaces #9602
## Solution
- Replaced `EntityCommand` implementation for `FnOnce` to apply to
`FnOnce(EntityMut)` instead of `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)`
---
## Changelog
- `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)` no longer implements `EntityCommand`.
This is a breaking change.
## Migration Guide
### 1. New-Type `FnOnce`
Create an `EntityCommand` type which implements the method you
previously wrote:
```rust
pub struct ClassicEntityCommand<F>(pub F);
impl<F> EntityCommand for ClassicEntityCommand<F>
where
F: FnOnce(Entity, &mut World) + Send + 'static,
{
fn apply(self, id: Entity, world: &mut World) {
(self.0)(id, world);
}
}
commands.add(ClassicEntityCommand(|id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
}));
```
### 2. Extract `(Entity, &mut World)` from `EntityMut`
The method `into_world_mut` can be used to gain access to the `World`
from an `EntityMut`.
```rust
let old = |id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
};
let new = |mut entity: EntityMut| {
let id = entity.id();
let world = entity.into_world_mut();
/* ... */
};
```
# Objective
#5483 allows for the creation of non-`Sync` locals. However, it's not
actually possible to use these types as there is a `Sync` bound on the
`Deref` impls.
## Solution
Remove the unnecessary bounds.
# Objective
Any time we wish to transform the output of a system, we currently use
system piping to do so:
```rust
my_system.pipe(|In(x)| do_something(x))
```
Unfortunately, system piping is not a zero cost abstraction. Each call
to `.pipe` requires allocating two extra access sets: one for the second
system and one for the combined accesses of both systems. This also adds
extra work to each call to `update_archetype_component_access`, which
stacks as one adds multiple layers of system piping.
## Solution
Add the `AdapterSystem` abstraction: similar to `CombinatorSystem`, this
allows you to implement a trait to generically control how a system is
run and how its inputs and outputs are processed. Unlike
`CombinatorSystem`, this does not have any overhead when computing world
accesses which makes it ideal for simple operations such as inverting or
ignoring the output of a system.
Add the extension method `.map(...)`: this is similar to `.pipe(...)`,
only it accepts a closure as an argument instead of an `In<T>` system.
```rust
my_system.map(do_something)
```
This has the added benefit of making system names less messy: a system
that ignores its output will just be called `my_system`, instead of
`Pipe(my_system, ignore)`
---
## Changelog
TODO
## Migration Guide
The `system_adapter` functions have been deprecated: use `.map` instead,
which is a lightweight alternative to `.pipe`.
```rust
// Before:
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::ignore)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::unwrap)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::new(T::from))
// After:
my_system.map(std::mem::drop)
my_system.map(Result::unwrap)
my_system.map(T::from)
// Before:
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::info)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::dbg)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::warn)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::error)
// After:
my_system.map(bevy_utils::info)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::dbg)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::warn)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::error)
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
* `Local` and `SystemName` implement `Debug` manually, but they could
derive it.
* `QueryState` and `dyn System` have unconventional debug formatting.
Add a `RunSystem` extension trait to allow for immediate execution of
systems on a `World` for debugging and/or testing purposes.
# Objective
Fixes#6184
Initially, I made this CL as `ApplyCommands`. After a discussion with
@cart , we decided a more generic implementation would be better to
support all systems. This is the new revised CL. Sorry for the long
delay! 😅
This CL allows users to do this:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::ecs::system::RunSystem;
struct T(usize);
impl Resource for T {}
fn system(In(n): In<usize>, mut commands: Commands) -> usize {
commands.insert_resource(T(n));
n + 1
}
let mut world = World::default();
let n = world.run_system_with(1, system);
assert_eq!(n, 2);
assert_eq!(world.resource::<T>().0, 1);
```
## Solution
This is implemented as a trait extension and not included in any
preludes to ensure it's being used consciously.
Internally, it just initializes and runs a systems, and applies any
deferred parameters all "in place".
The trait has 2 functions (one of which calls the other by default):
- `run_system_with` is the general implementation, which allows user to
pass system input parameters
- `run_system` is the ergonomic wrapper for systems with no input
parameter (to avoid having the user pass `()` as input).
~~Additionally, this trait is also implemented for `&mut App`. I added
this mainly for ergonomics (`app.run_system` vs.
`app.world.run_system`).~~ (Removed based on feedback)
---------
Co-authored-by: Pascal Hertleif <killercup@gmail.com>
# Objective
The `lifetimeless` module has been a source of confusion for bevy users
for a while now.
## Solution
Add a couple paragraph explaining that, yes, you can use one of the type
alias safely, without ever leaking any memory.
# Objective
Fixes#9200
Switches ()'s to []'s when talking about the optional `_mut` suffix in
the ECS Query Struct page to have more idiomatic docs.
## Solution
Replace `()` with `[]` in appropriate doc pages.
# Objective
Fix typos throughout the project.
## Solution
[`typos`](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos) project was used for
scanning, but no automatic corrections were applied. I checked
everything by hand before fixing.
Most of the changes are documentation/comments corrections. Also, there
are few trivial changes to code (variable name, pub(crate) function name
and a few error/panic messages).
## Unsolved
`bevy_reflect_derive` has
[typo](1b51053f19/crates/bevy_reflect/bevy_reflect_derive/src/type_path.rs (L76))
in enum variant name that I didn't fix. Enum is `pub(crate)`, so there
shouldn't be any trouble if fixed. However, code is tightly coupled with
macro usage, so I decided to leave it for more experienced contributor
just in case.
# Objective
`World::entity`, `World::entity_mut` and `Commands::entity` should be
marked with `track_caller` to display where (in user code) the call with
the invalid `Entity` was made. `Commands::entity` already has the
attibute, but it does nothing due to the call to `unwrap_or_else`.
## Solution
- Apply the `track_caller` attribute to the `World::entity_mut` and
`World::entity`.
- Remove the call to `unwrap_or_else` which makes the `track_caller`
attribute useless (because `unwrap_or_else` is not `track_caller`
itself). The avoid eager evaluation of the panicking branch it is never
inlined.
---------
Co-authored-by: Giacomo Stevanato <giaco.stevanato@gmail.com>
# Objective
Partially address #5504. Fix#4278. Provide "whole entity" access in
queries. This can be useful when you don't know at compile time what
you're accessing (i.e. reflection via `ReflectComponent`).
## Solution
Implement `WorldQuery` for `EntityRef`.
- This provides read-only access to the entire entity, and supports
anything that `EntityRef` can normally do.
- It matches all archetypes and tables and will densely iterate when
possible.
- It marks all of the ArchetypeComponentIds of a matched archetype as
read.
- Adding it to a query will cause it to panic if used in conjunction
with any other mutable access.
- Expanded the docs on Query to advertise this feature.
- Added tests to ensure the panics were working as intended.
- Added `EntityRef` to the ECS prelude.
To make this safe, `EntityRef::world` was removed as it gave potential
`UnsafeCell`-like access to other parts of the `World` including aliased
mutable access to the components it would otherwise read safely.
## Performance
Not great beyond the additional parallelization opportunity over
exclusive systems. The `EntityRef` is fetched from `Entities` like any
other call to `World::entity`, which can be very random access heavy.
This could be simplified if `ArchetypeRow` is available in
`WorldQuery::fetch`'s arguments, but that's likely not something we
should optimize for.
## Future work
An equivalent API where it gives mutable access to all components on a
entity can be done with a scoped version of `EntityMut` where it does
not provide `&mut World` access nor allow for structural changes to the
entity is feasible as well. This could be done as a safe alternative to
exclusive system when structural mutation isn't required or the target
set of entities is scoped.
---
## Changelog
Added: `Access::has_any_write`
Added: `EntityRef` now implements `WorldQuery`. Allows read-only access
to the entire entity, incompatible with any other mutable access, can be
mixed with `With`/`Without` filters for more targeted use.
Added: `EntityRef` to `bevy::ecs::prelude`.
Removed: `EntityRef::world`
## Migration Guide
TODO
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Weinberg <weinbergcarter@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <jakob.hellermann@protonmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Resolves#7558.
Systems that are known to never modify the world implement the trait
`ReadOnlySystem`. This is a perfect place to add a safe API for running
a system with a shared reference to a World.
---
## Changelog
- Added the trait method `ReadOnlySystem::run_readonly`, which allows a
system to be run using `&World`.
# Objective
Follow-up to #6404 and #8292.
Mutating the world through a shared reference is surprising, and it
makes the meaning of `&World` unclear: sometimes it gives read-only
access to the entire world, and sometimes it gives interior mutable
access to only part of it.
This is an up-to-date version of #6972.
## Solution
Use `UnsafeWorldCell` for all interior mutability. Now, `&World`
*always* gives you read-only access to the entire world.
---
## Changelog
TODO - do we still care about changelogs?
## Migration Guide
Mutating any world data using `&World` is now considered unsound -- the
type `UnsafeWorldCell` must be used to achieve interior mutability. The
following methods now accept `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of `&World`:
- `QueryState`: `get_unchecked`, `iter_unchecked`,
`iter_combinations_unchecked`, `for_each_unchecked`,
`get_single_unchecked`, `get_single_unchecked_manual`.
- `SystemState`: `get_unchecked_manual`
```rust
let mut world = World::new();
let mut query = world.query::<&mut T>();
// Before:
let t1 = query.get_unchecked(&world, entity_1);
let t2 = query.get_unchecked(&world, entity_2);
// After:
let world_cell = world.as_unsafe_world_cell();
let t1 = query.get_unchecked(world_cell, entity_1);
let t2 = query.get_unchecked(world_cell, entity_2);
```
The methods `QueryState::validate_world` and
`SystemState::matches_world` now take a `WorldId` instead of `&World`:
```rust
// Before:
query_state.validate_world(&world);
// After:
query_state.validate_world(world.id());
```
The methods `QueryState::update_archetypes` and
`SystemState::update_archetypes` now take `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`:
```rust
// Before:
query_state.update_archetypes(&world);
// After:
query_state.update_archetypes(world.as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly());
```
# Objective
Make a combined system cloneable if both systems are cloneable on their
own. This is necessary for using chained conditions (e.g
`cond1.and_then(cond2)`) with `distributive_run_if()`.
## Solution
Implement `Clone` for `CombinatorSystem<Func, A, B>` where `A, B:
Clone`.
# Objective
- Fixes#8811 .
## Solution
- Rename "write" method to "apply" in Command trait definition.
- Rename other implementations of command trait throughout bevy's code
base.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: `Command::write` has been changed to `Command::apply`
- Changed: `EntityCommand::write` has been changed to
`EntityCommand::apply`
## Migration Guide
- `Command::write` implementations need to be changed to implement
`Command::apply` instead. This is a mere name change, with no further
actions needed.
- `EntityCommand::write` implementations need to be changed to implement
`EntityCommand::apply` instead. This is a mere name change, with no
further actions needed.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Title.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Be consistent with `Resource`s and `Components` and have `Event` types
be more self-documenting.
Although not susceptible to accidentally using a function instead of a
value due to `Event`s only being initialized by their type, much of the
same reasoning for removing the blanket impl on `Resource` also applies
here.
* Not immediately obvious if a type is intended to be an event
* Prevent invisible conflicts if the same third-party or primitive types
are used as events
* Allows for further extensions (e.g. opt-in warning for missed events)
## Solution
Remove the blanket impl for the `Event` trait. Add a derive macro for
it.
---
## Changelog
- `Event` is no longer implemented for all applicable types. Add the
`#[derive(Event)]` macro for events.
## Migration Guide
* Add the `#[derive(Event)]` macro for events. Third-party types used as
events should be wrapped in a newtype.
# Objective
- `apply_system_buffers` is an unhelpful name: it introduces a new
internal-only concept
- this is particularly rough for beginners as reasoning about how
commands work is a critical stumbling block
## Solution
- rename `apply_system_buffers` to the more descriptive `apply_deferred`
- rename related fields, arguments and methods in the internals fo
bevy_ecs for consistency
- update the docs
## Changelog
`apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred`, to more
clearly communicate its intent and relation to `Deferred` system
parameters like `Commands`.
## Migration Guide
- `apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred`
- the `apply_system_buffers` method on the `System` trait has been
renamed to `apply_deferred`
- the `is_apply_system_buffers` function has been replaced by
`is_apply_deferred`
- `Executor::set_apply_final_buffers` is now
`Executor::set_apply_final_deferred`
- `Schedule::apply_system_buffers` is now `Schedule::apply_deferred`
---------
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Several of our built-in `Command` types are too public:
- `GetOrSpawn` is public, even though it only makes sense to call it
from within `Commands::get_or_spawn`.
- `Remove` and `RemoveResource` contain public `PhantomData` marker
fields.
## Solution
Remove `GetOrSpawn` and use an anonymous command. Make the marker fields
private.
---
## Migration Guide
The `Command` types `Remove` and `RemoveResource` may no longer be
constructed manually.
```rust
// Before:
commands.add(Remove::<T> {
entity: id,
phantom: PhantomData,
});
// After:
commands.add(Remove::<T>::new(id));
// Before:
commands.add(RemoveResource::<T> { phantom: PhantomData });
// After:
commands.add(RemoveResource::<T>::new());
```
The command type `GetOrSpawn` has been removed. It was not possible to
use this type outside of `bevy_ecs`.
# Objective
Add documentation to `Query` and `QueryState` errors in bevy_ecs
(`QuerySingleError`, `QueryEntityError`, `QueryComponentError`)
## Solution
- Change display message for `QueryEntityError::QueryDoesNotMatch`: this
error can also happen when the entity has a component which is filtered
out (with `Without<C>`)
- Fix wrong reference in the documentation of `Query::get_component` and
`Query::get_component_mut` from `QueryEntityError` to
`QueryComponentError`
- Complete the documentation of the three error enum variants.
- Add examples for `QueryComponentError::MissingReadAccess` and
`QueryComponentError::MissingWriteAccess`
- Add reference to `QueryState` in `QueryEntityError`'s documentation.
---
## Migration Guide
Expect `QueryEntityError::QueryDoesNotMatch`'s display message to
change? Not sure that counts.
---------
Co-authored-by: harudagondi <giogdeasis@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#7833.
Safety comments in the multi-threaded executor don't really talk about
system world accesses, which makes it unclear if the code is actually
valid.
## Solution
Update the `System` trait to use `UnsafeWorldCell`. This type's API is
written in a way that makes it much easier to cleanly maintain safety
invariants. Use this type throughout the multi-threaded executor, with a
liberal use of safety comments.
---
## Migration Guide
The `System` trait now uses `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of `&World`. This
type provides a robust API for interior mutable world access.
- The method `run_unsafe` uses this type to manage world mutations
across multiple threads.
- The method `update_archetype_component_access` uses this type to
ensure that only world metadata can be used.
```rust
let mut system = IntoSystem::into_system(my_system);
system.initialize(&mut world);
// Before:
system.update_archetype_component_access(&world);
unsafe { system.run_unsafe(&world) }
// After:
system.update_archetype_component_access(world.as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly());
unsafe { system.run_unsafe(world.as_unsafe_world_cell()) }
```
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Links in the api docs are nice. I noticed that there were several places
where structs / functions and other things were referenced in the docs,
but weren't linked. I added the links where possible / logical.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Follow-up to #8377.
As the system module has been refactored, there are many types that no
longer make sense to live in the files that they do:
- The `IntoSystem` trait is in `function_system.rs`, even though this
trait is relevant to all kinds of systems. Same for the `In<T>` type.
- `PipeSystem` is now just an implementation of `CombinatorSystem`, so
`system_piping.rs` no longer needs its own file.
## Solution
- Move `IntoSystem`, `In<T>`, and system piping combinators & tests into
the top-level `mod.rs` file for `bevy_ecs::system`.
- Move `PipeSystem` into `combinator.rs`.
# Objective
- Currently, it is not possible to call `.pipe` on a system that takes
any input other than `()`.
- The `IntoPipeSystem` trait is currently very difficult to parse due to
its use of generics.
## Solution
Remove the `IntoPipeSystem` trait, and move the `pipe` method to
`IntoSystem`.
---
## Changelog
- System piping has been made more flexible: it is now possible to call
`.pipe` on a system that takes an input.
## Migration Guide
The `IntoPipeSystem` trait has been removed, and the `pipe` method has
been moved to the `IntoSystem` trait.
```rust
// Before:
use bevy_ecs::system::IntoPipeSystem;
schedule.add_systems(first.pipe(second));
// After:
use bevy_ecs::system::IntoSystem;
schedule.add_systems(first.pipe(second));
```
# Objective
The implementation of `System::run_unsafe` for `FunctionSystem` requires
that the world is the same one used to initialize the system. However,
the `System` trait has no requirements that the world actually matches,
which makes this implementation unsound.
This was previously mentioned in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7605#issuecomment-1426491871
Fixes part of #7833.
## Solution
Add the safety invariant that
`System::update_archetype_component_access` must be called prior to
`System::run_unsafe`. Since
`FunctionSystem::update_archetype_component_access` properly validates
the world, this ensures that `run_unsafe` is not called with a
mismatched world.
Most exclusive systems are not required to be run on the same world that
they are initialized with, so this is not a concern for them. Systems
formed by combining an exclusive system with a regular system *do*
require the world to match, however the validation is done inside of
`System::run` when needed.
# Objective
This PR attempts to improve query compatibility checks in scenarios
involving `Or` filters.
Currently, for the following two disjoint queries, Bevy will throw a
panic:
```
fn sys(_: Query<&mut C, Or<(With<A>, With<B>)>>, _: Query<&mut C, (Without<A>, Without<B>)>) {}
```
This PR addresses this particular scenario.
## Solution
`FilteredAccess::with` now stores a vector of `AccessFilters`
(representing a pair of `with` and `without` bitsets), where each member
represents an `Or` "variant".
Filters like `(With<A>, Or<(With<B>, Without<C>)>` are expected to be
expanded into `A * B + A * !C`.
When calculating whether queries are compatible, every `AccessFilters`
of a query is tested for incompatibility with every `AccessFilters` of
another query.
---
## Changelog
- Improved system and query data access compatibility checks in
scenarios involving `Or` filters
---------
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
The behavior of change detection within `PipeSystem` is very tricky and
subtle, and is not currently covered by any of our tests as far as I'm
aware.
Fixes issue mentioned in PR #8285.
_Note: By mistake, this is currently dependent on #8285_
# Objective
Ensure consistency in the spelling of the documentation.
Exceptions:
`crates/bevy_mikktspace/src/generated.rs` - Has not been changed from
licence to license as it is part of a licensing agreement.
Maybe for further consistency,
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website should also be given a look.
## Solution
### Changed the spelling of the current words (UK/CN/AU -> US) :
cancelled -> canceled (Breaking API changes in #8285)
behaviour -> behavior (Breaking API changes in #8285)
neighbour -> neighbor
grey -> gray
recognise -> recognize
centre -> center
metres -> meters
colour -> color
### ~~Update [`engine_style_guide.md`]~~ Moved to #8324
---
## Changelog
Changed UK spellings in documentation to US
## Migration Guide
Non-breaking changes*
\* If merged after #8285
# Objective
The type `&World` is currently in an awkward place, since it has two
meanings:
1. Read-only access to the entire world.
2. Interior mutable access to the world; immutable and/or mutable access
to certain portions of world data.
This makes `&World` difficult to reason about, and surprising to see in
function signatures if one does not know about the interior mutable
property.
The type `UnsafeWorldCell` was added in #6404, which is meant to
alleviate this confusion by adding a dedicated type for interior mutable
world access. However, much of the engine still treats `&World` as an
interior mutable-ish type. One of those places is `SystemParam`.
## Solution
Modify `SystemParam::get_param` to accept `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. Simplify the safety invariants, since the `UnsafeWorldCell`
type encapsulates the concept of constrained world access.
---
## Changelog
`SystemParam::get_param` now accepts an `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. This type provides a high-level API for unsafe interior
mutable world access.
## Migration Guide
For manual implementers of `SystemParam`: the function `get_item` now
takes `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of `&World`. To access world data, use:
* `.get_entity()`, which returns an `UnsafeEntityCell` which can be used
to access component data.
* `get_resource()` and its variants, to access resource data.
# Objective
Follow-up to #8030.
Now that `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` are implemented for
`PhantomData`, the `ignore` attributes are now unnecessary.
---
## Changelog
- Removed the attributes `#[system_param(ignore)]` and
`#[world_query(ignore)]`.
## Migration Guide
The attributes `#[system_param(ignore)]` and `#[world_query]` ignore
have been removed. If you were using either of these with `PhantomData`
fields, you can simply remove the attribute:
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
struct MyParam<'w, 's, Marker> {
...
// Before:
#[system_param(ignore)
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
// After:
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
struct MyQuery<Marker> {
...
// Before:
#[world_query(ignore)
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
// After:
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
}
```
If you were using this for another type that implements `Default`,
consider wrapping that type in `Local<>` (this only works for
`SystemParam`):
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
struct MyParam<'w, 's> {
// Before:
#[system_param(ignore)]
value: MyDefaultType, // This will be initialized using `Default` each time `MyParam` is created.
// After:
value: Local<MyDefaultType>, // This will be initialized using `Default` the first time `MyParam` is created.
}
```
If you are implementing either trait and need to preserve the exact
behavior of the old `ignore` attributes, consider manually implementing
`SystemParam` or `WorldQuery` for a wrapper struct that uses the
`Default` trait:
```rust
// Before:
#[derive(WorldQuery)
struct MyQuery {
#[world_query(ignore)]
str: String,
}
// After:
#[derive(WorldQuery)
struct MyQuery {
str: DefaultQuery<String>,
}
pub struct DefaultQuery<T: Default>(pub T);
unsafe impl<T: Default> WorldQuery for DefaultQuery<T> {
type Item<'w> = Self;
...
unsafe fn fetch<'w>(...) -> Self::Item<'w> {
Self(T::default())
}
}
```
# Objective
Our regression tests for `SystemParam` currently consist of a bunch of
loosely dispersed struct definitions. This is messy, and doesn't fully
test their functionality.
## Solution
Group the struct definitions into functions annotated with `#[test]`.
This not only makes the module more organized, but it allows us to call
`assert_is_system`, which has the potential to catch some bugs that
would have been missed with the old approach. Also, this approach is
consistent with how `WorldQuery` regression tests are organized.
# Objective
When using `PhantomData` fields with the `#[derive(SystemParam)]` or
`#[derive(WorldQuery)]` macros, the user is required to add the
`#[system_param(ignore)]` attribute so that the macro knows to treat
that field specially. This is undesirable, since it makes the macro more
fragile and less consistent.
## Solution
Implement `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` for `PhantomData`. This makes
the `ignore` attributes unnecessary.
Some internal changes make the derive macro compatible with types that
have invariant lifetimes, which fixes#8192. From what I can tell, this
fix requires `PhantomData` to implement `SystemParam` in order to ensure
that all of a type's generic parameters are always constrained.
---
## Changelog
+ Implemented `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` for `PhantomData<T>`.
+ Fixed a miscompilation caused when invariant lifetimes were used with
the `SystemParam` macro.
# Objective
I ran into a case where I need to create a `CommandQueue` and push
standard `Command` actions like `Insert` or `Remove` to it manually. I
saw that `Remove` looked as follows:
```rust
struct Remove<T> {
entity: Entity,
phantom: PhantomData<T>
}
```
so naturally, I tried to use `Remove::<Foo>::from(entity)` but it didn't
exist. We need to specify the `PhantomData` explicitly when creating
this command action. The same goes for `RemoveResource` and
`InitResource`
## Solution
This PR implements the following:
- `From<Entity>` for `Remove<T>`
- `Default` for `RemoveResource` and `InitResource`
- use these traits in the implementation of methods of `Commands`
- rename `phantom` field on the structs above to `_phantom` to have a
more uniform field naming scheme for the command actions
---
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no
externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
- Added: implemented `From<Entity>` for `Remove<T>` and `Default` for
`RemoveResource` and `InitResource` for ergonomics
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Documentation should no longer be using pre-stageless terminology to
avoid confusion.
## Solution
- update all docs referring to stages to instead refer to sets/schedules
where appropriate
- also mention `apply_system_buffers` for anything system-buffer-related
that previously referred to buffers being applied "at the end of a
stage"
# Objective
Fix#1727Fix#8010
Meta types generated by the `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` derive macros
can conflict with user-defined types if they happen to have the same
name.
## Solution
In order to check if an identifier would conflict with user-defined
types, we can just search the original `TokenStream` passed to the macro
to see if it contains the identifier (since the meta types are defined
in an anonymous scope, it's only possible for them to conflict with the
struct definition itself). When generating an identifier for meta types,
we can simply check if it would conflict, and then add additional
characters to the name until it no longer conflicts with anything.
The `WorldQuery` "Item" and read-only structs are a part of a module's
public API, and thus it is intended for them to conflict with
user-defined types.
# Objective
The function `assert_is_system` is used in documentation tests to ensure
that example code actually produces valid systems. Currently,
`assert_is_system` just checks that each function parameter implements
`SystemParam`. To further check the validity of the system, we should
initialize the passed system so that it will be checked for conflicting
accesses. Not only does this enforce the validity of our examples, but
it provides a convenient way to demonstrate conflicting accesses via a
`should_panic` example, which is nicely rendered by rustdoc:
## Solution
Initialize the system with an empty world to trigger its internal access
conflict checks.
---
## Changelog
The function `bevy::ecs::system::assert_is_system` now panics when
passed a system with conflicting world accesses, as does
`assert_is_read_only_system`.
## Migration Guide
The functions `assert_is_system` and `assert_is_read_only_system` (in
`bevy_ecs::system`) now panic if the passed system has invalid world
accesses. Any tests that called this function on a system with invalid
accesses will now fail. Either fix the system's conflicting accesses, or
specify that the test is meant to fail:
1. For regular tests (that is, functions annotated with `#[test]`), add
the `#[should_panic]` attribute to the function.
2. For documentation tests, add `should_panic` to the start of the code
block: ` ```should_panic`
# Objective
- A more intuitive distinction between the two. `remove_intersection` is verbose and unclear.
- `EntityMut::remove` and `Commands::remove` should match.
## Solution
- What the title says.
---
## Migration Guide
Before
```rust
fn clear_children(parent: Entity, world: &mut World) {
if let Some(children) = world.entity_mut(parent).remove::<Children>() {
for &child in &children.0 {
world.entity_mut(child).remove_intersection::<Parent>();
}
}
}
```
After
```rust
fn clear_children(parent: Entity, world: &mut World) {
if let Some(children) = world.entity_mut(parent).take::<Children>() {
for &child in &children.0 {
world.entity_mut(child).remove::<Parent>();
}
}
}
```
# Objective
While we use `#[doc(hidden)]` to try and hide marker generics from the user, these types reveal themselves in compiler errors, adding visual noise and confusion.
## Solution
Replace the `AlreadyWasSystem` marker generic with `()`, to reduce visual noise in error messages. This also makes it possible to return `impl Condition<()>` from combinators.
For function systems, use their function signature as the marker type. This should drastically improve the legibility of some error messages.
The `InputMarker` type has been removed, since it is unnecessary.
# Objective
Several places in the ECS use marker generics to avoid overlapping trait implementations, but different places alternately refer to it as `Params` and `Marker`. This is potentially confusing, since it might not be clear that the same pattern is being used. Additionally, users might be misled into thinking that the `Params` type corresponds to the `SystemParam`s of a system.
## Solution
Rename `Params` to `Marker`.
# Objective
Fix#7584.
## Solution
Add an abstraction for creating custom system combinators with minimal boilerplate. Use this to implement AND/OR combinators. Use this to simplify the implementation of `PipeSystem`.
## Example
Feel free to bikeshed on the syntax.
I chose the names `and_then`/`or_else` to emphasize the fact that these short-circuit, while I chose method syntax to empasize that the arguments are *not* treated equally.
```rust
app.add_systems((
my_system.run_if(resource_exists::<R>().and_then(resource_equals(R(0)))),
our_system.run_if(resource_exists::<R>().or_else(resource_exists::<S>())),
));
```
---
## Todo
- [ ] Decide on a syntax
- [x] Write docs
- [x] Write tests
## Changelog
+ Added the extension methods `.and_then(...)` and `.or_else(...)` to run conditions, which allows combining run conditions with short-circuiting behavior.
+ Added the trait `Combine`, which can be used with the new `CombinatorSystem` to create system combinators with custom behavior.
# Objective
- Fixes#5432
- Fixes#6680
## Solution
- move code responsible for generating the `impl TypeUuid` from `type_uuid_derive` into a new function, `gen_impl_type_uuid`.
- this allows the new proc macro, `impl_type_uuid`, to call the code for generation.
- added struct `TypeUuidDef` and implemented `syn::Parse` to allow parsing of the input for the new macro.
- finally, used the new macro `impl_type_uuid` to implement `TypeUuid` for the standard library (in `crates/bevy_reflect/src/type_uuid_impl.rs`).
- fixes#6680 by doing a wrapping add of the param's index to its `TYPE_UUID`
Co-authored-by: dis-da-moe <84386186+dis-da-moe@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The `SystemParamFunction` (and `ExclusiveSystemParamFunction`) trait is very cumbersome to use, due to it requiring four generic type parameters. These are currently all used as marker parameters to satisfy rust's trait coherence rules.
### Example (before)
```rust
pub fn pipe<AIn, Shared, BOut, A, AParam, AMarker, B, BParam, BMarker>(
mut system_a: A,
mut system_b: B,
) -> impl FnMut(In<AIn>, ParamSet<(AParam, BParam)>) -> BOut
where
A: SystemParamFunction<AIn, Shared, AParam, AMarker>,
B: SystemParamFunction<Shared, BOut, BParam, BMarker>,
AParam: SystemParam,
BParam: SystemParam,
```
## Solution
Turn the `In`, `Out`, and `Param` generics into associated types. Merge the marker types together to retain coherence.
### Example (after)
```rust
pub fn pipe<A, B, AMarker, BMarker>(
mut system_a: A,
mut system_b: B,
) -> impl FnMut(In<A::In>, ParamSet<(A::Param, B::Param)>) -> B::Out
where
A: SystemParamFunction<AMarker>,
B: SystemParamFunction<BMarker, In = A::Out>,
```
---
## Changelog
+ Simplified the `SystemParamFunction` and `ExclusiveSystemParamFunction` traits.
## Migration Guide
For users of the `SystemParamFunction` trait, the generic type parameters `In`, `Out`, and `Param` have been turned into associated types. The same has been done with the `ExclusiveSystemParamFunction` trait.
# Objective
Run conditions are a special type of system that do not modify the world, and which return a bool. Due to the way they are currently implemented, you can *only* use bare function systems as a run condition. Among other things, this prevents the use of system piping with run conditions. This make very basic constructs impossible, such as `my_system.run_if(my_condition.pipe(not))`.
Unblocks a basic solution for #7202.
## Solution
Add the trait `ReadOnlySystem`, which is implemented for any system whose parameters all implement `ReadOnlySystemParam`. Allow any `-> bool` system implementing this trait to be used as a run condition.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the trait `ReadOnlySystem`, which is implemented for any `System` type whose parameters all implement `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
+ Added the function `bevy::ecs::system::assert_is_read_only_system`.
# Objective
One pattern to increase parallelism is deferred mutation: instead of directly mutating the world (and preventing other systems from running at the same time), you queue up operations to be applied to the world at the end of the stage. The most common example of this pattern uses the `Commands` SystemParam.
In order to avoid the overhead associated with commands, some power users may want to add their own deferred mutation behavior. To do this, you must implement the unsafe trait `SystemParam`, which interfaces with engine internals in a way that we'd like users to be able to avoid.
## Solution
Add the `Deferred<T>` primitive `SystemParam`, which encapsulates the deferred mutation pattern.
This can be combined with other types of `SystemParam` to safely and ergonomically create powerful custom types.
Essentially, this is just a variant of `Local<T>` which can run code at the end of the stage.
This type is used in the engine to derive `Commands` and `ParallelCommands`, which removes a bunch of unsafe boilerplate.
### Example
```rust
use bevy_ecs::system::{Deferred, SystemBuffer};
/// Sends events with a delay, but may run in parallel with other event writers.
#[derive(SystemParam)]
pub struct BufferedEventWriter<'s, E: Event> {
queue: Deferred<'s, EventQueue<E>>,
}
struct EventQueue<E>(Vec<E>);
impl<'s, E: Event> BufferedEventWriter<'s, E> {
/// Queues up an event to be sent at the end of this stage.
pub fn send(&mut self, event: E) {
self.queue.0.push(event);
}
}
// The `SystemBuffer` trait controls how [`Deferred`] gets applied at the end of the stage.
impl<E: Event> SystemBuffer for EventQueue<E> {
fn apply(&mut self, world: &mut World) {
let mut events = world.resource_mut::<Events<E>>();
for e in self.0.drain(..) {
events.send(e);
}
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
+ Added the `SystemParam` type `Deferred<T>`, which can be used to defer `World` mutations. Powered by the new trait `SystemBuffer`.
# Objective
- Implementing logic used by system params and `UnsafeWorldCell` on `&World` is sus since `&World` generally denotes shared read only access to world but this is a lie in the above situations. Move most/all logic that uses `&World` to mean `UnsafeWorldCell` onto `UnsafeWorldCell`
- Add a way to take a `&mut World` out of `UnsafeWorldCell` and use this in `WorldCell`'s `Drop` impl instead of a `UnsafeCell` field
---
## Changelog
- changed some `UnsafeWorldCell` methods to take `self` instead of `&self`/`&mut self` since there is literally no point to them doing that
- `UnsafeWorldCell::world` is now used to get immutable access to the whole world instead of just the metadata which can now be done via `UnsafeWorldCell::world_metadata`
- `UnsafeWorldCell::world_mut` now exists and can be used to get a `&mut World` out of `UnsafeWorldCell`
- removed `UnsafeWorldCell::storages` since that is probably unsound since storages contains the actual component/resource data not just metadata
## Migration guide
N/A none of the breaking changes here make any difference for a 0.9->0.10 transition since `UnsafeWorldCell` did not exist in 0.9
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
Removal events are unwieldy and require some knowledge of when to put systems that need to catch events for them, it is very easy to end up missing one and end up with memory leak-ish issues where you don't clean up after yourself.
## Solution
Consolidate removals with the benefits of `Events<...>` (such as double buffering and per system ticks for reading the events) and reduce the special casing of it, ideally I was hoping to move the removals to a `Resource` in the world, but that seems a bit more rough to implement/maintain because of double mutable borrowing issues.
This doesn't go the full length of change detection esque removal detection a la https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/44.
Just tries to make the current workflow a bit more user friendly so detecting removals isn't such a scheduling nightmare.
---
## Changelog
- RemovedComponents<T> is now backed by an `Events<Entity>` for the benefits of double buffering.
## Migration Guide
- Add a `mut` for `removed: RemovedComponents<T>` since we are now modifying an event reader internally.
- Iterating over removed components now requires `&mut removed_components` or `removed_components.iter()` instead of `&removed_components`.
# Objective
The trait method `SystemParam::apply` allows a `SystemParam` type to defer world mutations, which is internally used to apply `Commands` at the end of the stage. Any operations that require `&mut World` access must be deferred in this way, since parallel systems do not have exclusive access to the world.
The `ExclusiveSystemParam` trait (added in #6083) has an `apply` method which serves the same purpose. However, deferring mutations in this way does not make sense for exclusive systems since they already have `&mut World` access: there is no need to wait until a hard sync point, as the system *is* a hard sync point. World mutations can and should be performed within the body of the system.
## Solution
Remove the method. There were no implementations of this method in the engine.
---
## Changelog
*Note for maintainers: this changelog makes more sense if it's placed above the one for #6919.*
- Removed the method `ExclusiveSystemParamState::apply`.
## Migration Guide
*Note for maintainers: this migration guide makes more sense if it's placed above the one for #6919.*
The trait method `ExclusiveSystemParamState::apply` has been removed. If you have an exclusive system with buffers that must be applied, you should apply them within the body of the exclusive system.
# Objective
Fixes#7434.
This is my first time contributing to a Rust project, so please let me know if this wasn't the change intended by the linked issue.
## Solution
Adds a test with a system that panics to `bevy_ecs`.
I'm not sure if this is the intended panic message, but this is what the test currently results in:
```
thread 'system::tests::panic_inside_system' panicked at 'called `Option::unwrap()` on a `None` value', /Users/bjorn/workplace/bevy/crates/bevy_tasks/src/task_pool.rs:354:49
```
# Objective
Fix#7447.
The `SystemParam` derive uses the wrong lifetimes for ignored fields.
## Solution
Use type inference instead of explicitly naming the types of ignored fields. This allows the compiler to automatically use the correct lifetime.
# Objective
I found several words in code and docs are incorrect. This should be fixed.
## Solution
- Fix several minor typos
Co-authored-by: Chris Ohk <utilforever@gmail.com>
alternative to #5922, implements #5956
builds on top of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6402
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5956 goes into more detail, but the TLDR is:
- bevy systems ensure disjoint accesses to resources and components, and for that to work there are methods `World::get_resource_unchecked_mut(&self)`, ..., `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked(&self)` etc.
- we don't have these unchecked methods for `by_id` variants, so third-party crate authors cannot build their own safe disjoint-access abstractions with these
- having `_unchecked_mut` methods is not great, because in their presence safe code can accidentally violate subtle invariants. Having to go through `world.as_unsafe_world_cell().unsafe_method()` forces you to stop and think about what you want to write in your `// SAFETY` comment.
The alternative is to keep exposing `_unchecked_mut` variants for every operation that we want third-party crates to build upon, but we'd prefer to avoid using these methods alltogether: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5922#issuecomment-1241954543
Also, this is something that **cannot be implemented outside of bevy**, so having either this PR or #5922 as an escape hatch with lots of discouraging comments would be great.
## Solution
- add `UnsafeWorldCell` with `unsafe fn get_resource(&self)`, `unsafe fn get_resource_mut(&self)`
- add `fn World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&mut self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>` (and `as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly(&self)`)
- add `UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef` with `unsafe fn get`, `unsafe fn get_mut` and the other utilities on `EntityRef` (no methods for spawning, despawning, insertion)
- use the `UnsafeWorldCell` abstraction in `ReflectComponent`, `ReflectResource` and `ReflectAsset`, so these APIs are easier to reason about
- remove `World::get_resource_mut_unchecked`, `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked` and use `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_mut() }` and `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_entity(entity)?.get_mut() }` instead
This PR does **not** make use of `UnsafeWorldCell` for anywhere else in `bevy_ecs` such as `SystemParam` or `Query`. That is a much larger change, and I am convinced that having `UnsafeWorldCell` is already useful for third-party crates.
Implemented API:
```rust
struct World { .. }
impl World {
fn as_unsafe_world_cell(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>;
}
struct UnsafeWorldCell<'w>(&'w World);
impl<'w> UnsafeWorldCell {
unsafe fn world(&self) -> &World;
fn get_entity(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w>; // returns 'w which is `'self` of the `World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&'w self)`
unsafe fn get_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_by_id(&self, ComponentId) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut_by_id(&self) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>>;
// not included: remove, remove_resource, despawn, anything that might change archetypes
}
struct UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> { .. }
impl UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> {
unsafe fn get<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_mut<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_mut_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_change_ticks<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
// fn id, archetype, contains, contains_id, containts_type_id
}
```
<details>
<summary>UnsafeWorldCell docs</summary>
Variant of the [`World`] where resource and component accesses takes a `&World`, and the responsibility to avoid
aliasing violations are given to the caller instead of being checked at compile-time by rust's unique XOR shared rule.
### Rationale
In rust, having a `&mut World` means that there are absolutely no other references to the safe world alive at the same time,
without exceptions. Not even unsafe code can change this.
But there are situations where careful shared mutable access through a type is possible and safe. For this, rust provides the [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)
escape hatch, which allows you to get a `*mut T` from a `&UnsafeCell<T>` and around which safe abstractions can be built.
Access to resources and components can be done uniquely using [`World::resource_mut`] and [`World::entity_mut`], and shared using [`World::resource`] and [`World::entity`].
These methods use lifetimes to check at compile time that no aliasing rules are being broken.
This alone is not enough to implement bevy systems where multiple systems can access *disjoint* parts of the world concurrently. For this, bevy stores all values of
resources and components (and [`ComponentTicks`](crate::component::ComponentTicks)) in [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)s, and carefully validates disjoint access patterns using
APIs like [`System::component_access`](crate::system::System::component_access).
A system then can be executed using [`System::run_unsafe`](crate::system::System::run_unsafe) with a `&World` and use methods with interior mutability to access resource values.
access resource values.
### Example Usage
[`UnsafeWorldCell`] can be used as a building block for writing APIs that safely allow disjoint access into the world.
In the following example, the world is split into a resource access half and a component access half, where each one can
safely hand out mutable references.
```rust
use bevy_ecs::world::World;
use bevy_ecs::change_detection::Mut;
use bevy_ecs::system::Resource;
use bevy_ecs::world::unsafe_world_cell_world::UnsafeWorldCell;
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access resources in the world
struct OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access components in the world
struct OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
impl<'w> OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w> {
fn get_resource_mut<T: Resource>(&mut self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>> {
// SAFETY: resource access is allowed through this UnsafeWorldCell
unsafe { self.0.get_resource_mut::<T>() }
}
}
// impl<'w> OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w> {
// ...
// }
// the two interior mutable worlds borrow from the `&mut World`, so it cannot be accessed while they are live
fn split_world_access(world: &mut World) -> (OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'_>, OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'_>) {
let resource_access = OnlyResourceAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
let component_access = OnlyComponentAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
(resource_access, component_access)
}
```
</details>
# Objective
`bevy_ecs/system_param.rs` contains many seemingly-arbitrary struct definitions which serve as compile tests.
## Solution
Add a comment to each one, linking the issue or PR that motivated its addition.
# Objective
Fixes#3184. Fixes#6640. Fixes#4798. Using `Query::par_for_each(_mut)` currently requires a `batch_size` parameter, which affects how it chunks up large archetypes and tables into smaller chunks to run in parallel. Tuning this value is difficult, as the performance characteristics entirely depends on the state of the `World` it's being run on. Typically, users will just use a flat constant and just tune it by hand until it performs well in some benchmarks. However, this is both error prone and risks overfitting the tuning on that benchmark.
This PR proposes a naive automatic batch-size computation based on the current state of the `World`.
## Background
`Query::par_for_each(_mut)` schedules a new Task for every archetype or table that it matches. Archetypes/tables larger than the batch size are chunked into smaller tasks. Assuming every entity matched by the query has an identical workload, this makes the worst case scenario involve using a batch size equal to the size of the largest matched archetype or table. Conversely, a batch size of `max {archetype, table} size / thread count * COUNT_PER_THREAD` is likely the sweetspot where the overhead of scheduling tasks is minimized, at least not without grouping small archetypes/tables together.
There is also likely a strict minimum batch size below which the overhead of scheduling these tasks is heavier than running the entire thing single-threaded.
## Solution
- [x] Remove the `batch_size` from `Query(State)::par_for_each` and friends.
- [x] Add a check to compute `batch_size = max {archeytpe/table} size / thread count * COUNT_PER_THREAD`
- [x] ~~Panic if thread count is 0.~~ Defer to `for_each` if the thread count is 1 or less.
- [x] Early return if there is no matched table/archetype.
- [x] Add override option for users have queries that strongly violate the initial assumption that all iterated entities have an equal workload.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Query::par_for_each(_mut)` has been changed to `Query::par_iter(_mut)` and will now automatically try to produce a batch size for callers based on the current `World` state.
## Migration Guide
The `batch_size` parameter for `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)` has been removed. These calls will automatically compute a batch size for you. Remove these parameters from all calls to these functions.
Before:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_for_each(32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
After:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_iter().for_each(|comp| {
...
});
}
```
Co-authored-by: Arnav Choubey <56453634+x-52@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Corey Farwell <coreyf@rwell.org>
Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Safety comments for the `CommandQueue` type are quite sparse and very imprecise. Sometimes, they are right for the wrong reasons or use circular reasoning.
## Solution
- Document previously-implicit safety invariants.
- Rewrite safety comments to actually reflect the specific invariants of each operation.
- Use `OwningPtr` instead of raw pointers, to encode an invariant in the type system instead of via comments.
- Use typed pointer methods when possible to increase reliability.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the function `OwningPtr::read_unaligned`.
# Objective
Speed up the render phase of rendering. An extension of #6885.
`SystemState::get` increments the `World`'s change tick atomically every time it's called. This is notably more expensive than a unsynchronized increment, even without contention. It also updates the archetypes, even when there has been nothing to update when it's called repeatedly.
## Solution
Piggyback off of #6885. Split `SystemState::validate_world_and_update_archetypes` into `SystemState::validate_world` and `SystemState::update_archetypes`, and make the later `pub`. Then create safe variants of `SystemState::get_unchecked_manual` that still validate the `World` but do not update archetypes and do not increment the change tick using `World::read_change_tick` and `World::change_tick`. Update `RenderCommandState` to call `SystemState::update_archetypes` in `Draw::prepare` and `SystemState::get_manual` in `Draw::draw`.
## Performance
There's a slight perf benefit (~2%) for `main_opaque_pass_3d` on `many_foxes` (340.39 us -> 333.32 us)
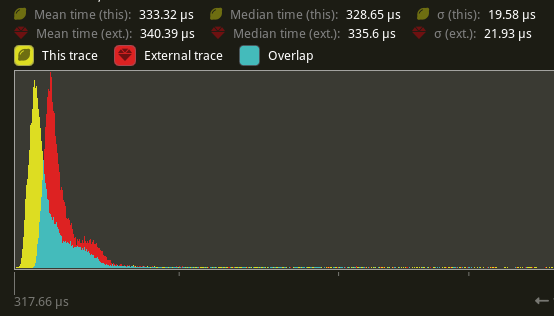
## Alternatives
We can change `SystemState::get` to not increment the `World`'s change tick. Though this would still put updating the archetypes and an atomic read on the hot-path.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SystemState::get_manual`
Added: `SystemState::get_manual_mut`
Added: `SystemState::update_archetypes`
# Objective
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParam` is not implemented for `Option<NonSend<>>`, even though it should be.
Follow-up to #7243. This fixes another mistake made in #6919.
## Solution
Add the missing impl.
# Objective
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParam` is implemented for `NonSendMut`, when it should not be. This mistake was made in #6919.
## Solution
Remove the incorrect impl.
# Objective
Complete the first part of the migration detailed in bevyengine/rfcs#45.
## Solution
Add all the new stuff.
### TODO
- [x] Impl tuple methods.
- [x] Impl chaining.
- [x] Port ambiguity detection.
- [x] Write docs.
- [x] ~~Write more tests.~~(will do later)
- [ ] Write changelog and examples here?
- [x] ~~Replace `petgraph`.~~ (will do later)
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Michael Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#5248.
## Solution
Support `In<T>` parameters and allow returning arbitrary types in exclusive systems.
---
## Changelog
- Exclusive systems may now be used with system piping.
## Migration Guide
Exclusive systems (systems that access `&mut World`) now support system piping, so the `ExclusiveSystemParamFunction` trait now has generics for the `In`put and `Out`put types.
```rust
// Before
fn my_generic_system<T, Param>(system_function: T)
where T: ExclusiveSystemParamFunction<Param>
{ ... }
// After
fn my_generic_system<T, In, Out, Param>(system_function: T)
where T: ExclusiveSystemParamFunction<In, Out, Param>
{ ... }
```
# Objective
- Fixes#7066
## Solution
- Split the ChangeDetection trait into ChangeDetection and ChangeDetectionMut
- Added Ref as equivalent to &T with change detection
---
## Changelog
- Support for Ref which allow inspecting change detection flags in an immutable way
## Migration Guide
- While bevy prelude includes both ChangeDetection and ChangeDetectionMut any code explicitly referencing ChangeDetection might need to be updated to ChangeDetectionMut or both. Specifically any reading logic requires ChangeDetection while writes requires ChangeDetectionMut.
use bevy_ecs::change_detection::DetectChanges -> use bevy_ecs::change_detection::{DetectChanges, DetectChangesMut}
- Previously Res had methods to access change detection `is_changed` and `is_added` those methods have been moved to the `DetectChanges` trait. If you are including bevy prelude you will have access to these types otherwise you will need to `use bevy_ecs::change_detection::DetectChanges` to continue using them.
`Query`'s fields being `pub(crate)` means that the struct can be constructed via safe code from anywhere in `bevy_ecs` . This is Not Good since it is intended that all construction of this type goes through `Query::new` which is an `unsafe fn` letting various `Query` methods rely on those invariants holding even though they can be trivially bypassed.
This has no user facing impact
# Objective
- Fix#7103.
- The issue is caused because I forgot to add a where clause to a generated struct in #7056.
## Solution
- Add the where clause.
`Query` relies on the `World` it stores being the same as the world used for creating the `QueryState` it stores. If they are not the same then everything is very unsound. This was not actually being checked anywhere, `Query::new` did not have a safety invariant or even an assertion that the `WorldId`'s are the same.
This shouldn't have any user facing impact unless we have really messed up in bevy and have unsoundness elsewhere (in which case we would now get a panic instead of being unsound).
# Objective
The type `Local<T>` unnecessarily has the bound `T: Sync` when the local is used in an exclusive system.
## Solution
Lift the bound.
---
## Changelog
Removed the bound `T: Sync` from `Local<T>` when used as an `ExclusiveSystemParam`.
# Objective
Fixes#3310. Fixes#6282. Fixes#6278. Fixes#3666.
## Solution
Split out `!Send` resources into `NonSendResources`. Add a `origin_thread_id` to all `!Send` Resources, check it on dropping `NonSendResourceData`, if there's a mismatch, panic. Moved all of the checks that `MainThreadValidator` would do into `NonSendResources` instead.
All `!Send` resources now individually track which thread they were inserted from. This is validated against for every access, mutation, and drop that could be done against the value.
A regression test using an altered version of the example from #3310 has been added.
This is a stopgap solution for the current status quo. A full solution may involve fully removing `!Send` resources/components from `World`, which will likely require a much more thorough design on how to handle the existing in-engine and ecosystem use cases.
This PR also introduces another breaking change:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Resource)]
struct Resource(u32);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
world.insert_resource(Resource(1));
world.insert_non_send_resource(Resource(2));
let res = world.get_resource_mut::<Resource>().unwrap();
assert_eq!(res.0, 2);
}
```
This code will run correctly on 0.9.1 but not with this PR, since NonSend resources and normal resources have become actual distinct concepts storage wise.
## Changelog
Changed: Fix soundness bug with `World: Send`. Dropping a `World` that contains a `!Send` resource on the wrong thread will now panic.
## Migration Guide
Normal resources and `NonSend` resources no longer share the same backing storage. If `R: Resource`, then `NonSend<R>` and `Res<R>` will return different instances from each other. If you are using both `Res<T>` and `NonSend<T>` (or their mutable variants), to fetch the same resources, it's strongly advised to use `Res<T>`.