# Objective
The method `UnsafeWorldCell::world_mut` is a special case, since its
safety contract is more difficult to satisfy than the other methods on
`UnsafeWorldCell`. Rewrite its documentation to be specific about when
it can and cannot be used. Provide examples and emphasize that it is
unsound to call in most cases.
# Objective
The method `UnsafeWorldCell::read_change_tick` is longer than it needs
to be. `World` only has a method called this because it has two methods
for getting a change tick: one that takes `&self` and one that takes
`&mut self`. Since this distinction is not applicable to
`UnsafeWorldCell`, we should just call this method `change_tick`.
## Solution
Deprecate the current method and add a new one called `change_tick`.
---
## Changelog
- Renamed `UnsafeWorldCell::read_change_tick` to `change_tick`.
## Migration Guide
The `UnsafeWorldCell` method `read_change_tick` has been renamed to
`change_tick`.
# Objective
Fixes#8528
## Solution
Manually implement `PartialEq`, `Eq`, `PartialOrd`, `Ord`, and `Hash`
for `bevy_ecs::event::EventId`. These new implementations do not rely on
the `Event` implementing the same traits allowing `EventId` to be used
in more cases.
# Objective
After fixing dynamic scene to only map specific entities, we want
map_entities to default to the less error prone behavior and have the
previous behavior renamed to "map_all_entities." As this is a breaking
change, it could not be pushed out with the bug fix.
## Solution
Simple rename and refactor.
## Changelog
### Changed
- `map_entities` now accepts a list of entities to apply to, with
`map_all_entities` retaining previous behavior of applying to all
entities in the map.
## Migration Guide
- In `bevy_ecs`, `ReflectMapEntities::map_entites` now requires an
additional `entities` parameter to specify which entities it applies to.
To keep the old behavior, use the new
`ReflectMapEntities::map_all_entities`, but consider if passing the
entities in specifically might be better for your use case to avoid
bugs.
# Objective
- Handle dangling entity references inside scenes
- Handle references to entities with generation > 0 inside scenes
- Fix a latent bug in `Parent`'s `MapEntities` implementation, which
would, if the parent was outside the scene, cause the scene to be loaded
into the new world with a parent reference potentially pointing to some
random entity in that new world.
- Fixes#4793 and addresses #7235
## Solution
- DynamicScenes now identify entities with a `Entity` instead of a u32,
therefore including generation
- `World` exposes a new `reserve_generations` function that despawns an
entity and advances its generation by some extra amount.
- `MapEntities` implementations have a new `get_or_reserve` function
available that will always return an `Entity`, establishing a new
mapping to a dead entity when the entity they are called with is not in
the `EntityMap`. Subsequent calls with that same `Entity` will return
the same newly created dead entity reference, preserving equality
semantics.
- As a result, after loading a scene containing references to dead
entities (or entities otherwise outside the scene), those references
will all point to different generations on a single entity id in the new
world.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- In serialized scenes, entities are now identified by a u64 instead of
a u32.
- In serialized scenes, components with entity references now have those
references serialize as u64s instead of structs.
### Fixed
- Scenes containing components with entity references will now
deserialize and add to a world reliably.
## Migration Guide
- `MapEntities` implementations must change from a `&EntityMap`
parameter to a `&mut EntityMapper` parameter and can no longer return a
`Result`. Finally, they should switch from calling `EntityMap::get` to
calling `EntityMapper::get_or_reserve`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
Links in the api docs are nice. I noticed that there were several places
where structs / functions and other things were referenced in the docs,
but weren't linked. I added the links where possible / logical.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Methods for interacting with world schedules currently have two
variants: one that takes `impl ScheduleLabel` and one that takes `&dyn
ScheduleLabel`. Operations such as `run_schedule` or `schedule_scope`
only use the label by reference, so there is little reason to have an
owned variant of these functions.
## Solution
Decrease maintenance burden by merging the `ref` variants of these
functions with the owned variants.
---
## Changelog
- Deprecated `World::run_schedule_ref`. It is now redundant, since
`World::run_schedule` can take values by reference.
## Migration Guide
The method `World::run_schedule_ref` has been deprecated, and will be
removed in the next version of Bevy. Use `run_schedule` instead.
# Objective
Label traits such as `ScheduleLabel` currently have a major footgun: the
trait is implemented for `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>`, but the
implementation does not function as one would expect since `Box<T>` is
considered to be a distinct type from `T`. This is because the behavior
of the `ScheduleLabel` trait is specified mainly through blanket
implementations, which prevents `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>` from being
properly special-cased.
## Solution
Replace the blanket-implemented behavior with a series of methods
defined on `ScheduleLabel`. This allows us to fully special-case
`Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>` .
---
## Changelog
Fixed a bug where boxed label types (such as `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>`)
behaved incorrectly when compared with concretely-typed labels.
## Migration Guide
The `ScheduleLabel` trait has been refactored to no longer depend on the
traits `std::any::Any`, `bevy_utils::DynEq`, and `bevy_utils::DynHash`.
Any manual implementations will need to implement new trait methods in
their stead.
```rust
impl ScheduleLabel for MyType {
// Before:
fn dyn_clone(&self) -> Box<dyn ScheduleLabel> { ... }
// After:
fn dyn_clone(&self) -> Box<dyn ScheduleLabel> { ... }
fn as_dyn_eq(&self) -> &dyn DynEq {
self
}
// No, `mut state: &mut` is not a typo.
fn dyn_hash(&self, mut state: &mut dyn Hasher) {
self.hash(&mut state);
// Hashing the TypeId isn't strictly necessary, but it prevents collisions.
TypeId::of::<Self>().hash(&mut state);
}
}
```
Added helper extracted from #7711. that PR contains some controversy
conditions, but this one should be good to go.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `any_component_removed` condition.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Follow-up to #8377.
As the system module has been refactored, there are many types that no
longer make sense to live in the files that they do:
- The `IntoSystem` trait is in `function_system.rs`, even though this
trait is relevant to all kinds of systems. Same for the `In<T>` type.
- `PipeSystem` is now just an implementation of `CombinatorSystem`, so
`system_piping.rs` no longer needs its own file.
## Solution
- Move `IntoSystem`, `In<T>`, and system piping combinators & tests into
the top-level `mod.rs` file for `bevy_ecs::system`.
- Move `PipeSystem` into `combinator.rs`.
# Objective
- Currently, it is not possible to call `.pipe` on a system that takes
any input other than `()`.
- The `IntoPipeSystem` trait is currently very difficult to parse due to
its use of generics.
## Solution
Remove the `IntoPipeSystem` trait, and move the `pipe` method to
`IntoSystem`.
---
## Changelog
- System piping has been made more flexible: it is now possible to call
`.pipe` on a system that takes an input.
## Migration Guide
The `IntoPipeSystem` trait has been removed, and the `pipe` method has
been moved to the `IntoSystem` trait.
```rust
// Before:
use bevy_ecs::system::IntoPipeSystem;
schedule.add_systems(first.pipe(second));
// After:
use bevy_ecs::system::IntoSystem;
schedule.add_systems(first.pipe(second));
```
# Objective
- Fixes unclear warning when `insert_non_send_resource` is called on a
Send resource
## Solution
- Add a message to the asssert statement that checks this
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
The implementation of `System::run_unsafe` for `FunctionSystem` requires
that the world is the same one used to initialize the system. However,
the `System` trait has no requirements that the world actually matches,
which makes this implementation unsound.
This was previously mentioned in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7605#issuecomment-1426491871
Fixes part of #7833.
## Solution
Add the safety invariant that
`System::update_archetype_component_access` must be called prior to
`System::run_unsafe`. Since
`FunctionSystem::update_archetype_component_access` properly validates
the world, this ensures that `run_unsafe` is not called with a
mismatched world.
Most exclusive systems are not required to be run on the same world that
they are initialized with, so this is not a concern for them. Systems
formed by combining an exclusive system with a regular system *do*
require the world to match, however the validation is done inside of
`System::run` when needed.
# Objective
This PR attempts to improve query compatibility checks in scenarios
involving `Or` filters.
Currently, for the following two disjoint queries, Bevy will throw a
panic:
```
fn sys(_: Query<&mut C, Or<(With<A>, With<B>)>>, _: Query<&mut C, (Without<A>, Without<B>)>) {}
```
This PR addresses this particular scenario.
## Solution
`FilteredAccess::with` now stores a vector of `AccessFilters`
(representing a pair of `with` and `without` bitsets), where each member
represents an `Or` "variant".
Filters like `(With<A>, Or<(With<B>, Without<C>)>` are expected to be
expanded into `A * B + A * !C`.
When calculating whether queries are compatible, every `AccessFilters`
of a query is tested for incompatibility with every `AccessFilters` of
another query.
---
## Changelog
- Improved system and query data access compatibility checks in
scenarios involving `Or` filters
---------
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
If you want to execute a schedule on the world using arbitrarily complex
behavior, you currently need to use "hokey-pokey strats": remove the
schedule from the world, do your thing, and add it back to the world.
Not only is this cumbersome, it's potentially error-prone as one might
forget to re-insert the schedule.
## Solution
Add the `World::{try}schedule_scope{ref}` family of functions, which is
a convenient abstraction over hokey pokey strats. This method
essentially works the same way as `World::resource_scope`.
### Example
```rust
// Run the schedule five times.
world.schedule_scope(MySchedule, |world, schedule| {
for _ in 0..5 {
schedule.run(world);
}
});
```
---
## Changelog
Added the `World::schedule_scope` family of methods, which provide a way
to get mutable access to a world and one of its schedules at the same
time.
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
The behavior of change detection within `PipeSystem` is very tricky and
subtle, and is not currently covered by any of our tests as far as I'm
aware.
# Objective
Upon closer inspection, there are a few functions in the ECS that are
not being inlined, even with the highest optimizations and LTO enabled:
- Almost all
[WorldQuery::init_fetch](9fd5f20e25/results/query_get.s (L57))
calls. Affects `Query::get` calls in hot loops. In particular, the
`WorldQuery` implementation for `()` is used *everywhere* as the default
filter and is effectively a no-op.
-
[Entities::get](9fd5f20e25/results/query_get.s (L39)).
Affects `Query::get`, `World::get`, and any component insertion or
removal.
-
[Entities::set](9fd5f20e25/results/entity_remove.s (L2487)).
Affects any component insertion or removal.
-
[Tick::new](9fd5f20e25/results/entity_insert.s (L1368)).
I've only seen this in component insertion and spawning.
- ArchetypeRow::new
- BlobVec::set_len
Almost all of these have trivial or even empty implementations or have
significant opportunity to be optimized into surrounding code when
inlined with LTO enabled.
## Solution
Inline them
# Objective
The method `World::try_run_schedule` currently panics if the `Schedules`
resource does not exist, but it should just return an `Err`. Similarly,
`World::add_schedule` panics unnecessarily if the resource does not
exist.
Also, the documentation for `World::add_schedule` is completely wrong.
## Solution
When the `Schedules` resource does not exist, we now treat it the same
as if it did exist but was empty. When calling `add_schedule`, we
initialize it if it does not exist.
# Objective
Fixes#8215 and #8152. When systems panic, it causes the main thread to
panic as well, which clutters the output.
## Solution
Resolves the panic in the multi-threaded scheduler. Also adds an extra
message that tells the user the system that panicked.
Using the example from the issue, here is what the messages now look
like:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_systems(Update, panicking_system)
.run();
}
fn panicking_system() {
panic!("oooh scary");
}
```
### Before
```
Compiling bevy_test v0.1.0 (E:\Projects\Rust\bevy_test)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 2m 58s
Running `target\debug\bevy_test.exe`
2023-03-30T22:19:09.234932Z INFO bevy_diagnostic::system_information_diagnostics_plugin::internal: SystemInfo { os: "Windows 10 Pro", kernel: "19044", cpu: "AMD Ryzen 5 2600 Six-Core Processor", core_count: "6", memory: "15.9 GiB" }
thread 'Compute Task Pool (5)' panicked at 'oooh scary', src\main.rs:11:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
thread 'Compute Task Pool (5)' panicked at 'A system has panicked so the executor cannot continue.: RecvError', E:\Projects\Rust\bevy\crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\executor\multi_threaded.rs:194:60
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Option::unwrap()` on a `None` value', E:\Projects\Rust\bevy\crates\bevy_tasks\src\task_pool.rs:376:49
error: process didn't exit successfully: `target\debug\bevy_test.exe` (exit code: 101)
```
### After
```
Compiling bevy_test v0.1.0 (E:\Projects\Rust\bevy_test)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 2.39s
Running `target\debug\bevy_test.exe`
2023-03-30T22:11:24.748513Z INFO bevy_diagnostic::system_information_diagnostics_plugin::internal: SystemInfo { os: "Windows 10 Pro", kernel: "19044", cpu: "AMD Ryzen 5 2600 Six-Core Processor", core_count: "6", memory: "15.9 GiB" }
thread 'Compute Task Pool (5)' panicked at 'oooh scary', src\main.rs:11:5
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
Encountered a panic in system `bevy_test::panicking_system`!
Encountered a panic in system `bevy_app::main_schedule::Main::run_main`!
error: process didn't exit successfully: `target\debug\bevy_test.exe` (exit code: 101)
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#8191.
Currently, a state transition will be triggered whenever the `NextState`
resource has a value, even if that "transition" is to the same state as
the previous one. This caused surprising/meaningless behavior, such as
the existence of an `OnTransition { from: A, to: A }` schedule.
## Solution
State transition schedules now only run if the new state is not equal to
the old state. Change detection works the same way, only being triggered
when the states compare not equal.
---
## Changelog
- State transition schedules are no longer run when transitioning to and
from the same state.
## Migration Guide
State transitions are now only triggered when the exited and entered
state differ. This means that if the world is currently in state `A`,
the `OnEnter(A)` schedule (or `OnExit`) will no longer be run if you
queue up a state transition to the same state `A`.
# Objective
Noticed while writing #7728 that we are using `trace!` logs in our event
functions. This has shown to have significant overhead, even trace level
logs are disabled globally, as seen in #7639.
## Solution
Use the `detailed_trace!` macro introduced in #7639. Also removed the
`event_trace` function that was only used in one location.
---
## Changelog
Changed: Event trace logs are now feature gated behind the
`detailed-trace` feature.
Fixes#8333
# Objective
Fixes issue which causes failure to compile if using
`#![deny(missing_docs)]`.
## Solution
Added some very basic commenting to the generated read-only fields.
honestly I feel this to be up for debate since the comments are very
basic and give very little useful information but the purpose of this PR
is to fix the issue at hand.
---
## Changelog
Added comments to the derive macro and the projects now successfully
compile.
---------
Co-authored-by: lupan <kallll5@hotmail.com>
Fixes issue mentioned in PR #8285.
_Note: By mistake, this is currently dependent on #8285_
# Objective
Ensure consistency in the spelling of the documentation.
Exceptions:
`crates/bevy_mikktspace/src/generated.rs` - Has not been changed from
licence to license as it is part of a licensing agreement.
Maybe for further consistency,
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website should also be given a look.
## Solution
### Changed the spelling of the current words (UK/CN/AU -> US) :
cancelled -> canceled (Breaking API changes in #8285)
behaviour -> behavior (Breaking API changes in #8285)
neighbour -> neighbor
grey -> gray
recognise -> recognize
centre -> center
metres -> meters
colour -> color
### ~~Update [`engine_style_guide.md`]~~ Moved to #8324
---
## Changelog
Changed UK spellings in documentation to US
## Migration Guide
Non-breaking changes*
\* If merged after #8285
# Objective
The clippy lint `type_complexity` is known not to play well with bevy.
It frequently triggers when writing complex queries, and taking the
lint's advice of using a type alias almost always just obfuscates the
code with no benefit. Because of this, this lint is currently ignored in
CI, but unfortunately it still shows up when viewing bevy code in an
IDE.
As someone who's made a fair amount of pull requests to this repo, I
will say that this issue has been a consistent thorn in my side. Since
bevy code is filled with spurious, ignorable warnings, it can be very
difficult to spot the *real* warnings that must be fixed -- most of the
time I just ignore all warnings, only to later find out that one of them
was real after I'm done when CI runs.
## Solution
Suppress this lint in all bevy crates. This was previously attempted in
#7050, but the review process ended up making it more complicated than
it needs to be and landed on a subpar solution.
The discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/pull/10571
explores some better long-term solutions to this problem. Since there is
no timeline on when these solutions may land, we should resolve this
issue in the meantime by locally suppressing these lints.
### Unresolved issues
Currently, these lints are not suppressed in our examples, since that
would require suppressing the lint in every single source file. They are
still ignored in CI.
# Objective
State requires a kind of awkward `state.0` to get the current state and
exposes the field directly to manipulation.
## Solution
Make it accessible through a getter method as well as privatize the
field to make sure false assumptions about setting the state aren't
made.
## Migration Guide
- Use `State::get` instead of accessing the tuple field directly.
# Objective
The `#[derive(WorldQuery)]` macro currently only supports structs with
named fields.
Same motivation as #6957. Remove sharp edges from the derive macro, make
it just work more often.
## Solution
Support tuple structs.
---
## Changelog
+ Added support for tuple structs to the `#[derive(WorldQuery)]` macro.
# Objective
While migrating the engine to use the `Tick` type in #7905, I forgot to
update `UnsafeWorldCell::increment_change_tick`.
## Solution
Update the function.
---
## Changelog
- The function `UnsafeWorldCell::increment_change_tick` is now
strongly-typed, returning a value of type `Tick` instead of a raw `u32`.
## Migration Guide
The function `UnsafeWorldCell::increment_change_tick` is now
strongly-typed, returning a value of type `Tick` instead of a raw `u32`.
# Objective
The type `&World` is currently in an awkward place, since it has two
meanings:
1. Read-only access to the entire world.
2. Interior mutable access to the world; immutable and/or mutable access
to certain portions of world data.
This makes `&World` difficult to reason about, and surprising to see in
function signatures if one does not know about the interior mutable
property.
The type `UnsafeWorldCell` was added in #6404, which is meant to
alleviate this confusion by adding a dedicated type for interior mutable
world access. However, much of the engine still treats `&World` as an
interior mutable-ish type. One of those places is `SystemParam`.
## Solution
Modify `SystemParam::get_param` to accept `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. Simplify the safety invariants, since the `UnsafeWorldCell`
type encapsulates the concept of constrained world access.
---
## Changelog
`SystemParam::get_param` now accepts an `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. This type provides a high-level API for unsafe interior
mutable world access.
## Migration Guide
For manual implementers of `SystemParam`: the function `get_item` now
takes `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of `&World`. To access world data, use:
* `.get_entity()`, which returns an `UnsafeEntityCell` which can be used
to access component data.
* `get_resource()` and its variants, to access resource data.
# Objective
The function `SyncUnsafeCell::from_mut` returns `&SyncUnsafeCell<T>`,
even though it could return `&mut SyncUnsafeCell<T>`. This means it is
not possible to call `get_mut` on the returned value, so you need to use
unsafe code to get exclusive access back.
## Solution
Return `&mut Self` instead of `&Self` in `SyncUnsafeCell::from_mut`.
This is consistent with my proposal for `UnsafeCell::from_mut`:
https://github.com/rust-lang/libs-team/issues/198.
Replace an unsafe pointer dereference with a safe call to `get_mut`.
---
## Changelog
+ The function `bevy_utils::SyncUnsafeCell::get_mut` now returns a value
of type `&mut SyncUnsafeCell<T>`. Previously, this returned an immutable
reference.
## Migration Guide
The function `bevy_utils::SyncUnsafeCell::get_mut` now returns a value
of type `&mut SyncUnsafeCell<T>`. Previously, this returned an immutable
reference.
# Objective
The documentation on `QueryState::for_each_unchecked` incorrectly says
that it can only be used with read-only queries.
## Solution
Remove the inaccurate sentence.
# Objective
Follow-up to #8030.
Now that `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` are implemented for
`PhantomData`, the `ignore` attributes are now unnecessary.
---
## Changelog
- Removed the attributes `#[system_param(ignore)]` and
`#[world_query(ignore)]`.
## Migration Guide
The attributes `#[system_param(ignore)]` and `#[world_query]` ignore
have been removed. If you were using either of these with `PhantomData`
fields, you can simply remove the attribute:
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
struct MyParam<'w, 's, Marker> {
...
// Before:
#[system_param(ignore)
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
// After:
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
struct MyQuery<Marker> {
...
// Before:
#[world_query(ignore)
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
// After:
_marker: PhantomData<Marker>,
}
```
If you were using this for another type that implements `Default`,
consider wrapping that type in `Local<>` (this only works for
`SystemParam`):
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
struct MyParam<'w, 's> {
// Before:
#[system_param(ignore)]
value: MyDefaultType, // This will be initialized using `Default` each time `MyParam` is created.
// After:
value: Local<MyDefaultType>, // This will be initialized using `Default` the first time `MyParam` is created.
}
```
If you are implementing either trait and need to preserve the exact
behavior of the old `ignore` attributes, consider manually implementing
`SystemParam` or `WorldQuery` for a wrapper struct that uses the
`Default` trait:
```rust
// Before:
#[derive(WorldQuery)
struct MyQuery {
#[world_query(ignore)]
str: String,
}
// After:
#[derive(WorldQuery)
struct MyQuery {
str: DefaultQuery<String>,
}
pub struct DefaultQuery<T: Default>(pub T);
unsafe impl<T: Default> WorldQuery for DefaultQuery<T> {
type Item<'w> = Self;
...
unsafe fn fetch<'w>(...) -> Self::Item<'w> {
Self(T::default())
}
}
```
# Objective
Our regression tests for `SystemParam` currently consist of a bunch of
loosely dispersed struct definitions. This is messy, and doesn't fully
test their functionality.
## Solution
Group the struct definitions into functions annotated with `#[test]`.
This not only makes the module more organized, but it allows us to call
`assert_is_system`, which has the potential to catch some bugs that
would have been missed with the old approach. Also, this approach is
consistent with how `WorldQuery` regression tests are organized.
# Objective
- Fixes#7659
## Solution
The idea of anonymous system sets or "implicit hidden organizational
sets" was briefly mentioned by @cart here:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7634#issuecomment-1428619449.
- `Schedule::add_systems` creates an implicit, anonymous system set of
all systems in `SystemConfigs`.
- All dependencies and conditions from the `SystemConfigs` are now
applied to the implicit system set, instead of being applied to each
individual system. This should not change the behavior, AFAIU, because
`before`, `after`, `run_if` and `ambiguous_with` are transitive
properties from a set to its members.
- The newly added `AnonymousSystemSet` stores the names of its members
to provide better error messages.
- The names are stored in a reference counted slice, allowing fast
clones of the `AnonymousSystemSet`.
- However, only the pointer of the slice is used for hash and equality
operations
- This ensures that two `AnonymousSystemSet` are not equal, even if they
have the same members / member names.
- So two identical `add_systems` calls will produce two different
`AnonymousSystemSet`s.
- Clones of the same `AnonymousSystemSet` will be equal.
## Drawbacks
If my assumptions are correct, the observed behavior should stay the
same. But the number of system sets in the `Schedule` will increase with
each `add_systems` call. If this has negative performance implications,
`add_systems` could be changed to only create the implicit system set if
necessary / when a run condition was added.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
With the removal of base sets, some variants of `ScheduleBuildError` can
never occur and should be removed.
## Solution
- Remove the obsolete variants of `ScheduleBuildError`.
- Also fix a doc comment which mentioned base sets.
---
## Changelog
### Removed
- Remove `ScheduleBuildError::SystemInMultipleBaseSets` and
`ScheduleBuildError::SetInMultipleBaseSets`.
# Objective
When using `PhantomData` fields with the `#[derive(SystemParam)]` or
`#[derive(WorldQuery)]` macros, the user is required to add the
`#[system_param(ignore)]` attribute so that the macro knows to treat
that field specially. This is undesirable, since it makes the macro more
fragile and less consistent.
## Solution
Implement `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` for `PhantomData`. This makes
the `ignore` attributes unnecessary.
Some internal changes make the derive macro compatible with types that
have invariant lifetimes, which fixes#8192. From what I can tell, this
fix requires `PhantomData` to implement `SystemParam` in order to ensure
that all of a type's generic parameters are always constrained.
---
## Changelog
+ Implemented `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` for `PhantomData<T>`.
+ Fixed a miscompilation caused when invariant lifetimes were used with
the `SystemParam` macro.
# Objective
I ran into a case where I need to create a `CommandQueue` and push
standard `Command` actions like `Insert` or `Remove` to it manually. I
saw that `Remove` looked as follows:
```rust
struct Remove<T> {
entity: Entity,
phantom: PhantomData<T>
}
```
so naturally, I tried to use `Remove::<Foo>::from(entity)` but it didn't
exist. We need to specify the `PhantomData` explicitly when creating
this command action. The same goes for `RemoveResource` and
`InitResource`
## Solution
This PR implements the following:
- `From<Entity>` for `Remove<T>`
- `Default` for `RemoveResource` and `InitResource`
- use these traits in the implementation of methods of `Commands`
- rename `phantom` field on the structs above to `_phantom` to have a
more uniform field naming scheme for the command actions
---
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no
externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
- Added: implemented `From<Entity>` for `Remove<T>` and `Default` for
`RemoveResource` and `InitResource` for ergonomics
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix a bug with scene reload.
(This is a copy of #7570 but without the breaking API change, in order
to allow the bugfix to be introduced in 0.10.1)
When a scene was reloaded, it was corrupting components that weren't
native to the scene itself. In particular, when a DynamicScene was
created on Entity (A), all components in the scene without parents are
automatically added as children of Entity (A). But if that scene was
reloaded and the same ID of Entity (A) was a scene ID as well*, that
parent component was corrupted, causing the hierarchy to become
malformed and bevy to panic.
*For example, if Entity (A)'s ID was 3, and the scene contained an
entity with ID 3
This issue could affect any components that:
* Implemented `MapEntities`, basically components that contained
references to other entities
* Were added to entities from a scene file but weren't defined in the
scene file
- Fixes#7529
## Solution
The solution was to keep track of entities+components that had
`MapEntities` functionality during scene load, and only apply the entity
update behavior to them. They were tracked with a HashMap from the
component's TypeID to a vector of entity ID's. Then the
`ReflectMapEntities` struct was updated to hold a function that took a
list of entities to be applied to, instead of naively applying itself to
all values in the EntityMap.
(See this PR comment
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7570#issuecomment-1432302796 for
a story-based explanation of this bug and solution)
## Changelog
### Fixed
- Components that implement `MapEntities` added to scene entities after
load are not corrupted during scene reload.
# Objective
Documentation should no longer be using pre-stageless terminology to
avoid confusion.
## Solution
- update all docs referring to stages to instead refer to sets/schedules
where appropriate
- also mention `apply_system_buffers` for anything system-buffer-related
that previously referred to buffers being applied "at the end of a
stage"
# Objective
`Or<T>` should be a new type of `PhantomData<T>` instead of `T`.
## Solution
Make `Or<T>` a new type of `PhantomData<T>`.
## Migration Guide
`Or<T>` is just used as a type annotation and shouldn't be constructed.
# Objective
When using the `#[derive(WorldQuery)]` macro, the `ReadOnly` struct
generated has default (private) visibility for each field, regardless of
the visibility of the original field.
## Solution
For each field of a read-only `WorldQuery` variant, use the visibility
of the associated field defined on the original struct.
# Objective
Fix#1727Fix#8010
Meta types generated by the `SystemParam` and `WorldQuery` derive macros
can conflict with user-defined types if they happen to have the same
name.
## Solution
In order to check if an identifier would conflict with user-defined
types, we can just search the original `TokenStream` passed to the macro
to see if it contains the identifier (since the meta types are defined
in an anonymous scope, it's only possible for them to conflict with the
struct definition itself). When generating an identifier for meta types,
we can simply check if it would conflict, and then add additional
characters to the name until it no longer conflicts with anything.
The `WorldQuery` "Item" and read-only structs are a part of a module's
public API, and thus it is intended for them to conflict with
user-defined types.
# Objective
The function `assert_is_system` is used in documentation tests to ensure
that example code actually produces valid systems. Currently,
`assert_is_system` just checks that each function parameter implements
`SystemParam`. To further check the validity of the system, we should
initialize the passed system so that it will be checked for conflicting
accesses. Not only does this enforce the validity of our examples, but
it provides a convenient way to demonstrate conflicting accesses via a
`should_panic` example, which is nicely rendered by rustdoc:
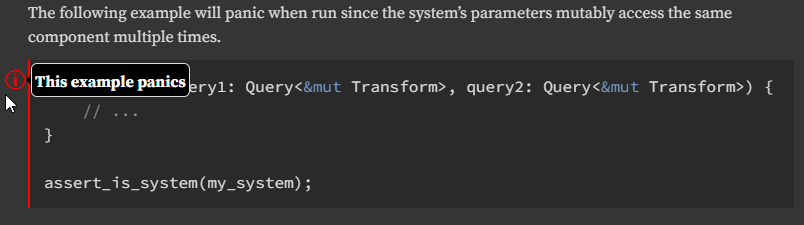
## Solution
Initialize the system with an empty world to trigger its internal access
conflict checks.
---
## Changelog
The function `bevy::ecs::system::assert_is_system` now panics when
passed a system with conflicting world accesses, as does
`assert_is_read_only_system`.
## Migration Guide
The functions `assert_is_system` and `assert_is_read_only_system` (in
`bevy_ecs::system`) now panic if the passed system has invalid world
accesses. Any tests that called this function on a system with invalid
accesses will now fail. Either fix the system's conflicting accesses, or
specify that the test is meant to fail:
1. For regular tests (that is, functions annotated with `#[test]`), add
the `#[should_panic]` attribute to the function.
2. For documentation tests, add `should_panic` to the start of the code
block: ` ```should_panic`
# Objective
We're currently using an unconditional `unwrap` in multiple locations
when inserting bundles into an entity when we know it will never fail.
This adds a large amount of extra branching that could be avoided on in
release builds.
## Solution
Use `DebugCheckedUnwrap` in bundle insertion code where relevant. Add
and update the safety comments to match.
This should remove the panicking branches from release builds, which has
a significant impact on the generated code:
https://github.com/james7132/bevy_asm_tests/compare/less-panicking-bundles#diff-e55a27cfb1615846ed3b6472f15a1aed66ed394d3d0739b3117f95cf90f46951R2086
shows about a 10% reduction in the number of generated instructions for
`EntityMut::insert`, `EntityMut::remove`, `EntityMut::take`, and related
functions.
---------
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This MR is a rebased and alternative proposal to
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5602
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4447 implemented untyped
(using component ids instead of generics and TypeId) APIs for
inserting/accessing resources and accessing components, but left
inserting components for another PR (this one)
## Solution
- add `EntityMut::insert_by_id`
- split `Bundle` into `DynamicBundle` with `get_components` and `Bundle:
DynamicBundle`. This allows the `BundleInserter` machinery to be reused
for bundles that can only be written, not read, and have no statically
available `ComponentIds`
- Compared to the original MR this approach exposes unsafe endpoints and
requires the user to manage instantiated `BundleIds`. This is quite easy
for the end user to do and does not incur the performance penalty of
checking whether component input is correctly provided for the
`BundleId`.
- This MR does ensure that constructing `BundleId` itself is safe
---
## Changelog
- add methods for inserting bundles and components to:
`world.entity_mut(entity).insert_by_id`
# Objective
#7863 introduced a potential footgun. When trying to incorrectly add a user-defined type using `in_base_set`, the compiler will suggest that the user implement `BaseSystemSet` for their type. This is a reasonable-sounding suggestion, however this is not the correct way to make a base set, and will lead to a confusing panic message when a marker trait is implemented for the wrong type.
## Solution
Rewrite the documentation for these traits, making it more clear that `BaseSystemSet` is a marker for types that are already base sets, and not a way to define a base set.
# Objective
The trait `IntoSystemConfig<>` requires each implementer to repeat every single member method, even though they can all be implemented by just deferring to `SystemConfig`.
## Solution
Add default implementations to most member methods.
# Objective
Base sets, added in #7466 are a special type of system set. Systems can only be added to base sets via `in_base_set`, while non-base sets can only be added via `in_set`. Unfortunately this is currently guarded by a runtime panic, which presents an unfortunate toe-stub when the wrong method is used. The delayed response between writing code and encountering the error (possibly hours) makes the distinction between base sets and other sets much more difficult to learn.
## Solution
Add the marker traits `BaseSystemSet` and `FreeSystemSet`. `in_base_set` and `in_set` now respectively accept these traits, which moves the runtime panic to a compile time error.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the marker trait `BaseSystemSet`, which is distinguished from a `FreeSystemSet`. These are both subtraits of `SystemSet`.
## Migration Guide
None if merged with 0.10
…or's ticker for one thread.
# Objective
- Fix debug_asset_server hang.
## Solution
- Reuse the thread_local executor for MainThreadExecutor resource, so there will be only one ThreadExecutor for main thread.
- If ThreadTickers from same executor, they are conflict with each other. Then only tick one.
# Objective
The `ScheduleBuildError` type has a `Display` implementation which beautifully formats the error. However, schedule build errors are currently reported using `unwrap()`, which uses the `Debug` implementation and makes the error message look unfished.
## Solution
Use `unwrap_or_else` so we can customize the formatting of the error message.
# Objective
Several `Query` methods unnecessarily place the call to `Query::update_archetypes` inside of unsafe blocks.
## Solution
Move the method calls out of the unsafe blocks.
# Objective
There is a panic that occurs when creating a run condition that accesses `NonSend` resources, but it refers to them as 'thread-local' resources instead.
## Solution
Correct the terminology.
# Objective
This is a follow-up to #7745. An unbounded `async_channel` occasionally allocates whenever it exceeds the capacity of the current buffer in it's internal linked list. This is avoidable.
This also used to be a bounded channel before stageless, which was introduced in #4919.
## Solution
Use a bounded channel to avoid allocations on system completion.
This shouldn't conflict with #7745, as it's impossible for the scheduler to exceed the channel capacity, even if somehow every system completed at the same time.
`EntityMut::move_entity_from_remove` had two soundness bugs:
- When removing the entity from the archetype, the swapped entity had its table row updated to the same as the removed entity's
- When removing the entity from the table, the swapped entity did not have its table row updated
`BundleInsert::insert` had two/three soundness bugs
- When moving an entity to a new archetype from an `insert`, the swapped entity had its table row set to a different entities
- When moving an entity to a new table from an `insert`, the swapped entity did not have its table row updated
See added tests for examples that trigger those bugs
`EntityMut::despawn` had two soundness bugs
- When despawning an entity, the swapped entity had its table row set to a different entities even if the table didnt change
- When despawning an entity, the swapped entity did not have its table row updated
# Objective
- A more intuitive distinction between the two. `remove_intersection` is verbose and unclear.
- `EntityMut::remove` and `Commands::remove` should match.
## Solution
- What the title says.
---
## Migration Guide
Before
```rust
fn clear_children(parent: Entity, world: &mut World) {
if let Some(children) = world.entity_mut(parent).remove::<Children>() {
for &child in &children.0 {
world.entity_mut(child).remove_intersection::<Parent>();
}
}
}
```
After
```rust
fn clear_children(parent: Entity, world: &mut World) {
if let Some(children) = world.entity_mut(parent).take::<Children>() {
for &child in &children.0 {
world.entity_mut(child).remove::<Parent>();
}
}
}
```
# Objective
Support the following syntax for adding systems:
```rust
App::new()
.add_system(setup.on_startup())
.add_systems((
show_menu.in_schedule(OnEnter(GameState::Paused)),
menu_ssytem.in_set(OnUpdate(GameState::Paused)),
hide_menu.in_schedule(OnExit(GameState::Paused)),
))
```
## Solution
Add the traits `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which provide the extension methods necessary for configuring which schedule a system belongs to. These extension methods return `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which `App::add_system{s}` uses to choose which schedule to add systems to.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the extension methods `in_schedule(label)` and `on_startup()` for configuring the schedule a system belongs to.
## Future Work
* Replace all uses of `add_startup_system` in the engine.
* Deprecate this method
# Objective
While we use `#[doc(hidden)]` to try and hide marker generics from the user, these types reveal themselves in compiler errors, adding visual noise and confusion.
## Solution
Replace the `AlreadyWasSystem` marker generic with `()`, to reduce visual noise in error messages. This also makes it possible to return `impl Condition<()>` from combinators.
For function systems, use their function signature as the marker type. This should drastically improve the legibility of some error messages.
The `InputMarker` type has been removed, since it is unnecessary.
# Objective
Several places in the ECS use marker generics to avoid overlapping trait implementations, but different places alternately refer to it as `Params` and `Marker`. This is potentially confusing, since it might not be clear that the same pattern is being used. Additionally, users might be misled into thinking that the `Params` type corresponds to the `SystemParam`s of a system.
## Solution
Rename `Params` to `Marker`.
# Objective
Fixes#3980
## Solution
Added examples to show how to run a `Schedule`, one with a unique system, and another with several systems
---
## Changelog
- Added: examples in docs to show how to run a `Schedule`
Co-authored-by: remiCzn <77072160+remiCzn@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The `BoxedCondition` type alias does not require the underlying system to be read-only.
## Solution
Define the type alias using `ReadOnlySystem` instead of `System`.
Graph theory make head hurty. Closes#7367.
Basically, when we topologically sort the dependency graph, we already find its strongly-connected components (a really [neat algorithm][1]). This PR adds an algorithm that can dissect those into simple cycles, giving us more useful error reports.
test: `system_build_errors::dependency_cycle`
```
schedule has 1 before/after cycle(s):
cycle 1: system set 'A' must run before itself
system set 'A'
... which must run before system set 'B'
... which must run before system set 'A'
```
```
schedule has 1 before/after cycle(s):
cycle 1: system 'foo' must run before itself
system 'foo'
... which must run before system 'bar'
... which must run before system 'foo'
```
test: `system_build_errors::hierarchy_cycle`
```
schedule has 1 in_set cycle(s):
cycle 1: system set 'A' contains itself
system set 'A'
... which contains system set 'B'
... which contains system set 'A'
```
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tarjan%27s_strongly_connected_components_algorithm