This is a continuation of this PR: #8062
# Objective
- Reorder render schedule sets to allow data preparation when phase item
order is known to support improved batching
- Part of the batching/instancing etc plan from here:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/89#issuecomment-1379249074
- The original idea came from @inodentry and proved to be a good one.
Thanks!
- Refactor `bevy_sprite` and `bevy_ui` to take advantage of the new
ordering
## Solution
- Move `Prepare` and `PrepareFlush` after `PhaseSortFlush`
- Add a `PrepareAssets` set that runs in parallel with other systems and
sets in the render schedule.
- Put prepare_assets systems in the `PrepareAssets` set
- If explicit dependencies are needed on Mesh or Material RenderAssets
then depend on the appropriate system.
- Add `ManageViews` and `ManageViewsFlush` sets between
`ExtractCommands` and Queue
- Move `queue_mesh*_bind_group` to the Prepare stage
- Rename them to `prepare_`
- Put systems that prepare resources (buffers, textures, etc.) into a
`PrepareResources` set inside `Prepare`
- Put the `prepare_..._bind_group` systems into a `PrepareBindGroup` set
after `PrepareResources`
- Move `prepare_lights` to the `ManageViews` set
- `prepare_lights` creates views and this must happen before `Queue`
- This system needs refactoring to stop handling all responsibilities
- Gather lights, sort, and create shadow map views. Store sorted light
entities in a resource
- Remove `BatchedPhaseItem`
- Replace `batch_range` with `batch_size` representing how many items to
skip after rendering the item or to skip the item entirely if
`batch_size` is 0.
- `queue_sprites` has been split into `queue_sprites` for queueing phase
items and `prepare_sprites` for batching after the `PhaseSort`
- `PhaseItem`s are still inserted in `queue_sprites`
- After sorting adjacent compatible sprite phase items are accumulated
into `SpriteBatch` components on the first entity of each batch,
containing a range of vertex indices. The associated `PhaseItem`'s
`batch_size` is updated appropriately.
- `SpriteBatch` items are then drawn skipping over the other items in
the batch based on the value in `batch_size`
- A very similar refactor was performed on `bevy_ui`
---
## Changelog
Changed:
- Reordered and reworked render app schedule sets. The main change is
that data is extracted, queued, sorted, and then prepared when the order
of data is known.
- Refactor `bevy_sprite` and `bevy_ui` to take advantage of the
reordering.
## Migration Guide
- Assets such as materials and meshes should now be created in
`PrepareAssets` e.g. `prepare_assets<Mesh>`
- Queueing entities to `RenderPhase`s continues to be done in `Queue`
e.g. `queue_sprites`
- Preparing resources (textures, buffers, etc.) should now be done in
`PrepareResources`, e.g. `prepare_prepass_textures`,
`prepare_mesh_uniforms`
- Prepare bind groups should now be done in `PrepareBindGroups` e.g.
`prepare_mesh_bind_group`
- Any batching or instancing can now be done in `Prepare` where the
order of the phase items is known e.g. `prepare_sprites`
## Next Steps
- Introduce some generic mechanism to ensure items that can be batched
are grouped in the phase item order, currently you could easily have
`[sprite at z 0, mesh at z 0, sprite at z 0]` preventing batching.
- Investigate improved orderings for building the MeshUniform buffer
- Implementing batching across the rest of bevy
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Wireframe currently don't display since #9416
- There is an error
```
2023-08-20T10:06:54.190347Z ERROR bevy_render::render_resource::pipeline_cache: failed to process shader:
error: no definition in scope for identifier: 'vertex_no_morph'
┌─ crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/wireframe.wgsl:26:94
│
26 │ let model = bevy_pbr::mesh_functions::get_model_matrix(vertex_no_morph.instance_index);
│ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ unknown identifier
│
= no definition in scope for identifier: 'vertex_no_morph'
```
## Solution
- Use the correct identifier
# Objective
- Significantly reduce the size of MeshUniform by only including
necessary data.
## Solution
Local to world, model transforms are affine. This means they only need a
4x3 matrix to represent them.
`MeshUniform` stores the current, and previous model transforms, and the
inverse transpose of the current model transform, all as 4x4 matrices.
Instead we can store the current, and previous model transforms as 4x3
matrices, and we only need the upper-left 3x3 part of the inverse
transpose of the current model transform. This change allows us to
reduce the serialized MeshUniform size from 208 bytes to 144 bytes,
which is over a 30% saving in data to serialize, and VRAM bandwidth and
space.
## Benchmarks
On an M1 Max, running `many_cubes -- sphere`, main is in yellow, this PR
is in red:
<img width="1484" alt="Screenshot 2023-08-11 at 02 36 43"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/7d99c7b3-f2bb-4004-a8d0-4c00f755cb0d">
A reduction in frame time of ~14%.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Redefined `MeshUniform` to improve performance by using 4x3
affine transforms and reconstructing 4x4 matrices in the shader. Helper
functions were added to `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` to unpack the data.
`affine_to_square` converts the packed 4x3 in 3x4 matrix data to a 4x4
matrix. `mat2x4_f32_to_mat3x3` converts the 3x3 in mat2x4 + f32 matrix
data back into a 3x3.
## Migration Guide
Shader code before:
```
var model = mesh[instance_index].model;
```
Shader code after:
```
#import bevy_pbr::mesh_functions affine_to_square
var model = affine_to_square(mesh[instance_index].model);
```
naga and wgpu should polyfill WGSL instance_index functionality where it
is not available in GLSL. Until that is done, we can work around it in
bevy using a push constant which is converted to a uniform by naga and
wgpu.
# Objective
- Fixes#9375
## Solution
- Use a push constant to pass in the base instance to the shader on
WebGL2 so that base instance + gl_InstanceID is used to correctly
represent the instance index.
## TODO
- [ ] Benchmark vs per-object dynamic offset MeshUniform as this will
now push a uniform value per-draw as well as update the dynamic offset
per-batch.
- [x] Test on DX12 AMD/NVIDIA to check that this PR does not regress any
problems that were observed there. (@Elabajaba @robtfm were testing that
last time - help appreciated. <3 )
---
## Changelog
- Added: `bevy_render::instance_index` shader import which includes a
workaround for the lack of a WGSL `instance_index` polyfill for WebGL2
in naga and wgpu for the time being. It uses a push_constant which gets
converted to a plain uniform by naga and wgpu.
## Migration Guide
Shader code before:
```
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
...
}
@vertex
fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
...
var model = mesh[vertex_no_morph.instance_index].model;
```
After:
```
#import bevy_render::instance_index
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
...
}
@vertex
fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
...
var model = mesh[bevy_render::instance_index::get_instance_index(vertex_no_morph.instance_index)].model;
```
# Objective
- Fix shader_material_glsl example
## Solution
- Expose the `PER_OBJECT_BUFFER_BATCH_SIZE` shader def through the
default `MeshPipeline` specialization.
- Make use of it in the `custom_material.vert` shader to access the mesh
binding.
---
## Changelog
- Added: Exposed the `PER_OBJECT_BUFFER_BATCH_SIZE` shader def through
the default `MeshPipeline` specialization to use in custom shaders not
using bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings that still want to use the mesh binding in
some way.
# Objective
- Reduce the number of rebindings to enable batching of draw commands
## Solution
- Use the new `GpuArrayBuffer` for `MeshUniform` data to store all
`MeshUniform` data in arrays within fewer bindings
- Sort opaque/alpha mask prepass, opaque/alpha mask main, and shadow
phases also by the batch per-object data binding dynamic offset to
improve performance on WebGL2.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Per-object `MeshUniform` data is now managed by
`GpuArrayBuffer` as arrays in buffers that need to be indexed into.
## Migration Guide
Accessing the `model` member of an individual mesh object's shader
`Mesh` struct the old way where each `MeshUniform` was stored at its own
dynamic offset:
```rust
struct Vertex {
@location(0) position: vec3<f32>,
};
fn vertex(vertex: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
var out: VertexOutput;
out.clip_position = mesh_position_local_to_clip(
mesh.model,
vec4<f32>(vertex.position, 1.0)
);
return out;
}
```
The new way where one needs to index into the array of `Mesh`es for the
batch:
```rust
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
@location(0) position: vec3<f32>,
};
fn vertex(vertex: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
var out: VertexOutput;
out.clip_position = mesh_position_local_to_clip(
mesh[vertex.instance_index].model,
vec4<f32>(vertex.position, 1.0)
);
return out;
}
```
Note that using the instance_index is the default way to pass the
per-object index into the shader, but if you wish to do custom rendering
approaches you can pass it in however you like.
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Elabajaba <Elabajaba@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fix typos throughout the project.
## Solution
[`typos`](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos) project was used for
scanning, but no automatic corrections were applied. I checked
everything by hand before fixing.
Most of the changes are documentation/comments corrections. Also, there
are few trivial changes to code (variable name, pub(crate) function name
and a few error/panic messages).
## Unsolved
`bevy_reflect_derive` has
[typo](1b51053f19/crates/bevy_reflect/bevy_reflect_derive/src/type_path.rs (L76))
in enum variant name that I didn't fix. Enum is `pub(crate)`, so there
shouldn't be any trouble if fixed. However, code is tightly coupled with
macro usage, so I decided to leave it for more experienced contributor
just in case.
# Objective
Since 10f5c92, parallax mapping was broken.
When #5703 was merged, the change from `in.uv` to `uv` in the pbr shader
was reverted. So the shader would use the wrong coordinate to sample the
various textures.
## Solution
We revert to using the correct uv.
# Objective
- This fixes a crash when loading shaders, when running an Adreno GPU
and using WebGL mode.
- Fixes#8506
- Fixes#8047
## Solution
- The shader pbr_functions.wgsl, will fail in apply_fog function, trying
to access values that are null on Adreno chipsets using WebGL, these
devices are commonly found in android handheld devices.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
#5703 caused the normal prepass to fail as the prepass uses
`pbr_functions::apply_normal_mapping`, which uses
`mesh_view_bindings::view` to determine mip bias, which conflicts with
`prepass_bindings::view`.
## Solution
pass the mip bias to the `apply_normal_mapping` function explicitly.
# Objective
operate on naga IR directly to improve handling of shader modules.
- give codespan reporting into imported modules
- allow glsl to be used from wgsl and vice-versa
the ultimate objective is to make it possible to
- provide user hooks for core shader functions (to modify light
behaviour within the standard pbr pipeline, for example)
- make automatic binding slot allocation possible
but ... since this is already big, adds some value and (i think) is at
feature parity with the existing code, i wanted to push this now.
## Solution
i made a crate called naga_oil (https://github.com/robtfm/naga_oil -
unpublished for now, could be part of bevy) which manages modules by
- building each module independantly to naga IR
- creating "header" files for each supported language, which are used to
build dependent modules/shaders
- make final shaders by combining the shader IR with the IR for imported
modules
then integrated this into bevy, replacing some of the existing shader
processing stuff. also reworked examples to reflect this.
## Migration Guide
shaders that don't use `#import` directives should work without changes.
the most notable user-facing difference is that imported
functions/variables/etc need to be qualified at point of use, and
there's no "leakage" of visible stuff into your shader scope from the
imports of your imports, so if you used things imported by your imports,
you now need to import them directly and qualify them.
the current strategy of including/'spreading' `mesh_vertex_output`
directly into a struct doesn't work any more, so these need to be
modified as per the examples (e.g. color_material.wgsl, or many others).
mesh data is assumed to be in bindgroup 2 by default, if mesh data is
bound into bindgroup 1 instead then the shader def `MESH_BINDGROUP_1`
needs to be added to the pipeline shader_defs.
# Objective
- Closes#7323
- Reduce texture blurriness for TAA
## Solution
- Add a `MipBias` component and view uniform.
- Switch material `textureSample()` calls to `textureSampleBias()`.
- Add a `-1.0` bias to TAA.
---
## Changelog
- Added `MipBias` camera component, mostly for internal use.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Add morph targets to `bevy_pbr` (closes#5756) & load them from glTF
- Supersedes #3722
- Fixes#6814
[Morph targets][1] (also known as shape interpolation, shape keys, or
blend shapes) allow animating individual vertices with fine grained
controls. This is typically used for facial expressions. By specifying
multiple poses as vertex offset, and providing a set of weight of each
pose, it is possible to define surprisingly realistic transitions
between poses. Blending between multiple poses also allow composition.
Morph targets are part of the [gltf standard][2] and are a feature of
Unity and Unreal, and babylone.js, it is only natural to implement them
in bevy.
## Solution
This implementation of morph targets uses a 3d texture where each pixel
is a component of an animated attribute. Each layer is a different
target. We use a 2d texture for each target, because the number of
attribute×components×animated vertices is expected to always exceed the
maximum pixel row size limit of webGL2. It copies fairly closely the way
skinning is implemented on the CPU side, while on the GPU side, the
shader morph target implementation is a relatively trivial detail.
We add an optional `morph_texture` to the `Mesh` struct. The
`morph_texture` is built through a method that accepts an iterator over
attribute buffers.
The `MorphWeights` component, user-accessible, controls the blend of
poses used by mesh instances (so that multiple copy of the same mesh may
have different weights), all the weights are uploaded to a uniform
buffer of 256 `f32`. We limit to 16 poses per mesh, and a total of 256
poses.
More literature:
* Old babylone.js implementation (vertex attribute-based):
https://www.eternalcoding.com/dev-log-1-morph-targets/
* Babylone.js implementation (similar to ours):
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBPRmGgU0PE
* GPU gems 3:
https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/gpugems3/part-i-geometry/chapter-3-directx-10-blend-shapes-breaking-limits
* Development discord thread
https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1083325980615114772https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26321040/231181046-3bca2ab2-d4d9-472e-8098-639f1871ce2e.mp4https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/26321040/d2a0c544-0ef8-45cf-9f99-8c3792f5a258
## Acknowledgements
* Thanks to `storytold` for sponsoring the feature
* Thanks to `superdump` and `james7132` for guidance and help figuring
out stuff
## Future work
- Handling of less and more attributes (eg: animated uv, animated
arbitrary attributes)
- Dynamic pose allocation (so that zero-weighted poses aren't uploaded
to GPU for example, enables much more total poses)
- Better animation API, see #8357
----
## Changelog
- Add morph targets to bevy meshes
- Support up to 64 poses per mesh of individually up to 116508 vertices,
animation currently strictly limited to the position, normal and tangent
attributes.
- Load a morph target using `Mesh::set_morph_targets`
- Add `VisitMorphTargets` and `VisitMorphAttributes` traits to
`bevy_render`, this allows defining morph targets (a fairly complex and
nested data structure) through iterators (ie: single copy instead of
passing around buffers), see documentation of those traits for details
- Add `MorphWeights` component exported by `bevy_render`
- `MorphWeights` control mesh's morph target weights, blending between
various poses defined as morph targets.
- `MorphWeights` are directly inherited by direct children (single level
of hierarchy) of an entity. This allows controlling several mesh
primitives through a unique entity _as per GLTF spec_.
- Add `MorphTargetNames` component, naming each indices of loaded morph
targets.
- Load morph targets weights and buffers in `bevy_gltf`
- handle morph targets animations in `bevy_animation` (previously, it
was a `warn!` log)
- Add the `MorphStressTest.gltf` asset for morph targets testing, taken
from the glTF samples repo, CC0.
- Add morph target manipulation to `scene_viewer`
- Separate the animation code in `scene_viewer` from the rest of the
code, reducing `#[cfg(feature)]` noise
- Add the `morph_targets.rs` example to show off how to manipulate morph
targets, loading `MorpStressTest.gltf`
## Migration Guide
- (very specialized, unlikely to be touched by 3rd parties)
- `MeshPipeline` now has a single `mesh_layouts` field rather than
separate `mesh_layout` and `skinned_mesh_layout` fields. You should
handle all possible mesh bind group layouts in your implementation
- You should also handle properly the new `MORPH_TARGETS` shader def and
mesh pipeline key. A new function is exposed to make this easier:
`setup_moprh_and_skinning_defs`
- The `MeshBindGroup` is now `MeshBindGroups`, cached bind groups are
now accessed through the `get` method.
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morph_target_animation
[2]:
https://registry.khronos.org/glTF/specs/2.0/glTF-2.0.html#morph-targets
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#8645
## Solution
Cascaded shadow maps use a technique commonly called shadow pancaking to
enhance shadow map resolution by restricting the orthographic projection
used in creating the shadow maps to the frustum slice for the cascade.
The implication of this restriction is that shadow casters can be closer
than the near plane of the projection volume.
Prior to this PR, we address clamp the depth of the prepass vertex
output to ensure that these shadow casters do not get clipped, resulting
in shadow loss. However, a flaw / bug of the prior approach is that the
depth that gets written to the shadow map isn't quite correct - the
depth was previously derived by interpolated the clamped clip position,
resulting in depths that are further than they should be. This creates
artifacts that are particularly noticeable when a very 'long' object
intersects the near plane close to perpendicularly.
The fix in this PR is to propagate the unclamped depth to the prepass
fragment shader and use that depth value directly.
A complementary solution would be to use
[DEPTH_CLIP_CONTROL](https://docs.rs/wgpu/latest/wgpu/struct.Features.html#associatedconstant.DEPTH_CLIP_CONTROL)
to request `unclipped_depth`. However due to the relatively low support
of the feature on Vulkan (I believe it's ~38%), I went with this
solution for now to get the broadest fix out first.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: Shadows from directional lights were sometimes incorrectly
omitted when the shadow caster was partially out of view.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Better consistency with `add_systems`.
- Deprecating `add_plugin` in favor of a more powerful `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing `Plugin` to `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing tuples to `add_plugins`.
## Solution
- `App::add_plugins` now takes an `impl Plugins` parameter.
- `App::add_plugin` is deprecated.
- `Plugins` is a new sealed trait that is only implemented for `Plugin`,
`PluginGroup` and tuples over `Plugins`.
- All examples, benchmarks and tests are changed to use `add_plugins`,
using tuples where appropriate.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- `App::add_plugins` now accepts all types that implement `Plugins`,
which is implemented for:
- Types that implement `Plugin`.
- Types that implement `PluginGroup`.
- Tuples (up to 16 elements) over types that implement `Plugins`.
- Deprecated `App::add_plugin` in favor of `App::add_plugins`.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `app.add_plugin(plugin)` calls with `app.add_plugins(plugin)`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix broken normals when the NormalPrepass is enabled
## Solution
- Don't use the normal prepass for the world_normal
- Only loadthe normal prepass
- when msaa is disabled
- for opaque or alpha mask meshes and only for use it for N not
world_normal
# Objective
- Some reflect components weren't properly registered.
## Solution
- We register them
- I also sorted the register lines in `Plugin::build` in `bevy_ui`
### Note
How I did I find them:
- I picked up the list of `Component`s from the `Component` trait page
in rustdoc.
- Then I tried to register all of them. Removing the registration when
it doesn't implement `Reflect` to pass compilation.
- Then I added `app.register_type_data::<T, Foo>()`, for all Reflect
components. It panics if `T` is not registered.
- I repeated the last line N times until bevy stopped panicking at
startup
---
## Changelog
- Register the following components: `PrimaryWindow` `Fxaa`
`FogSettings` `NotShadowCaster` `NotShadowReceiver` `CalculatedClip`
`RelativeCursorPosition`
# Objective
- Make #8015 easier to review;
## Solution
- This commit contains changes not directly related to transmission
required by #8015, in easier-to-review, one-change-per-commit form.
---
## Changelog
### Fixed
- Clear motion vector prepass using `0.0` instead of `1.0`, to avoid TAA
artifacts on transparent objects against the background;
### Added
- The `E` mathematical constant is now available for use in shaders,
exposed under `bevy_pbr::utils`;
- A new `TAA` shader def is now available, for conditionally enabling
shader logic via `#ifdef` when TAA is enabled; (e.g. for jittering
texture samples)
- A new `FallbackImageZero` resource is introduced, for when a fallback
image filled with zeroes is required;
- A new `RenderPhase<I>::render_range()` method is introduced, for
render phases that need to render their items in multiple parceled out
“steps”;
### Changed
- The `MainTargetTextures` struct now holds both `Texture` and
`TextureViews` for the main textures;
- The fog shader functions under `bevy_pbr::fog` now take the a `Fog`
structure as their first argument, instead of relying on the global
`fog` uniform;
- The main textures can now be used as copy sources;
## Migration Guide
- `ViewTarget::main_texture()` and `ViewTarget::main_texture_other()`
now return `&Texture` instead of `&TextureView`. If you were relying on
these methods, replace your usage with
`ViewTarget::main_texture_view()`and
`ViewTarget::main_texture_other_view()`, respectively;
- `ViewTarget::sampled_main_texture()` now returns `Option<&Texture>`
instead of a `Option<&TextureView>`. If you were relying on this method,
replace your usage with `ViewTarget::sampled_main_texture_view()`;
- The `apply_fog()`, `linear_fog()`, `exponential_fog()`,
`exponential_squared_fog()` and `atmospheric_fog()` functions now take a
configurable `Fog` struct. If you were relying on them, update your
usage by adding the global `fog` uniform as their first argument;
# Objective
- Right now we can't really benefit from [early depth
testing](https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Early_Fragment_Test) in our
PBR shader because it includes codepaths with `discard`, even for
situations where they are not necessary.
## Solution
- This PR introduces a new `MeshPipelineKey` and shader def,
`MAY_DISCARD`;
- All possible material/mesh options that that may result in `discard`s
being needed must set `MAY_DISCARD` ahead of time:
- Right now, this is only `AlphaMode::Mask(f32)`, but in the future
might include other options/effects; (e.g. one effect I'm personally
interested in is bayer dither pseudo-transparency for LOD transitions of
opaque meshes)
- Shader codepaths that can `discard` are guarded by an `#ifdef
MAY_DISCARD` preprocessor directive:
- Right now, this is just one branch in `alpha_discard()`;
- If `MAY_DISCARD` is _not_ set, the `@early_depth_test` attribute is
added to the PBR fragment shader. This is a not yet documented, possibly
non-standard WGSL extension I found browsing Naga's source code. [I
opened a PR to document it
there](https://github.com/gfx-rs/naga/pull/2132). My understanding is
that for backends where this attribute is supported, it will force an
explicit opt-in to early depth test. (e.g. via
`layout(early_fragment_tests) in;` in GLSL)
## Caveats
- I included `@early_depth_test` for the sake of us being explicit, and
avoiding the need for the driver to be “smart” about enabling this
feature. That way, if we make a mistake and include a `discard`
unguarded by `MAY_DISCARD`, it will either produce errors or noticeable
visual artifacts so that we'll catch early, instead of causing a
performance regression.
- I'm not sure explicit early depth test is supported on the naga Metal
backend, which is what I'm currently using, so I can't really test the
explicit early depth test enable, I would like others with Vulkan/GL
hardware to test it if possible;
- I would like some guidance on how to measure/verify the performance
benefits of this;
- If I understand it correctly, this, or _something like this_ is needed
to fully reap the performance gains enabled by #6284;
- This will _most definitely_ conflict with #6284 and #6644. I can fix
the conflicts as needed, depending on whether/the order they end up
being merging in.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- Early depth tests are now enabled whenever possible for meshes using
`StandardMaterial`, reducing the number of fragments evaluated for
scenes with lots of occlusions.
# Objective
- Support WebGPU
- alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await
- fixes#8315
- Surprise fix#7318
## Solution
### For async renderer initialisation
- Update the plugin lifecycle:
- app builds the plugin
- calls `plugin.build`
- registers the plugin
- app starts the event loop
- event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same
order
- returns `true` by default
- then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as
registered
- then execute the schedule
In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async:
- building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send
back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource
- `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource
- `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected
resources by other plugins
- other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are
called and they are able to set up their pipelines
- `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering
### For WebGPU support
- update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api
webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support
- feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now
in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for
this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32`
---
## Migration Guide
- `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup`
- `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should
do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build`
```rust
// Before
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>()
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
}
// After
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) {
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>();
}
}
```
# Objective
- Updated to wgpu 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal 0.16.0
---
## Changelog
1. Upgrade wgpu to 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal to 0.16.0
2. Fix the error in native when using a filterable
`TextureSampleType::Float` on a multisample `BindingType::Texture`.
([https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686))
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
The default StandardMaterial values of `pbr_material.rs` and
`pbr_types.wgsl` are out of sync.
I think they are out of sync since
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7664.
## Solution
Adapt the values: `metallic = 0.0`, `perceptual_roughness = 0.5`.
Fixes issue mentioned in PR #8285.
_Note: By mistake, this is currently dependent on #8285_
# Objective
Ensure consistency in the spelling of the documentation.
Exceptions:
`crates/bevy_mikktspace/src/generated.rs` - Has not been changed from
licence to license as it is part of a licensing agreement.
Maybe for further consistency,
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website should also be given a look.
## Solution
### Changed the spelling of the current words (UK/CN/AU -> US) :
cancelled -> canceled (Breaking API changes in #8285)
behaviour -> behavior (Breaking API changes in #8285)
neighbour -> neighbor
grey -> gray
recognise -> recognize
centre -> center
metres -> meters
colour -> color
### ~~Update [`engine_style_guide.md`]~~ Moved to #8324
---
## Changelog
Changed UK spellings in documentation to US
## Migration Guide
Non-breaking changes*
\* If merged after #8285
# Objective
- We support enabling a normal prepass, but the main pass never actually
uses it and recomputes the normals in the main pass. This isn't ideal
since it's doing redundant work.
## Solution
- Use the normal texture from the prepass in the main pass
## Notes
~~I used `NORMAL_PREPASS_ENABLED` as a shader_def because
`NORMAL_PREPASS` is currently used to signify that it is running in the
prepass while this shader_def need to indicate the prepass is done and
the normal prepass was ran before. I'm not sure if there's a better way
to name this.~~

# Objective
- Implement an alternative antialias technique
- TAA scales based off of view resolution, not geometry complexity
- TAA filters textures, firefly pixels, and other aliasing not covered
by MSAA
- TAA additionally will reduce noise / increase quality in future
stochastic rendering techniques
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3663
## Solution
- Add a temporal jitter component
- Add a motion vector prepass
- Add a TemporalAntialias component and plugin
- Combine existing MSAA and FXAA examples and add TAA
## Followup Work
- Prepass motion vector support for skinned meshes
- Move uniforms needed for motion vectors into a separate bind group,
instead of using different bind group layouts
- Reuse previous frame's GPU view buffer for motion vectors, instead of
recomputing
- Mip biasing for sharper textures, and or unjitter texture UVs
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7323
- Compute shader for better performance
- Investigate FSR techniques
- Historical depth based disocclusion tests, for geometry disocclusion
- Historical luminance/hue based tests, for shading disocclusion
- Pixel "locks" to reduce blending rate / revamp history confidence
mechanism
- Orthographic camera support for TemporalJitter
- Figure out COD's 1-tap bicubic filter
---
## Changelog
- Added MotionVectorPrepass and TemporalJitter
- Added TemporalAntialiasPlugin, TemporalAntialiasBundle, and
TemporalAntialiasSettings
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Chia <danstryder@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Brandon Dyer <brandondyer64@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
- Fixes#7965
- Code quality improvements.
- Removes the unreferenced function `dither` in pbr_functions.wgsl
introduced in 72fbcc7, but made obsolete in c069c54.
- Makes the reference to `screen_space_dither` in pbr.wgsl conditional
on `#ifdef TONEMAP_IN_SHADER`, as the required import is conditional on
the same, as deband dithering can only occur if tonemapping is also
occurring.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Currently, the render graph slots are only used to pass the
view_entity around. This introduces significant boilerplate for very
little value. Instead of using slots for this, make the view_entity part
of the `RenderGraphContext`. This also means we won't need to have
`IN_VIEW` on every node and and we'll be able to use the default impl of
`Node::input()`.
## Solution
- Add `view_entity: Option<Entity>` to the `RenderGraphContext`
- Update all nodes to use this instead of entity slot input
---
## Changelog
- Add optional `view_entity` to `RenderGraphContext`
## Migration Guide
You can now get the view_entity directly from the `RenderGraphContext`.
When implementing the Node:
```rust
// 0.10
struct FooNode;
impl FooNode {
const IN_VIEW: &'static str = "view";
}
impl Node for FooNode {
fn input(&self) -> Vec<SlotInfo> {
vec![SlotInfo::new(Self::IN_VIEW, SlotType::Entity)]
}
fn run(
&self,
graph: &mut RenderGraphContext,
// ...
) -> Result<(), NodeRunError> {
let view_entity = graph.get_input_entity(Self::IN_VIEW)?;
// ...
Ok(())
}
}
// 0.11
struct FooNode;
impl Node for FooNode {
fn run(
&self,
graph: &mut RenderGraphContext,
// ...
) -> Result<(), NodeRunError> {
let view_entity = graph.view_entity();
// ...
Ok(())
}
}
```
When adding the node to the graph, you don't need to specify a slot_edge
for the view_entity.
```rust
// 0.10
let mut graph = RenderGraph::default();
graph.add_node(FooNode::NAME, node);
let input_node_id = draw_2d_graph.set_input(vec![SlotInfo::new(
graph::input::VIEW_ENTITY,
SlotType::Entity,
)]);
graph.add_slot_edge(
input_node_id,
graph::input::VIEW_ENTITY,
FooNode::NAME,
FooNode::IN_VIEW,
);
// add_node_edge ...
// 0.11
let mut graph = RenderGraph::default();
graph.add_node(FooNode::NAME, node);
// add_node_edge ...
```
## Notes
This PR paired with #8007 will help reduce a lot of annoying boilerplate
with the render nodes. Depending on which one gets merged first. It will
require a bit of clean up work to make both compatible.
I tagged this as a breaking change, because using the old system to get
the view_entity will break things because it's not a node input slot
anymore.
## Notes for reviewers
A lot of the diffs are just removing the slots in every nodes and graph
creation. The important part is mostly in the
graph_runner/CameraDriverNode.
# Objective
- @mockersf identified a performance regression of about 25% longer frame times introduced by #7784 in a complex scene with the Amazon Lumberyard bistro scene with both exterior and interior variants and a number of point lights with shadow mapping enabled
- The additional time seemed to be spent in the `ShadowPassNode`
- `ShadowPassNode` encodes the draw commands for the shadow phase. Roughly the same numbers of entities were having draw commands encoded, so something about the way they were being encoded had changed.
- One thing that definitely changed was that the pipeline used will be different depending on the alpha mode, and the scene has lots entities with opaque and blend materials. This suggested that maybe the pipeline was changing a lot so I tried a quick hack to see if it was the problem.
## Solution
- Sort the shadow phase items by their pipeline id
- This groups phase items by their pipeline id, which significantly reduces pipeline rebinding required to the point that the performance regression was gone.
# Objective
revert combining pipelines for AlphaMode::Blend and AlphaMode::Premultiplied & Add
the recent blend state pr changed `AlphaMode::Blend` to use a blend state of `Blend::PREMULTIPLIED_ALPHA_BLENDING`, and recovered the original behaviour by multiplying colour by alpha in the standard material's fragment shader.
this had some advantages (specifically it means more material instances can be batched together in future), but this also means that custom materials that specify `AlphaMode::Blend` now get a premultiplied blend state, so they must also multiply colour by alpha.
## Solution
revert that combination to preserve 0.9 behaviour for custom materials with AlphaMode::Blend.
# Objective
- Remove dead code after #7784
# Changelog
- Removed `SetShadowViewBindGroup`, `queue_shadow_view_bind_group()`, and `LightMeta::shadow_view_bind_group` in favor of reusing the prepass view bind group.
# Migration Guide
- Removed `SetShadowViewBindGroup`, `queue_shadow_view_bind_group()`, and `LightMeta::shadow_view_bind_group` in favor of reusing the prepass view bind group.
# Objective
- Fixes#4372.
## Solution
- Use the prepass shaders for the shadow passes.
- Move `DEPTH_CLAMP_ORTHO` from `ShadowPipelineKey` to `MeshPipelineKey` and the associated clamp operation from `depth.wgsl` to `prepass.wgsl`.
- Remove `depth.wgsl` .
- Replace `ShadowPipeline` with `ShadowSamplers`.
Instead of running the custom `ShadowPipeline` we run the `PrepassPipeline` with the `DEPTH_PREPASS` flag and additionally the `DEPTH_CLAMP_ORTHO` flag for directional lights as well as the `ALPHA_MASK` flag for materials that use `AlphaMode::Mask(_)`.
# Objective
- Use the prepass textures in webgl
## Solution
- Bind the prepass textures even when using webgl, but only if msaa is disabled
- Also did some refactors to centralize how textures are bound, similar to the EnvironmentMapLight PR
- ~~Also did some refactors of the example to make it work in webgl~~
- ~~To make the example work in webgl, I needed to use a sampler for the depth texture, the resulting code looks a bit weird, but it's simple enough and I think it's worth it to show how it works when using webgl~~
# Objective
Support the following syntax for adding systems:
```rust
App::new()
.add_system(setup.on_startup())
.add_systems((
show_menu.in_schedule(OnEnter(GameState::Paused)),
menu_ssytem.in_set(OnUpdate(GameState::Paused)),
hide_menu.in_schedule(OnExit(GameState::Paused)),
))
```
## Solution
Add the traits `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which provide the extension methods necessary for configuring which schedule a system belongs to. These extension methods return `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which `App::add_system{s}` uses to choose which schedule to add systems to.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the extension methods `in_schedule(label)` and `on_startup()` for configuring the schedule a system belongs to.
## Future Work
* Replace all uses of `add_startup_system` in the engine.
* Deprecate this method
# Objective
- ambiguities bad
## Solution
- solve ambiguities
- by either ignoring (e.g. on `queue_mesh_view_bind_groups` since `LightMeta` access is different)
- by introducing a dependency (`prepare_windows -> prepare_*` because the latter use the fallback Msaa)
- make `prepare_assets` public so that we can do a proper `.after`
# Objective
Currently, it is quite awkward to use the `pbr` function in a custom shader without binding a mesh bind group.
This is because the `pbr` function depends on the `MESH_FLAGS_SHADOW_RECEIVER_BIT` flag.
## Solution
I have removed this dependency by adding the flag as a parameter to the `PbrInput` struct.
I am not sure if this is the ideal solution since the mesh flag indicates both `MESH_FLAGS_SIGN_DETERMINANT_MODEL_3X3_BIT` and `MESH_FLAGS_SHADOW_RECEIVER_BIT`.
The former seems to be unrelated to PBR. Maybe the flag should be split.
# Objective
- Fix the environment map shader not working under webgl due to textureNumLevels() not being supported
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7722
## Solution
- Instead of using textureNumLevels(), put an extra field in the GpuLights uniform to store the mip count
# Objective
Splits tone mapping from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6677 into a separate PR.
Address https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264.
Adds tone mapping options:
- None: Bypasses tonemapping for instances where users want colors output to match those set.
- Reinhard
- Reinhard Luminance: Bevy's exiting tonemapping
- [ACES](https://github.com/TheRealMJP/BakingLab/blob/master/BakingLab/ACES.hlsl) (Fitted version, based on the same implementation that Godot 4 uses) see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264
- [AgX](https://github.com/sobotka/AgX)
- SomewhatBoringDisplayTransform
- TonyMcMapface
- Blender Filmic
This PR also adds support for EXR images so they can be used to compare tonemapping options with reference images.
## Migration Guide
- Tonemapping is now an enum with NONE and the various tonemappers.
- The DebandDither is now a separate component.
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Allow for creating pipelines that use push constants. To be able to use push constants. Fixes#4825
As of right now, trying to call `RenderPass::set_push_constants` will trigger the following error:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In a RenderPass
note: encoder = `<CommandBuffer-(0, 59, Vulkan)>`
In a set_push_constant command
provided push constant is for stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT, however the pipeline layout has no push constant range for the stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT
```
## Solution
Add a field push_constant_ranges to` RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`.
This PR supersedes #4908 which now contains merge conflicts due to significant changes to `bevy_render`.
Meanwhile, this PR also made the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor` non-optional. If the user do not need to specify the bind group layouts, they can simply supply an empty vector here. No need for it to be optional.
---
## Changelog
- Add a field push_constant_ranges to RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor
- Made the `layout` field of RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor non-optional.
## Migration Guide
- Add push_constant_ranges: Vec::new() to every `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`
- Unwrap the optional values on the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`. If the descriptor has no layout, supply an empty vector.
Co-authored-by: Zhixing Zhang <me@neoto.xin>
fixes#6799
# Objective
We should be able to reuse the `Globals` or `View` shader struct definitions from anywhere (including third party plugins) without needing to worry about defining unrelated shader defs.
Also we'd like to refactor these structs to not be repeatedly defined.
## Solution
Refactor both `Globals` and `View` into separate importable shaders.
Use the imports throughout.
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com>
(Before)

(After)

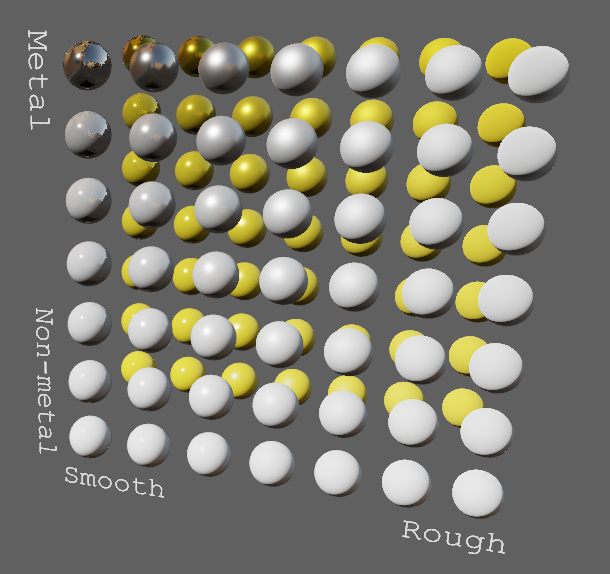
# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
add a hook for ambient occlusion to the pbr shader
## Solution
add a hook for ambient occlusion to the pbr shader
Co-authored-by: atlas dostal <rodol@rivalrebels.com>