# Objective
`bevy_reflect` as different kinds of reflected types (each with their own trait), `trait Struct: Reflect`, `trait List: Reflect`, `trait Map: Reflect`, ...
Types that don't fit either of those are called reflect value types, they are opaque and can't be deconstructed further.
`bevy_reflect` can serialize `dyn Reflect` values. Any container types (struct, list, map) get deconstructed and their elements serialized separately, which can all happen without serde being involved ever (happens [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_reflect/src/serde/ser.rs#L50-L85=)).
The only point at which we require types to be serde-serializable is for *value types* (happens [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_reflect/src/serde/ser.rs#L104=)).
So reflect array serializing is solved, since arrays are container types which don't require serde.
#1213 also introduced added the `serialize` method and `Serialize` impls for `dyn Array` and `DynamicArray` which use their element's `Reflect::serializable` function. This is 1. unnecessary, because it is not used for array serialization, and 2. annoying for removing the `Serialize` bound on container types, because these impls don't have access to the `TypeRegistry`, so we can't move the serialization code there.
# Solution
Remove these impls and `fn serialize`. It's not used and annoying for other changes.
# Objective
- The `scene_viewer` example assumes the `animation` feature is enabled, which it is by default. However, animations may have a performance cost that is undesirable when testing performance, for example. Then it is useful to be able to disable the `animation` feature and one would still like the `scene_viewer` example to work.
## Solution
- Gate animation code in `scene_viewer` on the `animation` feature being enabled.
# Objective
Increase compatibility with a fairly common format of padded spritesheets, in which half the padding value occurs before the first sprite box begins. The original behaviour falls out when `Vec2::ZERO` is used for `offset`.
See below unity screenshot for an example of a spritesheet with padding
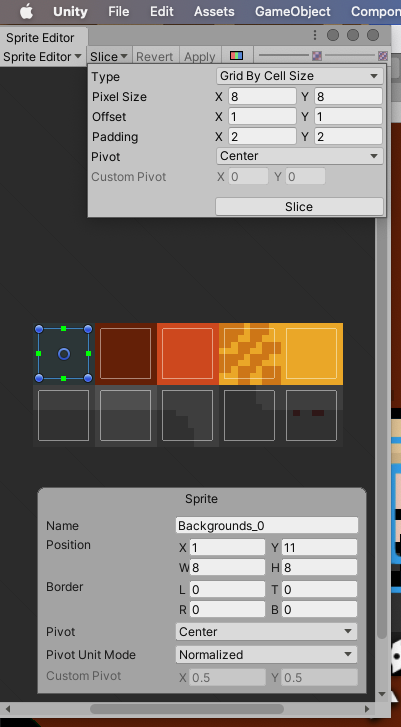
## Solution
Tiny change to `crates/bevy_sprite/src/texture_atlas.rs`
## Migration Guide
Calls to `TextureAtlas::from_grid_with_padding` should be modified to include a new parameter, which can be set to `Vec2::ZERO` to retain old behaviour.
```rust
from_grid_with_padding(texture, tile_size, columns, rows, padding)
|
V
from_grid_with_padding(texture, tile_size, columns, rows, padding, Vec2::ZERO)
```
Co-authored-by: FraserLee <30442265+FraserLee@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Currently, `FromReflect` makes a couple assumptions:
* Ignored fields must implement `Default`
* Active fields must implement `FromReflect`
* The reflected must be fully populated for active fields (can't use an empty `DynamicStruct`)
However, one or both of these requirements might be unachievable, such as for external types. In these cases, it might be nice to tell `FromReflect` to use a custom default.
## Solution
Added the `#[reflect(default)]` derive helper attribute. This attribute can be applied to any field (ignored or not) and will allow a default value to be specified in place of the regular `from_reflect()` call.
It takes two forms: `#[reflect(default)]` and `#[reflect(default = "some_func")]`. The former specifies that `Default::default()` should be used while the latter specifies that `some_func()` should be used. This is pretty much [how serde does it](https://serde.rs/field-attrs.html#default).
### Example
```rust
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct MyStruct {
// Use `Default::default()`
#[reflect(default)]
foo: String,
// Use `get_bar_default()`
#[reflect(default = "get_bar_default")]
#[reflect(ignore)]
bar: usize,
}
fn get_bar_default() -> usize {
123
}
```
### Active Fields
As an added benefit, this also allows active fields to be completely missing from their dynamic object. This is because the attribute tells `FromReflect` how to handle missing active fields (it still tries to use `from_reflect` first so the `FromReflect` trait is still required).
```rust
let dyn_struct = DynamicStruct::default();
// We can do this without actually including the active fields since they have `#[reflect(default)]`
let my_struct = <MyStruct as FromReflect>::from_reflect(&dyn_struct);
```
### Container Defaults
Also, with the addition of #3733, people will likely start adding `#[reflect(Default)]` to their types now. Just like with the fields, we can use this to mark the entire container as "defaultable". This grants us the ability to completely remove the field markers altogether if our type implements `Default` (and we're okay with fields using that instead of their own `Default` impls):
```rust
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
#[reflect(Default)]
struct MyStruct {
foo: String,
#[reflect(ignore)]
bar: usize,
}
impl Default for MyStruct {
fn default() -> Self {
Self {
foo: String::from("Hello"),
bar: 123,
}
}
}
// Again, we can now construct this from nothing pretty much
let dyn_struct = DynamicStruct::default();
let my_struct = <MyStruct as FromReflect>::from_reflect(&dyn_struct);
```
Now if _any_ field is missing when using `FromReflect`, we simply fallback onto the container's `Default` implementation.
This behavior can be completely overridden on a per-field basis, of course, by simply defining those same field attributes like before.
### Related
* #3733
* #1395
* #2377
---
## Changelog
* Added `#[reflect(default)]` field attribute for `FromReflect`
* Allows missing fields to be given a default value when using `FromReflect`
* `#[reflect(default)]` - Use the field's `Default` implementation
* `#[reflect(default = "some_fn")]` - Use a custom function to get the default value
* Allow `#[reflect(Default)]` to have a secondary usage as a container attribute
* Allows missing fields to be given a default value based on the container's `Default` impl when using `FromReflect`
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` for convenience and consistency
## Solution
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` similar to `ExtractComponentPlugin` but for ECS `Resource`s. The system that is executed simply clones the main world resource into a render world resource, if and only if the main world resource was either added or changed since the last execution of the system.
- Add an `ExtractResource` trait with a `fn extract_resource(res: &Self) -> Self` function. This is used by the `ExtractResourcePlugin` to extract the resource
- Add a derive macro for `ExtractResource` on a `Resource` with the `Clone` trait, that simply returns `res.clone()`
- Use `ExtractResourcePlugin` wherever both possible and appropriate
This was first done in 7b4e3a5, but was then reverted when the new
renderer for 0.6 was merged (ffecb05).
I'm assuming it was simply a mistake when merging.
# Objective
- Same as #2740, I think it was reverted by mistake when merging.
> # Objective
>
> - Make it easy to use HexColorError with `thiserror`, i.e. converting it into other error types.
>
> Makes this possible:
>
> ```rust
> #[derive(Debug, thiserror::Error)]
> pub enum LdtkError {
> #[error("An error occured while deserializing")]
> Json(#[from] serde_json::Error),
> #[error("An error occured while parsing a color")]
> HexColor(#[from] bevy::render::color::HexColorError),
> }
> ```
>
> ## Solution
>
> - Derive thiserror::Error the same way we do elsewhere (see query.rs for instance)
# Objective
- Higher order system could not be created by users.
- However, a simple change to `SystemParamFunction` allows this.
- Higher order systems in this case mean functions which return systems created using other systems, such as `chain` (which is basically equivalent to map)
## Solution
- Change `SystemParamFunction` to be a safe abstraction over `FnMut([In<In>,] ...params)->Out`.
- Note that I believe `SystemParamFunction` should not have been counted as part of our public api before this PR.
- This is because its only use was an unsafe function without an actionable safety comment.
- The safety comment was basically 'call this within bevy code'.
- I also believe that there are no external users in its current form.
- A quick search on Google and in the discord confirmed this.
## See also
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4666, which uses this and subsumes the example here
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `SystemParamFunction`, which can be used to create higher order systems.
# Objective
Fixes#4353. Fixes#4431. Picks up fixes for a panic for `gilrs` when `getGamepads()` is not available.
## Solution
Update the `gilrs` to `v0.9.0`. Changelog can be seen here: dba36f9186
EDIT: Updated `uuid` to 1.1 to avoid duplicate dependencies. Added `nix`'s two dependencies as exceptions until `rodio` updates their deps.
# Objective
- Add Vertex Color support to 2D meshes and ColorMaterial. This extends the work from #4528 (which in turn builds on the excellent tangent handling).
## Solution
- Added `#ifdef` wrapped support for vertex colors in the 2D mesh shader and `ColorMaterial` shader.
- Added an example, `mesh2d_vertex_color_texture` to demonstrate it in action.

---
## Changelog
- Added optional (ifdef wrapped) vertex color support to the 2dmesh and color material systems.
# Objective
- Sometimes, people might load an asset as one type, then use it with an `Asset`s for a different type.
- See e.g. #4784.
- This is especially likely with the Gltf types, since users may not have a clear conceptual model of what types the assets will be.
- We had an instance of this ourselves, in the `scene_viewer` example
## Solution
- Make `Assets::get` require a type safe handle.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- `Assets::<T>::get` and `Assets::<T>::get_mut` now require that the passed handles are `Handle<T>`, improving the type safety of handles.
### Added
- `HandleUntyped::typed_weak`, a helper function for creating a weak typed version of an exisitng `HandleUntyped`.
## Migration Guide
`Assets::<T>::get` and `Assets::<T>::get_mut` now require that the passed handles are `Handle<T>`, improving the type safety of handles. If you were previously passing in:
- a `HandleId`, use `&Handle::weak(id)` instead, to create a weak handle. You may have been able to store a type safe `Handle` instead.
- a `HandleUntyped`, use `&handle_untyped.typed_weak()` to create a weak handle of the specified type. This is most likely to be the useful when using [load_folder](https://docs.rs/bevy_asset/latest/bevy_asset/struct.AssetServer.html#method.load_folder)
- a `Handle<U>` of of a different type, consider whether this is the correct handle type to store. If it is (i.e. the same handle id is used for multiple different Asset types) use `Handle::weak(handle.id)` to cast to a different type.
# Objective
Fixes#4791. `ParallelExecutor` inserts a default `CompteTaskPool` if there isn't one stored as a resource, including when it runs on a different world. When spawning the render sub-app, the main world's `ComputeTaskPool` is not cloned and inserted into the render app's, which causes a second `ComputeTaskPool` with the default configuration to be spawned. This results in an excess number of threads being spawned.
## Solution
Copy the task pools from the main world to the subapps upon creating them.
## Alternative
An alternative to this would be to make the task pools global, as seen in #2250 or bevyengine/rfcs#54.
# Objective
Resolves#4753
## Solution
Using rust doc I added documentation to the struct. Decided to not provide an example in the doc comment but instead refer to the example file that shows the usage.
# Objective
Use less memory to store SparseSet components.
## Solution
Change `ComponentSparseSet` to only use `Entity::id` in it's key internally, and change the usize value in it's SparseArray to use u32 instead, as it cannot have more than u32::MAX live entities stored at once.
This should reduce the overhead of storing components in sparse set storage by 50%.
# Objective
Fixes#3183. Requiring a `&TaskPool` parameter is sort of meaningless if the only correct one is to use the one provided by `Res<ComputeTaskPool>` all the time.
## Solution
Have `QueryState` save a clone of the `ComputeTaskPool` which is used for all `par_for_each` functions.
~~Adds a small overhead of the internal `Arc` clone as a part of the startup, but the ergonomics win should be well worth this hardly-noticable overhead.~~
Updated the docs to note that it will panic the task pool is not present as a resource.
# Future Work
If https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/54 is approved, we can replace these resource lookups with a static function call instead to get the `ComputeTaskPool`.
---
## Changelog
Removed: The `task_pool` parameter of `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)`. These calls will use the `World`'s `ComputeTaskPool` resource instead.
## Migration Guide
The `task_pool` parameter for `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)` has been removed. Remove these parameters from all calls to these functions.
Before:
```rust
fn parallel_system(
task_pool: Res<ComputeTaskPool>,
query: Query<&MyComponent>,
) {
query.par_for_each(&task_pool, 32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
After:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_for_each(32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
If using `Query(State)` outside of a system run by the scheduler, you may need to manually configure and initialize a `ComputeTaskPool` as a resource in the `World`.
# Objective
The `ComponentId` in `Column` is redundant as it's stored in parallel in the surrounding `SparseSet` all the time.
## Solution
Remove it. Add `SparseSet::iter(_mut)` to parallel `HashMap::iter(_mut)` to allow iterating pairs of columns and their IDs.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SparseSet::iter` and `SparseSet::iter_mut`.
# Objective
- Rebase of #3159.
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3156
- add #[inline] to single related functions so that they matches with other function defs
## Solution
* added functions to QueryState
* get_single_unchecked_manual
* get_single_unchecked
* get_single
* get_single_mut
* single
* single_mut
* make Query::get_single use QueryState::get_single_unchecked_manual
* added #[inline]
---
## Changelog
### Added
Functions `QueryState::single`, `QueryState::get_single`, `QueryState::single_mut`, `QueryState::get_single_mut`, `QueryState::get_single_unchecked`, `QueryState::get_single_unchecked_manual`.
### Changed
`QuerySingleError` is now in the `state` module.
## Migration Guide
Change `query::QuerySingleError` to `state::QuerySingleError`
Co-authored-by: 2ne1ugly <chattermin@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: 2ne1ugly <47616772+2ne1ugly@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
the code in these fns are always identical so stop having two functions
## Solution
make them the same function
---
## Changelog
change `matches_archetype` and `matches_table` to `fn matches_component_set(&self, &SparseArray<ComponentId, usize>) -> bool` then do extremely boring updating of all `FetchState` impls
## Migration Guide
- move logic of `matches_archetype` and `matches_table` into `matches_component_set` in any manual `FetchState` impls
# Objective
Debugging reflected types can be somewhat frustrating since all `dyn Reflect` trait objects return something like `Reflect(core::option::Option<alloc::string::String>)`.
It would be much nicer to be able to see the actual value— or even use a custom `Debug` implementation.
## Solution
Added `Reflect::debug` which allows users to customize the debug output. It sets defaults for all `ReflectRef` subtraits and falls back to `Reflect(type_name)` if no `Debug` implementation was registered.
To register a custom `Debug` impl, users can add `#[reflect(Debug)]` like they can with other traits.
### Example
Using the following structs:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
pub struct Foo {
a: usize,
nested: Bar,
#[reflect(ignore)]
_ignored: NonReflectedValue,
}
#[derive(Reflect)]
pub struct Bar {
value: Vec2,
tuple_value: (i32, String),
list_value: Vec<usize>,
// We can't determine debug formatting for Option<T> yet
unknown_value: Option<String>,
custom_debug: CustomDebug
}
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(Debug)]
struct CustomDebug;
impl Debug for CustomDebug {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {
write!(f, "This is a custom debug!")
}
}
pub struct NonReflectedValue {
_a: usize,
}
```
We can do:
```rust
let value = Foo {
a: 1,
_ignored: NonReflectedValue { _a: 10 },
nested: Bar {
value: Vec2::new(1.23, 3.21),
tuple_value: (123, String::from("Hello")),
list_value: vec![1, 2, 3],
unknown_value: Some(String::from("World")),
custom_debug: CustomDebug
},
};
let reflected_value: &dyn Reflect = &value;
println!("{:#?}", reflected_value)
```
Which results in:
```rust
Foo {
a: 2,
nested: Bar {
value: Vec2(
1.23,
3.21,
),
tuple_value: (
123,
"Hello",
),
list_value: [
1,
2,
3,
],
unknown_value: Reflect(core::option::Option<alloc::string::String>),
custom_debug: This is a custom debug!,
},
}
```
Notice that neither `Foo` nor `Bar` implement `Debug`, yet we can still deduce it. This might be a concern if we're worried about leaking internal values. If it is, we might want to consider a way to exclude fields (possibly with a `#[reflect(hide)]` macro) or make it purely opt in (as opposed to the default implementation automatically handled by ReflectRef subtraits).
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Even if bevy itself does not provide any builtin scripting or modding APIs, it should have the foundations for building them yourself.
For that it should be enough to have APIs that are not tied to the actual rust types with generics, but rather accept `ComponentId`s and `bevy_ptr` ptrs.
## Solution
Add the following APIs to bevy
```rust
fn EntityRef::get_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'w>>;
fn EntityMut::get_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'_>>;
fn EntityMut::get_mut_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'_>>;
fn World::get_resource_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'_>>;
fn World::get_resource_mut_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'_>>;
// Safety: `value` must point to a valid value of the component
unsafe fn World::insert_resource_by_id(ComponentId, value: OwningPtr);
fn ComponentDescriptor::new_with_layout(..) -> Self;
fn World::init_component_with_descriptor(ComponentDescriptor) -> ComponentId;
```
~~This PR would definitely benefit from #3001 (lifetime'd pointers) to make sure that the lifetimes of the pointers are valid and the my-move pointer in `insert_resource_by_id` could be an `OwningPtr`, but that can be adapter later if/when #3001 is merged.~~
### Not in this PR
- inserting components on entities (this is very tied to types with bundles and the `BundleInserter`)
- an untyped version of a query (needs good API design, has a large implementation complexity, can be done in a third-party crate)
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
One way to avoid texture atlas bleeding is to ensure that every vertex is
placed at an integer pixel coordinate. This is a particularly appealing
solution for regular structures like tile maps.
Doing so is currently harder than necessary when the WindowSize scaling
mode and Center origin are used: For odd window width or height, the
origin of the coordinate system is placed in the middle of a pixel at
some .5 offset.
## Solution
Avoid this issue by rounding the half width and height values.
# Objective
- Coming from 7a596f1910 (r876310734)
- Simplify the examples regarding addition of `Msaa` Resource with default value.
## Solution
- Remove addition of `Msaa` Resource with default value from examples,
Updates the requirements on [tracing-tracy](https://github.com/nagisa/rust_tracy_client) to permit the latest version.
<details>
<summary>Commits</summary>
<ul>
<li><a href="13b335a710"><code>13b335a</code></a> Remove ability to disable the client at runtime</li>
<li><a href="69e44977ee"><code>69e4497</code></a> The upgrades to 0.8.1</li>
<li><a href="c204b60c7a"><code>c204b60</code></a> Cancel the old test runs</li>
<li><a href="939bd04c1c"><code>939bd04</code></a> Remove the thread initialization calls</li>
<li><a href="7024e776bb"><code>7024e77</code></a> Update Tracy client bindings to v0.8.1</li>
<li><a href="5c54baa244"><code>5c54baa</code></a> tracy-client 0.12.7</li>
<li><a href="f183050b20"><code>f183050</code></a> Non-allocating <code>span!</code> macro</li>
<li><a href="15936ea751"><code>15936ea</code></a> tracy-client 0.12.6</li>
<li><a href="26d0c50542"><code>26d0c50</code></a> Relax literal the requirement of the create_plot macro so that it can be used...</li>
<li>See full diff in <a href="https://github.com/nagisa/rust_tracy_client/compare/tracing-tracy-v0.8.0...tracing-tracy-v0.9.0">compare view</a></li>
</ul>
</details>
<br />
Dependabot will resolve any conflicts with this PR as long as you don't alter it yourself. You can also trigger a rebase manually by commenting `@dependabot rebase`.
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-start)
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-end)
---
<details>
<summary>Dependabot commands and options</summary>
<br />
You can trigger Dependabot actions by commenting on this PR:
- `@dependabot rebase` will rebase this PR
- `@dependabot recreate` will recreate this PR, overwriting any edits that have been made to it
- `@dependabot merge` will merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot squash and merge` will squash and merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot cancel merge` will cancel a previously requested merge and block automerging
- `@dependabot reopen` will reopen this PR if it is closed
- `@dependabot close` will close this PR and stop Dependabot recreating it. You can achieve the same result by closing it manually
- `@dependabot ignore this major version` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this major version (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this minor version` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this minor version (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this dependency` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this dependency (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
</details>
# Objective
- Make bevy_app's optional bevy_reflect dependency actually optional
- Because bevy_ecs has a default dependency on bevy_reflect, bevy_app includes bevy_reflect transitively even with default-features=false, despite the optional dependency indicating that it was intended to be able to leave out bevy_reflect.
## Solution
- Make bevy_app not enable bevy_ecs's default features, and then use [the `dep:` syntax](https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/features.html#optional-dependencies) introduced in 1.60 to make the default bevy_reflect feature enable bevy_ecs's bevy_reflect feature/dependency.
---
## Changelog
- bevy_app no longer enables bevy_ecs's `bevy_reflect` feature when included without its own `bevy_reflect` feature (which is on by default).
# Objective
Reduce the catch-all grab-bag of functionality in bevy_core by minimally splitting off time functionality into bevy_time. Functionality like that provided by #3002 would increase the complexity of bevy_time, so this is a good candidate for pulling into its own unit.
A step in addressing #2931 and splitting bevy_core into more specific locations.
## Solution
Pull the time module of bevy_core into a new crate, bevy_time.
# Migration guide
- Time related types (e.g. `Time`, `Timer`, `Stopwatch`, `FixedTimestep`, etc.) should be imported from `bevy::time::*` rather than `bevy::core::*`.
- If you were adding `CorePlugin` manually, you'll also want to add `TimePlugin` from `bevy::time`.
- The `bevy::core::CorePlugin::Time` system label is replaced with `bevy::time::TimeSystem`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- As noticed in #4333 by @x-52, the exact purpose and logic of `HasRawWIndowHandleWrapper` is unclear
- Unfortunately, there are rather good reasons why this design is needed (and why we can't just `impl HasRawWindowHandle for RawWindowHandleWrapper`
## Solution
- Rename `HasRawWindowHandleWrapper` to `ThreadLockedRawWindowHandleWrapper`, reflecting the primary distinction
- Document how this design is intended to be used
- Leave comments explaining why this design must exist
## Migration Guide
- renamed `HasRawWindowHandleWrapper` to `ThreadLockedRawWindowHandleWrapper`
# Objective
Make the function consistent with returned values and `as_hsla` method
Fixes#4826
## Solution
- Rename the method
## Migration Guide
- Rename the method
# Objective
This fails constantly and causes more pain than it is worth.
## Solution
Remove dead link checks.
Alternative to #4837, which is more granular but ironically still fails to build. I'm in favor of the nuclear option.
Fixes#4575
Currently Bevy's web canvases are "fixed size". They are manually set to specific dimensions. This might be fine for some games and website layouts, but for sites with flexible layouts, or games that want to "fill" the browser window, Bevy doesn't provide the tools needed to make this easy out of the box.
There are third party plugins like [bevy-web-resizer](https://github.com/frewsxcv/bevy-web-resizer/) that listen for window resizes, take the new dimensions, and resize the winit window accordingly. However this only covers a subset of cases and this is common enough functionality that it should be baked into Bevy.
A significant motivating use case here is the [Bevy WASM Examples page](https://bevyengine.org/examples/). This scales the canvas to fit smaller windows (such as mobile). But this approach both breaks winit's mouse events and removes pixel-perfect rendering (which means we might be rendering too many or too few pixels). https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website/issues/371
In an ideal world, winit would support this behavior out of the box. But unfortunately that seems blocked for now: https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/pull/2074. And it builds on the ResizeObserver api, which isn't supported in all browsers yet (and is only supported in very new versions of the popular browsers).
While we wait for a complete winit solution, I've added a `fit_canvas_to_parent` option to WindowDescriptor / Window, which when enabled will listen for window resizes and resize the Bevy canvas/window to fit its parent element. This enables users to scale bevy canvases using arbitrary CSS, by "inheriting" their parents' size. Note that the wrapper element _is_ required because winit overrides the canvas sizing with absolute values on each resize.
There is one limitation worth calling out here: while the majority of canvas resizes will be triggered by window resizes, modifying element layout at runtime (css animations, javascript-driven element changes, dev-tool-injected changes, etc) will not be detected here. I'm not aware of a good / efficient event-driven way to do this outside of the ResizeObserver api. In practice, window-resize-driven canvas resizing should cover the majority of use cases. Users that want to actively poll for element resizes can just do that (or we can build another feature and let people choose based on their specific needs).
I also took the chance to make a couple of minor tweaks:
* Made the `canvas` window setting available on all platforms. Users shouldn't need to deal with cargo feature selection to support web scenarios. We can just ignore the value on non-web platforms. I added documentation that explains this.
* Removed the redundant "initial create windows" handler. With the addition of the code in this pr, the code duplication was untenable.
This enables a number of patterns:
## Easy "fullscreen window" mode for the default canvas
The "parent element" defaults to the `<body>` element.
```rust
app
.insert_resource(WindowDescriptor {
fit_canvas_to_parent: true,
..default()
})
```
And CSS:
```css
html, body {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
```
## Fit custom canvas to "wrapper" parent element
```rust
app
.insert_resource(WindowDescriptor {
fit_canvas_to_parent: true,
canvas: Some("#bevy".to_string()),
..default()
})
```
And the HTML:
```html
<div style="width: 50%; height: 100%">
<canvas id="bevy"></canvas>
</div>
```
# Objective
Allow `Box<dyn Reflect>` to be converted into a `Box<dyn MyTrait>` using the `#[reflect_trait]` macro. The other methods `get` and `get_mut` only provide a reference to the reflected object.
## Solution
Add a `get_boxed` method to the `Reflect***` struct generated by the `#[reflect_trait]` macro. This method takes in a `Box<dyn Reflect>` and returns a `Box<dyn MyTrait>`.
Co-authored-by: MrGVSV <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#4657
Example code that wasnt panic'ing before this PR (and so was unsound):
```rust
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn option_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<(Option<&A>, &mut B)>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn any_of_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<(AnyOf<(&A, ())>, &mut B)>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn or_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<&mut B, Or<(With<A>, With<B>)>>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
```
## Solution
- Only add the intersection of `with`/`without` accesses of all the elements in `Or/AnyOf` to the world query's `FilteredAccess<ComponentId>` instead of the union.
- `Option`'s fix can be thought of the same way since its basically `AnyOf<T, ()>` but its impl is just simpler as `()` has no `with`/`without` accesses
---
## Changelog
- `Or`/`AnyOf`/`Option` will now report more query conflicts in order to fix unsoundness
## Migration Guide
- If you are now getting query conflicts from `Or`/`AnyOf`/`Option` rip to you and ur welcome for it now being caught
# Objective
We have duplicated code between `QueryIter` and `QueryIterationCursor`. Reuse that code.
## Solution
- Reuse `QueryIterationCursor` inside `QueryIter`.
- Slim down `QueryIter` by removing the `&'w World`. It was only being used by the `size_hint` and `ExactSizeIterator` impls, which can use the QueryState and &Archetypes in the type already.
- Benchmark to make sure there is no significant regression.
Relevant benchmark results seem to show that there is no tangible difference between the two. Everything seems to be either identical or within a workable margin of error here.
```
group embed-cursor main
----- ------------ ----
fragmented_iter/base 1.00 387.4±19.70ns ? ?/sec 1.07 413.1±27.95ns ? ?/sec
many_maps_iter 1.00 27.3±0.22ms ? ?/sec 1.00 27.4±0.10ms ? ?/sec
simple_iter/base 1.00 13.8±0.07µs ? ?/sec 1.00 13.7±0.17µs ? ?/sec
simple_iter/sparse 1.00 61.9±0.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 62.2±0.64µs ? ?/sec
simple_iter/system 1.00 13.7±0.34µs ? ?/sec 1.00 13.7±0.10µs ? ?/sec
sparse_fragmented_iter/base 1.00 11.0±0.54ns ? ?/sec 1.03 11.3±0.48ns ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_sparse 1.08 105.0±2.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 97.5±2.18µs ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_table 1.00 27.3±0.13µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.3±0.37µs ? ?/sec
```
# Objective
Quick followup to #4712.
While updating some [other PRs](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4218), I realized the `ReflectTraits` struct could be improved. The issue with the current implementation is that `ReflectTraits::get_xxx_impl(...)` returns just the _logic_ to the corresponding `Reflect` trait method, rather than the entire function.
This makes it slightly more annoying to manage since the variable names need to be consistent across files. For example, `get_partial_eq_impl` uses a `value` variable. But the name "value" isn't defined in the `get_partial_eq_impl` method, it's defined in three other methods in a completely separate file.
It's not likely to cause any bugs if we keep it as it is since differing variable names will probably just result in a compile error (except in very particular cases). But it would be useful to someone who wanted to edit/add/remove a method.
## Solution
Made `get_hash_impl`, `get_partial_eq_impl` and `get_serialize_impl` return the entire method implementation for `reflect_hash`, `reflect_partial_eq`, and `serializable`, respectively.
As a result of this, those three `Reflect` methods were also given default implementations. This was fairly simple to do since all three could just be made to return `None`.
---
## Changelog
* Small cleanup/refactor to `ReflectTraits` in `bevy_reflect_derive`
* Gave `Reflect::reflect_hash`, `Reflect::reflect_partial_eq`, and `Reflect::serializable` default implementations
# Objective
Support returning data out of with_children to enable the use case of changing the parent commands with data created inside the child builder.
## Solution
Change the with_children closure to return T.
Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2817.
---
## Changelog
`BuildChildren::add_children` was added with the ability to return data to use outside the closure (for spawning a new child builder on a returned entity for example).
# Objective
Fixes#4751, zld link error.
## Solution
- Change the `zld` file path in the example to the one homebrew installs to by default, `/usr/local/bin/zld`.
# Objective
- We do a lot of function pointer calls in a hot loop (clearing entities in render). This is slow, since calling function pointers cannot be optimised out. We can avoid that in the cases where the function call is a no-op.
- Alternative to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2897
- On my machine, in `many_cubes`, this reduces dropping time from ~150μs to ~80μs.
## Solution
- Make `drop` in `BlobVec` an `Option`, recording whether the given drop impl is required or not.
- Note that this does add branching in some cases - we could consider splitting this into two fields, i.e. unconditionally call the `drop` fn pointer.
- My intuition of how often types stored in `World` should have non-trivial drops makes me think that would be slower, however.
N.B. Even once this lands, we should still test having a 'drop_multiple' variant - for types with a real `Drop` impl, the current implementation is definitely optimal.
# Objective
- Part of the splitting process of #3692.
## Solution
- Document `keyboard.rs` inside of `bevy_input`.
Co-authored-by: KDecay <KDecayMusic@protonmail.com>
# Objective
Partially addresses #3594.
## Solution
This adds basic benchmarks for `List`, `Map`, and `Struct` implementors, both concrete (`Vec`, `HashMap`, and defined struct types) and dynamic (`DynamicList`, `DynamicMap` and `DynamicStruct`).
A few insights from the benchmarks (all measurements are local on my machine):
- Applying a list with many elements to a list with no elements is slower than applying to a list of the same length:
- 3-4x slower when applying to a `Vec`
- 5-6x slower when applying to a `DynamicList`
I suspect this could be improved by `reserve()`ing the correct length up front, but haven't tested.
- Applying a `DynamicMap` to another `Map` is linear in the number of elements, but applying a `HashMap` seems to be at least quadratic. No intuition on this one.
- Applying like structs (concrete -> concrete, `DynamicStruct` -> `DynamicStruct`) seems to be faster than applying unlike structs.
# Objective
- Transform propogation could stack overflow when there was a cycle.
- I think https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4203 would use all available memory.
## Solution
- Make sure that the child entity's `Parent`s are their parents.
This is also required for when parallelising, although as noted in the comment, the naïve solution would be UB.
(The best way to fix this would probably be an `&mut UnsafeCell<T>` `WorldQuery`, or wrapper type with the same effect)