2022-05-16 13:53:20 +00:00
|
|
|
//! This is a guided introduction to Bevy's "Entity Component System" (ECS)
|
|
|
|
|
//! All Bevy app logic is built using the ECS pattern, so definitely pay attention!
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! Why ECS?
|
|
|
|
|
//! * Data oriented: Functionality is driven by data
|
|
|
|
|
//! * Clean Architecture: Loose coupling of functionality / prevents deeply nested inheritance
|
|
|
|
|
//! * High Performance: Massively parallel and cache friendly
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! ECS Definitions:
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! Component: just a normal Rust data type. generally scoped to a single piece of functionality
|
|
|
|
|
//! Examples: position, velocity, health, color, name
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! Entity: a collection of components with a unique id
|
|
|
|
|
//! Examples: Entity1 { Name("Alice"), Position(0, 0) },
|
|
|
|
|
//! Entity2 { Name("Bill"), Position(10, 5) }
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! Resource: a shared global piece of data
|
|
|
|
|
//! Examples: asset storage, events, system state
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! System: runs logic on entities, components, and resources
|
|
|
|
|
//! Examples: move system, damage system
|
|
|
|
|
//!
|
|
|
|
|
//! Now that you know a little bit about ECS, lets look at some Bevy code!
|
|
|
|
|
//! We will now make a simple "game" to illustrate what Bevy's ECS looks like in practice.
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-07-17 01:47:51 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy::{
|
2023-05-10 16:46:21 +00:00
|
|
|
app::{AppExit, ScheduleRunnerPlugin},
|
2020-07-17 01:47:51 +00:00
|
|
|
prelude::*,
|
2020-11-22 00:38:24 +00:00
|
|
|
utils::Duration,
|
2020-07-17 01:47:51 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
use rand::random;
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
// COMPONENTS: Pieces of functionality we add to entities. These are just normal Rust data types
|
|
|
|
|
//
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// Our game will have a number of "players". Each player has a name that identifies them
|
2021-10-03 19:23:44 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Component)]
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
struct Player {
|
|
|
|
|
name: String,
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Each player also has a score. This component holds on to that score
|
2021-10-03 19:23:44 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Component)]
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
struct Score {
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
value: usize,
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
// RESOURCES: "Global" state accessible by systems. These are also just normal Rust data types!
|
|
|
|
|
//
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// This resource holds information about the game:
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Resource, Default)]
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
struct GameState {
|
|
|
|
|
current_round: usize,
|
|
|
|
|
total_players: usize,
|
|
|
|
|
winning_player: Option<String>,
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:48:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// This resource provides rules for our "game".
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Resource)]
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
struct GameRules {
|
|
|
|
|
winning_score: usize,
|
|
|
|
|
max_rounds: usize,
|
|
|
|
|
max_players: usize,
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// SYSTEMS: Logic that runs on entities, components, and resources. These generally run once each
|
|
|
|
|
// time the app updates.
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
//
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:48:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// This is the simplest type of system. It just prints "This game is fun!" on each run:
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
fn print_message_system() {
|
|
|
|
|
println!("This game is fun!");
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// Systems can also read and modify resources. This system starts a new "round" on each update:
|
2020-05-03 07:48:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// NOTE: "mut" denotes that the resource is "mutable"
|
2020-05-14 00:52:47 +00:00
|
|
|
// Res<GameRules> is read-only. ResMut<GameState> can modify the resource
|
|
|
|
|
fn new_round_system(game_rules: Res<GameRules>, mut game_state: ResMut<GameState>) {
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
game_state.current_round += 1;
|
|
|
|
|
println!(
|
|
|
|
|
"Begin round {} of {}",
|
|
|
|
|
game_state.current_round, game_rules.max_rounds
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-06-27 19:06:12 +00:00
|
|
|
// This system updates the score for each entity with the "Player" and "Score" component.
|
2020-07-10 04:18:35 +00:00
|
|
|
fn score_system(mut query: Query<(&Player, &mut Score)>) {
|
2022-07-11 15:28:50 +00:00
|
|
|
for (player, mut score) in &mut query {
|
2020-06-27 19:06:12 +00:00
|
|
|
let scored_a_point = random::<bool>();
|
|
|
|
|
if scored_a_point {
|
|
|
|
|
score.value += 1;
|
|
|
|
|
println!(
|
|
|
|
|
"{} scored a point! Their score is: {}",
|
|
|
|
|
player.name, score.value
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
} else {
|
|
|
|
|
println!(
|
|
|
|
|
"{} did not score a point! Their score is: {}",
|
|
|
|
|
player.name, score.value
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// this game isn't very fun is it :)
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// This system runs on all entities with the "Player" and "Score" components, but it also
|
|
|
|
|
// accesses the "GameRules" resource to determine if a player has won.
|
|
|
|
|
fn score_check_system(
|
2020-05-14 00:52:47 +00:00
|
|
|
game_rules: Res<GameRules>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut game_state: ResMut<GameState>,
|
2020-10-30 06:39:55 +00:00
|
|
|
query: Query<(&Player, &Score)>,
|
2020-05-28 20:36:48 +00:00
|
|
|
) {
|
2022-07-11 15:28:50 +00:00
|
|
|
for (player, score) in &query {
|
2020-05-28 20:36:48 +00:00
|
|
|
if score.value == game_rules.winning_score {
|
|
|
|
|
game_state.winning_player = Some(player.name.clone());
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// This system ends the game if we meet the right conditions. This fires an AppExit event, which
|
|
|
|
|
// tells our App to quit. Check out the "event.rs" example if you want to learn more about using
|
|
|
|
|
// events.
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
fn game_over_system(
|
2020-05-14 00:52:47 +00:00
|
|
|
game_rules: Res<GameRules>,
|
|
|
|
|
game_state: Res<GameState>,
|
2021-03-07 20:42:04 +00:00
|
|
|
mut app_exit_events: EventWriter<AppExit>,
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
if let Some(ref player) = game_state.winning_player {
|
2022-10-28 21:03:01 +00:00
|
|
|
println!("{player} won the game!");
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
app_exit_events.send(AppExit);
|
|
|
|
|
} else if game_state.current_round == game_rules.max_rounds {
|
|
|
|
|
println!("Ran out of rounds. Nobody wins!");
|
|
|
|
|
app_exit_events.send(AppExit);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// This is a "startup" system that runs exactly once when the app starts up. Startup systems are
|
|
|
|
|
// generally used to create the initial "state" of our game. The only thing that distinguishes a
|
|
|
|
|
// "startup" system from a "normal" system is how it is registered: Startup:
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// app.add_systems(Startup, startup_system) Normal: app.add_systems(Update, normal_system)
|

Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor::new::<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
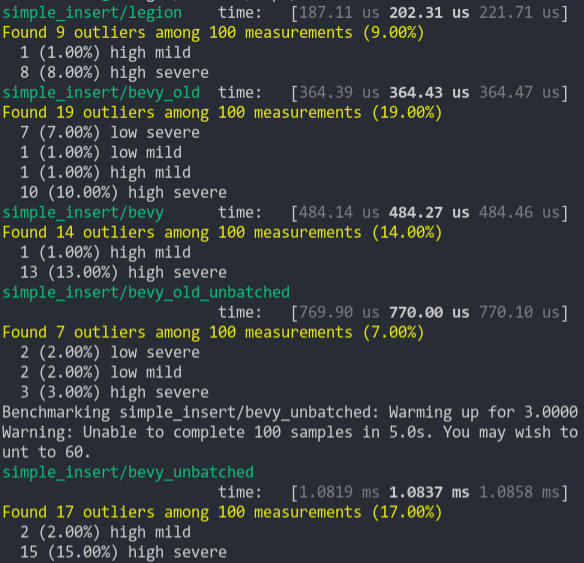
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)
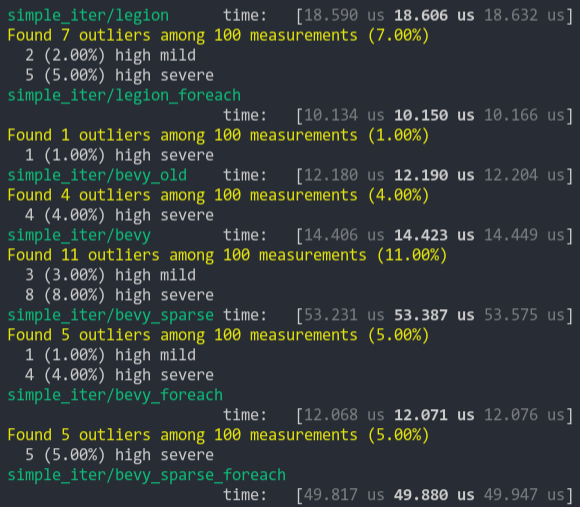
### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
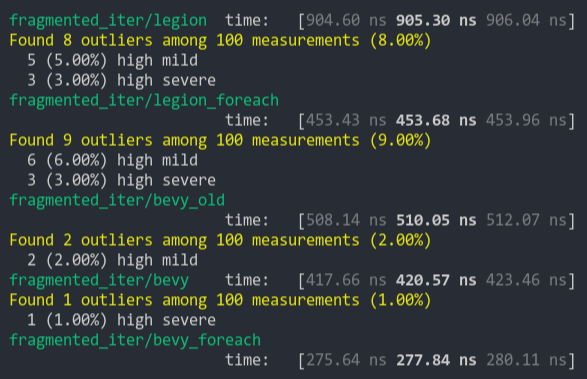
### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
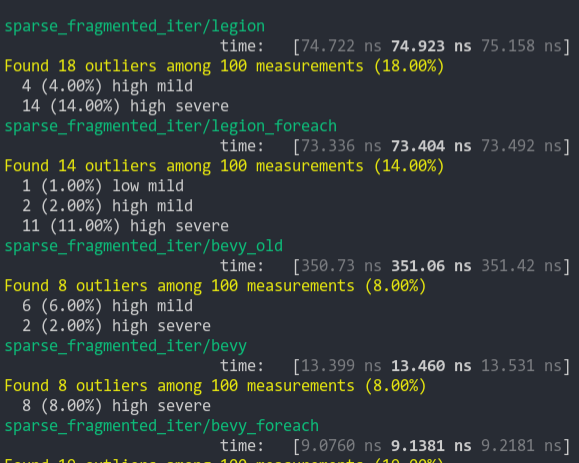
### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes
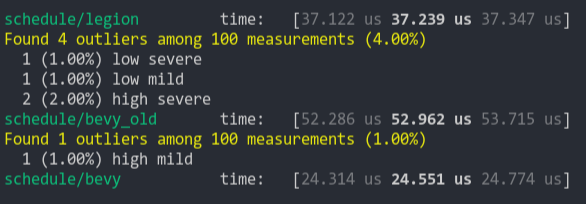
### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)
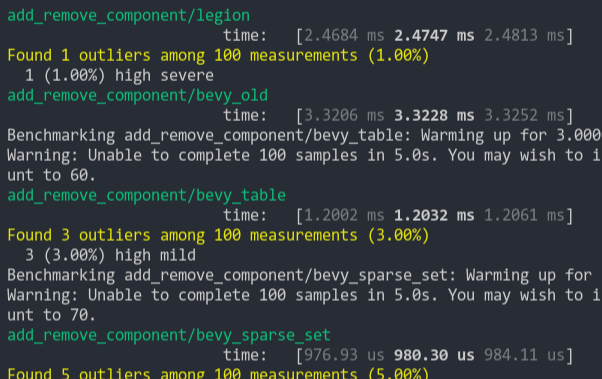
### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)
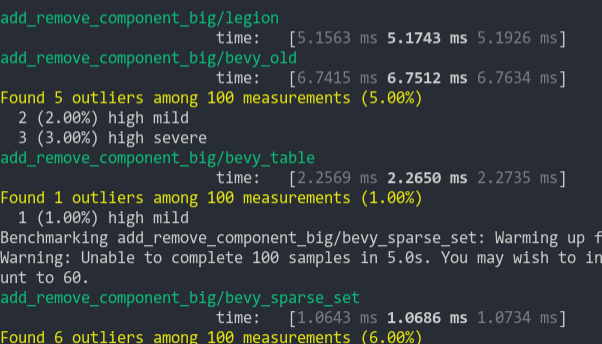
### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed
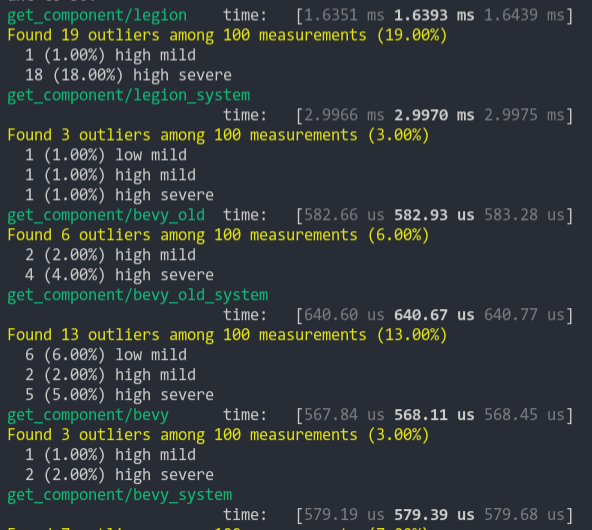
### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times
2021-03-05 07:54:35 +00:00
|
|
|
fn startup_system(mut commands: Commands, mut game_state: ResMut<GameState>) {
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// Create our game rules resource
|
2020-11-01 22:32:48 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.insert_resource(GameRules {
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
max_rounds: 10,
|
|
|
|
|
winning_score: 4,
|
|
|
|
|
max_players: 4,
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// Add some players to our world. Players start with a score of 0 ... we want our game to be
|
|
|
|
|
// fair!
|
2020-11-01 22:32:48 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn_batch(vec![
|
2020-07-10 04:18:35 +00:00
|
|
|
(
|
|
|
|
|
Player {
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Alice".to_string(),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
Score { value: 0 },
|
|
|
|
|
),
|
|
|
|
|
(
|
|
|
|
|
Player {
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Bob".to_string(),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
Score { value: 0 },
|
|
|
|
|
),
|
|
|
|
|
]);
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 07:48:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// set the total players to "2"
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
game_state.total_players = 2;
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// This system uses a command buffer to (potentially) add a new player to our game on each
|
|
|
|
|
// iteration. Normal systems cannot safely access the World instance directly because they run in
|
|
|
|
|
// parallel. Our World contains all of our components, so mutating arbitrary parts of it in parallel
|
|
|
|
|
// is not thread safe. Command buffers give us the ability to queue up changes to our World without
|
|
|
|
|
// directly accessing it
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
fn new_player_system(
|

Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor::new::<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes

### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed

### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times

2021-03-05 07:54:35 +00:00
|
|
|
mut commands: Commands,
|
2020-05-14 00:52:47 +00:00
|
|
|
game_rules: Res<GameRules>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut game_state: ResMut<GameState>,
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
// Randomly add a new player
|
|
|
|
|
let add_new_player = random::<bool>();
|
|
|
|
|
if add_new_player && game_state.total_players < game_rules.max_players {
|
|
|
|
|
game_state.total_players += 1;
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn((
|
2020-07-10 04:18:35 +00:00
|
|
|
Player {
|
|
|
|
|
name: format!("Player {}", game_state.total_players),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
Score { value: 0 },
|
|
|
|
|
));
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
println!("Player {} joined the game!", game_state.total_players);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-01-08 22:36:33 +00:00
|
|
|
// If you really need full, immediate read/write access to the world or resources, you can use an
|
|
|
|
|
// "exclusive system".
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// WARNING: These will block all parallel execution of other systems until they finish, so they
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// should generally be avoided if you want to maximize parallelism.
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
#[allow(dead_code)]
|
2022-01-08 22:36:33 +00:00
|
|
|
fn exclusive_player_system(world: &mut World) {
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// this does the same thing as "new_player_system"
|
2022-02-27 22:37:18 +00:00
|
|
|
let total_players = world.resource_mut::<GameState>().total_players;
|

Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor::new::<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes

### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed

### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times

2021-03-05 07:54:35 +00:00
|
|
|
let should_add_player = {
|
2022-02-27 22:37:18 +00:00
|
|
|
let game_rules = world.resource::<GameRules>();
|

Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor::new::<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes

### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed

### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times

2021-03-05 07:54:35 +00:00
|
|
|
let add_new_player = random::<bool>();
|
|
|
|
|
add_new_player && total_players < game_rules.max_players
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// Randomly add a new player
|

Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor::new::<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes

### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)

### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed

### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times

2021-03-05 07:54:35 +00:00
|
|
|
if should_add_player {
|
2022-06-26 13:58:56 +00:00
|
|
|
println!("Player {} has joined the game!", total_players + 1);
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
world.spawn((
|
2020-07-10 04:18:35 +00:00
|
|
|
Player {
|
2022-06-26 13:58:56 +00:00
|
|
|
name: format!("Player {}", total_players + 1),
|
2020-07-10 04:18:35 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
Score { value: 0 },
|
|
|
|
|
));
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-02-27 22:37:18 +00:00
|
|
|
let mut game_state = world.resource_mut::<GameState>();
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
game_state.total_players += 1;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-04-04 21:16:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// Sometimes systems need to be stateful. Bevy's ECS provides the `Local` system parameter
|
|
|
|
|
// for this case. A `Local<T>` refers to a value owned by the system of type `T`, which is automatically
|
|
|
|
|
// initialized using `T`'s `FromWorld`* implementation. In this system's `Local` (`counter`), `T` is `u32`.
|
|
|
|
|
// Therefore, on the first turn, `counter` has a value of 0.
|
|
|
|
|
//
|
|
|
|
|
// *: `FromWorld` is a trait which creates a value using the contents of the `World`.
|
|
|
|
|
// For any type which is `Default`, like `u32` in this example, `FromWorld` creates the default value.
|
|
|
|
|
fn print_at_end_round(mut counter: Local<u32>) {
|
|
|
|
|
*counter += 1;
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
println!("In set 'Last' for the {}th time", *counter);
|
2022-04-04 21:16:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// Print an empty line between rounds
|
|
|
|
|
println!();
|
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
/// A group of related system sets, used for controlling the order of systems. Systems can be
|
|
|
|
|
/// added to any number of sets.
|
|
|
|
|
#[derive(SystemSet, Debug, Hash, PartialEq, Eq, Clone)]
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
enum MySet {
|
2021-02-18 21:20:37 +00:00
|
|
|
BeforeRound,
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
Round,
|
2021-02-18 21:20:37 +00:00
|
|
|
AfterRound,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
// Our Bevy app's entry point
|
|
|
|
|
fn main() {
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// Bevy apps are created using the builder pattern. We use the builder to add systems,
|
|
|
|
|
// resources, and plugins to our app
|
2021-07-27 20:21:06 +00:00
|
|
|
App::new()
|
2022-04-04 21:16:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// Resources that implement the Default or FromWorld trait can be added like this:
|
|
|
|
|
.init_resource::<GameState>()
|
2020-11-03 02:38:37 +00:00
|
|
|
// Plugins are just a grouped set of app builder calls (just like we're doing here).
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// We could easily turn our game into a plugin, but you can check out the plugin example for
|
2023-05-10 16:46:21 +00:00
|
|
|
// that :) The plugin below runs our app's "system schedule" once every 5 seconds.
|
2023-06-21 20:51:03 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_plugins(ScheduleRunnerPlugin::run_loop(Duration::from_secs(5)))
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// `Startup` systems run exactly once BEFORE all other systems. These are generally used for
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// app initialization code (ex: adding entities and resources)
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_systems(Startup, startup_system)
|
|
|
|
|
// `Update` systems run once every update. These are generally used for "real-time app logic"
|
|
|
|
|
.add_systems(Update, print_message_system)
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// SYSTEM EXECUTION ORDER
|
|
|
|
|
//
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
// Each system belongs to a `Schedule`, which controls the execution strategy and broad order
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// of the systems within each tick. The `Startup` schedule holds
|
|
|
|
|
// startup systems, which are run a single time before `Update` runs. `Update` runs once per app update,
|
|
|
|
|
// which is generally one "frame" or one "tick".
|
2021-02-16 19:18:08 +00:00
|
|
|
//
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// By default, all systems in a `Schedule` run in parallel, except when they require mutable access to a
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// piece of data. This is efficient, but sometimes order matters.
|
|
|
|
|
// For example, we want our "game over" system to execute after all other systems to ensure
|
|
|
|
|
// we don't accidentally run the game for an extra round.
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
//
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
// You can force an explicit ordering between systems using the `.before` or `.after` methods.
|
|
|
|
|
// Systems will not be scheduled until all of the systems that they have an "ordering dependency" on have
|
2021-03-11 00:27:30 +00:00
|
|
|
// completed.
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// There are other schedules, such as `Last` which runs at the very end of each run.
|
|
|
|
|
.add_systems(Last, print_at_end_round)
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
// We can also create new system sets, and order them relative to other system sets.
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// Here is what our games execution order will look like:
|
2020-05-06 01:44:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// "before_round": new_player_system, new_round_system
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// "round": print_message_system, score_system
|
2020-05-03 07:48:36 +00:00
|
|
|
// "after_round": score_check_system, game_over_system
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
.configure_sets(
|
|
|
|
|
Update,
|
|
|
|
|
// chain() will ensure sets run in the order they are listed
|
|
|
|
|
(MySet::BeforeRound, MySet::Round, MySet::AfterRound).chain(),
|
2022-04-04 21:16:36 +00:00
|
|
|
)
|
2023-03-18 01:45:34 +00:00
|
|
|
// The add_systems function is powerful. You can define complex system configurations with ease!
|
|
|
|
|
.add_systems(
|
|
|
|
|
Update,
|
|
|
|
|
(
|
|
|
|
|
// These `BeforeRound` systems will run before `Round` systems, thanks to the chained set configuration
|
|
|
|
|
(
|
|
|
|
|
// You can also chain systems! new_round_system will run first, followed by new_player_system
|
|
|
|
|
(new_round_system, new_player_system).chain(),
|
|
|
|
|
exclusive_player_system,
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
// All of the systems in the tuple above will be added to this set
|
|
|
|
|
.in_set(MySet::BeforeRound),
|
|
|
|
|
// This `Round` system will run after the `BeforeRound` systems thanks to the chained set configuration
|
|
|
|
|
score_system.in_set(MySet::Round),
|
|
|
|
|
// These `AfterRound` systems will run after the `Round` systems thanks to the chained set configuration
|
|
|
|
|
(
|
|
|
|
|
score_check_system,
|
|
|
|
|
// In addition to chain(), you can also use `before(system)` and `after(system)`. This also works
|
|
|
|
|
// with sets!
|
|
|
|
|
game_over_system.after(score_check_system),
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
.in_set(MySet::AfterRound),
|
|
|
|
|
),
|
2021-02-16 19:18:08 +00:00
|
|
|
)
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
// This call to run() starts the app we just built!
|
2020-05-03 01:20:42 +00:00
|
|
|
.run();
|
2020-05-03 07:21:32 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|