2023-04-23 19:28:36 +02:00
|
|
|
//! Create and play an animation defined by code that operates on the [`Transform`] component.
|
2022-05-16 13:53:20 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-08-30 19:52:11 +00:00
|
|
|
use std::f32::consts::PI;
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
use bevy::prelude::*;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn main() {
|
|
|
|
|
App::new()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
|
|
|
|
|
.insert_resource(AmbientLight {
|
|
|
|
|
color: Color::WHITE,
|
|
|
|
|
brightness: 1.0,
|
|
|
|
|
})
|
2023-03-17 18:45:34 -07:00
|
|
|
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
.run();
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn setup(
|
|
|
|
|
mut commands: Commands,
|
|
|
|
|
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut animations: ResMut<Assets<AnimationClip>>,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
// Camera
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn(Camera3dBundle {
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
transform: Transform::from_xyz(-2.0, 2.5, 5.0).looking_at(Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::Y),
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// The animation API uses the `Name` component to target entities
|
|
|
|
|
let planet = Name::new("planet");
|
|
|
|
|
let orbit_controller = Name::new("orbit_controller");
|
|
|
|
|
let satellite = Name::new("satellite");
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Creating the animation
|
|
|
|
|
let mut animation = AnimationClip::default();
|
|
|
|
|
// A curve can modify a single part of a transform, here the translation
|
|
|
|
|
animation.add_curve_to_path(
|
|
|
|
|
EntityPath {
|
|
|
|
|
parts: vec![planet.clone()],
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
VariableCurve {
|
|
|
|
|
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
|
|
|
|
|
keyframes: Keyframes::Translation(vec![
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::new(1.0, 0.0, 1.0),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::new(-1.0, 0.0, 1.0),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::new(1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
|
|
|
|
|
// in case seamless looping is wanted, the last keyframe should
|
|
|
|
|
// be the same as the first one
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::new(1.0, 0.0, 1.0),
|
|
|
|
|
]),
|

support all types of animation interpolation from gltf (#10755)
# Objective
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
## Solution
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
Tested with
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/InterpolationTest
expected:
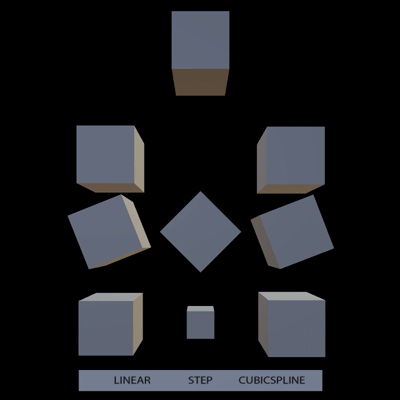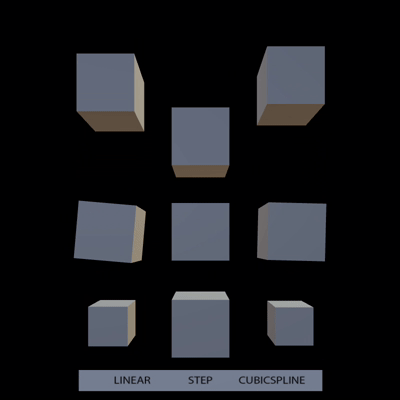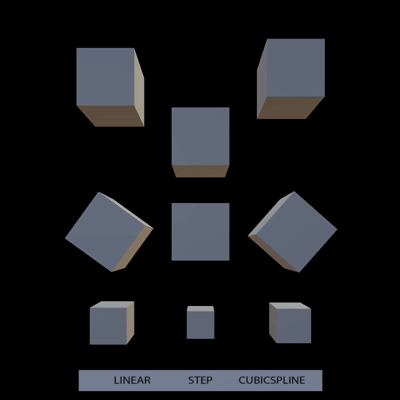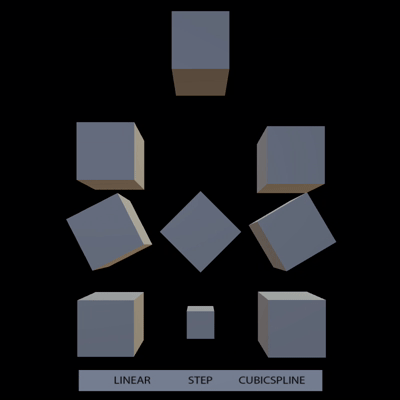
result:

---
## Migration Guide
When manually specifying an animation `VariableCurve`, the interpolation
type must be specified:
- Bevy 0.12
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
},
```
- Bevy 0.13
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
},
```
2023-12-31 19:01:50 +01:00
|
|
|
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
// Or it can modify the rotation of the transform.
|
2023-03-01 10:20:56 +00:00
|
|
|
// To find the entity to modify, the hierarchy will be traversed looking for
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
// an entity with the right name at each level
|
|
|
|
|
animation.add_curve_to_path(
|
|
|
|
|
EntityPath {
|
|
|
|
|
parts: vec![planet.clone(), orbit_controller.clone()],
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
VariableCurve {
|
|
|
|
|
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
|
|
|
|
|
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
|
2022-08-30 19:52:11 +00:00
|
|
|
Quat::IDENTITY,
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::IDENTITY,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
]),
|

support all types of animation interpolation from gltf (#10755)
# Objective
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
## Solution
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
Tested with
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/InterpolationTest
expected:

result:

---
## Migration Guide
When manually specifying an animation `VariableCurve`, the interpolation
type must be specified:
- Bevy 0.12
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
},
```
- Bevy 0.13
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
},
```
2023-12-31 19:01:50 +01:00
|
|
|
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
// If a curve in an animation is shorter than the other, it will not repeat
|
|
|
|
|
// until all other curves are finished. In that case, another animation should
|
|
|
|
|
// be created for each part that would have a different duration / period
|
|
|
|
|
animation.add_curve_to_path(
|
|
|
|
|
EntityPath {
|
|
|
|
|
parts: vec![planet.clone(), orbit_controller.clone(), satellite.clone()],
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
VariableCurve {
|
|
|
|
|
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0],
|
|
|
|
|
keyframes: Keyframes::Scale(vec![
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(0.8),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(1.2),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(0.8),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(1.2),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(0.8),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(1.2),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(0.8),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(1.2),
|
|
|
|
|
Vec3::splat(0.8),
|
|
|
|
|
]),
|

support all types of animation interpolation from gltf (#10755)
# Objective
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
## Solution
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
Tested with
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/InterpolationTest
expected:

result:

---
## Migration Guide
When manually specifying an animation `VariableCurve`, the interpolation
type must be specified:
- Bevy 0.12
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
},
```
- Bevy 0.13
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
},
```
2023-12-31 19:01:50 +01:00
|
|
|
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
// There can be more than one curve targeting the same entity path
|
|
|
|
|
animation.add_curve_to_path(
|
|
|
|
|
EntityPath {
|
|
|
|
|
parts: vec![planet.clone(), orbit_controller.clone(), satellite.clone()],
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
VariableCurve {
|
|
|
|
|
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
|
|
|
|
|
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
|
2022-08-30 19:52:11 +00:00
|
|
|
Quat::IDENTITY,
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
|
|
|
|
|
Quat::IDENTITY,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
]),
|

support all types of animation interpolation from gltf (#10755)
# Objective
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
## Solution
- Support step and cubic spline interpolation from gltf
Tested with
https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/InterpolationTest
expected:

result:

---
## Migration Guide
When manually specifying an animation `VariableCurve`, the interpolation
type must be specified:
- Bevy 0.12
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
},
```
- Bevy 0.13
```rust
VariableCurve {
keyframe_timestamps: vec![0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0],
keyframes: Keyframes::Rotation(vec![
Quat::IDENTITY,
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 2.),
Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, PI / 2. * 3.),
Quat::IDENTITY,
]),
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
},
```
2023-12-31 19:01:50 +01:00
|
|
|
interpolation: Interpolation::Linear,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Create the animation player, and set it to repeat
|
|
|
|
|
let mut player = AnimationPlayer::default();
|
|
|
|
|
player.play(animations.add(animation)).repeat();
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Create the scene that will be animated
|
|
|
|
|
// First entity is the planet
|
|
|
|
|
commands
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
.spawn((
|
2022-09-21 21:47:53 +00:00
|
|
|
PbrBundle {
|
2022-11-14 22:34:27 +00:00
|
|
|
mesh: meshes.add(Mesh::try_from(shape::Icosphere::default()).unwrap()),
|

Use `impl Into<A>` for `Assets::add` (#10878)
# Motivation
When spawning entities into a scene, it is very common to create assets
like meshes and materials and to add them via asset handles. A common
setup might look like this:
```rust
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
) {
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial::from(Color::RED)),
..default()
});
}
```
Let's take a closer look at the part that adds the assets using `add`.
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial::from(Color::RED)),
```
Here, "mesh" and "material" are both repeated three times. It's very
explicit, but I find it to be a bit verbose. In addition to being more
code to read and write, the extra characters can sometimes also lead to
the code being formatted to span multiple lines even though the core
task, adding e.g. a primitive mesh, is extremely simple.
A way to address this is by using `.into()`:
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }.into()),
material: materials.add(Color::RED.into()),
```
This is fine, but from the names and the type of `meshes`, we already
know what the type should be. It's very clear that `Cube` should be
turned into a `Mesh` because of the context it's used in. `.into()` is
just seven characters, but it's so common that it quickly adds up and
gets annoying.
It would be nice if you could skip all of the conversion and let Bevy
handle it for you:
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
material: materials.add(Color::RED),
```
# Objective
Make adding assets more ergonomic by making `Assets::add` take an `impl
Into<A>` instead of `A`.
## Solution
`Assets::add` now takes an `impl Into<A>` instead of `A`, so e.g. this
works:
```rust
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
material: materials.add(Color::RED),
..default()
});
```
I also changed all examples to use this API, which increases consistency
as well because `Mesh::from` and `into` were being used arbitrarily even
in the same file. This also gets rid of some lines of code because
formatting is nicer.
---
## Changelog
- `Assets::add` now takes an `impl Into<A>` instead of `A`
- Examples don't use `T::from(K)` or `K.into()` when adding assets
## Migration Guide
Some `into` calls that worked previously might now be broken because of
the new trait bounds. You need to either remove `into` or perform the
conversion explicitly with `from`:
```rust
// Doesn't compile
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }.into()),
// These compile
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
```
## Concerns
I believe the primary concerns might be:
1. Is this too implicit?
2. Does this increase codegen bloat?
Previously, the two APIs were using `into` or `from`, and now it's
"nothing" or `from`. You could argue that `into` is slightly more
explicit than "nothing" in cases like the earlier examples where a
`Color` gets converted to e.g. a `StandardMaterial`, but I personally
don't think `into` adds much value even in this case, and you could
still see the actual type from the asset type.
As for codegen bloat, I doubt it adds that much, but I'm not very
familiar with the details of codegen. I personally value the user-facing
code reduction and ergonomics improvements that these changes would
provide, but it might be worth checking the other effects in more
detail.
Another slight concern is migration pain; apps might have a ton of
`into` calls that would need to be removed, and it did take me a while
to do so for Bevy itself (maybe around 20-40 minutes). However, I think
the fact that there *are* so many `into` calls just highlights that the
API could be made nicer, and I'd gladly migrate my own projects for it.
2024-01-09 00:14:43 +02:00
|
|
|
material: materials.add(Color::rgb(0.8, 0.7, 0.6)),
|
2022-09-21 21:47:53 +00:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
// Add the Name component, and the animation player
|
|
|
|
|
planet,
|
|
|
|
|
player,
|
|
|
|
|
))
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
.with_children(|p| {
|
|
|
|
|
// This entity is just used for animation, but doesn't display anything
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
p.spawn((
|
2022-12-25 00:39:29 +00:00
|
|
|
SpatialBundle::INHERITED_IDENTITY,
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
// Add the Name component
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
orbit_controller,
|
|
|
|
|
))
|
|
|
|
|
.with_children(|p| {
|
|
|
|
|
// The satellite, placed at a distance of the planet
|
|
|
|
|
p.spawn((
|
|
|
|
|
PbrBundle {
|
|
|
|
|
transform: Transform::from_xyz(1.5, 0.0, 0.0),
|

Use `impl Into<A>` for `Assets::add` (#10878)
# Motivation
When spawning entities into a scene, it is very common to create assets
like meshes and materials and to add them via asset handles. A common
setup might look like this:
```rust
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
) {
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial::from(Color::RED)),
..default()
});
}
```
Let's take a closer look at the part that adds the assets using `add`.
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial::from(Color::RED)),
```
Here, "mesh" and "material" are both repeated three times. It's very
explicit, but I find it to be a bit verbose. In addition to being more
code to read and write, the extra characters can sometimes also lead to
the code being formatted to span multiple lines even though the core
task, adding e.g. a primitive mesh, is extremely simple.
A way to address this is by using `.into()`:
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }.into()),
material: materials.add(Color::RED.into()),
```
This is fine, but from the names and the type of `meshes`, we already
know what the type should be. It's very clear that `Cube` should be
turned into a `Mesh` because of the context it's used in. `.into()` is
just seven characters, but it's so common that it quickly adds up and
gets annoying.
It would be nice if you could skip all of the conversion and let Bevy
handle it for you:
```rust
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
material: materials.add(Color::RED),
```
# Objective
Make adding assets more ergonomic by making `Assets::add` take an `impl
Into<A>` instead of `A`.
## Solution
`Assets::add` now takes an `impl Into<A>` instead of `A`, so e.g. this
works:
```rust
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
material: materials.add(Color::RED),
..default()
});
```
I also changed all examples to use this API, which increases consistency
as well because `Mesh::from` and `into` were being used arbitrarily even
in the same file. This also gets rid of some lines of code because
formatting is nicer.
---
## Changelog
- `Assets::add` now takes an `impl Into<A>` instead of `A`
- Examples don't use `T::from(K)` or `K.into()` when adding assets
## Migration Guide
Some `into` calls that worked previously might now be broken because of
the new trait bounds. You need to either remove `into` or perform the
conversion explicitly with `from`:
```rust
// Doesn't compile
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }.into()),
// These compile
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 }),
let mesh_handle = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })),
```
## Concerns
I believe the primary concerns might be:
1. Is this too implicit?
2. Does this increase codegen bloat?
Previously, the two APIs were using `into` or `from`, and now it's
"nothing" or `from`. You could argue that `into` is slightly more
explicit than "nothing" in cases like the earlier examples where a
`Color` gets converted to e.g. a `StandardMaterial`, but I personally
don't think `into` adds much value even in this case, and you could
still see the actual type from the asset type.
As for codegen bloat, I doubt it adds that much, but I'm not very
familiar with the details of codegen. I personally value the user-facing
code reduction and ergonomics improvements that these changes would
provide, but it might be worth checking the other effects in more
detail.
Another slight concern is migration pain; apps might have a ton of
`into` calls that would need to be removed, and it did take me a while
to do so for Bevy itself (maybe around 20-40 minutes). However, I think
the fact that there *are* so many `into` calls just highlights that the
API could be made nicer, and I'd gladly migrate my own projects for it.
2024-01-09 00:14:43 +02:00
|
|
|
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube { size: 0.5 }),
|
|
|
|
|
material: materials.add(Color::rgb(0.3, 0.9, 0.3)),
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
// Add the Name component
|
|
|
|
|
satellite,
|
|
|
|
|
));
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|