14 KiB
| description |
|---|
| source: https://medium.com/@nimmughal799/recon-like-a-boss-9a0065648d10 |
🔎 Recon Like a Boss
Reconnaissance, or recon for short, is the process of gathering information about a target with the goal of identifying vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors.
Effective recon is an essential part of any successful web security assessment or penetration testing engagement. However, many beginners find the process daunting and overwhelming, with a seemingly endless array of tools and techniques to choose from.
In this article, we’ll take a step-by-step approach to web recon, starting with the basics and building up to more advanced techniques.
Agenda
- Increase Your Attack Area
• Determine Technologies used by Website.
• Amazon Web Service (AWS) Recon & Hacking
• Github Recon
• Content Discovery
Increase Your Attack Area

Recon- Go Back in Time
Wayback Machine to view old files like robots.txt
and URLs
Tools are out to automate this
waybackurls.py
Download:
https://gist.github.com/mhmdia/adf6bff70142e5091792841d4b372050
waybackrobots.py
Download:
https://gist.github.com/mhmdiaa/2742c5e147d49a804b408bfed3d32d07
Sub-domains Discovery
- Brute force on main domain
- Some scripts to automate this task
– Knockpy:-
https://github.com/guelfoweb/knock
Usage: ./knockpy target.com

– Sublist3r:-
https://github.com/aboul3la/Sublist3r
Usage: python sublist3r.py -d target.com
- Find sub-domains with specific open ports
Usage: python sublist3r.py -d target.com -p 80,443

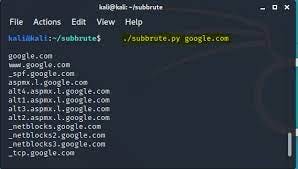
– SubBrute
https://github.com/TheRook/subbrute
Usage: ./subbrute.py google.com
- You can give list of domains like this
Usage: ./subbrute.py -t list.txt
Google Dork
site:target.com –site www.target.com
Online Resource:
– https://dnsdumpster.com/
– https://searchdns.netcraft.com/
– https://www.virustotal.com (Go to search and
type target.com)
– https://crt.sh/?q=%25paypal.com (Use “%target.com”. )
Don’t Stop Here!
Find Sub-domains of Sub-domain
- Some website have 5th and 6th level sub-domain
Tool: altdns (https://github.com/infosec-au/altdns)
Input : sub-domain list
Usage: ./altdns.py -i subdomains.txt -o
data_output -w words.txt -r -s output.txt
Tool: SubBrute
Usage:
./subbrute.py target.com > sudomains.txt
Then
./subbrute.py –t subdomains.txt
Now We Have
WaybackURls
+
Subdomains
+
Subdomains of Subdomains
Sub-domain Validation
Tool: EyeWitness (https://github.com/ChrisTruncer/EyeWitness)
- Provide list of sub-domains and it will give you
report with screenshots of sub-domain
Usage: ./EyeWitness.py -f subdomains.txt
Tool: Grab Them All (Mozilla addon)
Other sites on the same domain

Now We Have
WaybackURls
+
Subdomains
+
Subdomains of Subdomains
+
Other Sites on the same Domain
Target IP Range
Url: https://whois.arin.net
• Search by Target IP
- Yahoo! owns a massive block of IP addresses
• From 98.136.0.0–98.139.255.255
• Which is 260,000 unique IP addresses
Got Huge IP Range

Real Case Study
Patrik Fehrenbach (@ITSecurityguard)
Wrote a Bash script to download phpinfo.php
file (if found) from Yahoo! IP range
(98.136.0.0–98.139.255.255)
Bash Script
#!/bin/bash
for ipa in 98.13{6..9}.{0..255}.{0..255}; do
wget -t 1 -T 5 http://${ipa}/phpinfo.php; done&
Takeaways
• When hacking, consider a company’s entire
infrastructure. I know that Patrik has employed
similar techniques to find some more.
(Eg. Many people keep Backup.rar)
• Additionally, you’ll notice there was 260,000
potential addresses here, which would have been
impossible to scan manually.
• When performing this type of testing,
automation is hugely important.
Find New Endpoints from JS Files
- Tools used
1- Burp Suite: Proxy
2- Zscanner: A tool designed to scrape a list of
URLs. This tool will also scrape .js urls found
on each page
3- JS-Scan: A tool designed to scrape a list of .js
files and extract urls
How to use these tools together??

1- Burpsuite
- Run Spider tool on your target in Burp Suite
• Once the spider has finished right click on the host
and click “Copy Urls in this host“

2- Zscanner
- Once copied, paste them into urls.txt
• Put urls.txt file in the root of Zscanner
Eg. c/xampp/htdocs/zscanner/urls.txt
• Now open zscanner in browser

- Click on “Begin Scanner”
• 4 files are outputted in the /outputs/ folder:
JS-output.txt, GET-output.txt, POSTHost-
output.txt, POSTData-output.txt
• Copy JS-output.txt file and put it in the root of
JS-Scan root folder
Eg. c/xampp/js-scan/JS-output.txt
3- JS-Scan
- Open JS-Scan in browser

- Click on Run Scanner and you will see
something similar to this. That’s it.

Takeaways
• Endpoints extracted from JS files are more
vulnerable then Endpoints defined in
WebPages.
• Automated Scanners generally don’t scan
Endpoints defined in JS files.
• Developers & Testers don’t care about them.
Technologies Used by Web
• Wappalyzer (Mozilla Addon)

Amazon Web Services (AWS or S3 Buckets)
- AWS Simple Storage Service (often shortened
to S3) is used by companies that don’t want to
build and maintain their own storage
repositories
• By using Amazon Simple Storage Service, they
can store objects and files on a virtual server
instead of on physical racks - After the user has created their bucket, they
can start storing their source code,
certificates, passwords, content, databases
and other data.
What if target is vulnerable?
- You can get full access to S3 bucket
• You can download, upload and overwrite files
How to find S3 Buckets?
- Google Dork
site: amazonaws.com inurl: yahoo
• Tool: S3 bucket finder
(Download: https://digi.ninja/projects/bucket_finder.php)

- Burp Suite can also Help

AWS HACKING
- Install awscli in kali

- Interact with Bucket

- Find World Writable Directory.

Now We Have
WaybackURls
+
Subdomains
+
Subdomains of Subdomains
+
Other Sites on the same Domain
+
IP Range
+
New Endpoints From JS Files
+
S3 Buckets
Github Recon
What you can find on Github?
• FTP Credentials
• Secret Keys [API_key, Aws_secret key, etc.]
• Internal credentials [Employee credentials]
• API Endpoints
• Domain Patterns
- Go to github and search
Eg.
- “target.com” “dev”
- “dev.target.com”
- “target.com” API_key
- “target.com” password
- “api.target.com”

- Google can also help
Dork:
site: “github.com” + “Target” + password
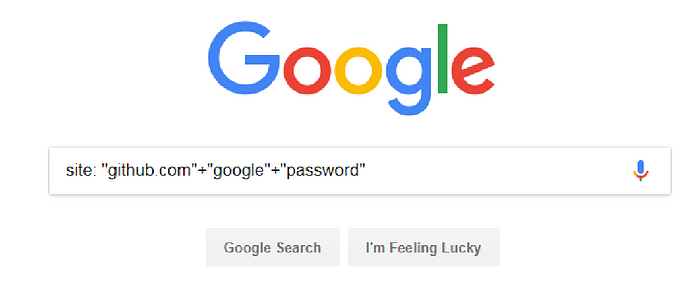
Tools are out to automate this
• Gitrob
• Git-all-secrets
• truffleHog
• Git-secrets
• Repo-supervisor
• Do it manually [Best way]
– All tools are available on github
Tool- truffleHog
- Usage:
truffleHog — regex — entropy=False https://github.com/dxa4481/truffleHog.git

Content Discovery
• Google is your friend
• Use Google Dork to find:-
- File Extensions
- Parameters
- Login Page
- Sometimes Directory Structure
- Important Stuff
• I often use Google Dork to find files with
specific extension which also reveal
technology used by Target.
- Google Dork:
-site:target.com filetype:php
- site:target.com filetype:aspx
- site:target.com filetype:swf (Shockwave Flash)
- site:target.com filetype:wsdl
Find Parameter
• Google Dork:
- site: target.com inurl:.php?id=
- site: target.com inurl:.php?user=
- site: target.com inurl:.php?book=
Find Login Page
• Google Dork
- site: target.com inurl:login.php
- site: target.com intext: “login”
- site: target.com inurl:portal.php
- site: target.com inurl:register.php
(Note: if site has register page, there are chances
that site also have login page)
Find Directory Structure
• Google Dork:
-site: target.com intext: “index of /”

Find important Stuff
• Google Dork:
-site: target.com filetype:txt
- site: target.com inurl:.php.txt
-site: target.com ext:txt
In most cases you will find robot.txt
But sometimes you will find really juicy stuff
Tools:
– GoBuster [https://github.com/OJ/gobuster]
Use:
gobuster –w wordlist.txt –u http://trgt.com
– Dirbuster

Thank you for taking the time to read my article . I hope that the information and insights shared here have been valuable and practical for you to apply in your own recon efforts.
If you found this article helpful, please consider following me for more content related to security, hacking, and Bugbounty.
