6698: Attach macro expansion errors to the right file r=jonas-schievink a=jonas-schievink
Previously it attached them to the result of the macro expansion (or, if no result was produced, to the file containing the invocation). Always use the file containing the invocation.
This doesn't seem to have any observable difference, but seems better in theory.
bors r+
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonasschievink@gmail.com>
6435: Test Fixture ExplicitRoot + ModuleResolutionRelativePathOutsideRoot. r=matklad a=rickvanprim
Updates `module_resolution_relative_path_outside_root` test to check valid paths outside of the root, by moving the root to a subpath so that paths outside of it are possible. If this would be more appropriate as a new test, or if the original check for an invalid path should be left, I'm happy to update.
Co-authored-by: James Leitch <rickvanprim@gmail.com>
It's very useful when `pub` is equivalent to "this is crate's public
API", let's enforce this!
Ideally, we should enforce it for local `cargo test`, and only during
CI, but that needs https://github.com/rust-lang/cargo/issues/5034.
6324: Improve #[cfg] diagnostics r=jonas-schievink a=jonas-schievink
Unfortunately I ran into https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/4058 while testing this on https://github.com/nrf-rs/nrf-hal/, so I didn't see much of it in action yet, but it does seem to work.
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonas.schievink@ferrous-systems.com>
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonasschievink@gmail.com>
6307: Add whitelist of safe intrinsics r=frazar a=frazar
This PR should fix#5996, where intrinsic operations where all marked as unsafe.
I'm rather new to this codebase, so I might be doing something *very* wrong. Please forgive me!
In particular, I'm not sure how to "check that we are in extern `rust-intrinsics`" as mentioned [in this comment](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/5996#issuecomment-709234802).
Co-authored-by: Francesco Zardi <frazar@users.noreply.github.com>
Declaration names sounds like a name of declaration -- something you
can use for analysis. It empathically isn't, and is just a label
displayed in various UI. It's important not to confuse the two, least
we accidentally mix semantics with UI (I believe, there's already a
case of this in the FamousDefs at least).
6130: Items case quick fix (snake_case / UPPER_SNAKE_CASE / CamelCase) r=matklad a=popzxc
Resolves#4598.
After a third try, it finally works. Boy, it appeared tougher than it seemed.
Initially I thought like "Ha, `rustc` already tells us where idents are named incorrectly. It shouldn't be that hard, should it?".
Well, the problems with the information provided by `rustc` appeared shortly:
- `rustc` warnings are `flycheck` warnings, which are slightly aside from our diagnostics with fixes.
When we map flycheck diagnostic to LSP, we can convert it into a fix, but only if it's marked as `Applicability::MachineApplicable`.
Name case fix is marked `Applicability::MaybeIncorrect`, and for a reason: it only suggest to rename symbol under cursor, without tracking any references.
- Warning spawned by `rustc` are identified by string labels rather than enum. It means that if one day the diagnostic will be renamed in `rustc`, `rust-analyzer` code will still compile, but won't find the required diagnostic by name anymore. If by chance this will happen when some unlucky guy will decide to create their first pull request, they'll be confused by suddenly failing tests (likely) not related to their changes.
- Even if we'll try to build fixes atop of `rustc` warnings, we'll have to do it in the `rust_analyzer::diagnostics::to_proto` module, which is far less
convenient for that matter than `ide` crate.
That's why I decided that it's worth a separate `rust-analyzer` diagnostic, which will implement `DiagnosticWithFix` trait.
After that, I discovered that currently `hir_ty::diagnostics` only check `DefWithBody` types, like function bodies. I had to add support for diagnostics
which look at any `ModuleDef`.
And of course, since I'd added a lot of new functionality, it required extensive testing.
That explains why the diff is so big for a (looking) relatively small feature.
I hope that this PR doesn't only add a small feature, but also creates a base for building another features.
## Example:
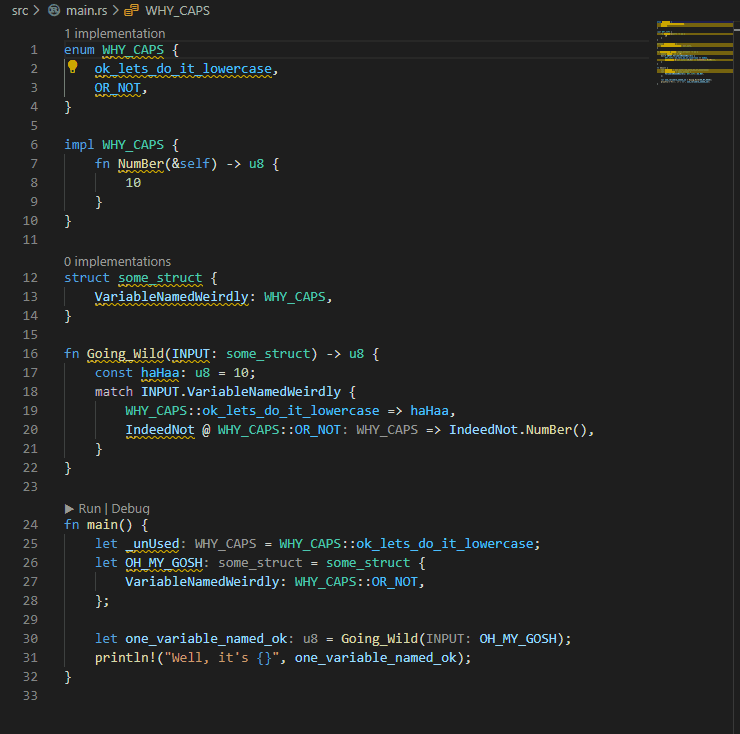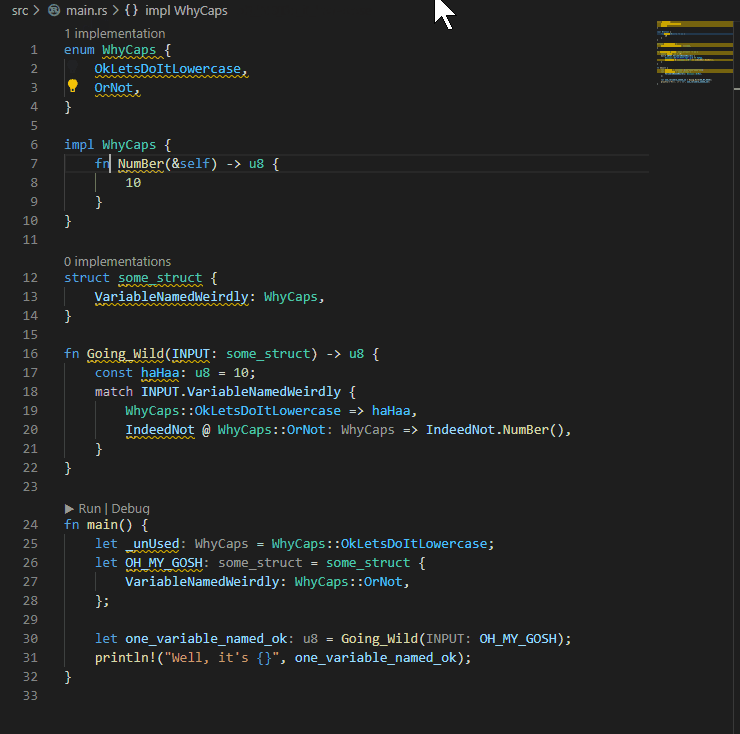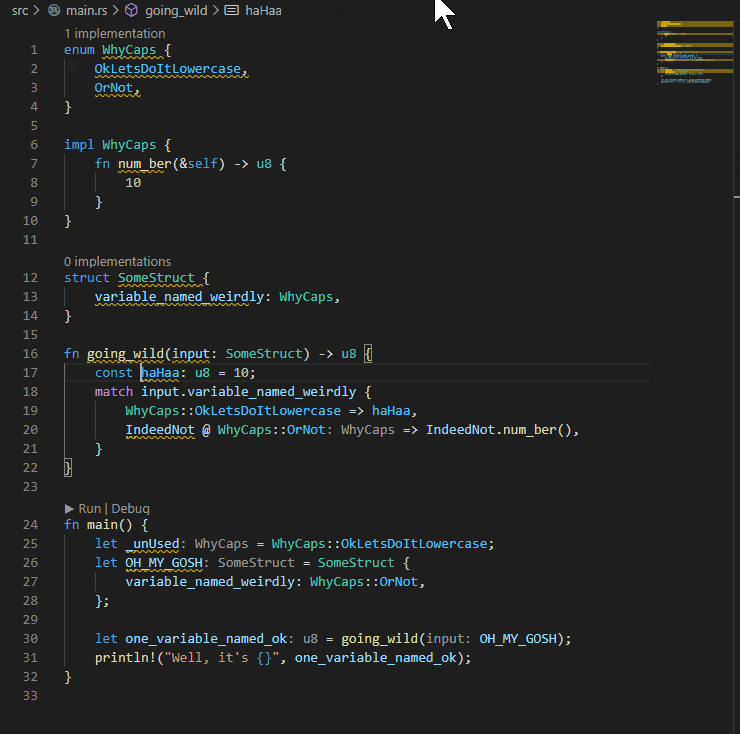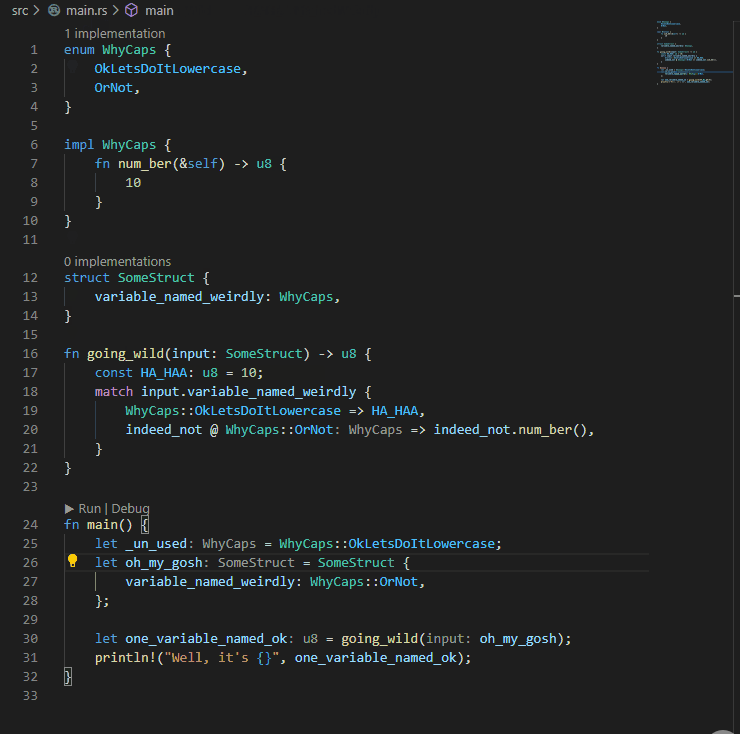
P.S. My eyes were bleeding when I had to write the code for the example...
6135: when generating new function, focus on return type instead of body r=matklad a=bnjjj
I made a little change when we use the assist to generate a new function, instead of focusing on the function body, it will focus on return type
Co-authored-by: Igor Aleksanov <popzxc@yandex.ru>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Coenen <5719034+bnjjj@users.noreply.github.com>
6199: Fix `mut self` not emitting mutable binding on `self` use r=matklad a=Veykril
Prior to this, when `self` in a function is taken by value and bound mutably, its use inside of the method body won't be marked `mutably`.
Fixes#5461
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
5917: Add a command to open docs for the symbol under the cursor r=matklad a=zacps
#### Todo
- [ ] Decide if there should be a default keybind or context menu entry
- [x] Figure out how to get the documentation path for methods and other non-top-level defs
- [x] Design the protocol extension. In future we'll probably want parameters for local/remote documentation URLs, so that should maybe be done in this PR?
- [x] Code organisation
- [x] Tests
Co-authored-by: Zac Pullar-Strecker <zacmps@gmail.com>
Previously, "find all references" on a variant field wouldn't find any
references outside the defining module. This is because variant fields
were incorrectly assumed to be private, like struct fields without
explicit visibility, but they actually inherit the enum's visibility.
Currently a method only has defaultness if it is a provided trait
method, but this will change when specialisation is available and may
need to become a concept known to hir.
I opted to go for a 'fewest changes' approach given specialisation is
still under development.
6124: Better normalized crate name usage r=jonas-schievink a=SomeoneToIgnore
Closes https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/5343
Closes https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/5932
Uses normalized name for code snippets (to be able to test the fix), hover messages and documentation rewrite links (are there any tests for those?).
Also renamed the field to better resemble the semantics.
Co-authored-by: Kirill Bulatov <mail4score@gmail.com>
6139: Make find_path_prefixed configurable r=matklad a=Veykril
This makes `find_path_prefixed` more configurable allowing one to choose whether it always returns absolute paths, self-prefixed paths or to ignore local imports when building the path.
The config names are just thrown in here, taking better names if they exist :)
This should fix#6131 as well?
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
6019: Remove make::path_from_text r=matklad a=Veykril
This removes the `make::path_from_text` function, which according to a note should've been private. I removed it since it didn't really serve a purpose as it was simply wrapping `make::ast_from_text`.
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
6033: Make name resolution resolve proc macros instead of relying purely on the build system r=matklad a=jonas-schievink
This makes name resolution look at proc-macro declaration attributes like `#[proc_macro_derive]` and defines the right proc macro in the macro namespace, fixing unresolved custom derives like `thiserror::Error` (which can cause false positives, now that we emit diagnostics for unresolved imports).
This works even when proc-macro support is turned off, in which case we fall back to a dummy expander that always returns an error. IMO this is the right way to handle at least the name resolution part of proc. macros, while the *expansion* itself should rely on the build system to build and provide the macro DLL. It does mean that they may go out of sync, but we can provide diagnostics if that happens (something like "could not find macro X in crate Y – ensure that all files of crate Y are saved").
I think it is valuable to be able to reason about proc macros even when we can't expand them, since proc macro expansion can break between Rust releases or users might not want to turn it on for performance reasons. It allows us to provide better diagnostics on any proc macro invocation we're not expanding (like a weak warning that informs the user that proc macro support is turned off, or that it has been disabled because the server crashed).
Fixes https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/5763
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonas.schievink@ferrous-systems.com>
6085: Mark unresolved imports diagnostic as experimental r=jonas-schievink a=jonas-schievink
It causes a lot of false positives for people. We collected all of the known ones during the last week.
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonas.schievink@ferrous-systems.com>
6016: Emit diagnostics for unresolved imports and extern crates r=jonas-schievink a=jonas-schievink
AFAIK, we don't have any major bugs in name resolution that would cause a lot of false positives here (except procedural attribute macro support and some rare issues around `#[path]` on module files), so these are *not* marked as experimental diagnostics right now.
I noticed that diagnostics in a file sometimes don't get displayed after opening, but require some edit to be performed. This seems like a preexisting issue though.
Co-authored-by: Jonas Schievink <jonas.schievink@ferrous-systems.com>
5971: Implement async blocks r=flodiebold a=oxalica
Fix#4018
@flodiebold already gave a generic guide in the issue. Here's some concern about implementation detail:
- Chalk doesn't support generator type yet.
- Adding generator type as a brand new type (ctor) can be complex and need to *re-introduced* builtin impls. (Like how we implement closures before native closure support of chalk, which is already removed in #5401 )
- The output type of async block should be known after type inference of the whole body.
- We cannot directly get the type from source like return-positon-impl-trait. But we still need to provide trait bounds when chalk asking for `opaque_ty_data`.
- During the inference, the output type of async block can be temporary unknown and participate the later inference.
`let a = async { None }; let _: i32 = a.await.unwrap();`
So in this PR, the type of async blocks is inferred as an opaque type parameterized by the `Future::Output` type it should be, like what we do with closure type.
And it really works now.
Well, I still have some questions:
- The bounds `AsyncBlockImplType<T>: Future<Output = T>` is currently generated in `opaque_ty_data`. I'm not sure if we should put this code here.
- Type of async block is now rendered as `impl Future<Output = OutputType>`. Do we need to special display to hint that it's a async block? Note that closure type has its special format, instead of `impl Fn(..) -> ..` or function type.
Co-authored-by: oxalica <oxalicc@pm.me>