4329: Look for `cargo`, `rustc`, and `rustup` in standard installation path r=matklad a=cdisselkoen
Discussed in #3118. This is approximately a 90% fix for the issue described there.
This PR creates a new crate `ra_env` with a function `get_path_for_executable()`; see docs there. `get_path_for_executable()` improves and generalizes the function `cargo_binary()` which was previously duplicated in the `ra_project_model` and `ra_flycheck` crates. (Both of those crates now depend on the new `ra_env` crate.) The new function checks (e.g.) `$CARGO` and `$PATH`, but also falls back on `~/.cargo/bin` manually before erroring out. This should allow most users to not have to worry about setting the `$CARGO` or `$PATH` variables for VSCode, which can be difficult e.g. on macOS as discussed in #3118.
I've attempted to replace all calls to `cargo`, `rustc`, and `rustup` in rust-analyzer with appropriate invocations of `get_path_for_executable()`; I don't think I've missed any in Rust code, but there is at least one invocation in TypeScript code which I haven't fixed. (I'm not sure whether it's affected by the same problem or not.) a4778ddb7a/editors/code/src/cargo.ts (L79)
I'm sure this PR could be improved a bunch, so I'm happy to take feedback/suggestions on how to solve this problem better, or just bikeshedding variable/function/crate names etc.
cc @Veetaha
Fixes#3118.
Co-authored-by: Craig Disselkoen <craigdissel@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
3998: Make add_function generate functions in other modules via qualified path r=matklad a=TimoFreiberg
Additional feature for #3639
- [x] Add tests for paths with more segments
- [x] Make generating the function in another file work
- [x] Add `pub` or `pub(crate)` to the generated function if it's generated in a different module
- [x] Make the assist jump to the edited file
- [x] Enable file support in the `check_assist` helper
4006: Syntax highlighting for format strings r=matklad a=ltentrup
I have an implementation for syntax highlighting for format string modifiers `{}`.
The first commit refactors the changes in #3826 into a separate struct.
The second commit implements the highlighting: first we check in a macro call whether the macro is a format macro from `std`. In this case, we remember the format string node. If we encounter this node during syntax highlighting, we check for the format modifiers `{}` using regular expressions.
There are a few places which I am not quite sure:
- Is the way I extract the macro names correct?
- Is the `HighlightTag::Attribute` suitable for highlighting the `{}`?
Let me know what you think, any feedback is welcome!
Co-authored-by: Timo Freiberg <timo.freiberg@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Leander Tentrup <leander.tentrup@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Leander Tentrup <ltentrup@users.noreply.github.com>
Move the task provider anonymous class into a real class, as this seems
to be how Microsoft do this in their documentation.
resolveTask is now implemented, which is used by VSCode to determine how
to execute tasks that the user has defined in tasks.json.
This is covered under vscode's "editor.semanticHighlighting.enabled"
setting plus the user has to have a theme that has opted into highlighting.
Bumps required vscode stable to 1.44
3817: vscode: highlight syntax tree ro editor r=matklad a=Veetaha
Small textmate grammar declaration to make rust-analyzer syntax tree more easily inspectable:
Btw, if we change the file extension of our `ra_syntax/test_data/**` files to `.rast` they should be highlighted in vscode too.
The colors of the tokens are actually going to be color-theme dependent, or you can customize them via:
```jsonc
{
"editor.tokenColorCustomizations": {
"textMateRules": [ { "scope": "name", "settings": { /* */ } } ]
}
}
```
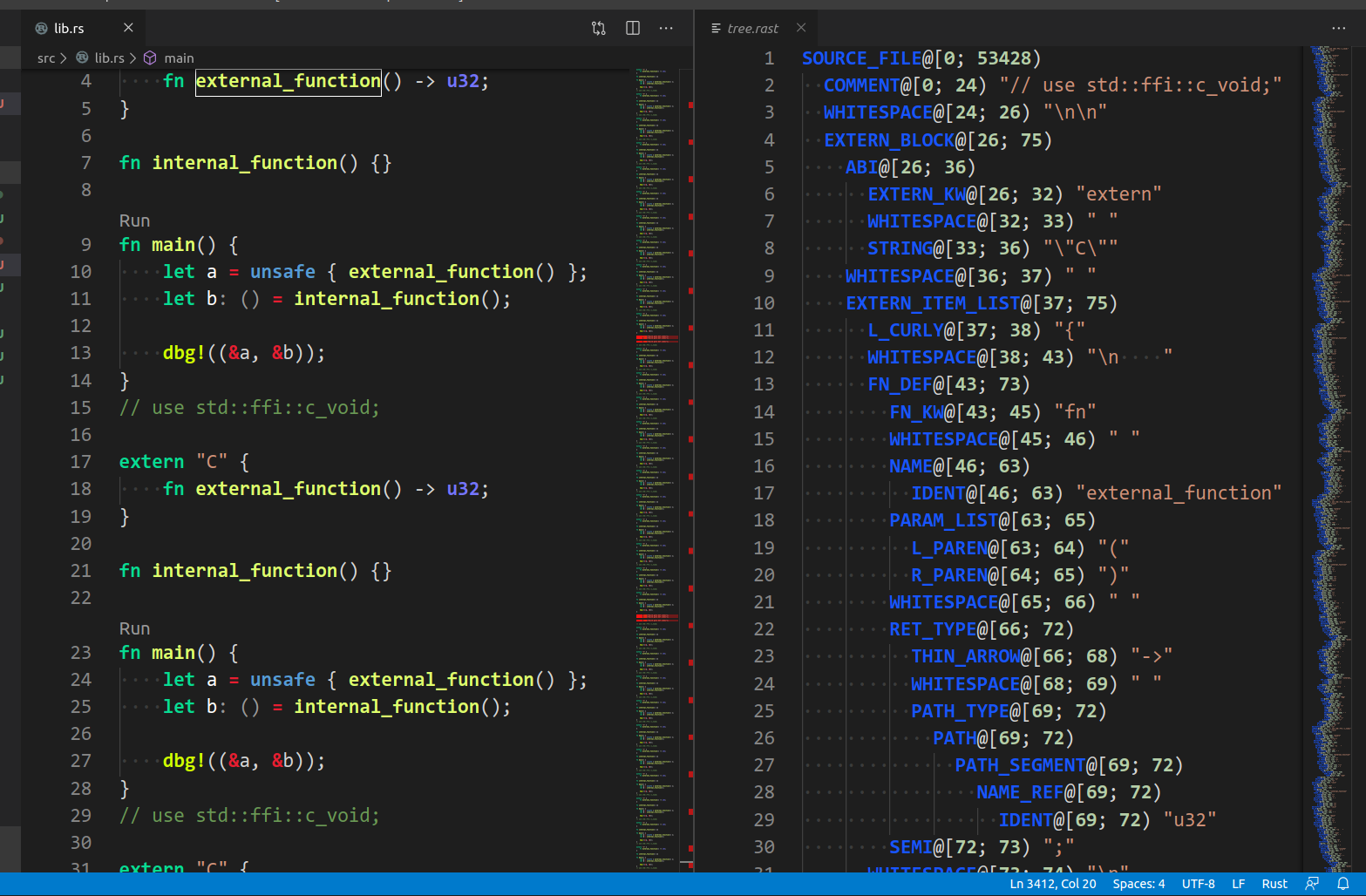
Related: #3682
Co-authored-by: veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
3780: Simplify r=matklad a=Veetaha
I absolutely love tha fact that removing `.clone()` simplifies the code comparing to other languages where it's actually the contrary (ahem ~~`std::move()`~~)
3787: vscode: add syntax tree inspection hovers and highlights r=matklad a=Veetaha
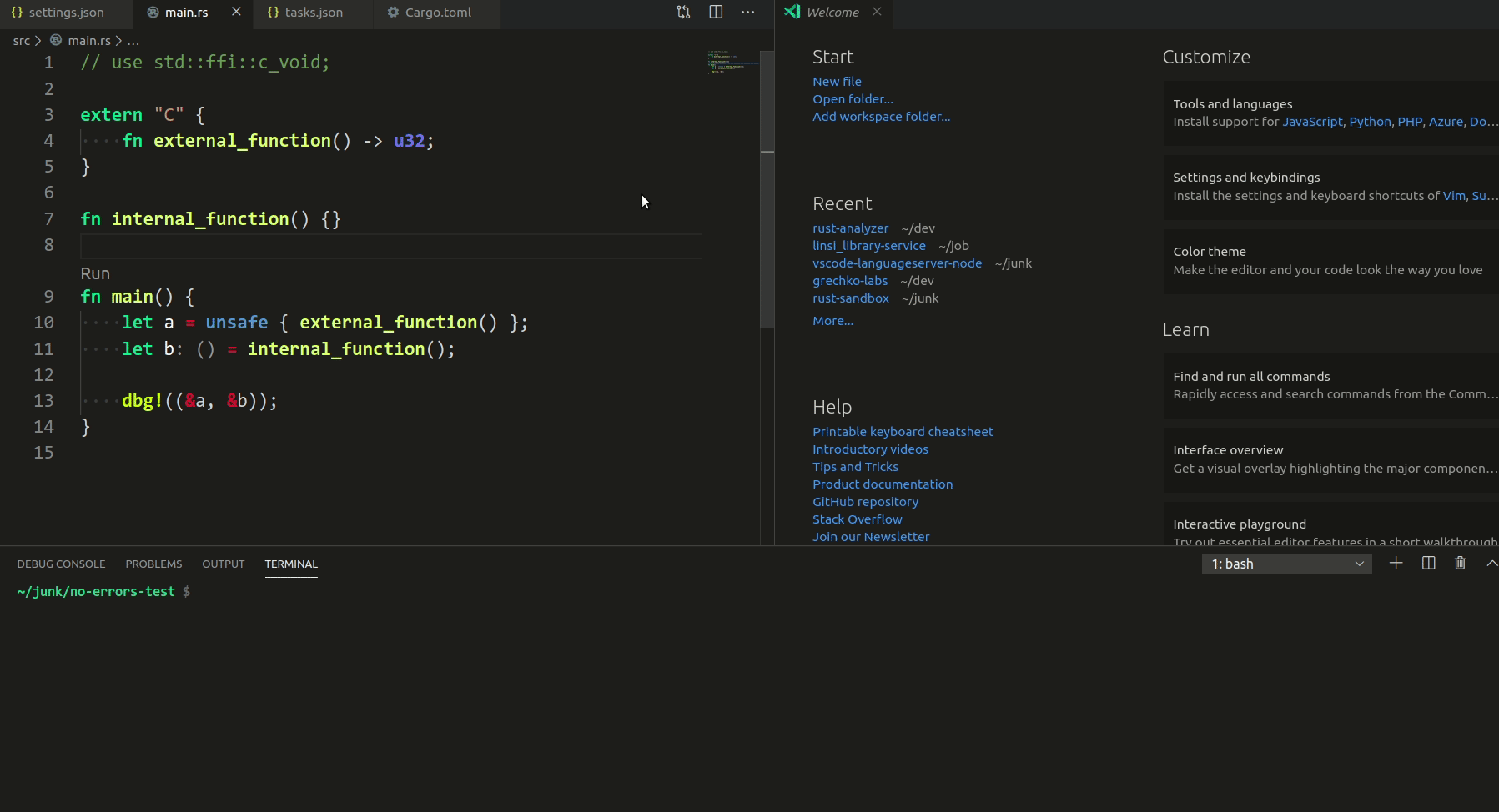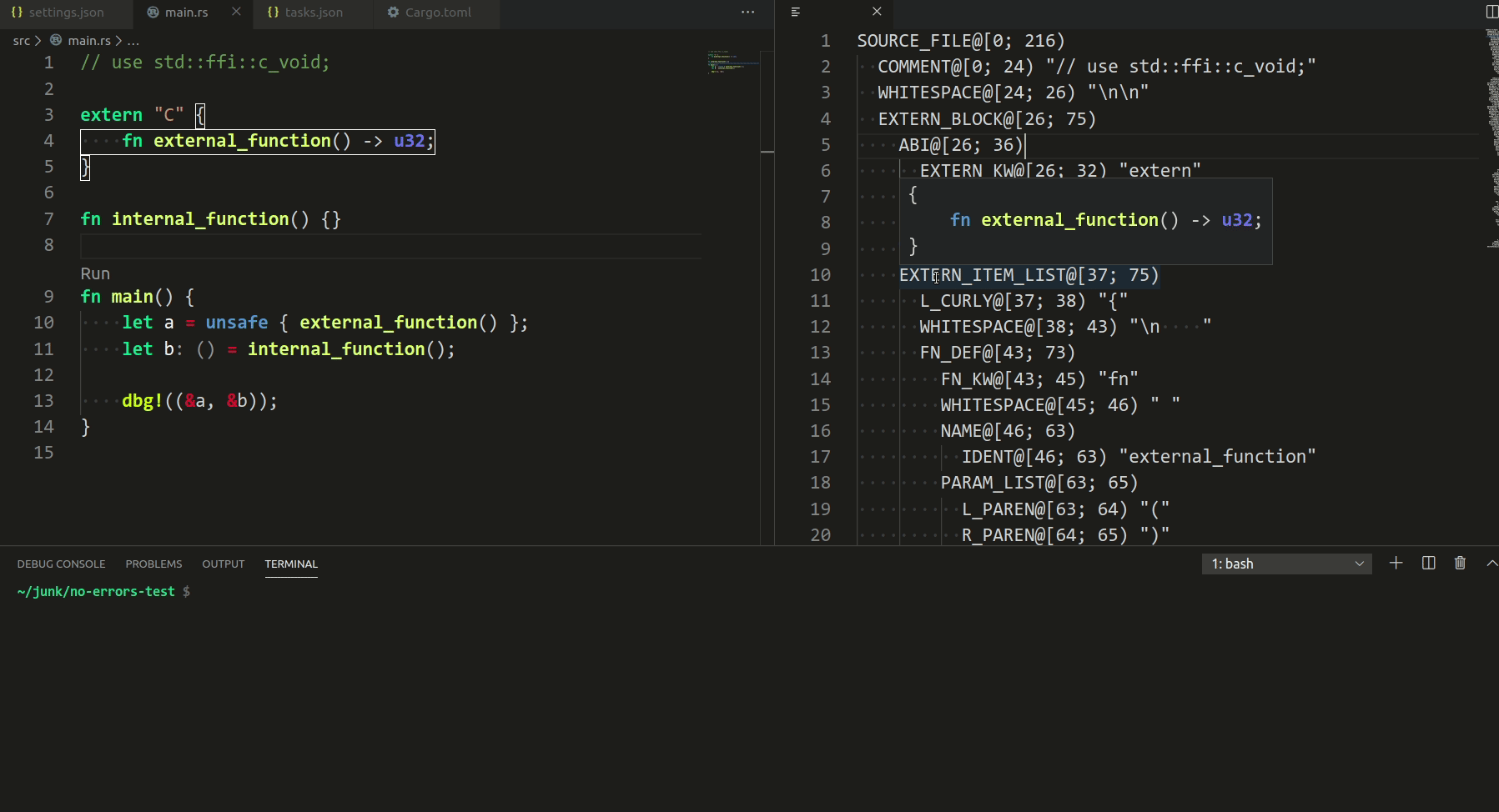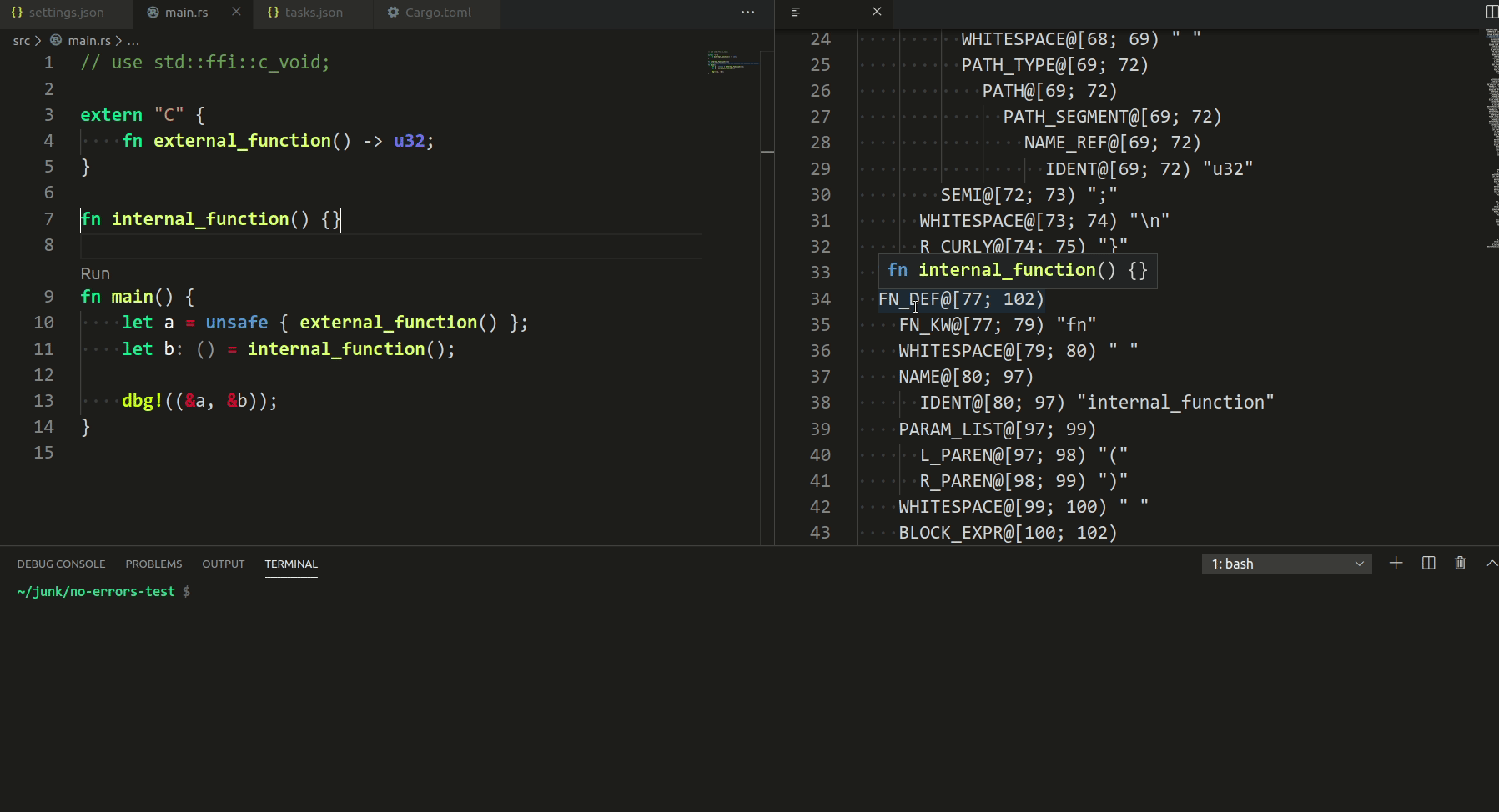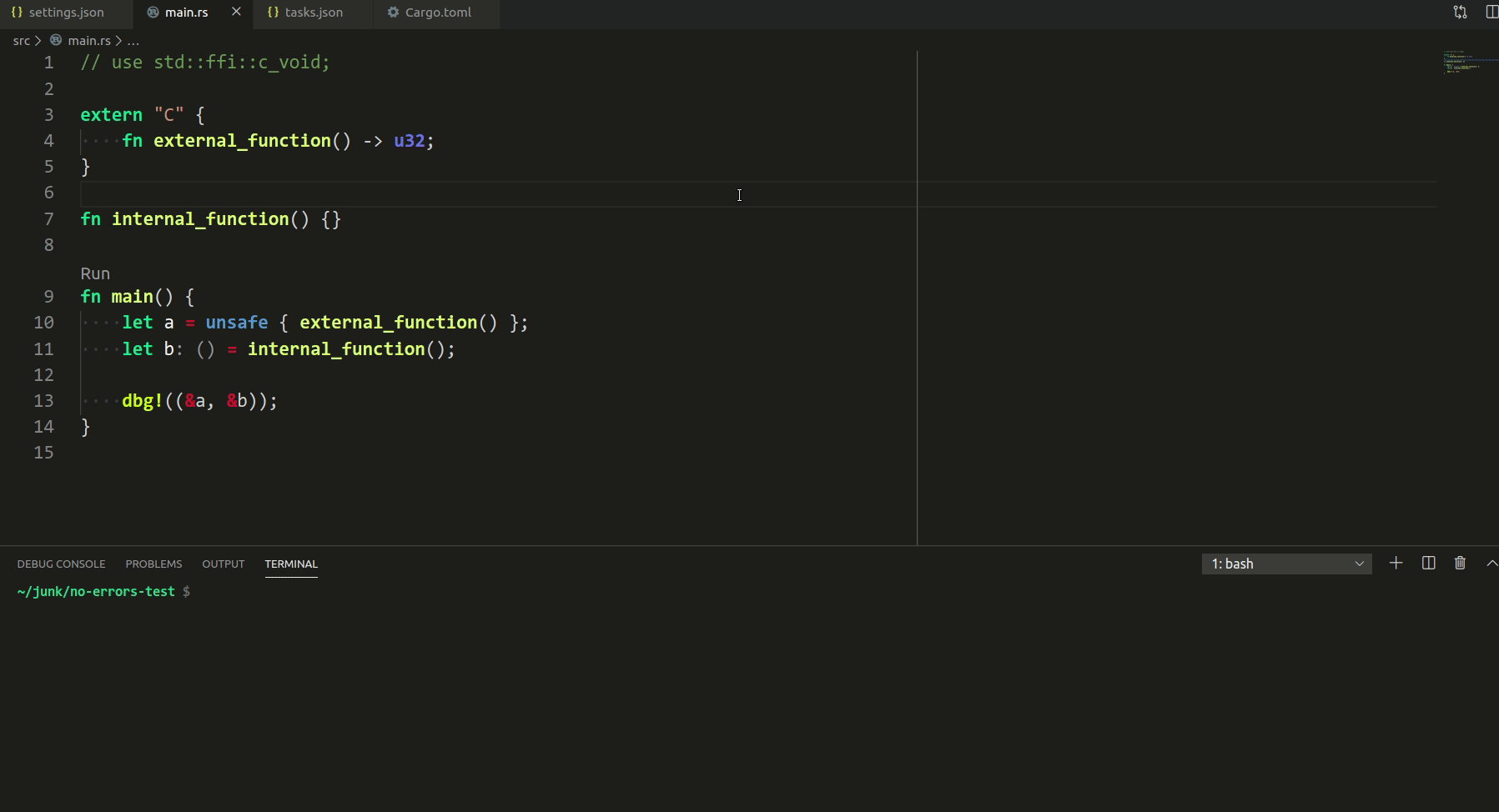
I implemented the reverse mapping (when you hover in the rust editor), but it seems overcomplicated, so I removed it
Related #3682
Co-authored-by: veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
3695: vscode: simplify and refactor config r=matklad a=Veetaha
Removed unnecessary interfaces, changed `cfg` to be a getter to ensure the fresh values any time possible.
Migrated from explicit casts to implicit.
Co-authored-by: veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
This cancel is unnecessary since we cancel the previous inlay hints requests in `fetchHints()` method itself. This is not a hard error, we just called cancel() 2 times.
Everything now happens in main.ts, in the bootstrap family of
functions. The current flow is:
* check everything only on extension installation.
* if the user is on nightly channel, try to download the nightly
extension and reload.
* when we install nightly extension, we persist its release id, so
that we can check if the current release is different.
* if server binary was not downloaded by the current version of the
extension, redownload it (we persist the version of ext that
downloaded the server).
3534: Feature: vscode impl nightlies download and installation r=Veetaha a=Veetaha
I need to test things more, but the core shape of the code is quite well-formed.
The main problem is that we save the release date only for nightlies and there are no means to get the release date of the stable extension (i.e. for this we would need to consult the github releases via a network request, or we would need to somehow save this info into package.json or any other file accessible from the extension code during the deployment step, but this will be very hard I guess).
So there is an invariant that the users can install nightly only from our extension and they can't do it manually, because when installing the nightly `.vsix` we actually save its release date to `globalState`
Closes: #3402
TODO:
- [x] More manual tests and documentation
cc @matklad @lnicola
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <gerzoh1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <veetaha2@gmail.com>
3561: feat: add debug code lens r=matklad a=hdevalke
Refs #3539
3577: Protect against infinite macro expansion in def collector r=edwin0cheng a=flodiebold
Something I noticed while trying to make macro expansion more resilient against errors.
There was a test for this, but it wasn't actually working because the first recursive expansion failed. (The comma...)
Even with this limit, that test (when fixed) still takes some time to pass because of the exponential growth of the expansions, so I disabled it and added a different one without growth.
CC @edwin0cheng
Co-authored-by: Hannes De Valkeneer <hannes@de-valkeneer.be>
Co-authored-by: hdevalke <2261239+hdevalke@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Florian Diebold <florian.diebold@freiheit.com>
3543: Parameter inlay hint separate from variable type inlay? #2876 r=matklad a=slyngbaek
Add setting to allow enabling either type inlay hints or parameter
inlay hints or both. Group the the max inlay hint length option
into the object.
- Add a new type for the inlayHint options.
- Add tests to ensure the inlays don't happen on the server side
Co-authored-by: Steffen Lyngbaek <steffenlyngbaek@gmail.com>
- Instead of a single object type, use several individual nested types
to allow toggling from the settings GUI
- Remove unused struct definitions
- Install and test that the toggles work
- Updated naming of config
- Define struct in ra_ide and use remote derive in rust-analyzer/config
- Make inlayConfig type more flexible to support more future types
- Remove constructor only used in tests
Add setting to allow enabling either type inlay hints or parameter
inlay hints or both. Group the the max inlay hint length option
into the object.
- Add a new type for the inlayHint options.
- Add tests to ensure the inlays don't happen on the server side
The new name seems much simpler and it doesn't limit
this config value only to downloading the server binary.
Thus we wouldn't need to create another config
properties to handle other downloads whatsoever.
Anyway, I believe (heuristically) that most of the users
would want to set "askBeforeDownload": false once
and never bother clicking on the notification again
(because otherwise there is no big point in installing rust-analyzer if it cannot install the server)
Also renamed BinarySource to ArtifactSource in anticipation of
nightlies installation that requires downloading
not a binary itself but .vsix package, thus generalized
to `artifact` term
3388: Remove inlay hint in diff views r=matklad a=vbfox
If the left side of a diff view that contain the old version of the file apply inlays they are misplaced and produce a weird display:
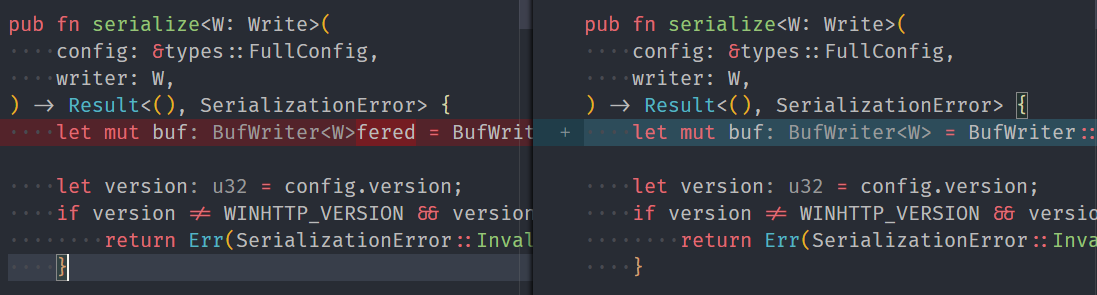
After the change:
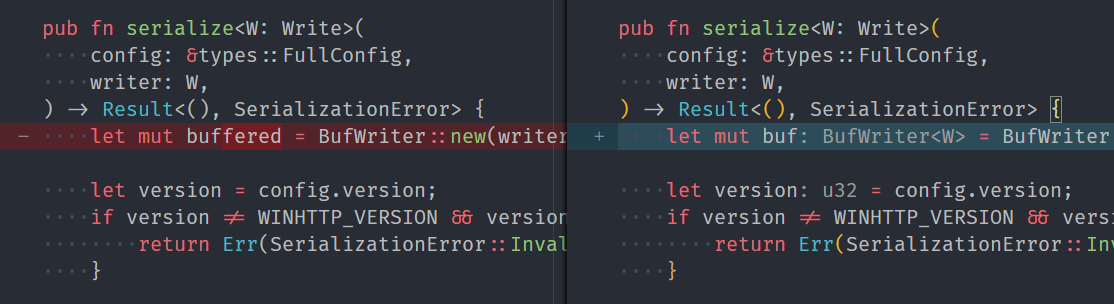
The detection is done by blacklisting the url schemes used by git and subversion scm extensions, whitelisting `file` is also possible but neither is perfect as VSCode now support both pluggable scm extensions and pluggable remote filesystems. But I suspect that the list of scm extensions is more easily manageable.
**Note**: I can rebase on #3378 if needed as it touches the same lines of code
Co-authored-by: Julien Roncaglia <julien@roncaglia.fr>
If the left side of a diff view that contain the old
version of the file apply inlays they are misplaced.
The detection is done by blacklisting the url schemes used
by git and subversion scm extensions.
3099: Init implementation of structural search replace r=matklad a=mikhail-m1
next steps:
* ignore space and other minor difference
* add support to ra_cli
* call rust parser to check pattern
* documentation
original issue #2267
Co-authored-by: Mikhail Modin <mikhailm1@gmail.com>
3162: Feature: vscode always downloads only the matching ra_lsp_server version r=matklad a=Veetaha
I tried to separate logically connected changes into separate commits, so enjoy!
Now TypeScript extension saves installed binary version in global state and always checks that the installed binary version equals the version of the TypeScript extension itself (to prevent version drifts).
Also, changed `fetchLatestArtifactReleaseInfo()` to `fetchArtifactReleaseInfo()` that takes an optional release tag (when not specified fetches the latest release). The version without a release tag will be useful in the future when adding auto-checking for updates.
I decided not to do `Download latest language server` command (I have stated the rationale for this in #3073) and let the extension itself decide which version of the binary it wants. This way the users will be able to get the latest `ra_lsp_server` binary after the approaching 2020-02-17 release, without having to manually delete the outdated one from `~/.config/Code/User/globalStorage/matklad.rust-analyzer`!
Closes#3073
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <gerzoh1@gmail.com>
3131: vscode: simplified config and to removed one source of truth of default values r=matklad a=Veetaha
Though not intended initially, the implementation of config design is alike [dart's one](https://github.com/Dart-Code/Dart-Code/blob/master/src/extension/config.ts) as pointed by @matklad in PM.
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <gerzoh1@gmail.com>
Instead only opt-in to CallHierarchy since it has a vscode API but LSP support
is still proposed.
Discovered while working on SemanticTokens which does not have a vscode API
and is still in the proposed state. Somehow enabling it would crash the
language server.
See https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-languageserver-node/issues/572
3083: Update some crates r=matklad a=kjeremy
3101: vscode: filter out arm linux from using prebuilt binaries r=matklad a=Veetaha
Closes#3076
Co-authored-by: kjeremy <kjeremy@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Veetaha <gerzoh1@gmail.com>
2964: Improve responsiveness of the cargo check status label r=matklad a=lnicola
This is still not ideal because the label displays the crate that was just checked, not the one that's currently being checked. But it should give the impression of being faster.
Co-authored-by: Laurențiu Nicola <lnicola@dend.ro>
2061: Theme loading and "editor.tokenColorCustomizations" support. r=matklad a=seivan
Fixes: [Issue#1294](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/1294#issuecomment-497450325)
TODO:
- [x] Load themes
- [x] Load existing `ralsp`-prefixed overrides from `"workbench.colorCustomizations"`.
- [x] Load overrides from `"editor.tokenColorCustomizations.textMateRules"`.
- [x] Use RA tags to load `vscode.DecorationRenderOptions` (colors) from theme & overrides.
- [x] Map RA tags to common TextMate scopes before loading colors.
- [x] Add default scope mappings in extension.
- [x] Cache mappings between settings updates.
- [x] Add scope mapping configuration manifest in `package.json`
- [x] Load configurable scope mappings from settings.
- [x] Load JSON Scheme for text mate scope rules in settings.
- [x] Update [Readme](https://github.com/seivan/rust-analyzer/blob/feature/themes/docs/user/README.md#settings).
Borrowed the theme loading (`scopes.ts`) from `Tree Sitter` with some modifications to reading `"editor.tokenColorCustomizations"` for merging with loaded themes and had to remove the async portions to be able to load it from settings updates.
~Just a PoC and an idea I toyed around with a lot of room for improvement.~
For starters, certain keywords aren't part of the standard TextMate grammar, so it still reads colors from the `ralsp` prefixed values in `"workbench.colorCustomizations"`.
But I think there's more value making the extension work with existing themes by maping some of the decoration tags to existing key or keys.
<img width="453" alt="Screenshot 2019-11-09 at 17 43 18" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/55424/68531968-71b4e380-0318-11ea-924e-cdbb8d5eae06.png">
<img width="780" alt="Screenshot 2019-11-09 at 17 41 45" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/55424/68531950-4b8f4380-0318-11ea-8f85-24a84efaf23b.png">
<img width="468" alt="Screenshot 2019-11-09 at 17 40 29" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/55424/68531952-51852480-0318-11ea-800a-6ae9215f5368.png">
These will merge with the default ones coming with the extension, so you don't have to implement all of them and works well with overrides defined in settings.
```jsonc
"editor.tokenColorCustomizations": {
"textMateRules": [
{
"scope": "keyword",
"settings": {
"fontStyle": "bold",
}
},
]
},
```
Edit: The idea is to work with 90% of the themes out there by working within existing scopes available that are generally styled. It's not to say I want to erase the custom Rust scopes - those should still remain and eventually worked into a custom grammar bundle for Rust specific themes that target those, I just want to make it work with generic themes offered on the market place for now.
A custom grammar bundle and themes for Rust specific scopes is out of... scope for this PR.
We'll make another round to tackle those issues.
Current fallbacks implemented
```typescript
[
'comment',
[
'comment',
'comment.block',
'comment.line',
'comment.block.documentation'
]
],
['string', ['string']],
['keyword', ['keyword']],
['keyword.control', ['keyword.control', 'keyword', 'keyword.other']],
[
'keyword.unsafe',
['storage.modifier', 'keyword.other', 'keyword.control', 'keyword']
],
['function', ['entity.name.function']],
['parameter', ['variable.parameter']],
['constant', ['constant', 'variable']],
['type', ['entity.name.type']],
['builtin', ['variable.language', 'support.type', 'support.type']],
['text', ['string', 'string.quoted', 'string.regexp']],
['attribute', ['keyword']],
['literal', ['string', 'string.quoted', 'string.regexp']],
['macro', ['support.other']],
['variable', ['variable']],
['variable.mut', ['variable', 'storage.modifier']],
[
'field',
[
'variable.object.property',
'meta.field.declaration',
'meta.definition.property',
'variable.other'
]
],
['module', ['entity.name.section', 'entity.other']]
```
Co-authored-by: Seivan Heidari <seivan.heidari@icloud.com>
2568: Add option to disable all-targets. r=matklad a=pftbest
Can be useful in embedded.
Co-authored-by: Vadzim Dambrouski <vadzim.dambrouski@promwad.com>
2508: Code: don't check for ra_lsp_server on Windows r=matklad a=lnicola
Workaround for https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/2503#issuecomment-562980020.
~~(not yet tested on Windows)~~
We can't run `ra_lsp_server --version` right now because the server doesn't seem to handle arguments (so it hangs).
Co-authored-by: Laurențiu Nicola <lnicola@dend.ro>
This commit implements a general truncation framework for HirFormatter
that keeps track of how much has been output so far. This information
can then be used to perform truncation inside the language server,
instead of relying on the client.
Initial support is implemented for truncating types hints using the
maxInlayHintLength server config option. The existing solution in the
VSCode extension has been removed in favor of letting the server
truncate type hints.
The old `vscode` package is outdated and it is recommened to switch to
these two new packages. This also solves a problem of a missing `.d.ts`
for `vscode` in Nixos.
1652: Improve type hints behavior r=matklad a=SomeoneToIgnore
This PR fixed the following type hints issues:
* Restructures the `InlayKind` enum contents based on the discussion here: https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/1606#issuecomment-515968055
* Races described in #1639
* Caches the latest decorations received for each file to show them the next time the file is opened (instead of a new server request)
Co-authored-by: Kirill Bulatov <mail4score@gmail.com>
1459: Include primary span label in VS Code diagnostics r=matklad a=etaoins
In most cases the primary label span repeats information found elsewhere in the diagnostic. For example, with E0061:
```json
{
"message": "this function takes 2 parameters but 3 parameters were supplied",
"spans": [{"label": "expected 2 parameters"}]
}
```
However, with some mismatched type errors (E0308) the expected type only appears in the primary span's label, e.g.:
```json
{
"message": "mismatched types",
"spans": [{"label": "expected usize, found u32"}]
}
```
I initially added the primary span label to the message unconditionally. However, for most error types the child diagnostics repeat the primary span label with more detail. `rustc` also renders the duplicate text but because the span label and child diagnostics appear in visually distinct places it's not as confusing.
This takes a heuristic approach where it will only add the primary span label if there are no child message lines. For most error types the child messages repeat the primary span label with more detail.
Co-authored-by: Ryan Cumming <etaoins@gmail.com>
This adds `unreachable_code` to the list of diagnostic codes we map to
`Unnecessary` in Visual Studio Code. This is consistent with what the
TypeScript language server does.
In most cases the primary label span repeats information found elsewhere
in the diagnostic. For example, with E0061:
```
{
"message": "this function takes 2 parameters but 3 parameters were supplied",
"spans": [{"label": "expected 2 parameters"}]
}
```
However, with some mismatched type errors (E0308) the expected type only
appears in the primary span's label, e.g.:
```
{
"message": "mismatched types",
"spans": [{"label": "expected usize, found u32"}]
}
```
I initially added the primary span label to the message unconditionally.
However, for most error types the child diagnostics repeat the primary
span label with more detail. `rustc` also renders the duplicate text but
because the span label and child diagnostics appear in visually distinct
places it's not as confusing.
This takes a heuristic approach where it will only add the primary span
label if there are no child message lines.
1454: Fix `cargo watch` code action filtering r=etaoins a=etaoins
There are two issues with the implementation of `provideCodeActions` introduced in #1439:
1. We're returning the code action based on the file its diagnostic is in; not the file the suggested fix is in. I'm not sure how often fixes are suggested cross-file but it's something we should handle.
2. We're not filtering code actions based on the passed range. The means if there is any suggestion in a file we'll show an action for every line of the file. I naively thought that VS Code would filter for us but that was wrong.
Unfortunately the VS Code `CodeAction` object is very complex - it can handle edits across multiple files, run commands, etc. This makes it complex to check them for equality or see if any of their edits intersects with a specified range.
To make it easier to work with suggestions this introduces a `SuggestedFix` model object and a `SuggestFixCollection` code action provider. This is a layer between the raw Rust JSON and VS Code's `CodeAction`s. I was reluctant to introduce another layer of abstraction here but my attempt to work directly with VS Code's model objects was worse.
Co-authored-by: Ryan Cumming <etaoins@gmail.com>
`tslint` doesn't catch this because TypeScript has had this check
builtin since 2.9. However, it's disabled by default so right now
nothing is checking for unused variables.
There are two issues with the implementation of `provideCodeActions`
introduced in #1439:
1. We're returning the code action based on the file its diagnostic is
in; not the file the suggested fix is in. I'm not sure how often
fixes are suggested cross-file but it's something we should handle.
2. We're not filtering code actions based on the passed range. The means
if there is any suggestion in a file we'll show an action for every
line of the file. I naively thought that VS Code would filter for us
but that was wrong.
Unfortunately the VS Code `CodeAction` object is very complex - it can
handle edits across multiple files, run commands, etc. This makes it
complex to check them for equality or see if any of their edits
intersects with a specified range.
To make it easier to work with suggestions this introduces a
`SuggestedFix` model object and a `SuggestFixCollection` code action
provider. This is a layer between the raw Rust JSON and VS Code's
`CodeAction`s. I was reluctant to introduce another layer of abstraction
here but my attempt to work directly with VS Code's model objects was
worse.
Currently all of our VS Code diagnostics are given the source of
`rustc`. However, if you have something like `cargo-watch.command` set
to `clippy` it will also watch for Clippy lints. The `rustc` source is a
bit misleading in that case.
Fortunately, Rust's tool lints (RFC 2103) line up perfectly with VS
Code's concept of `source`. This checks for lints scoped to a given tool
and then splits them in to a `source` and tool-specific `code`.
As promised in #1439 this is an initial attempt at unit testing the
VSCode extension. There are two separate parts to this: getting the test
framework working and unit testing the code in #1439.
The test framework nearly intact from the VSCode extension generator.
The main thing missing was `test/index.ts` which acts as an entry point
for Mocha. This was simply copied back in. I also needed to open the
test VSCode instance inside a workspace as our file URI generation
depends on a workspace being open.
There are two ways to run the test framework:
1. Opening the extension's source in VSCode, pressing F5 and selecting
the "Extensions Test" debug target.
2. Closing all copies of VSCode and running `npm test`. This is started
from the command line but actually opens a temporary VSCode window to
host the tests.
This doesn't attempt to wire this up to CI. That requires running a
headless X11 server which is a bit daunting. I'll assess the difficulty
of that in a follow-up branch. This PR is at least helpful for local
development without having to induce errors on a Rust project.
For the actual tests this uses snapshots of `rustc` output from a real
Rust project captured from the command line. Except for extracting the
`message` object and reformatting they're copied verbatim into fixture
JSON files.
Only four different types of diagnostics are tested but they represent
the main combinations of code actions and related information possible.
They can be considered the happy path tests; as we encounter
corner-cases we can introduce new tests fixtures.