Fix runnable detection for `#[tokio::test]`
fix#15141
It is hacky, and it wouldn't work for e.g. this case:
```Rust
use ::core::prelude;
#[prelude::v1::test]
fn foo() {
}
```
But it works for the tokio case. We should use the name resolution here somehow, and after that we should probably also get rid of the ast based `test_related_attribute` function.
internal: add `library` fixture meta
Currently, there is no way to specify `CrateOrigin` of a file fixture ([this] might be a bug?). This PR adds `library` meta to explicitly specify the fixture to be `CrateOrigin::Library` and also makes sure crates that belong to a library source root are set `CrateOrigin::Library`.
(`library` isn't really the best name. It essentially means that the crate is outside workspace but `non_workspace_member` feels a bit too long. Suggestions for the better name would be appreciated)
Additionally:
- documents the fixture meta syntax as thoroughly as possible
- refactors relevant code
[this]: 4b06d3c595/crates/base-db/src/fixture.rs (L450)
Fix `self` and `super` path resolution in block modules
This PR fixes `self` and `super` path resolution with block modules involved.
Previously, we were just going up the module tree count-of-`super` times without considering block modules in the way, and then if we ended up in a block `DefMap`, we adjust "to the containing crate-rooted module". While this seems to work in most real-world cases, we failed to resolve them within peculiar module structures.
`self` and `super` should actually be resolved to the nearest non-block module, and the paths don't necessarily resolve to a crate-rooted module. This PR makes sure every `self` and `super` segment in paths are resolved to a non-block module.
internal: support `#[rustc_coinductive]`
rust-lang/rust#100386 changed the trait solver so that `Sized` is treated as coinductive trait, just like auto traits. This is now controlled by the perma-unstable `#[rustc_coinductive]` attribute (rust-lang/rust#108033), which this PR adds support for.
In practice, I don't think this matters much if at all. Currently we don't give chalk enough information so chalk cannot precisely (dis)prove `Sized` bounds.
internal: Add run-tests command
This command is similar to `cargo test` except that it uses r-a to run tests instead of compiling and running them with rustc. This is slower than `cargo test` and it is only useful for me to see a bird view of what needs to be fixed. The current output is:
```
48 passed, 5028 failed, 2 ignored
All tests 174.74s, 648ginstr
```
48 is very low, but higher than what I originally thought.
Now that there is some passing tests, I can show the plan:
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/assets/45197576/76d7d777-1843-4ca4-b7fe-e463bdade6cb
That is, at the end, I want to be able to immediately re run every test after every change. (0.5s is not really immediate, but it's not finished yet, and it is way better than 8s that running a typical test in r-a will take on my system)
Change comparsion for checking if number is negative to include 128
The last byte in Little-Endian representation of negative integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
Potentially fixes#15096
Added a test near positive extermes and two test near negative
extermes as well one for 0.
Added a test using the `as` cast and one with comparison with 0.
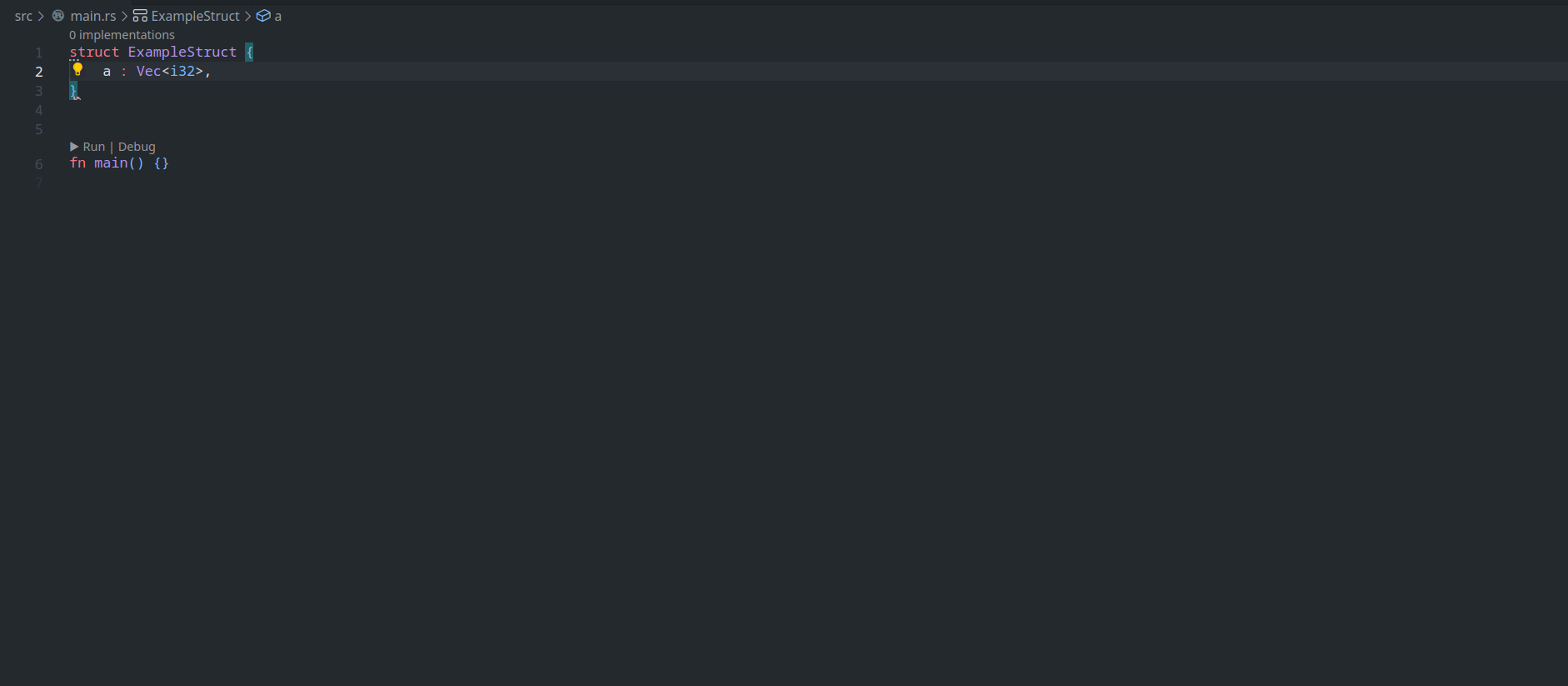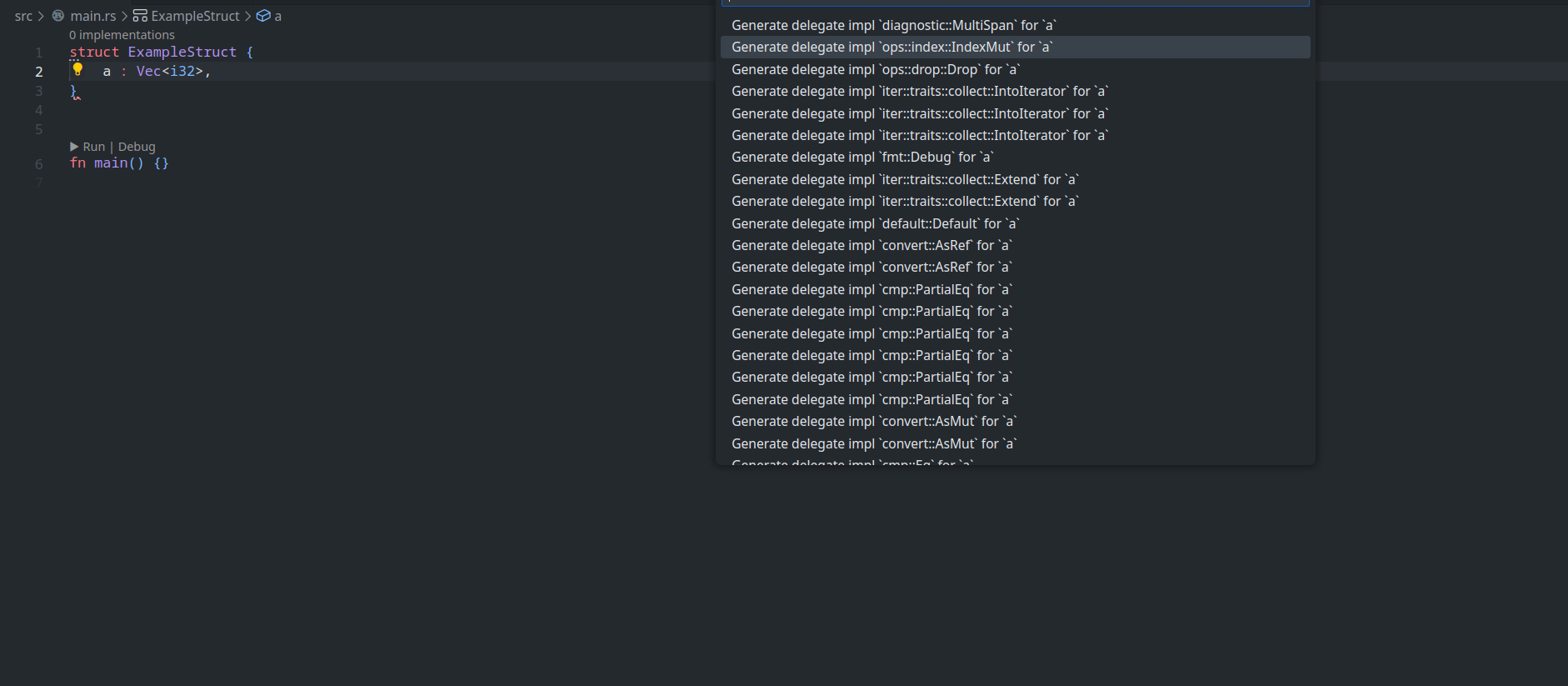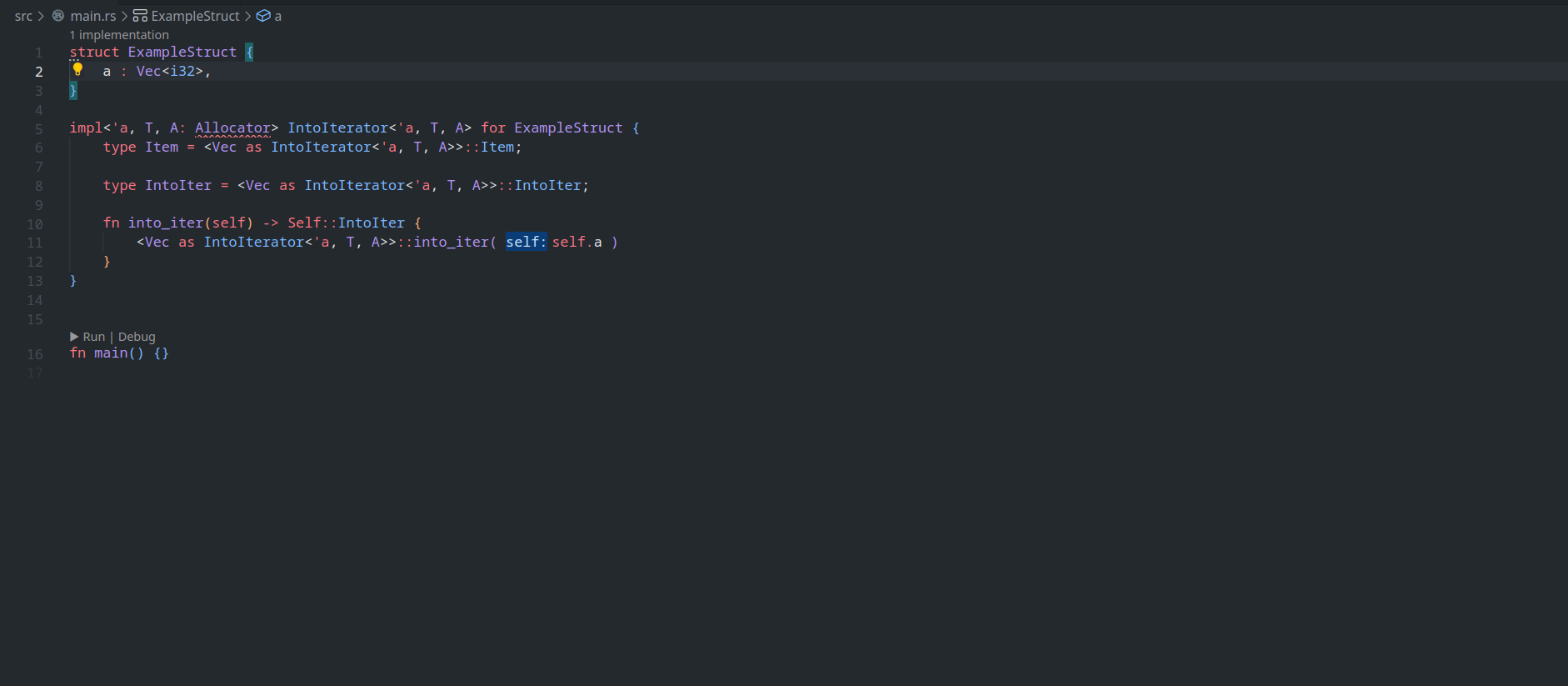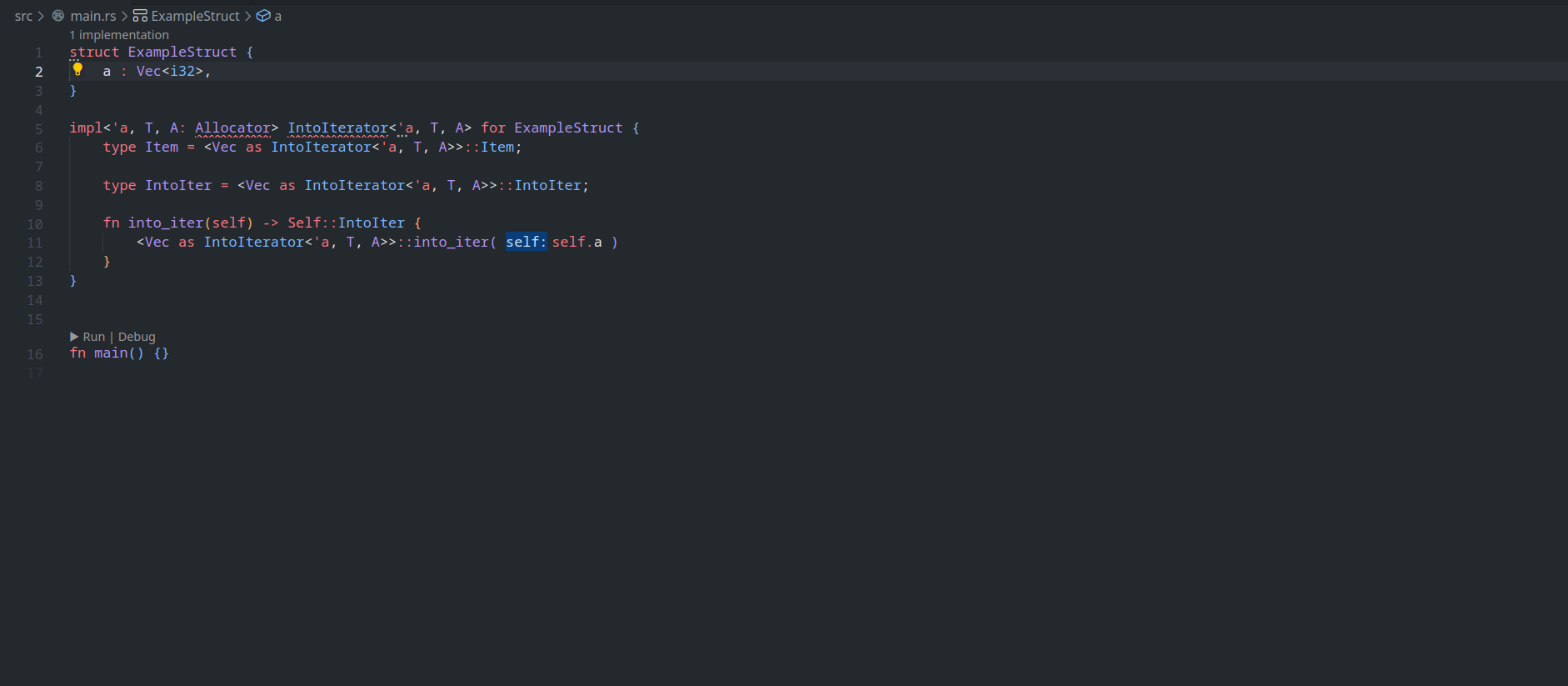
feature : assist delegate impl
This PR ( fixes#14386 ) introduces a new IDE assist that generates a trait impl for a struct that delegates a field. This is a draft because the current `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` produces some unwanted results when it deals with extern crates, an example of which I attach as a GIF.
GIFs :
1. A general case
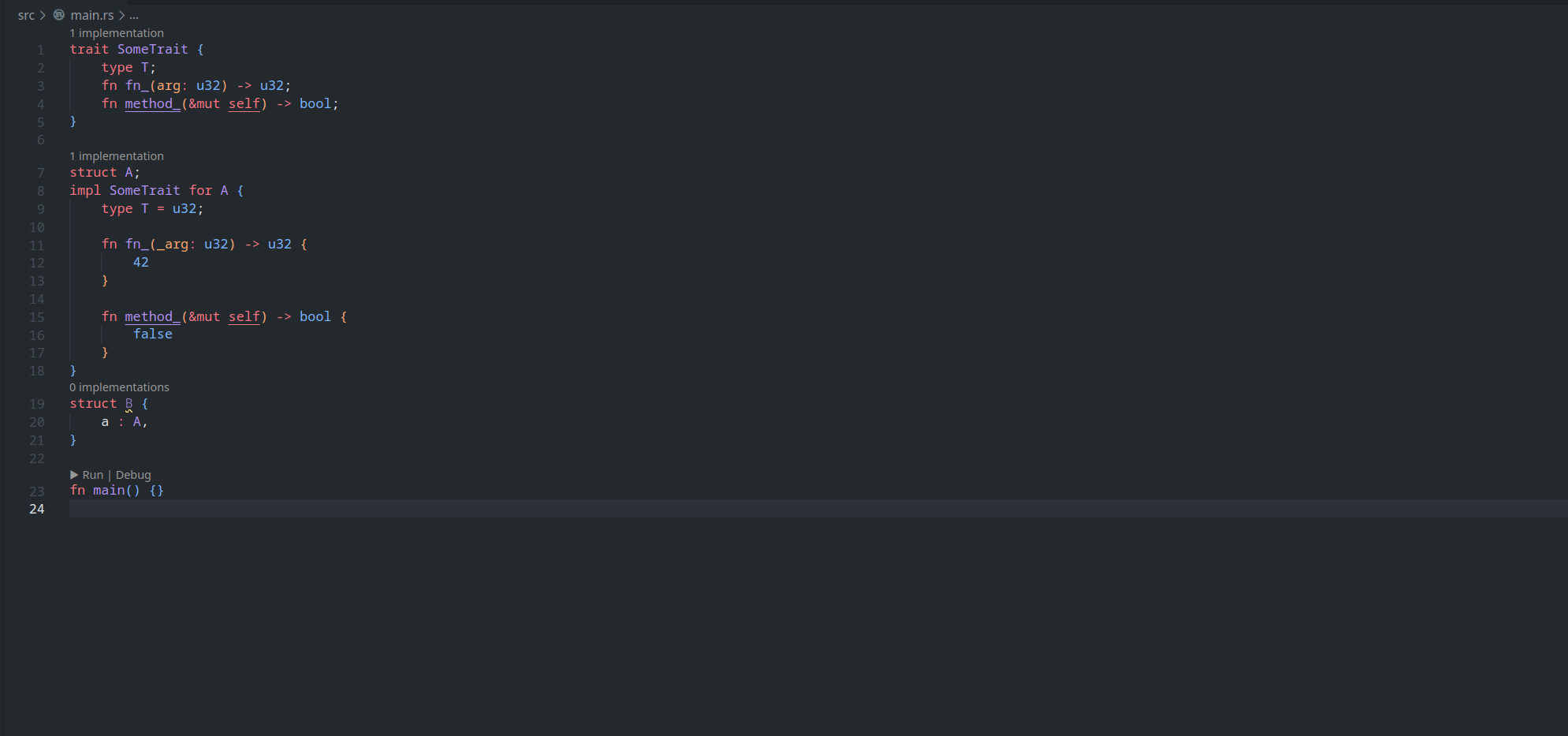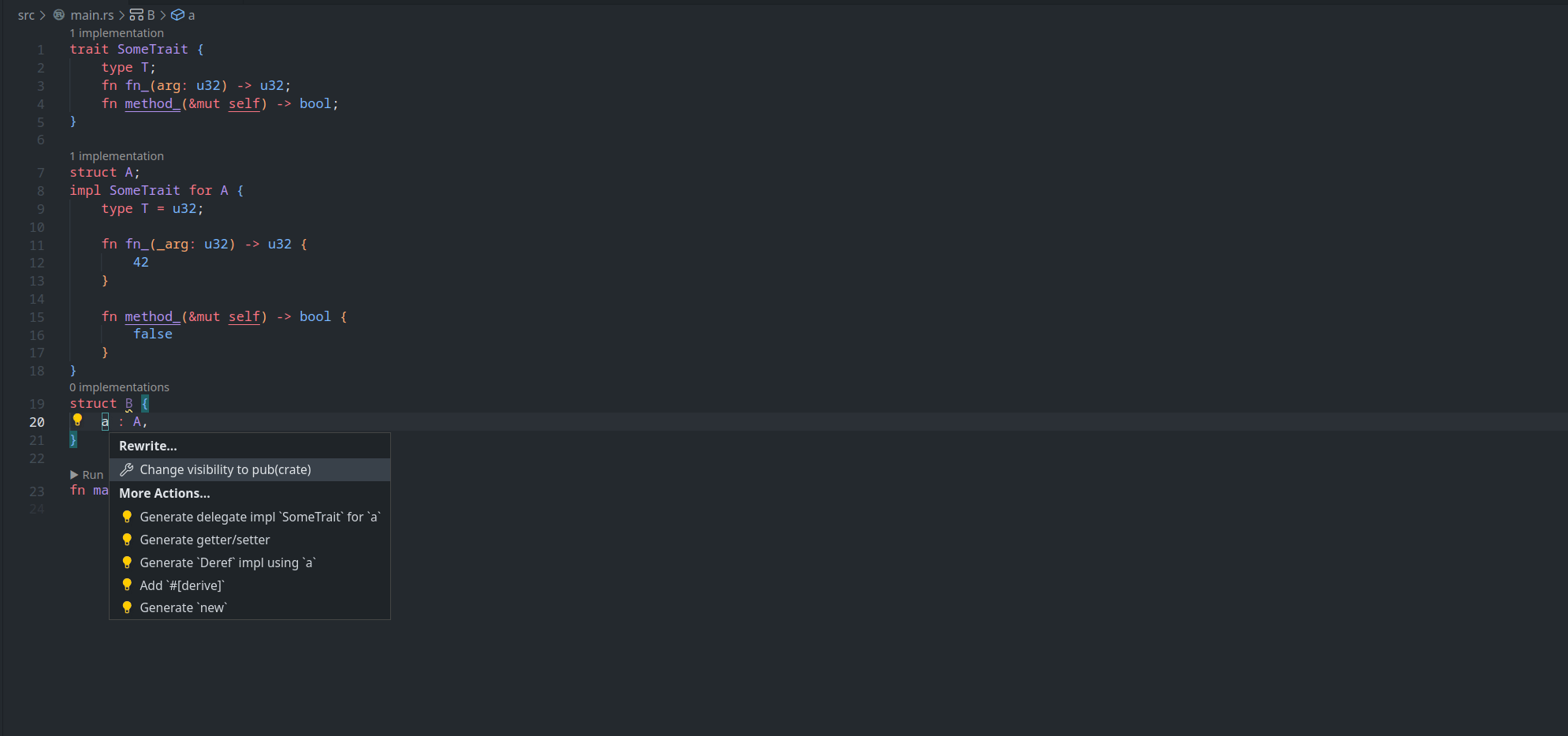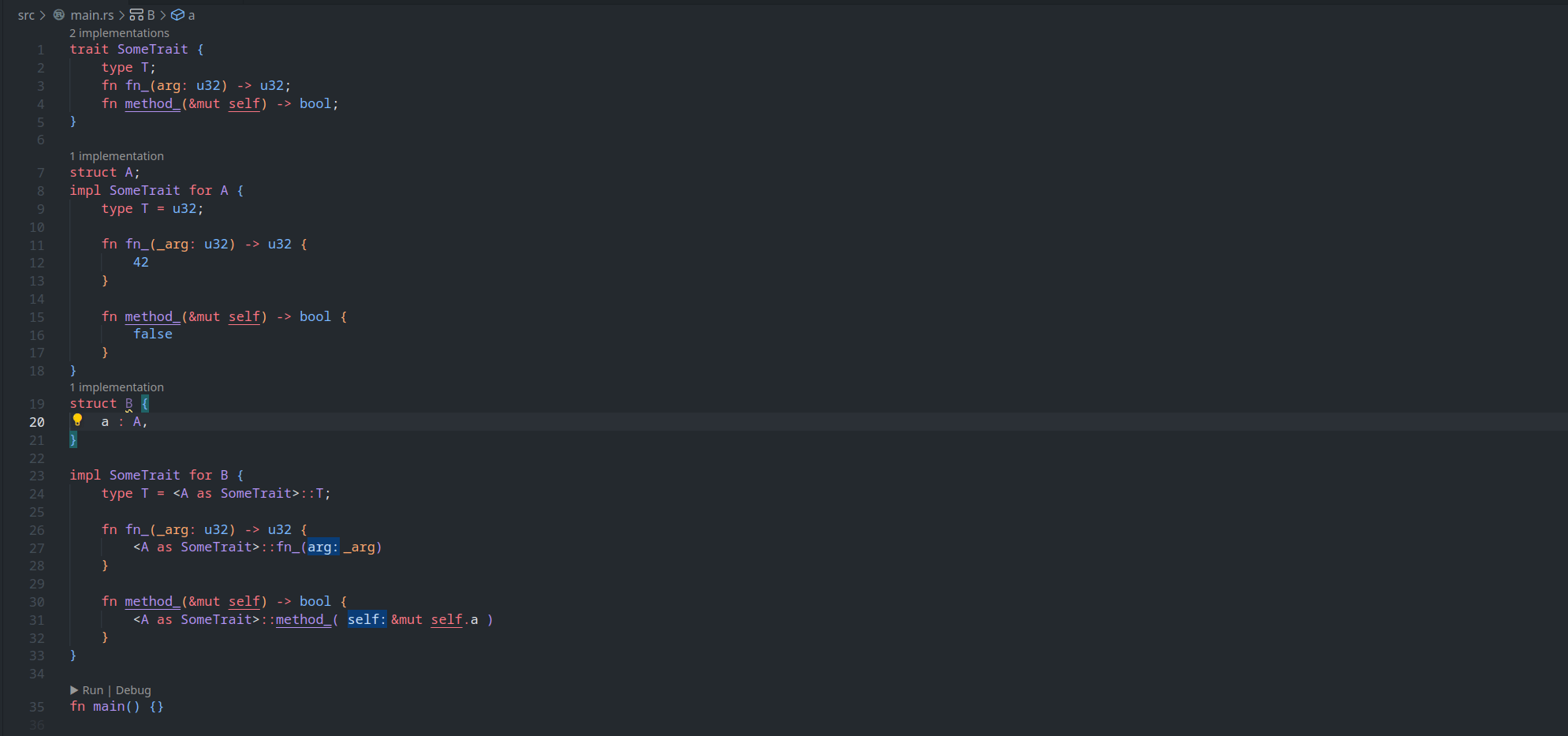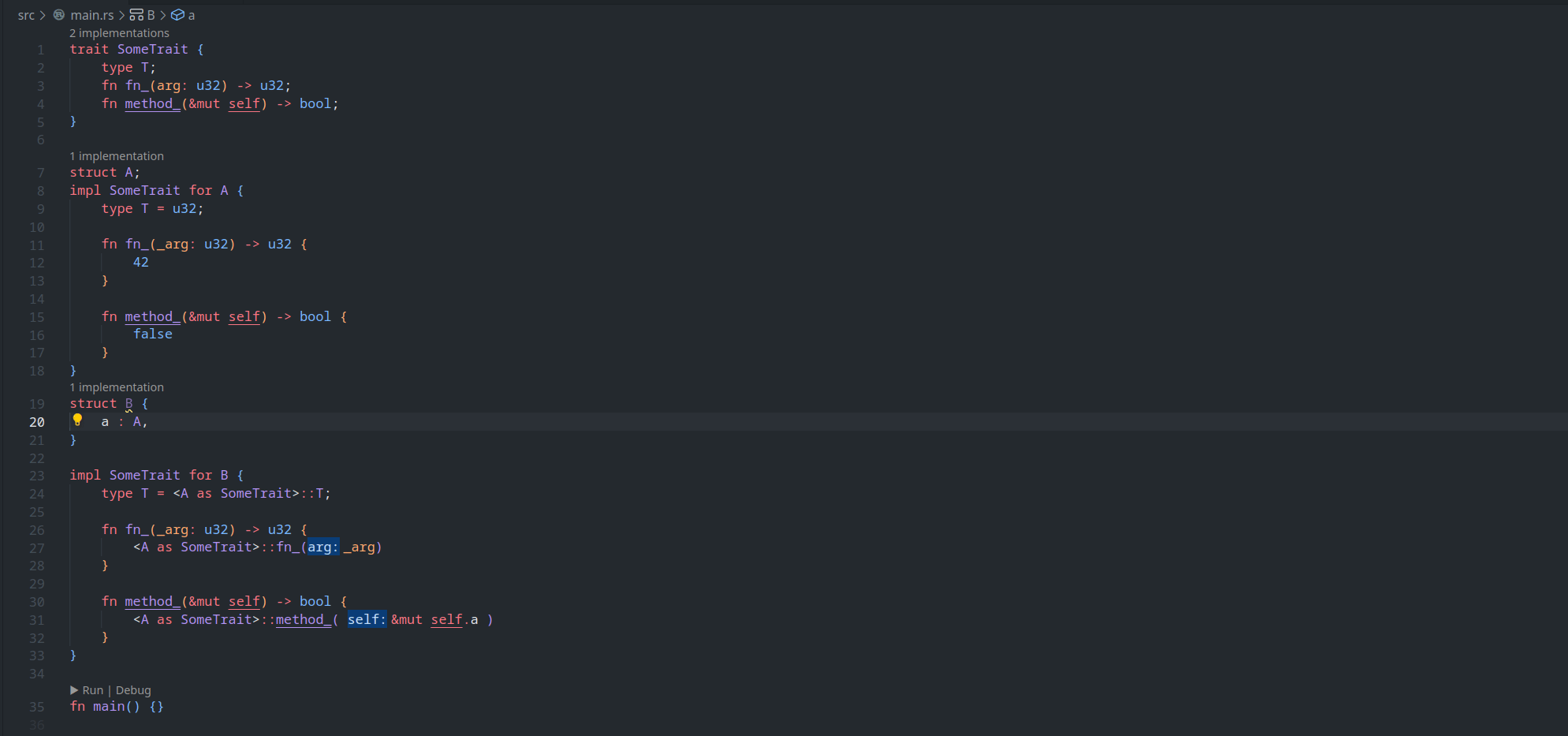
2. A case where `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` fails to correctly resolve a property ( take `Allocator` as an example ) to its full path, thus causing an error to occur. ( Not to even mention that resolving this causes another error `use of unstable library feature 'allocator_api'` to occur
Reason: The last byte in Little Endian representation of negative
integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before
the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
internal: remove spurious regex dependency
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place
where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
Remove scope_for_def calls as the definition have been removed entirely.
As a result of this change the problem with false path resolutions has been solved.
internal: Record file dependencies in crate graph construction
Should fix the bug mentioned in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/8623 where removing a crate root file will panic. I'm not too happy with the way this is done here but I can't think of a better way right now.
Deduplicate tuple indices for completion
Follow-up to #15026
A tuple struct may dereference to a primitive tuple (though unusual, which is why I previously overlooked this case). We should not show the same tuple index in completion in such cases.
Deduplication of indices among multiple tuple structs is already handled in the previous PR.
fix: deduplicate fields and types in completion
Fixes#15024
- `hir_ty::autoderef()` (which is only meant to be used outside `hir-ty`) now deduplicates types and completely resolves inference variables within.
- field completion now deduplicates fields of the same name and only picks such field of the first type in the deref chain.
Lower const params with a bad id
cc #7434
This PR adds an `InTypeConstId` which is a `DefWithBodyId` and lower const generic parameters into bodies using it, and evaluate them with the mir interpreter. I think this is the last unimplemented const generic feature relative to rustc stable.
But there is a problem: The id used in the `InTypeConstId` is the raw `FileAstId`, which changes frequently. So these ids and their bodies will be invalidated very frequently, which is bad for incremental analysis.
Due this problem, I disabled lowering for local crates (in library crate the id is stable since files won't be changed). This might be overreacting (const generic expressions are usually small, maybe it would be better enabled with bad performance than disabled) but it makes motivation for doing it in the correct way, and it splits the potential panic and breakages that usually comes with const generic PRs in two steps.
Other than the id, I think (at least I hope) other parts are in the right direction.
Properly format documentation for `SignatureHelpRequest`s
Properly formats function documentation instead of returning it raw when responding to `SignatureHelpRequest`s.
I added a test in `crates/rust-analyzer/tests/slow-tests/main.rs` -- not sure if this is the best location given the relevant code is in `crates/rust-analyzer` or if it's possible to test in a less heavyweight manner.
Closes#14958
fix: implemeted lifetime transformation fot assits
A part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/13363
I expect to implement transformation of const params in a separate PR
Other assists and a completion affected:
- `generate_function` currently just ignores lifetimes and, consequently, is not affected
- `inline_call` and `replace_derive_with...` don't seem to need lifetime transformation
- `trait_impl` (a completion) is fixed and tested
Add span to group.
This appears to fix#14959, but I've never contributed to rust-analyzer before and there were some things that confused me:
- I had to add the `fn byte_range` method to get it to build. This was added to rust in [April](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/109002), so I don't understand why it wasn't needed until now
- When testing, I ran into the fact that rust recently updated its `METADATA_VERSION`, so I had to test this with nightly-2023-05-20. But then I noticed that rust has its own copy of `rust-analyzer`, and the metadata version bump has already been [handled there](60e95e76d0). So I guess I don't really understand the relationship between the code there and the code here.
internal: Migrate some assists to use the structured snippet API
Migrates the following assists:
- `add_missing_impl_members`
- `extract_type_alias`
As an additional requirement, these assists are also migrated to use the mutable AST API, since otherwise there would be overlapping `Indel` spans
Infer return type for async function in `generate_function`
Part of #10122
In `generate_function` assist, when we infer the return type of async function we're generating, we should retrieve the type of parent await expression rather than the call expression itself.
Emit `'_` for lifetime generics in `HirDisplay`
This makes the generated code not linted by `rust_2018_idioms` lint. But that is an allow by default lint, so should we do this? Maybe we should only do this for `DisplayTarget::SourceCode`?
fix: consider outer binders when folding captured items' type
Fixes#14966
Basically, the crash is caused by us producing a broken type and passing it to chalk: `&dyn for<type> [for<> Implemented(^1.0: A<^0.0>)]` (notice the innermost bound var `^0.0` has no corresponding binder). It's created in `CapturedItemWithoutTy::with_ty()`, which didn't consider outer binders when folding types to replace placeholders with bound variables.
The fix is one-liner, but I've also refactored the surrounding code a little.
- use `DefWithBodyId::as_generic_def_id()`
- add comments on `InferenceResult` invariant
- move local helper function to bottom to comply with style guide
Fix drop scopes problems in mir
Fix false positives of `need-mut` emerged from #14955
There are still 5 `need-mut` false positives on self, all related to `izip!` macro hygenic issue. I will try to do something about that before monday release.
Fix Assist "replace named generic type with impl trait"
This is a follow-up PR to fix the assist "replace named generic type with impl trait" described in #14626 to filter invalid param types. It integrates the feedback given in PR #14816 .
The change updates the logic to determine when a function parameter is safe to replace a type param with its trait implementation. Some parameter definitions are invalid & should not be replaced by their traits, therefore skipping the assist completely.
First, all usages of the generic type under the cursor are determined. These usage references are checked to see if they occur outside the function parameter list. If an outside reference is found, e.g. in body, return type or where clause, the assist is skipped. All remaining usages need to appear only in the function param list. For each usage the param type is further inspected to see if it's valid. The logic to determine if a function parameter is valid, follows a heuristic and may not cover all possible parameter definitions.
With this change the following param types (as given in [this comment](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/pull/14816#discussion_r1206834603)) are not replaced & therefore skip the assist.
```rust
fn foo<P: Trait>(
_: <P as Trait>::Assoc, // within path type qualifier
_: <() as OtherTrait<P>>::Assoc, // same as above
_: P::Assoc, // associated type shorthand
_: impl OtherTrait<P> // generic arg in impl trait (note that associated type bindings are fine)
_: &dyn Fn(P) // param type and/or return type for Fn* traits
) {}
```
The change updates the logic to determine if a function parameter is
valid for replacing the type param with the trait implementation.
First all usages are determined, to check if they are used outside the function
parameter list. If an outside reference is found, e.g. in body, return type or
where clause, the assist is skipped. All remaining usages only appear in the
function param list. For each usage the param type is checked to see if
it's valid.
**Please note** the logic currently follows a heuristic and may not cover
all existing parameter declarations.
* determine valid usage references by checking ancestors (on AST level)
* split test into separate ones
fix: Fix nav target calculation discarding file ids from differing macro upmapping
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/14792
Turns out there was the assumption that upmapping from a macro will always end in the same root file, which is no longer the case thanks to `include!`
Add signature help for tuple patterns and expressions
~~These are somewhat wonky since their signature changes as you type depending on context but they help out nevertheless.~~ should be less wonky now with added parser and lowering recoveries
fix: Don't duplicate sysroot crates in rustc workspace
Since we handle `library` as the sysroot source directly in the rustc workspace, we now duplicate the crates there, once as sysroot and once as just plain workspace crate. This causes a variety of issues for `vec!` macros and similar that emit `$crate` tokens across crates.
Prioritize threads affected by user typing
To this end I’ve introduced a new custom thread pool type which can spawn threads using each QoS class. This way we can run latency-sensitive requests under one QoS class and everything else under another QoS class. The implementation is very similar to that of the `threadpool` crate (which is currently used by rust-analyzer) but with unused functionality stripped out.
I’ll have to rebase on master once #14859 is merged but I think everything else is alright :D
Fix edits for `convert_named_struct_to_tuple_struct`
Two fixes:
- When replacing syntax nodes, macro files weren't taken into account. Edits were simply made for `node.syntax().text_range()`, which would be wrong range when `node` is inside a macro file.
- We do ancestor node traversal for every struct name reference to find record expressions/patterns to edit, but we didn't verify that expressions/patterns do actually refer to the struct we're operating on.
Best reviewed one commit at a time.
Fixes#13780Fixes#14927
Previously we didn't verify that record expressions/patterns that were
found did actually point to the struct we're operating on. Moreover,
when that record expressions/patterns had missing child nodes, we would
continue traversing their ancestor nodes.
This code replaces the thread pool implementation we were using
previously (from the `threadpool` crate). By making the thread pool
aware of QoS, each job spawned on the thread pool can have a different
QoS class.
This commit also replaces every QoS class used previously with Default
as a temporary measure so that each usage can be chosen deliberately.
Specify thread types using Quality of Service API
<details>
<summary>Some background (in case you haven’t heard of QoS before)</summary>
Heterogenous multi-core CPUs are increasingly found in laptops and desktops (e.g. Alder Lake, Snapdragon 8cx Gen 3, M1). To maximize efficiency on this kind of hardware, it is important to provide the operating system with more information so threads can be scheduled on different core types appropriately.
The approach that XNU (the kernel of macOS, iOS, etc) and Windows have taken is to provide a high-level semantic API – quality of service, or QoS – which informs the OS of the program’s intent. For instance, you might specify that a thread is running a render loop for a game. This makes the OS provide this thread with as large a share of the system’s resources as possible. Specifying a thread is running an unimportant background task, on the other hand, is cause for it to be scheduled exclusively on high-efficiency cores instead of high-performance cores.
QoS APIs allows for easy configuration of many different parameters at once; for instance, setting QoS on XNU affects scheduling, timer latency, I/O priorities, and of course what core type the thread in question should run on. I don’t know any details on how QoS works on Windows, but I would guess it’s similar.
Hypothetically, taking advantage of these APIs would improve power consumption, thermals, battery life if applicable, etc.
</details>
# Relevance to rust-analyzer
From what I can tell the philosophy behind both the XNU and Windows QoS APIs is that _user interfaces should never stutter under any circumstances._ You can see this in the array of QoS classes which are available: the highest QoS class in both APIs is one intended explicitly for UI render loops.
Imagine rust-analyzer is performing CPU-intensive background work – maybe you just invoked Find Usages on `usize` or opened a large project – in this scenario the editor’s render loop should absolutely get higher priority than rust-analyzer, no matter what. You could view it in terms of “realtime-ness”: flight control software is hard realtime, audio software is soft realtime, GUIs are softer realtime, and rust-analyzer is not realtime at all. Of course, maximizing responsiveness is important, but respecting the rest of the system is more important.
# Implementation
I’ve tried my best to unify thread creation in `stdx`, where the new API I’ve introduced _requires_ specifying a QoS class. Different points along the performance/efficiency curve can make a great difference; the M1’s e-cores use around three times less power than the p-cores, so putting in this effort is worthwhile IMO.
It’s worth mentioning that Linux does not [yet](https://youtu.be/RfgPWpTwTQo) have a QoS API. Maybe translating QoS into regular thread priorities would be acceptable? From what I can tell the only scheduling-related code in rust-analyzer is Windows-specific, so ignoring QoS entirely on Linux shouldn’t cause any new issues. Also, I haven’t implemented support for the Windows QoS APIs because I don’t have a Windows machine to test on, and because I’m completely unfamiliar with Windows APIs :)
I noticed that rust-analyzer handles some requests on the main thread (using `.on_sync()`) and others on a threadpool (using `.on()`). I think it would make sense to run the main thread at the User Initiated QoS and the threadpool at Utility, but only if all requests that are caused by typing use `.on_sync()` and all that don’t use `.on()`. I don’t understand how the `.on_sync()`/`.on()` split that’s currently present was chosen, so I’ve let this code be for the moment. Let me know if changing this to what I proposed makes any sense.
To avoid having to change everything back in case I’ve misunderstood something, I’ve left all threads at the Utility QoS for now. Of course, this isn’t what I hope the code will look like in the end, but I figured I have to start somewhere :P
# References
<ul>
<li><a href="https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/Performance/Conceptual/power_efficiency_guidelines_osx/PrioritizeWorkAtTheTaskLevel.html">Apple documentation related to QoS</a></li>
<li><a href="67e155c940/include/pthread/qos.h">pthread API for setting QoS on XNU</a></li>
<li><a href="https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/quality-of-service">Windows’s QoS classes</a></li>
<li>
<details>
<summary>Full documentation of XNU QoS classes. This documentation is only available as a huge not-very-readable comment in a header file, so I’ve reformatted it and put it here for reference.</summary>
<ul>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_USER_INTERACTIVE</code>: A QOS class which indicates work performed by this thread is interactive with the user.</strong></p><p>Such work is requested to run at high priority relative to other work on the system. Specifying this QOS class is a request to run with nearly all available system CPU and I/O bandwidth even under contention. This is not an energy-efficient QOS class to use for large tasks. The use of this QOS class should be limited to critical interaction with the user such as handling events on the main event loop, view drawing, animation, etc.</p></li>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_USER_INITIATED</code>: A QOS class which indicates work performed by this thread was initiated by the user and that the user is likely waiting for the results.</strong></p><p>Such work is requested to run at a priority below critical user-interactive work, but relatively higher than other work on the system. This is not an energy-efficient QOS class to use for large tasks. Its use should be limited to operations of short enough duration that the user is unlikely to switch tasks while waiting for the results. Typical user-initiated work will have progress indicated by the display of placeholder content or modal user interface.</p></li>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_DEFAULT</code>: A default QOS class used by the system in cases where more specific QOS class information is not available.</strong></p><p>Such work is requested to run at a priority below critical user-interactive and user-initiated work, but relatively higher than utility and background tasks. Threads created by <code>pthread_create()</code> without an attribute specifying a QOS class will default to <code>QOS_CLASS_DEFAULT</code>. This QOS class value is not intended to be used as a work classification, it should only be set when propagating or restoring QOS class values provided by the system.</p></li>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_UTILITY</code>: A QOS class which indicates work performed by this thread may or may not be initiated by the user and that the user is unlikely to be immediately waiting for the results.</strong></p><p>Such work is requested to run at a priority below critical user-interactive and user-initiated work, but relatively higher than low-level system maintenance tasks. The use of this QOS class indicates the work should be run in an energy and thermally-efficient manner. The progress of utility work may or may not be indicated to the user, but the effect of such work is user-visible.</p></li>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_BACKGROUND</code>: A QOS class which indicates work performed by this thread was not initiated by the user and that the user may be unaware of the results.</strong></p><p>Such work is requested to run at a priority below other work. The use of this QOS class indicates the work should be run in the most energy and thermally-efficient manner.</p></li>
<li><p><strong><code>QOS_CLASS_UNSPECIFIED</code>: A QOS class value which indicates the absence or removal of QOS class information.</strong></p><p>As an API return value, may indicate that threads or pthread attributes were configured with legacy API incompatible or in conflict with the QOS class system.</p></li>
</ul>
</details>
</li>
</ul>
feat: Assist to replace generic with impl trait
This adds a new assist named "Replace named generic with impl". It is the inverse operation to the existing "Replace impl trait with generic" assist.
It allows to refactor the following statement:
```rust
// 👇 cursor
fn new<T$0: ToString>(input: T) -> Self {}
```
to be transformed into:
```rust
fn new(input: impl ToString) -> Self {}
```
* adds new helper function `impl_trait_type` to create AST node
* add method to remove an existing generic param type from param list
Closes#14626
This removes an existing generic param from the `GenericParamList`. It
also considers to remove the extra colon & whitespace to the previous
sibling.
* change order to get all param types first and mark them as mutable
before the first edit happens
* add helper function to remove a generic parameter
* fix test output
This adds a new assist named "replace named generic with impl" to move
the generic param type from the generic param list into the function
signature.
```rust
fn new<T: ToString>(input: T) -> Self {}
```
becomes
```rust
fn new(input: impl ToString) -> Self {}
```
The first step is to determine if the assist can be applied, there has
to be a match between generic trait param & function paramter types.
* replace function parameter type(s) with impl
* add new `impl_trait_type` function to generate the new trait bounds with `impl` keyword for use in the
function signature
fix: assists no longer break indentation
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/14674
These are _ad hoc_ patches for a number of assists that can produce incorrectly indented code, namely:
- generate_derive
- add_missing_impl_members
- add_missing_default_members
Some general solution is required in future, as the same problem arises in many other assists, e.g.
- replace_derive_with...
- generate_default_from_enum...
- generate_default_from_new
- generate_delegate_methods
(the list is incomplete)
Fix: a TODO and some clippy fixes
- fix(todo): implement IntoIterator for ArenaMap<IDX, V>
- chore: remove unused method
- fix: remove useless `return`s
- fix: various clippy lints
- fix: simplify boolean test to a single negation
fix: introduce new type var when expectation for ref pat is not ref
Fixes#14840
When we infer the type of ref patterns, its expected type may not be reference type: 1) expected type is an unresolved inference variable, or 2) expected type is erroneously other kind of type. In either case, we should produce a reference type with a new type variable rather than an error type so that we can continue inferring the inner patterns without further errors because of the (possible) type mismatch of this pattern.