Implement recursion in mir interpreter without recursion
This enables interpreting functions with deep stack + profiling. I also applied some changes to make it faster based on the profiling result.
Unify getter and setter assists
This PR combines what previously have been two different files into a single file. I want to talk about the reasons why I did this. The issue that prompted this PR ( and before I forget : this pr fixes#15080 ) mentions an interesting behavior. We combine these two assists into an assist group and the order in which the assists are listed in this group changes depending on the text range of the selected area. The reason for that is that VSCode prioritizes actions that have a bigger impact in a smaller area and until now generate setter assist was only possible to be invoked for a single field whereas you could generate multiple getters for the getter assist. So I used the latter's infra to make former applicable to multiple fields, hence the unification. So this PR solves in essence
1. Make `generate setter` applicable to multiple fields
2. Provide a consistent order of the said assists in listing.
Don't show `unresolved-field` diagnostic for missing names
I don't think reporting ``"no field `[missing name]` on type `SomeType`"`` makes much sense because it's a syntax error rather than a semantic error. We already report a syntax error for it and I find it sufficient.
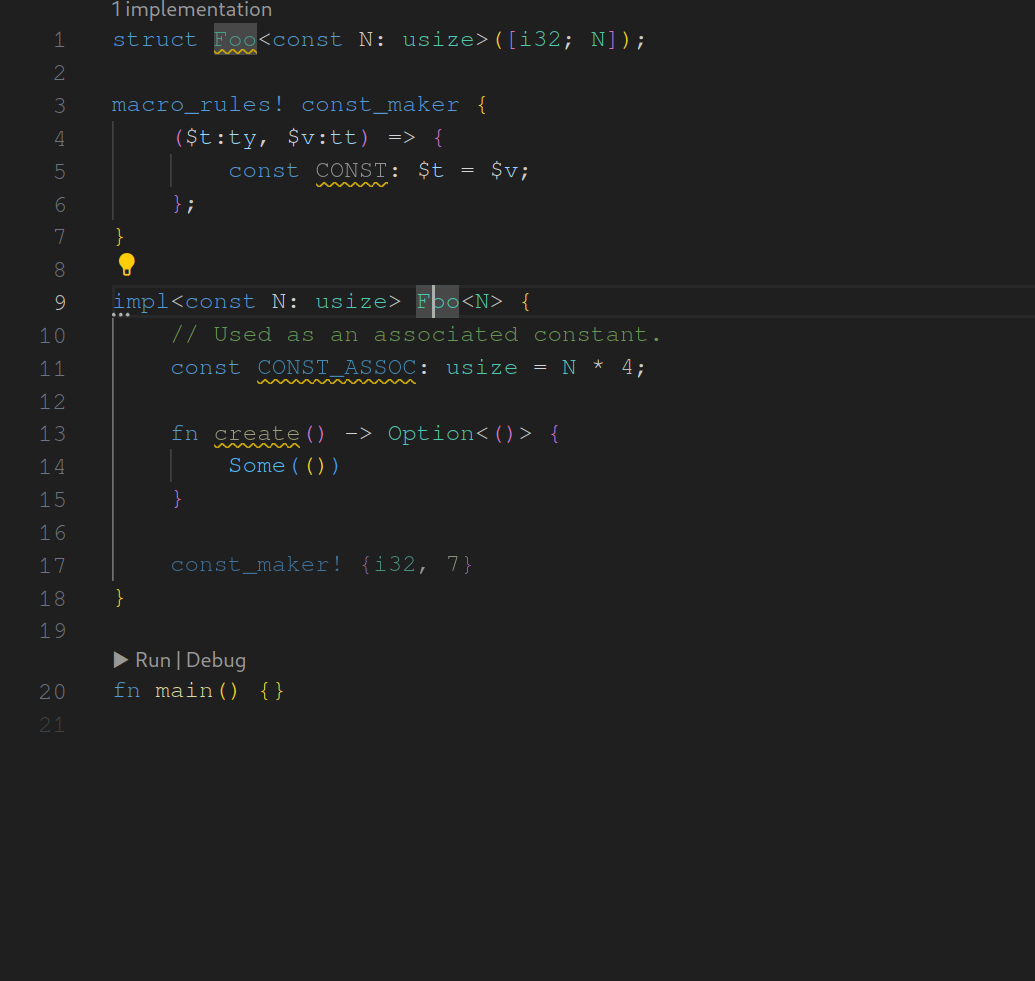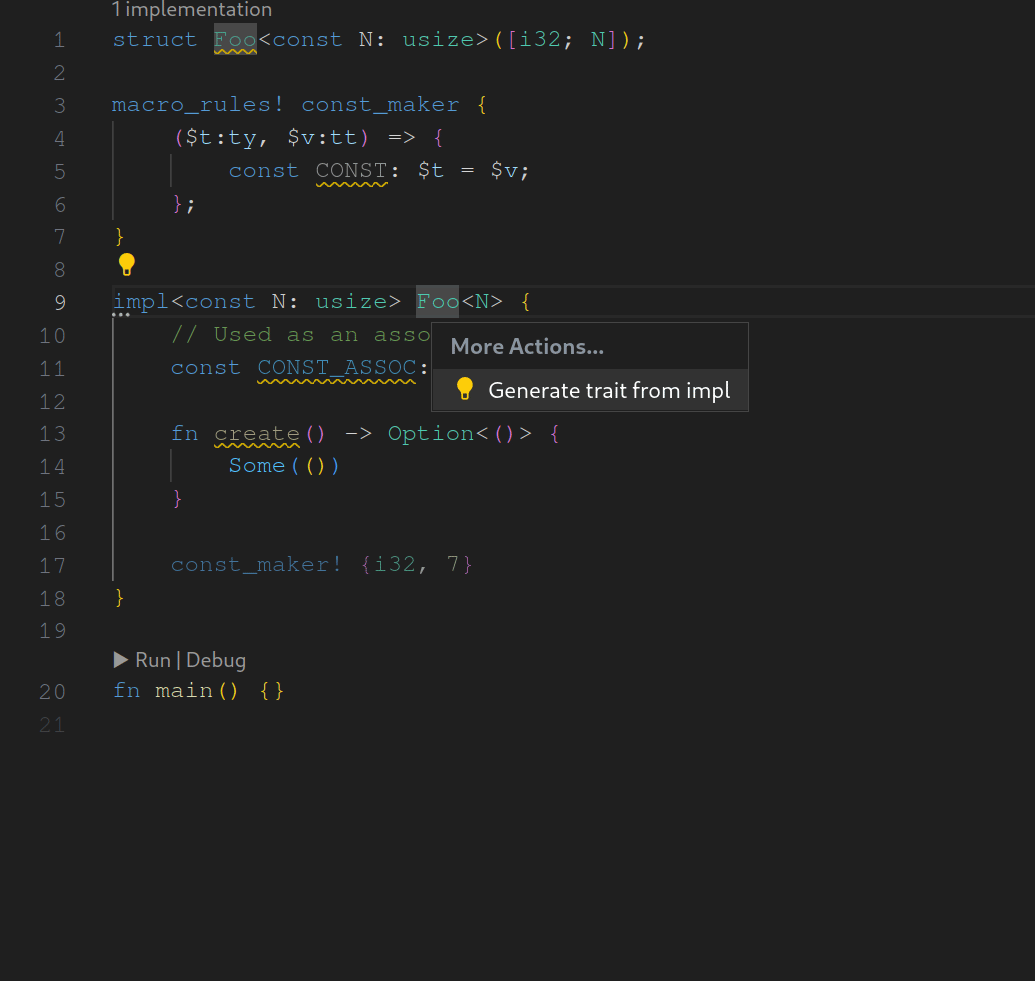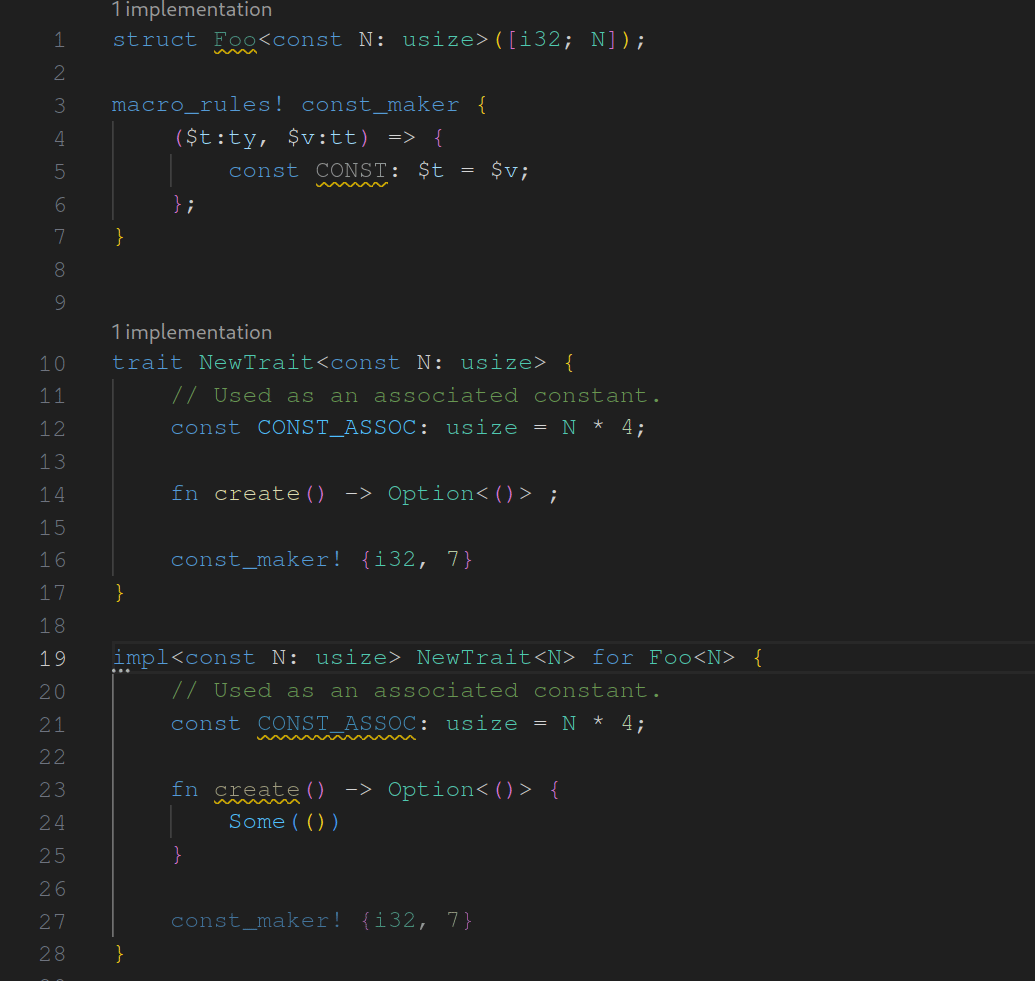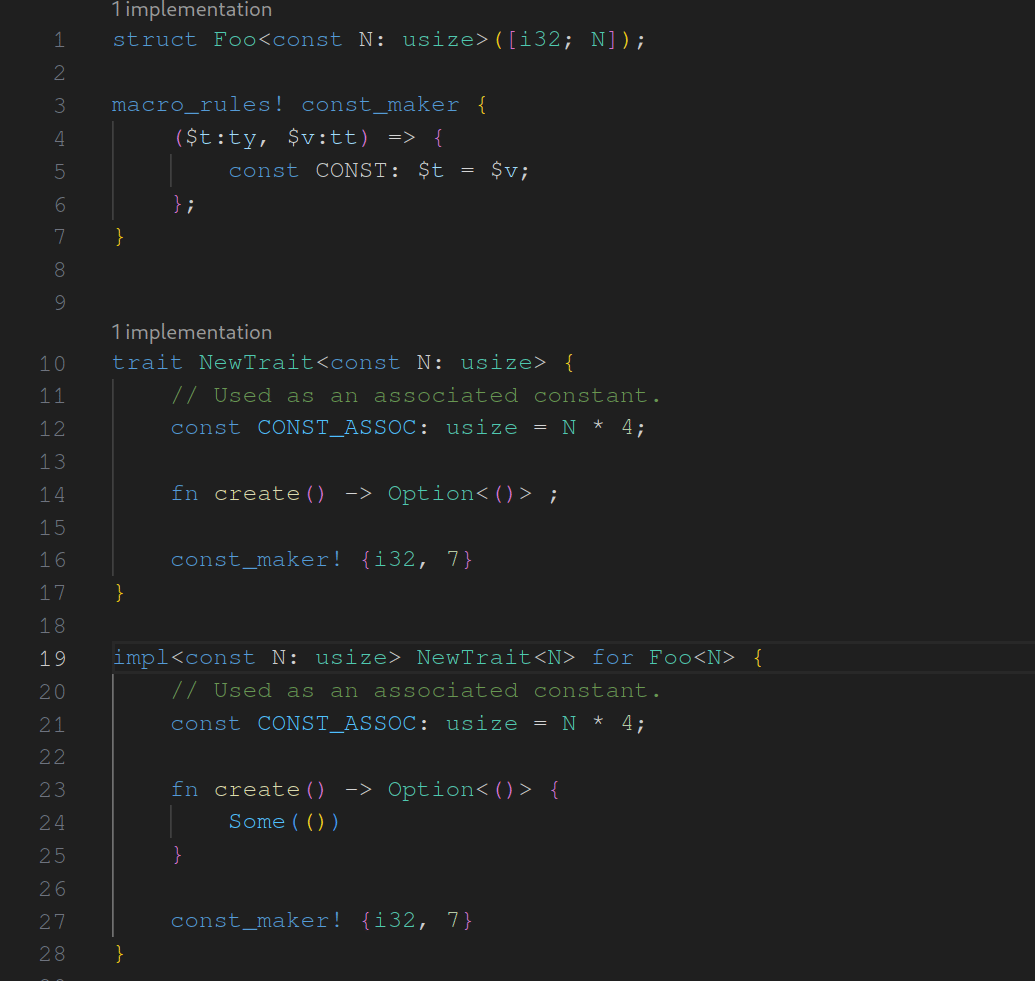
assist : generate trait from impl
fixes#14987 . As the name suggests this assist is used to generate traits from inherent impls while adapting the original impl to fit to the newly generated trait. I made some decisions regarding when the assist should be applicable. These are surely open to discussion. I looking forward to any feedback.
Disable remove unnecessary braces diagnotics for self imports
Disable `remove unnecessary braces` diagnostic if the there is a `self` inside the bracketed `use`
Fix#15191
Support GATs in bounds for associated types
Chalk has a dedicated IR for bounds on trait associated type: `rust_ir::InlineBound`. We have been failing to convert GATs inside those bounds from our IR to chalk IR. This PR provides an easy fix for it: properly take GATs into account during the conversion.
Map our diagnostics to rustc and clippy's ones
And control their severity by lint attributes `#[allow]`, `#[deny]` and ... .
It doesn't work with proc macros and I would like to fix that before merge but I don't know how to do it.
internal: Format let-else
As nightly finally got support for it I went ahead and formatted r-a with the latest nightly, then with the latest stable (in case other stuff changed)
Split out project loading capabilities from rust-analyzer crate
External tools currently depend on the entire lsp infra for no good reason so let's lift that out so those tools have something better to depend on
Clean up `ImportMap`
There are several things in `hir_def::import_map` that are never used. This PR removes them and restructures the code. Namely:
- Removes `Query::name_only`, because it's *always* true.
- Because of this, we never took advantage of storing items' full path. This PR removes `ImportPath` and changes `ImportInfo` to only store items' name, which should reduce the memory consumption to some extent.
- Removes `SearchMode::Contains` for `Query` because it's never used.
- Merges `Query::assoc_items_only` and `Query::exclude_import_kinds` into `Query::assoc_mode`, because the latter is never used besides filtering associated items out.
Best reviewed one commit at a time. I made sure each commit passes full test suite. I can squash the first three commits if needed.
Use anonymous lifetime where possible
Because anonymous lifetimes are *super* cool.
More seriously, I believe anonymous lifetimes, especially those in impl headers, reduce cognitive load to a certain extent because they usually signify that they are not relevant in the signature of the methods within (or that we can apply the usual lifetime elision rules even if they are relevant).
Fix runnable detection for `#[tokio::test]`
fix#15141
It is hacky, and it wouldn't work for e.g. this case:
```Rust
use ::core::prelude;
#[prelude::v1::test]
fn foo() {
}
```
But it works for the tokio case. We should use the name resolution here somehow, and after that we should probably also get rid of the ast based `test_related_attribute` function.
internal: add `library` fixture meta
Currently, there is no way to specify `CrateOrigin` of a file fixture ([this] might be a bug?). This PR adds `library` meta to explicitly specify the fixture to be `CrateOrigin::Library` and also makes sure crates that belong to a library source root are set `CrateOrigin::Library`.
(`library` isn't really the best name. It essentially means that the crate is outside workspace but `non_workspace_member` feels a bit too long. Suggestions for the better name would be appreciated)
Additionally:
- documents the fixture meta syntax as thoroughly as possible
- refactors relevant code
[this]: 4b06d3c595/crates/base-db/src/fixture.rs (L450)
Fix `self` and `super` path resolution in block modules
This PR fixes `self` and `super` path resolution with block modules involved.
Previously, we were just going up the module tree count-of-`super` times without considering block modules in the way, and then if we ended up in a block `DefMap`, we adjust "to the containing crate-rooted module". While this seems to work in most real-world cases, we failed to resolve them within peculiar module structures.
`self` and `super` should actually be resolved to the nearest non-block module, and the paths don't necessarily resolve to a crate-rooted module. This PR makes sure every `self` and `super` segment in paths are resolved to a non-block module.
internal: support `#[rustc_coinductive]`
rust-lang/rust#100386 changed the trait solver so that `Sized` is treated as coinductive trait, just like auto traits. This is now controlled by the perma-unstable `#[rustc_coinductive]` attribute (rust-lang/rust#108033), which this PR adds support for.
In practice, I don't think this matters much if at all. Currently we don't give chalk enough information so chalk cannot precisely (dis)prove `Sized` bounds.
internal: Add run-tests command
This command is similar to `cargo test` except that it uses r-a to run tests instead of compiling and running them with rustc. This is slower than `cargo test` and it is only useful for me to see a bird view of what needs to be fixed. The current output is:
```
48 passed, 5028 failed, 2 ignored
All tests 174.74s, 648ginstr
```
48 is very low, but higher than what I originally thought.
Now that there is some passing tests, I can show the plan:
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/assets/45197576/76d7d777-1843-4ca4-b7fe-e463bdade6cb
That is, at the end, I want to be able to immediately re run every test after every change. (0.5s is not really immediate, but it's not finished yet, and it is way better than 8s that running a typical test in r-a will take on my system)
Change comparsion for checking if number is negative to include 128
The last byte in Little-Endian representation of negative integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
Potentially fixes#15096
Added a test near positive extermes and two test near negative
extermes as well one for 0.
Added a test using the `as` cast and one with comparison with 0.
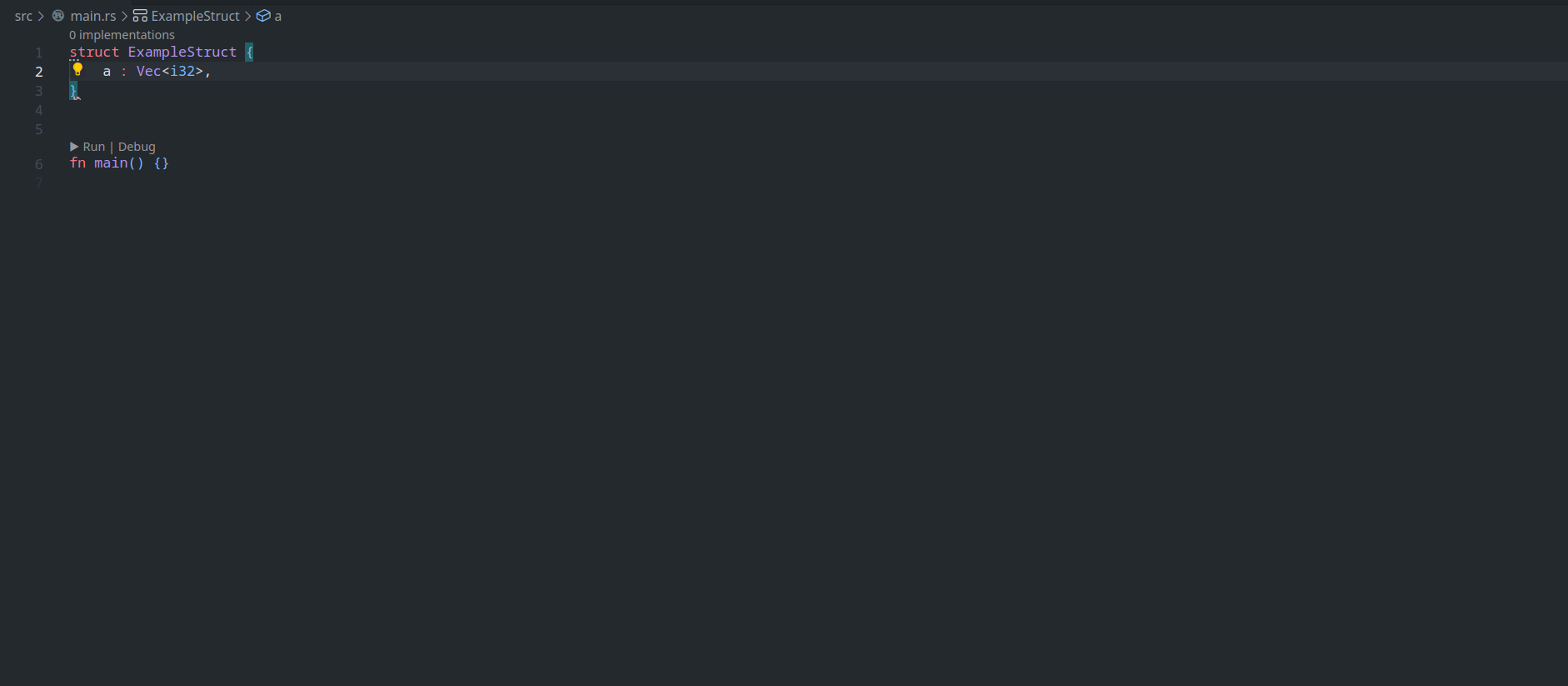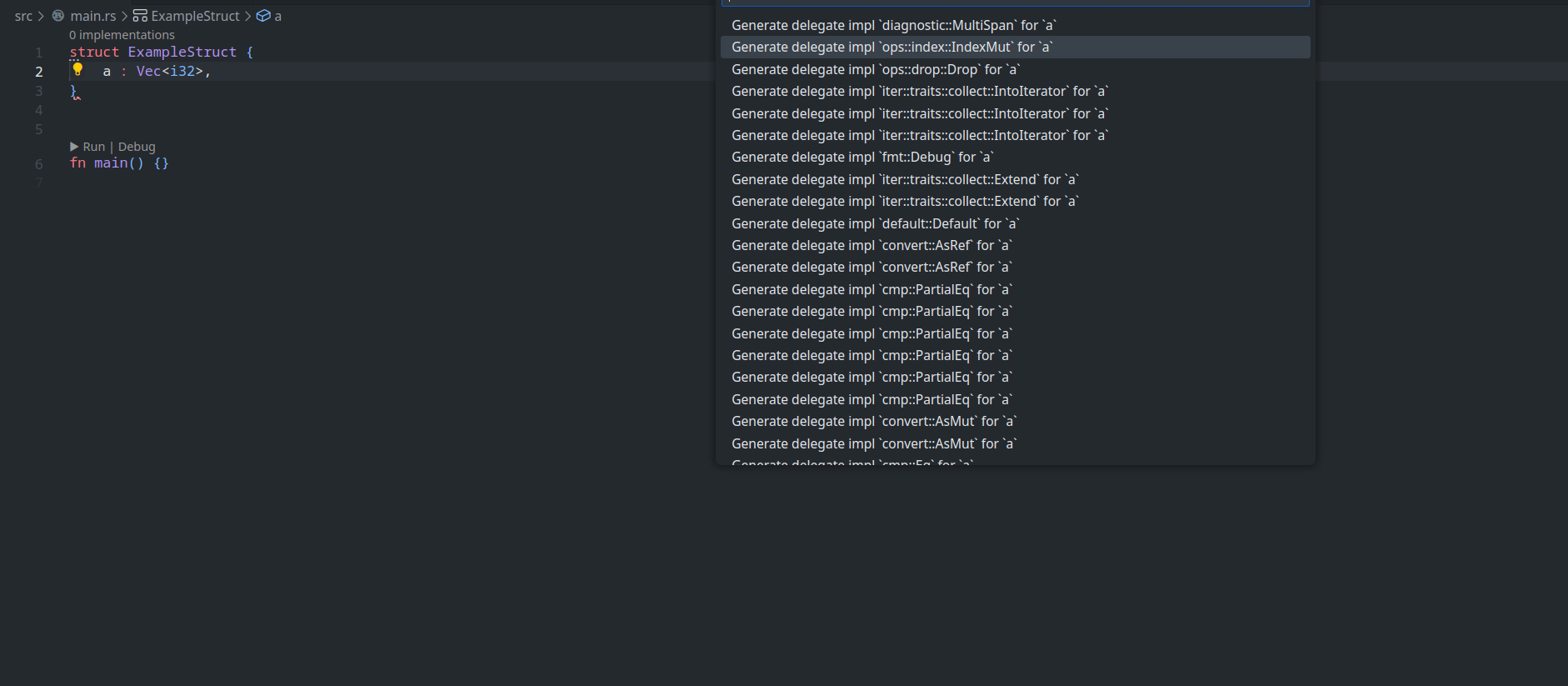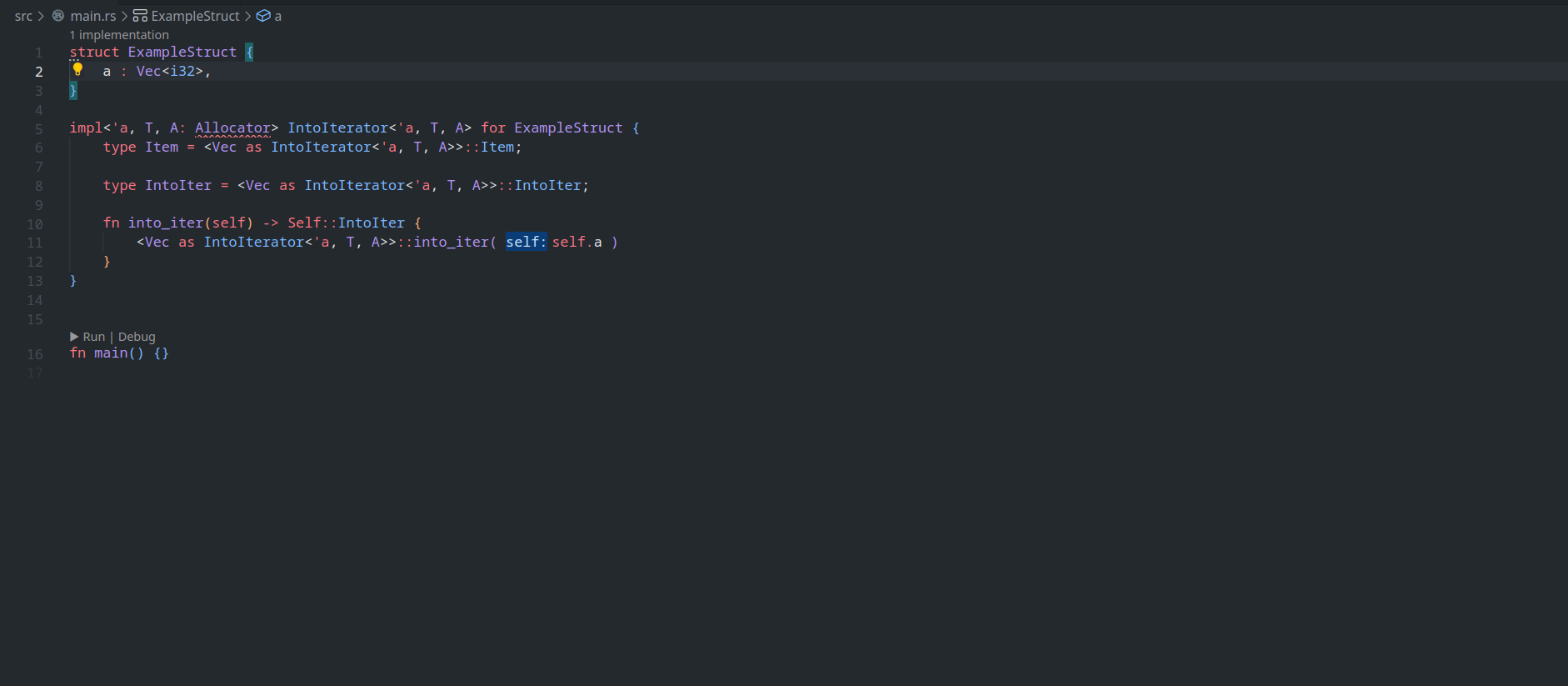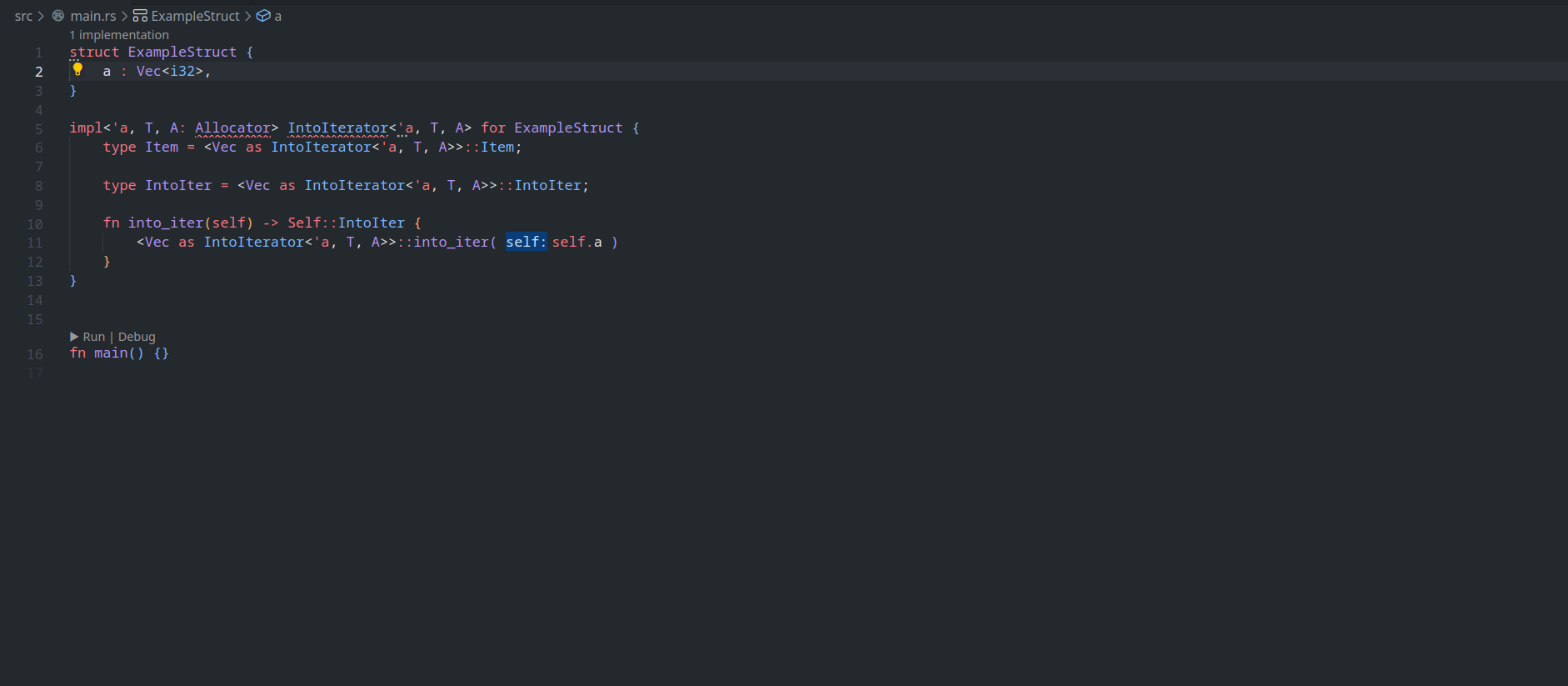
feature : assist delegate impl
This PR ( fixes#14386 ) introduces a new IDE assist that generates a trait impl for a struct that delegates a field. This is a draft because the current `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` produces some unwanted results when it deals with extern crates, an example of which I attach as a GIF.
GIFs :
1. A general case
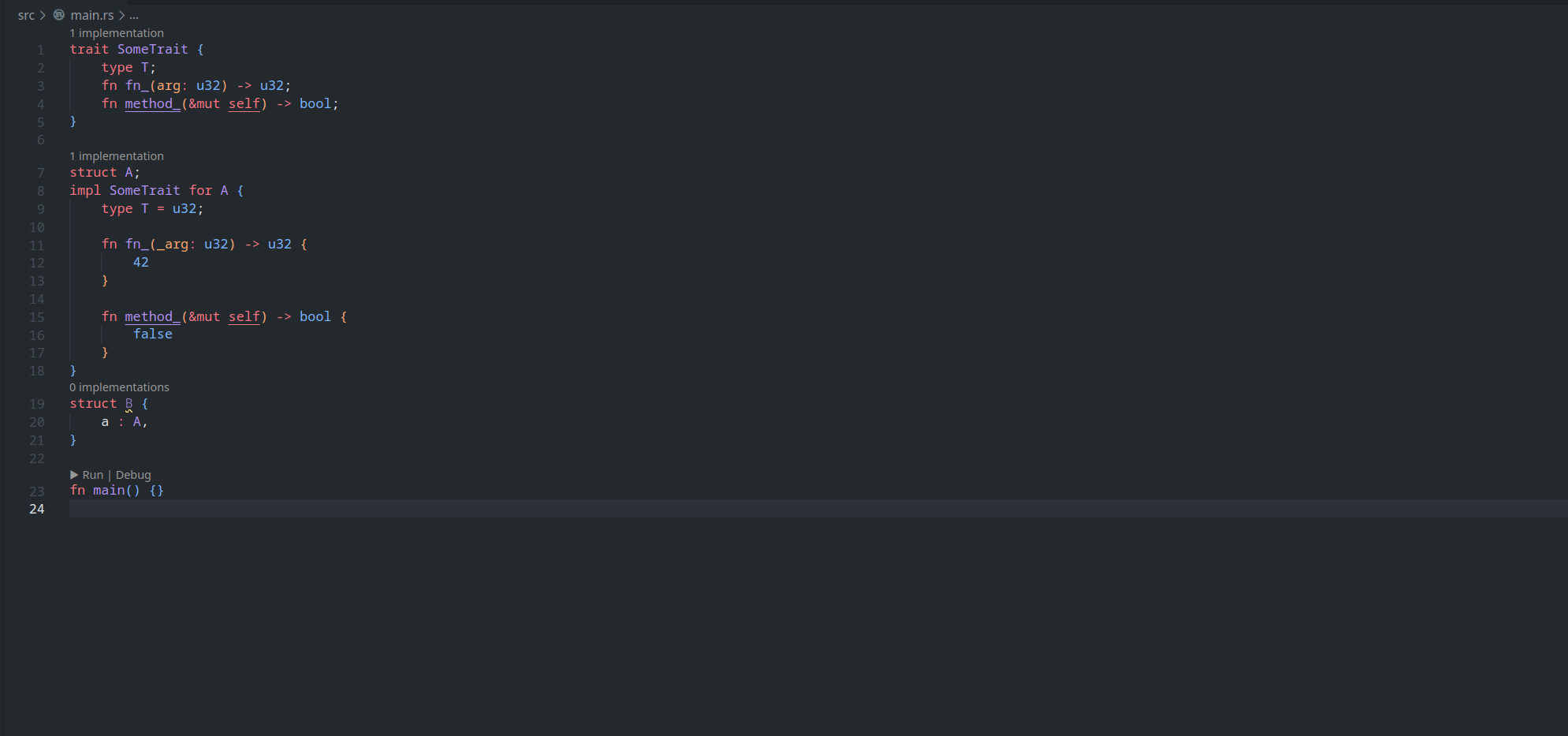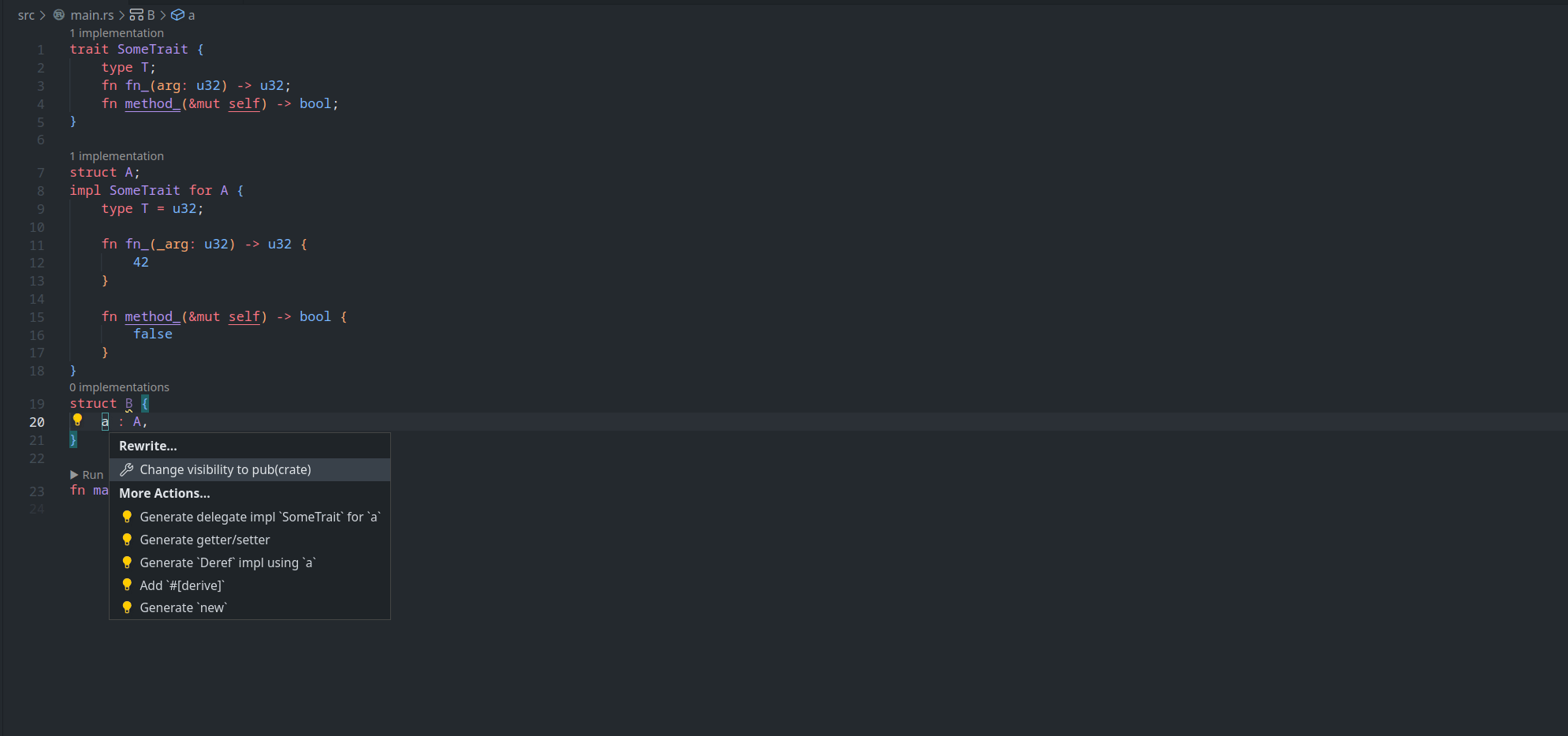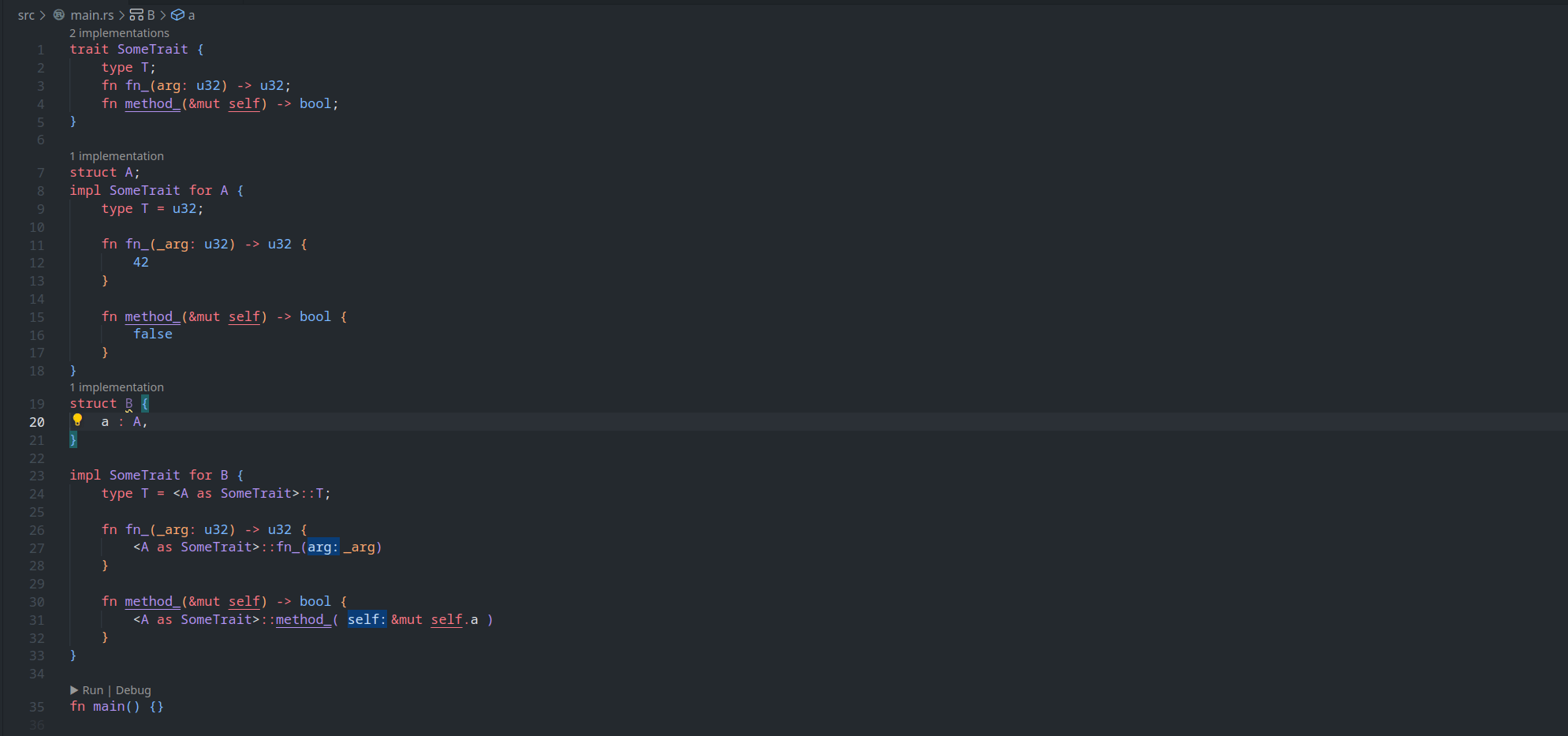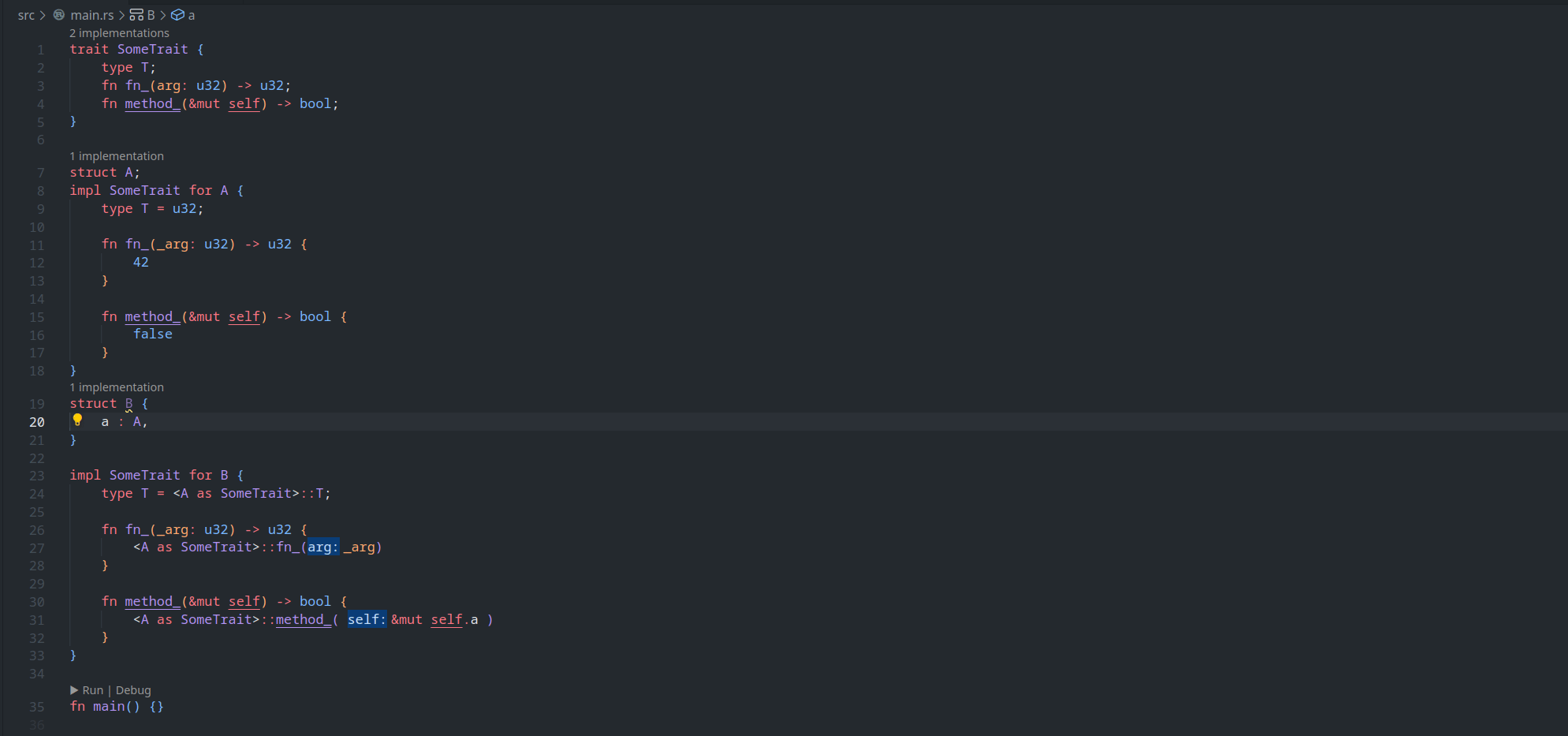
2. A case where `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` fails to correctly resolve a property ( take `Allocator` as an example ) to its full path, thus causing an error to occur. ( Not to even mention that resolving this causes another error `use of unstable library feature 'allocator_api'` to occur
Reason: The last byte in Little Endian representation of negative
integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before
the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
internal: remove spurious regex dependency
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place
where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
Remove scope_for_def calls as the definition have been removed entirely.
As a result of this change the problem with false path resolutions has been solved.
internal: Record file dependencies in crate graph construction
Should fix the bug mentioned in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/8623 where removing a crate root file will panic. I'm not too happy with the way this is done here but I can't think of a better way right now.
Deduplicate tuple indices for completion
Follow-up to #15026
A tuple struct may dereference to a primitive tuple (though unusual, which is why I previously overlooked this case). We should not show the same tuple index in completion in such cases.
Deduplication of indices among multiple tuple structs is already handled in the previous PR.
fix: deduplicate fields and types in completion
Fixes#15024
- `hir_ty::autoderef()` (which is only meant to be used outside `hir-ty`) now deduplicates types and completely resolves inference variables within.
- field completion now deduplicates fields of the same name and only picks such field of the first type in the deref chain.
Lower const params with a bad id
cc #7434
This PR adds an `InTypeConstId` which is a `DefWithBodyId` and lower const generic parameters into bodies using it, and evaluate them with the mir interpreter. I think this is the last unimplemented const generic feature relative to rustc stable.
But there is a problem: The id used in the `InTypeConstId` is the raw `FileAstId`, which changes frequently. So these ids and their bodies will be invalidated very frequently, which is bad for incremental analysis.
Due this problem, I disabled lowering for local crates (in library crate the id is stable since files won't be changed). This might be overreacting (const generic expressions are usually small, maybe it would be better enabled with bad performance than disabled) but it makes motivation for doing it in the correct way, and it splits the potential panic and breakages that usually comes with const generic PRs in two steps.
Other than the id, I think (at least I hope) other parts are in the right direction.
Properly format documentation for `SignatureHelpRequest`s
Properly formats function documentation instead of returning it raw when responding to `SignatureHelpRequest`s.
I added a test in `crates/rust-analyzer/tests/slow-tests/main.rs` -- not sure if this is the best location given the relevant code is in `crates/rust-analyzer` or if it's possible to test in a less heavyweight manner.
Closes#14958
fix: implemeted lifetime transformation fot assits
A part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/13363
I expect to implement transformation of const params in a separate PR
Other assists and a completion affected:
- `generate_function` currently just ignores lifetimes and, consequently, is not affected
- `inline_call` and `replace_derive_with...` don't seem to need lifetime transformation
- `trait_impl` (a completion) is fixed and tested
Add span to group.
This appears to fix#14959, but I've never contributed to rust-analyzer before and there were some things that confused me:
- I had to add the `fn byte_range` method to get it to build. This was added to rust in [April](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/109002), so I don't understand why it wasn't needed until now
- When testing, I ran into the fact that rust recently updated its `METADATA_VERSION`, so I had to test this with nightly-2023-05-20. But then I noticed that rust has its own copy of `rust-analyzer`, and the metadata version bump has already been [handled there](60e95e76d0). So I guess I don't really understand the relationship between the code there and the code here.
internal: Migrate some assists to use the structured snippet API
Migrates the following assists:
- `add_missing_impl_members`
- `extract_type_alias`
As an additional requirement, these assists are also migrated to use the mutable AST API, since otherwise there would be overlapping `Indel` spans
Infer return type for async function in `generate_function`
Part of #10122
In `generate_function` assist, when we infer the return type of async function we're generating, we should retrieve the type of parent await expression rather than the call expression itself.