Today, rust-analyzer (and rustc, and bat, and IntelliJ) fail badly on
some kinds of maliciously constructed code, like a deep sequence of
nested parenthesis.
"Who writes 100k nested parenthesis" you'd ask?
Well, in a language with macros, a run-away macro expansion might do
that (see the added tests)! Such expansion can be broad, rather than
deep, so it bypasses recursion check at the macro-expansion layer, but
triggers deep recursion in parser.
In the ideal world, the parser would just handle deeply nested structs
gracefully. We'll get there some day, but at the moment, let's try to be
simple, and just avoid expanding macros with unbalanced parenthesis in
the first place.
closes#9358
9808: fix: Look for enum variants and trait assoc functions when looking for lang items r=matklad a=Veykril
Examples for lang enum variants are the `Option` variants.
Assoc trait functions aren't being seen since they aren't declared in the direct module scope.
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
Fix ide_completion tests.
Move 'complete_record_literal' call to the main completion function.
Fix a rendering bug when snippet not available.
Checks if an expression is expected before adding completion for struct literal.
Move 'completion struct literal with private field' test to 'expressions.rs' test file.
Update 'expect' tests with new check in 'complete record literal'.
9764: fix: Don't use the module as the candidate node in fuzzy path flyimport r=Veykril a=Veykril
The problem was that the candidate node is whats being used for the scope, so using an inline module will yield the surrounding scope of the module instead of the scope of the module itself.
Also seems to fix the problem in this comment https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/9760#issuecomment-891125674, though I could not recreate that in a test for some reason.
Fixes#9760
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
9453: Add first-class limits. r=matklad,lnicola a=rbartlensky
Partially fixes#9286.
This introduces a new `Limits` structure which is passed as an input
to `SourceDatabase`. This makes limits accessible almost everywhere in
the code, since most places have a database in scope.
One downside of this approach is that whenever you query limits, you
essentially do an `Arc::clone` which is less than ideal.
Let me know if I missed anything, or would like me to take a different approach!
Co-authored-by: Robert Bartlensky <bartlensky.robert@gmail.com>
9567: remove unneded special case r=matklad a=matklad
bors r+
🤖
9568: feat: add 'for' postfix completion r=lnicola a=mahdi-frms
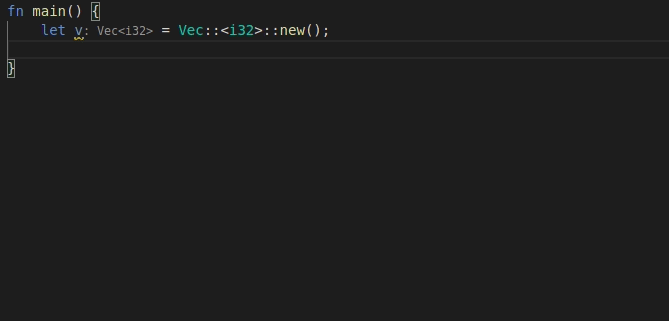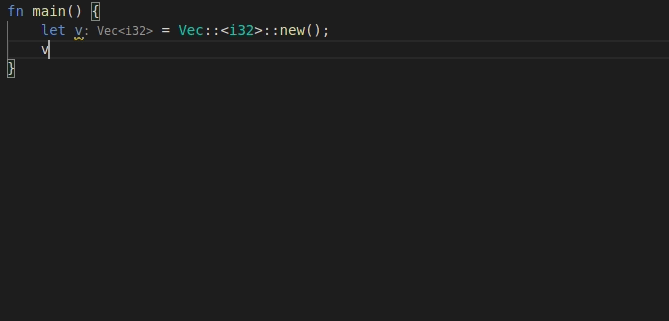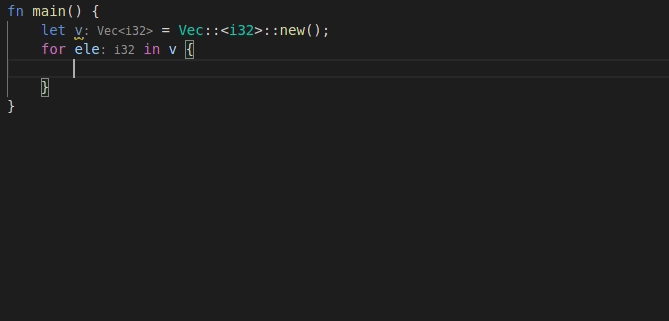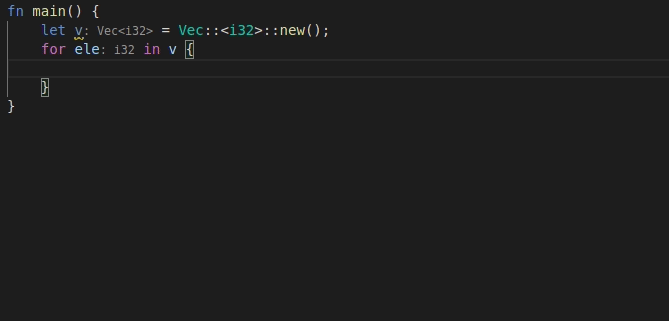
adds #9561
used ```ele``` as identifier for each element in the iteration
Co-authored-by: Aleksey Kladov <aleksey.kladov@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: mahdi-frms <mahdif1380@outlook.com>
Note that, while we don't currently have a fuzzy-matching score, it
makes sense to special-case postfix templates -- it's very annoying when
`.not()` gets sorted before `.not`. We might want to move this infra to
fuzzy matching, once we have that!
Before this PR, SourceChange used a bool and CompletionItem used an enum
to signify if edit is a snippet. It makes sense to use the same pattern
in both cases. `bool` feels simpler, as there's only one consumer of
this API, and all producers are encapsulated anyway (we check the
capability at the production site).
* Keep codegen adjacent to the relevant crates.
* Remove codgen deps from xtask, speeding-up from-source installation.
This regresses the release process a bit, as it now needs to run the
tests (and, by extension, compile the code).
The completion of cfg will look at the enabled cfg keys when
performing completion.
It will also look crate features when completing a feature cfg
option. A fixed list of known values for some cfg options are
provided.
For unknown keys it will look at the enabled values for that cfg key,
which means that completion will only show enabled options for those.