9979: fix: Incorrect up-mapping for tokens in derive attributes r=Veykril a=Veykril
Merely detaching the attributes causes incorrect spans to appear when mapping tokens up as the token ids resolve to the ranges of the stripped item so all the text ranges of its tokens are actually lower than the non-stripped ones.
Same fix as with attributes can be applied here, just replace the derive attribute with an equal amount of whitespace.
Fixes#9387
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
I don't think there's anything wrong with project_model depending on
proc_macro_api directly -- fundamentally, both are about gluing our pure
data model to the messy outside world.
However, it's easy enough to avoid the dependency, so why not.
As an additional consideration, `proc_macro_api` now pulls in `base_db`.
project_model should definitely not depend on that!
9975: minor: Fix panic caused by #9966 r=flodiebold a=flodiebold
Chalk can introduce new type variables when doing lazy normalization, so we have to do the proper 'fudging' after all.
Co-authored-by: Florian Diebold <flodiebold@gmail.com>
9965: minor: Don't ask for the builtin attribute input twice r=Veykril a=Veykril
`tt` and `item` here were the same, I misunderstood what the main input for attributes was in #9943
bors r+
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
9962: Add empty-body check to replace_match_with_if_let and re-prioritize choices r=elkowar a=elkowar
This PR changes some behaviour of the `replace_match_with_if_let` ide-assist.
Concretely, it makes two changes:
it introduces a check for empty expression bodies. This means that checks of the shape
```rs
match x {
A => {}
B => {
println!("hi");
}
}
```
will prefer to use the B branch as the first (and only) variant.
It also reprioritizes the importance of "happy" and "sad" patterns.
Concretely, if there are reasons to prefer having the sad pattern be the first (/only) pattern,
it will follow these.
This means that in the case of
```rs
match x {
Ok(_) => {
println!("Success");
}
Err(e) => {
println!("Failure: {}", e);
}
}
```
the `Err` variant will correctly be used as the first expression in the generated if.
Up until now, the generated code was actually invalid, as it would generate
```rs
if let Ok(_) = x {
println!("Success");
} else {
println!("Failure: {}", e);
}
```
where `e` in the else branch is not defined.
Co-authored-by: elkowar <5300871+elkowar@users.noreply.github.com>
9955: fix: Rename fails on renaming definitions created by macros instead of renaming the macro invocation r=Veykril a=Veykril
bors r+
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
9855: feature: Destructure Tuple Assist r=Veykril a=Booksbaum
Part of #8673. This PR only handles tuples, not TupleStruct and RecordStruct.
Code Assist to destructure a tuple into its items:
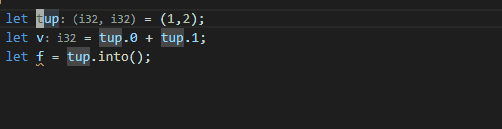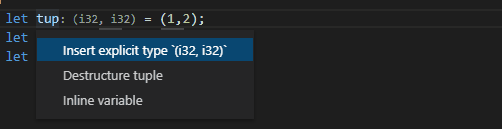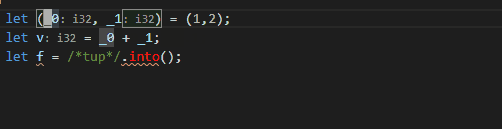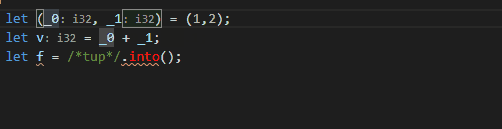
* Should work in nearly all pattern positions, like let assignment, function parameters, match arms, for loops, and nested variables (`if let Some($0t) = Some((1,2))`)
-> everywhere `IdentPat` is allowed
* Exception: If there's a sub-pattern (``@`):`
```rust
if let t @ (1..=3, 1..=3) = ... {}
// ^
```
-> `t` must be a `Name`; `TuplePat` (`(_0, _1)`) isn't allowed
* inside subpattern is ok:
```rust
let t @ (a, _) = ((1,2), 3);
// ^
```
->
```rust
let t @ ((_0, _1), _) = ((1,2), 3);
```
* Assist triggers only at tuple declaration, not tuple usage.
(might be useful especially when it creates a sub-pattern (after ``@`)` and only changes the usage under cursor -- but not part of this PR).
### References
References can be destructured:
```rust
let t = &(1,2);
// ^
let v = t.0;
```
->
```rust
let (_0, _1) = &(1,2);
let v = _0;
```
BUT: `t.0` and `_0` have different types (`i32` vs. `&i32`) -> `v` has now a different type.
I think that's acceptable: I think the destructure assist is mostly used in simple, immediate scopes and not huge existing code.
Additional Notes:
* `ref` has same behaviour (-> `ref` is kept for items)
```rust
let ref t = (1,2);
// ^
```
->
```rust
let (ref _0, ref _1) = (1,2);
```
* Rust IntelliJ Plugin: doesn't trigger with `&` or `ref` at all
### mutable
```rust
let mut t = (1,2);
// ^
```
->
```rust
let (mut _0, mut _1) = (1,2);
```
and
```rust
let t = &mut (1,2);
// ^
```
->
```rust
let (_0, _1) = &mut (1,2);
```
Again: with reference (`&mut`), `t.0` and `_0` have different types (`i32` vs `&mut i32`).
And there's an additional issue with `&mut` and assignment:
```rust
let t = &mut (1,2);
// ^
t.0 = 9;
```
->
```rust
let (_0, _1) = &mut (1,2);
_0 = 9;
// ^
// mismatched types
// expected `&mut {integer}`, found integer
// consider dereferencing here to assign to the mutable borrowed piece of memory
```
But I think that's quite a niche use case, so I don't catch that (`*_0 = 9;`)
Additional Notes:
* Rust IntelliJ Plugin: removes the `mut` (`let mut t = ...` -> `let (_0, _1) = ...`), doesn't trigger with `&mut`
### Binding after ``@``
Destructure tuple in sub-pattern is implemented:
```rust
let t = (1,2);
// ^
let v = t.0;
let f = t.into();
```
->
```rust
let t @ (_0, _1) = (1,2);
let v = _0;
let f = t.into();
```
BUT: Bindings after ``@`` aren't currently in stable and require `#![feature(bindings_after_at)]` (though should be generally [available quite soon](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/85305#event-5072889913) (with `1.56.0`)).
But I don't know how to check for an enabled feature -> Destructure tuple in sub-pattern [isn't enabled](a4ee6c7954/crates/ide_assists/src/handlers/destructure_tuple_binding.rs (L32)) yet.
* When Destructure in sub-pattern is enabled there are two assists:
* `Destructure tuple in place`:
```rust
let t = (1,2);
// ^
```
->
```rust
let (_0, _1) = (1,2);
let v = _0;
let f = /*t*/.into();
```
* `Destructure tuple in sub-pattern`:
```rust
let t = (1,2);
// ^
let v = t.0;
let f = t.into();
```
->
```rust
let t @ (_0, _1) = (1,2);
let v = _0;
let f = t.into();
```
* When Destructure in sub-pattern is disabled, only the first one is available and just named `Destructure tuple`
<br/>
<br/>
### Caveats
* Unlike in #8673 or IntelliJ rust plugin, I'm not leaving the previous tuple name at function calls.
**Reasoning**: It's not too unlikely the tuple variable shadows another variable. Destructuring the tuple while leaving the function call untouched, results in still a valid function call -- but now with another variable:
```rust
let t = (8,9);
let t = (1,2);
// ^
t.into()
```
=> Destructure Tuple
```rust
let t = (8,9);
let (_0, _1) = (1,2);
t.into()
```
`t.into()` is still valid -- using the first tuple.
Instead I comment out the tuple usage, which results in invalid code -> must be handled by user:
```rust
/*t*/.into()
```
* (though that might be a biased decision: For testing I just declared a lot of `t`s and quite ofen in lines next to each other...)
* Issue: there are some cases that results in still valid code:
* macro that accept the tuple as well as no arguments:
```rust
macro_rules! m {
() => { "foo" };
($e:expr) => { $e; "foo" };
}
let t = (1,2);
m!(t);
m!(/*t*/);
```
-> both calls are valid ([test](a4ee6c7954/crates/ide_assists/src/handlers/destructure_tuple_binding.rs (L1474)))
* Probably with tuple as return value. Changing the return value most likely results in an error -- but in another place; not where the tuple usage was.
-> not sure that's the best way....
Additional the tuple name surrounded by comment is more difficult to edit than just the name.
* Code Assists don't support snippet placeholder, and rust analyzer just the first `$0` -> unfortunately no editing of generated tuple item variables. Cursor (`$0`) is placed on first generated item.
<br/>
<br/>
### Issues
* Tuple index usage in macro calls aren't converted:
```rust
let t = (1,2);
// ^
let v = t.0;
println!("{}", t.0);
```
->
```rust
let (_0, _1) = (1,2);
let v = _0;
println!("{}", /*t*/.0);
```
([tests](a4ee6c7954/crates/ide_assists/src/handlers/destructure_tuple_binding.rs (L1294)))
* Issue is:
[name.syntax()](a4ee6c7954/crates/ide_assists/src/handlers/destructure_tuple_binding.rs (L242-L244)) in each [usage](a4ee6c7954/crates/ide_assists/src/handlers/destructure_tuple_binding.rs (L108-L113)) of a tuple is syntax & text_range in its file.
EXCEPT when tuple usage is in a macro call (`m!(t.0)`), the macro is expanded and syntax (and range) is based on that expanded macro, not in actual file.
That leads to several things:
* I cannot differentiate between calling the macro with the tuple or with tuple item:
```rust
macro_rules! m {
($t:expr, $i:expr) => { $t.0 + $i };
}
let t = (1,2);
m!(t, t.0);
```
-> both `t` usages are resolved as tuple index usage
* Range of resolved tuple index usage is in expanded macro, not in actual file
-> don't know where to replace index usage
-> tuple items passed into a macro are ignored, and only the tuple name itself is handled (uncommented)
* I'm not checking if the generated names conflict with already existing variables.
```rust
let _0 = 42; // >-|
let t = (1,2); // |
let v = _0; // <-|
// ^ 42
```
=> deconstruct tuple
```rust
let _0 = 42;
let (_0, _1) = (1,2); // >-|
let v = _0; // <-|
// ^ now 1
```
* I tried to get the scope at tuple declaration and its usages. And then iterate all names with [`process_all_names`](145b51f9da/crates/hir/src/semantics.rs (L935)). But that doesn't find all local names for declarations (`let t = (1,2)`) (for usages it does)
* This isn't unique to this Code Assist, but happen in others too (like `extract into variable` or `extract into function`). But here a name conflict is more likely (when destructuring multiple tuples, for examples nested ones (`let t = ((1,2),3)` -> `let (_0, _1) = ...` -> `let ((_0, _1), _1) = ...` -> error))
* IntelliJ rust plugin does handle this (-> name is `_00`)
Co-authored-by: BooksBaum <15612932+Booksbaum@users.noreply.github.com>
Note:
2nd Assist description is moved down: generated doc tests extracts now
all tests (previously only the first one). But it uses the first
`Assist` name -- which is the wrong one for the 2nd test. And 2nd assist
is currently disabled -> would fail anyway.
9921: Only add entries to SourceToDef dynmaps when they come from the same file r=matklad a=Veykril
Fixes https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/issues/9919
Running the test as described in the issue I do not get any eprintln output at all anymore.
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
cargo llvm-lines shows that path_to_error bloats the code. I don't think
I've needed this functionality recently, seems that we've fixed most of
the serialization problems. So let's just remove it. Should be easy to
add back if we ever need it, and it does make sense to keep the
`from_json` function around.
9896: internal: Only complete type annotations for patterns in function params r=Veykril a=Veykril
bors r+
Co-authored-by: Lukas Wirth <lukastw97@gmail.com>
Previously, we only inverted comparison operators (< and the like) if
the type implemented Ord. This doesn't make sense: if `<` works, then
`>=` will work as well!
Extra semantic checks greatly reduce robustness and predictability of
the assist, it's better to keep things simple.
9871: Jump to generated func r=mahdi-frms a=rylev
Worked on this with `@yoshuawuyts.`
We thought we ran into an issue with the `generate_function` assist where the code was not being generated in a certain situations. However, it wasn't actually a bug just a very confusing implementation where the cursor is not moved to the newly generated function. This happened when the return type was successfully inferred (and not unit). The function would be generated, but selection would not be changed.
This can be very confusing: If the function is generated somewhat far from where the assist is being invoked, the user never sees that the code was generated (nor are they given the chance to actually implement the function body).
This PR makes it so that the cursor is _always_ moved to somewhere in the newly generated function. In addition, if we can infer unit as the type, then we do not still generate `-> ()` as the return type. Instead, we simply omit the return type.
This means the selection will move to either one of two places:
* A generated `-> ()` return type when we cannot successfully infer the return type.
* The `todo!()` body when we can successfully infer the return type.
Co-authored-by: Ryan Levick <me@ryanlevick.com>
9863: feat: Generate default trait fn impl when generating `PartialEq` r=yoshuawuyts a=yoshuawuyts
Implements a default trait function body when generating the `PartialEq` trait for a type. Thanks!
r? `@veykril`
Co-authored-by: Yoshua Wuyts <yoshuawuyts@gmail.com>
9836: Refactor: quick clean-up of iteration idioms in the `vfs` crate r=matklad a=Some-Dood
This PR cleans up some of the iteration idioms used in the `vfs` crate. Most of the changes simply converted `for` loops into their `std::iter::Iterator`-method counterpart. Other changes required some inversion of logic to accommodate for better short-circuiting. Overall, there should be no behavioral changes. If there are any stylistic issues, I will gladly adhere to them and adjust the PR accordingly. Thanks!
Co-authored-by: Basti Ortiz <39114273+Some-Dood@users.noreply.github.com>
9828: Remove dependency on the system graphviz when rendering crate graph r=lnicola a=p32blo
This PR removes the need for having `graphviz` installed on the user system by using the `d3-graphviz` npm package.
The responsibility of rendering the svg output is moved to the extension while the rust side only handles the generation of the dot file.
This change also brings the following additional features:
- Allow zooming the view
- Ctrl+click to reset the zoom
- Adjust the color scheme to dark themes
- Works on any platform without installing graphviz locally
---
I’m not sure if this fits what you had in mind for the crates graph feature but I decided to submit it anyway to see if this is useful to anyone else.
A potential downside might be that it increases the extension size ( haven’t checked) but this feature already required the installation of graphviz on the user side, so the cost is just moved explicitly to the extension.
Feel free to make any suggestion or comments.
Co-authored-by: André Oliveira <p32blo@gmail.com>
9846: feat: Generate default trait fn impl when generating `Clone` r=Veykril a=yoshuawuyts
Implements a default trait function body when generating the `Clone` trait for a type. Thanks!
r? `@\veykril`
Co-authored-by: Yoshua Wuyts <yoshuawuyts@gmail.com>
9830: Enable more assists to generate default trait body impls r=Veykril a=yoshuawuyts
Enable more assists to benefit from trait body generation. Follow-up to #9825 and #9814.
__edit:__ I'd like to move the existing tests to this new file too, but I'll do that in a follow-up PR.
Co-authored-by: Yoshua Wuyts <yoshuawuyts@gmail.com>
9804: Generate method from call r=matklad a=mahdi-frms
Needs a bit of refactoring. Tests also should be added.
Co-authored-by: mahdi-frms <mahdif1380@outlook.com>
9825: Generate default impl when converting #[derive(Default)] to manual impl r=Veykril a=yoshuawuyts
Similar to https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/9814, but for `#[derive(Default)]`. Thanks!
## Follow-up steps
I've added the tests inside `handlers/replace_derive_with_manual_impl.rs` again, but I'm planning a follow-up PR to extract these to `utils/` so we can share them between assists - and maybe even add another assist just for the purpose of testing these impls (e.g. `generate_default_trait_body`).
The step after _that_ is likely to fill out the remaining traits, so we can make it so whenever RA auto-completes a trait which also can be derived, we provide a default function body.
Co-authored-by: Yoshua Wuyts <yoshuawuyts@gmail.com>
From the dawn of time, when dinosaurs roamed the and we didn't have
hierarchical profiling, there was the `latest_requests` infra we used to
track the time of ten last requests.
Today, no one is actually using it and, what's more, it itself became
pretty useless -- LSP grew way more chatty, and 10 requests don't really
paint any kind of picture.
Personally, it's been years since I last looked at latest requests in
the status output.
So, let's remove a tiny bit of state from the big ball of complexity
that is `GlobalState` and `main_loop`!
Today, rust-analyzer (and rustc, and bat, and IntelliJ) fail badly on
some kinds of maliciously constructed code, like a deep sequence of
nested parenthesis.
"Who writes 100k nested parenthesis" you'd ask?
Well, in a language with macros, a run-away macro expansion might do
that (see the added tests)! Such expansion can be broad, rather than
deep, so it bypasses recursion check at the macro-expansion layer, but
triggers deep recursion in parser.
In the ideal world, the parser would just handle deeply nested structs
gracefully. We'll get there some day, but at the moment, let's try to be
simple, and just avoid expanding macros with unbalanced parenthesis in
the first place.
closes#9358
We generally avoid "syntax only" helper wrappers, which don't do much:
they make code easier to write, but harder to read. They also make
investigations harder, as "find_usages" needs to be invoked both for the
wrapped and unwrapped APIs