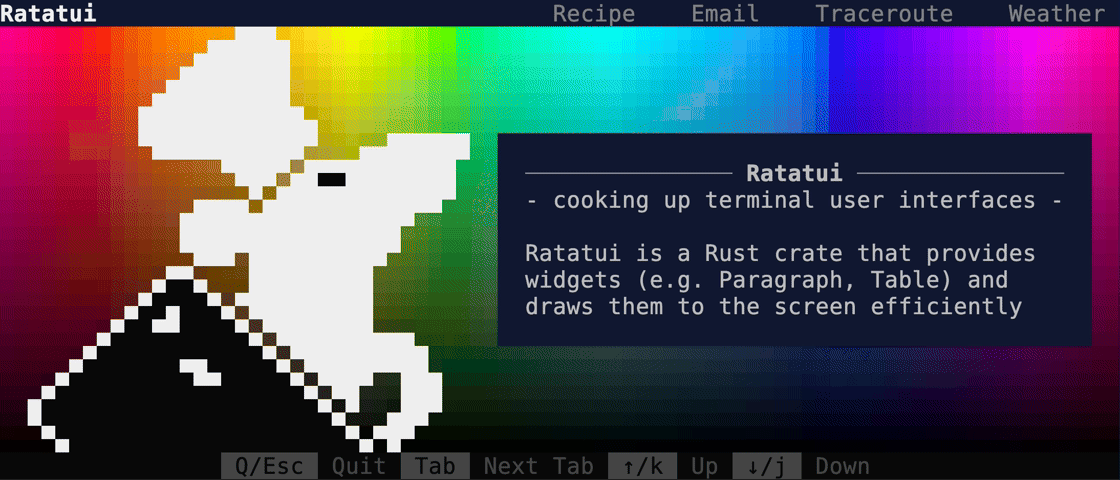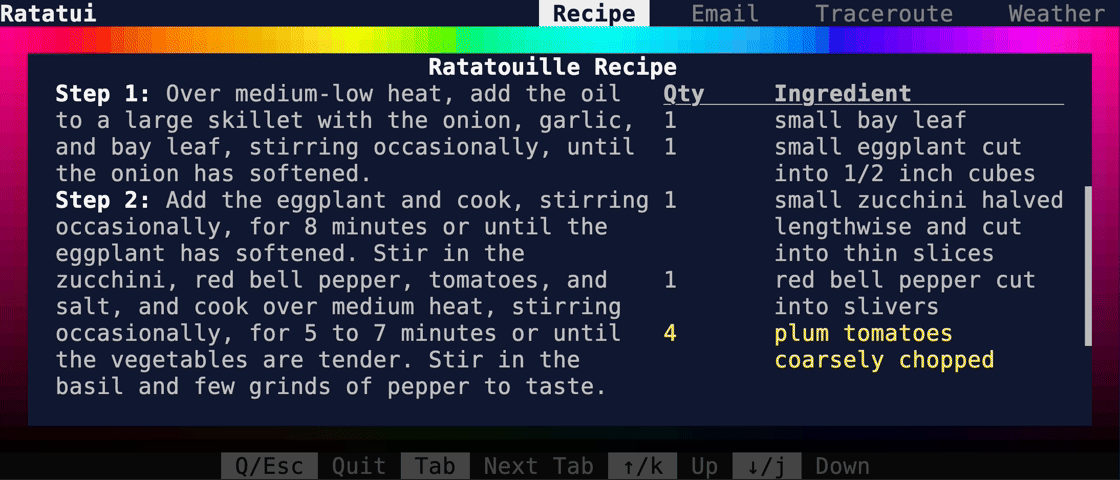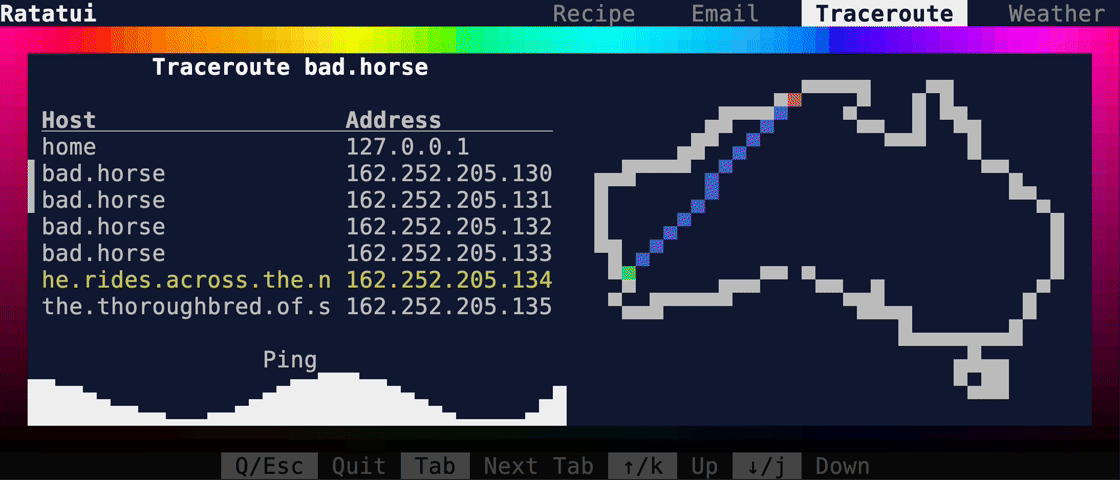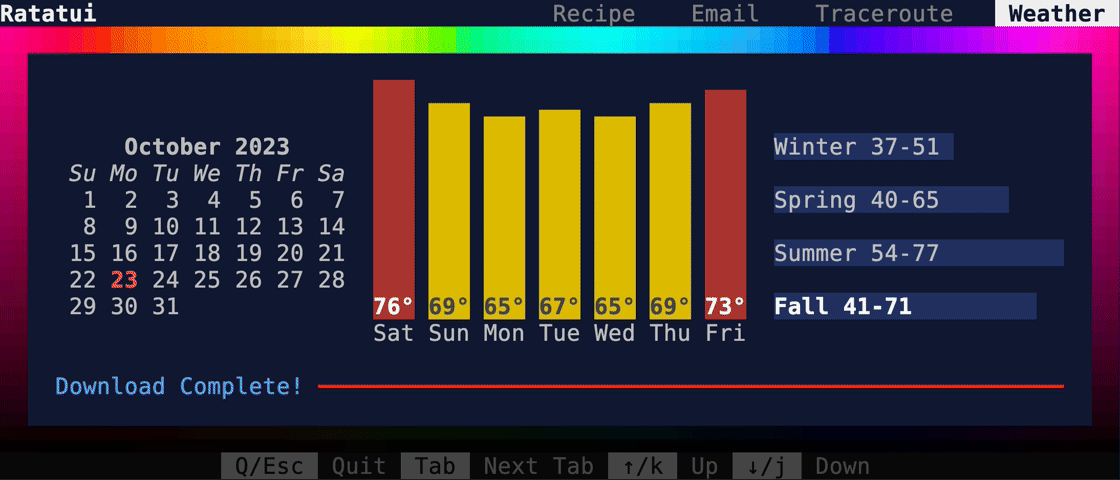
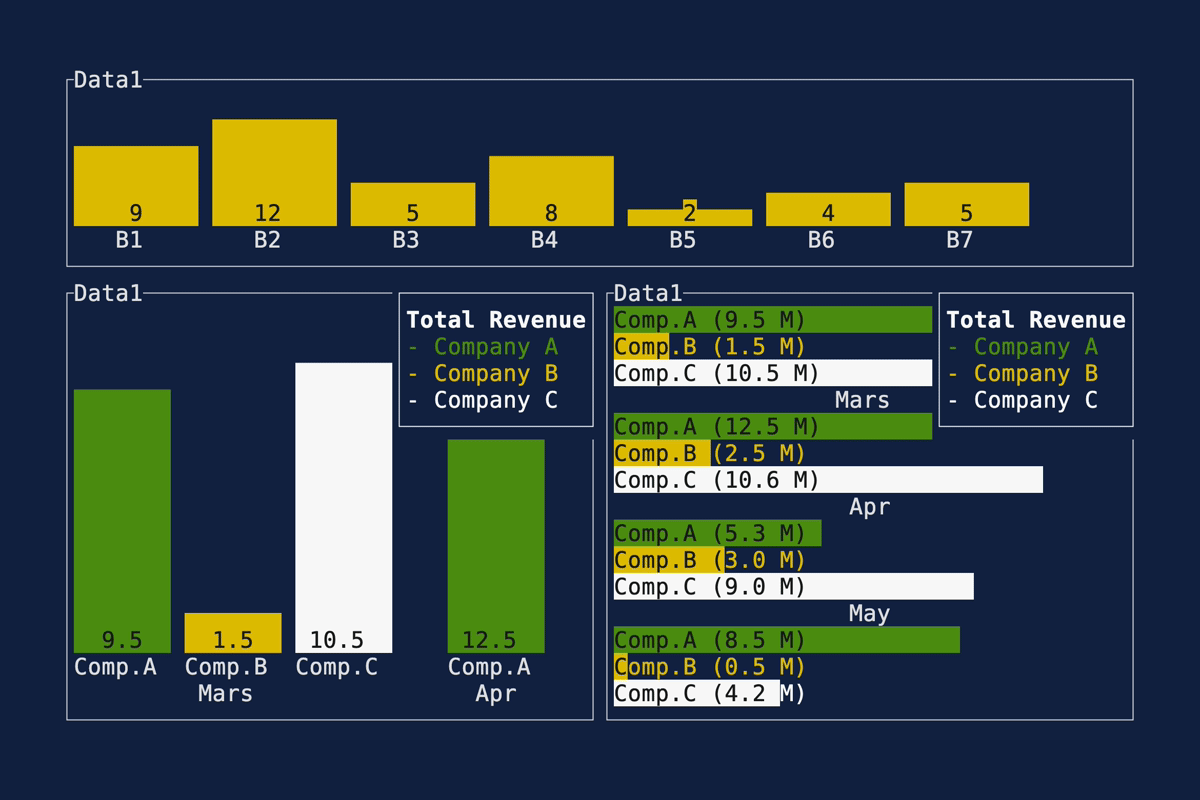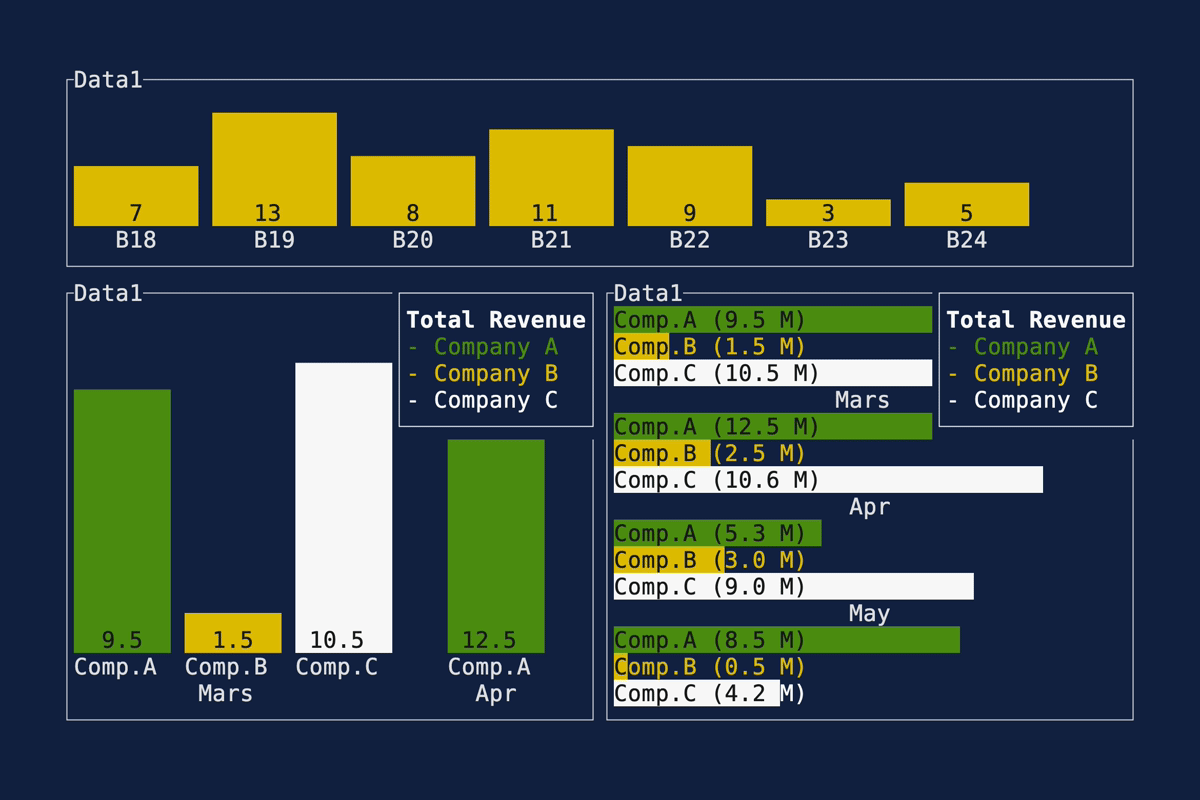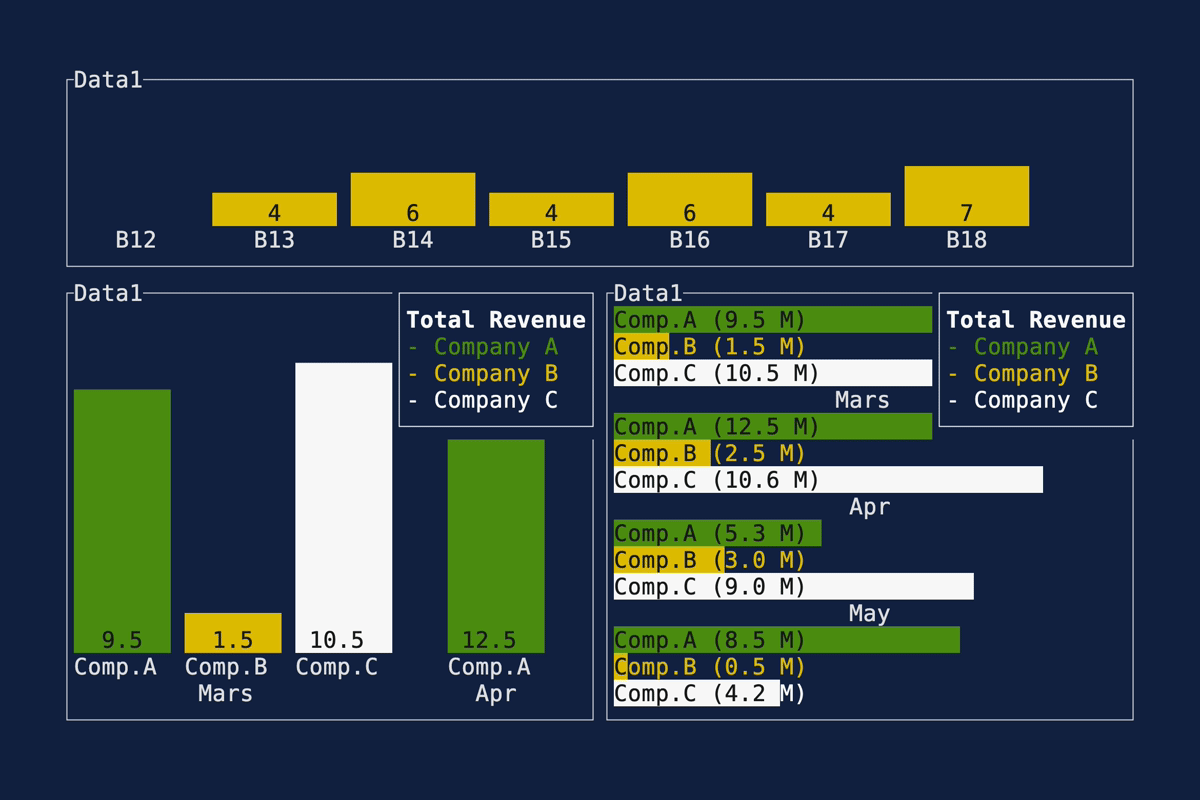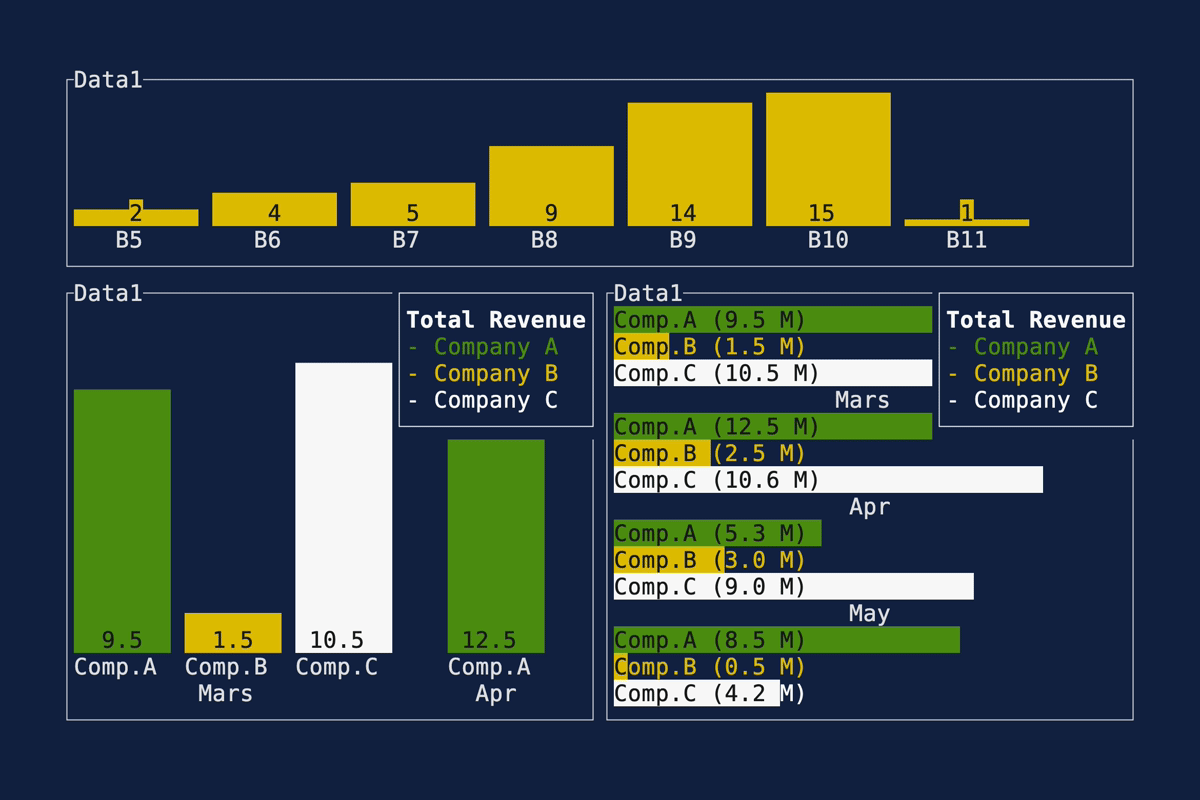
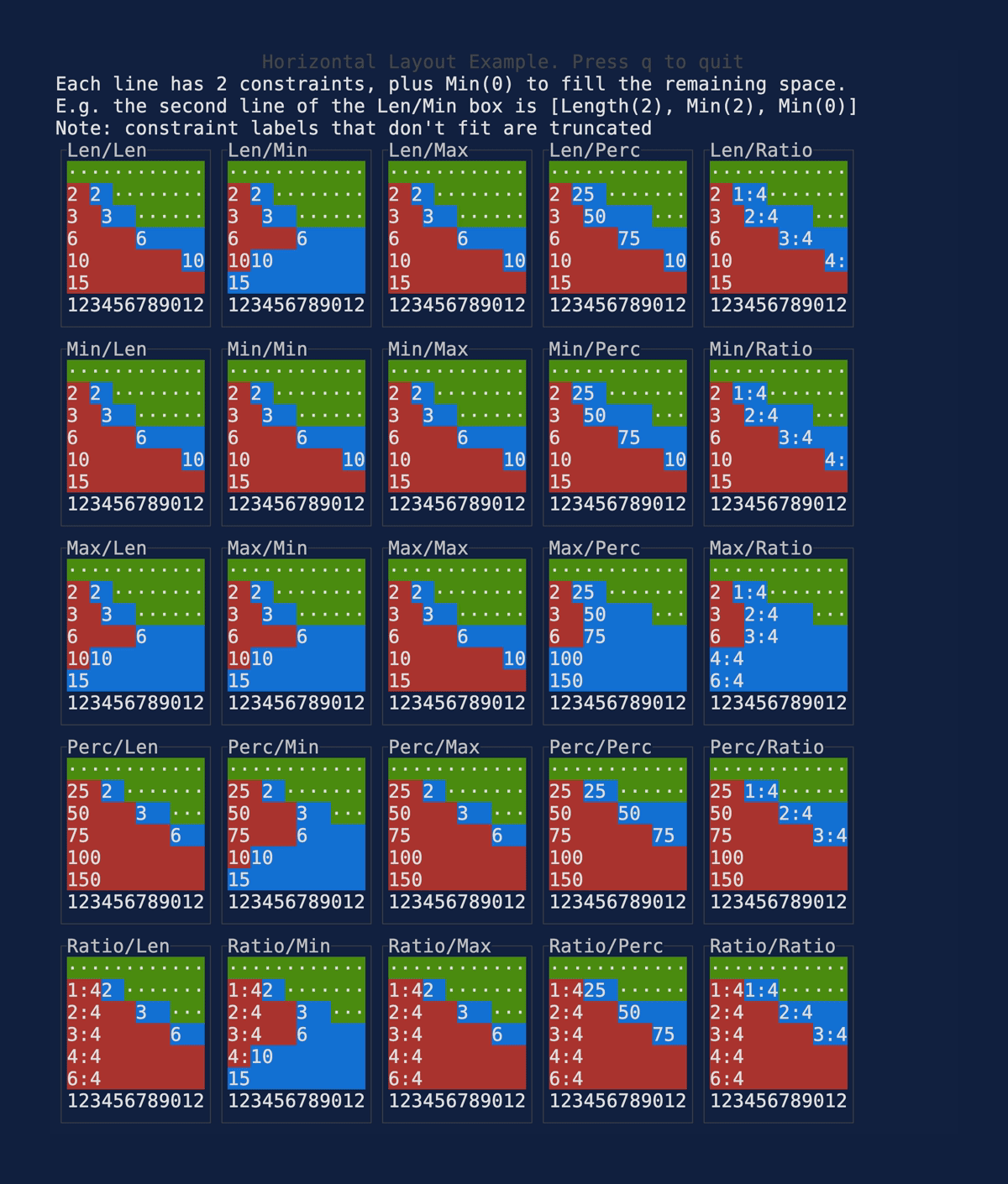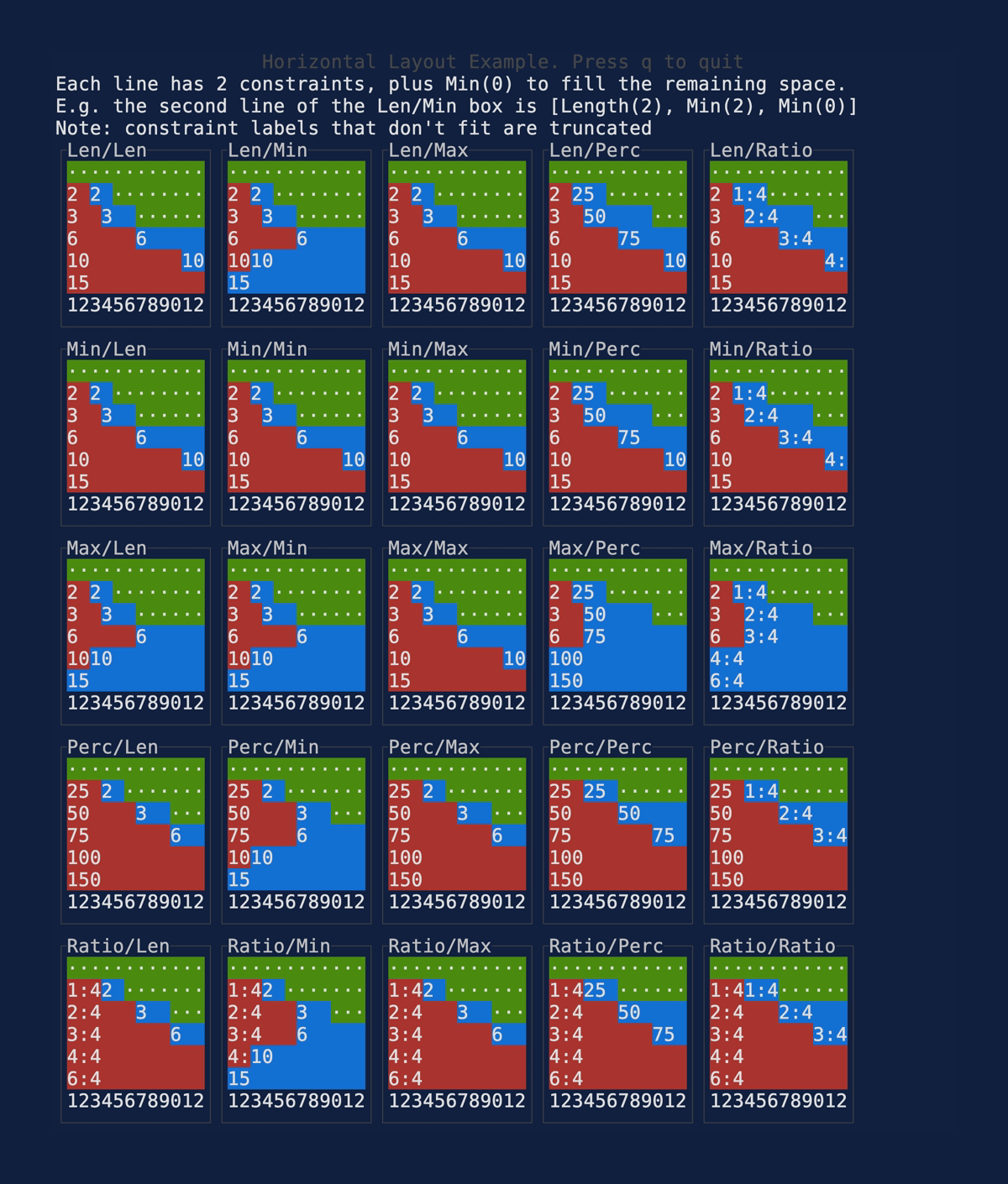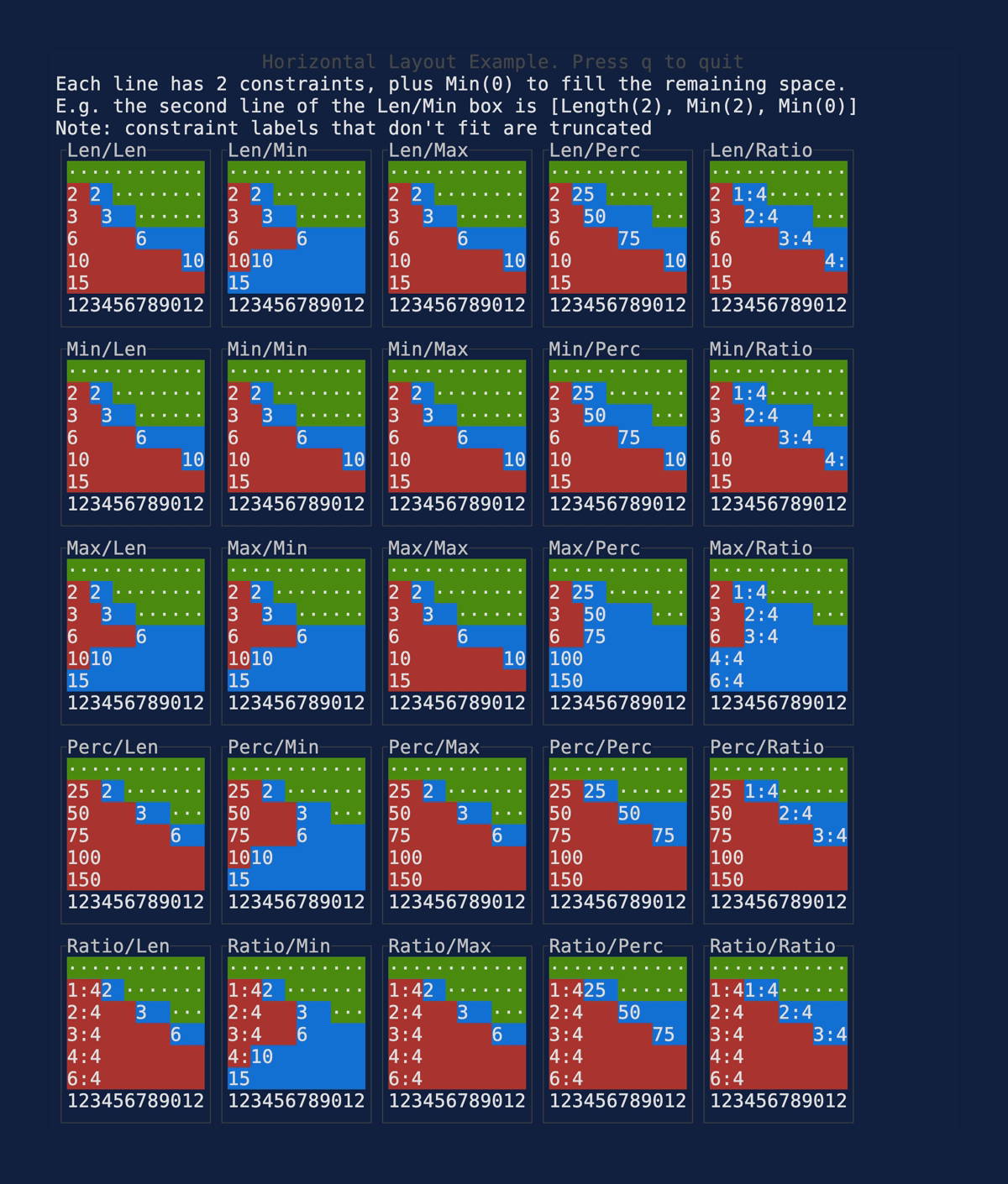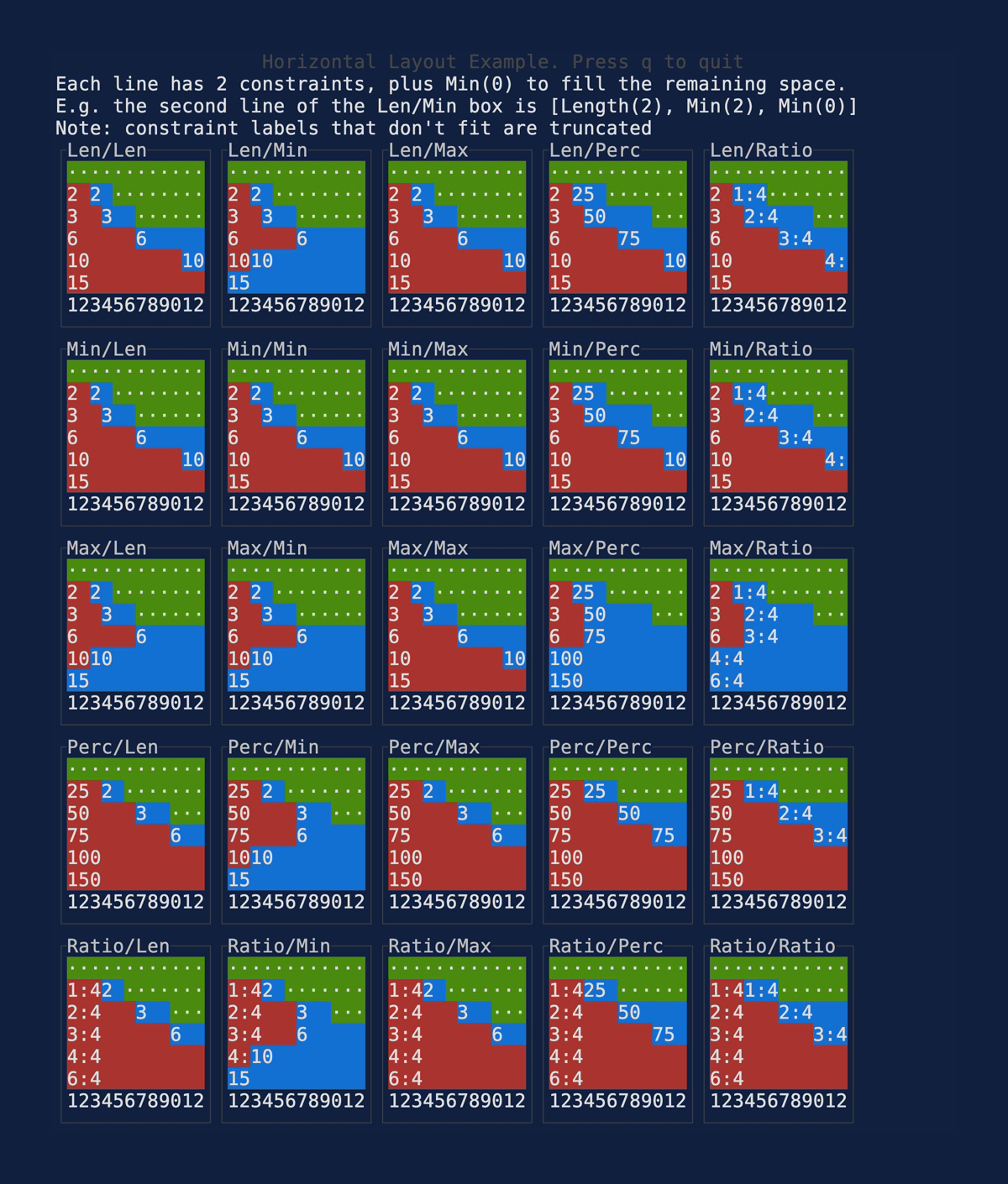
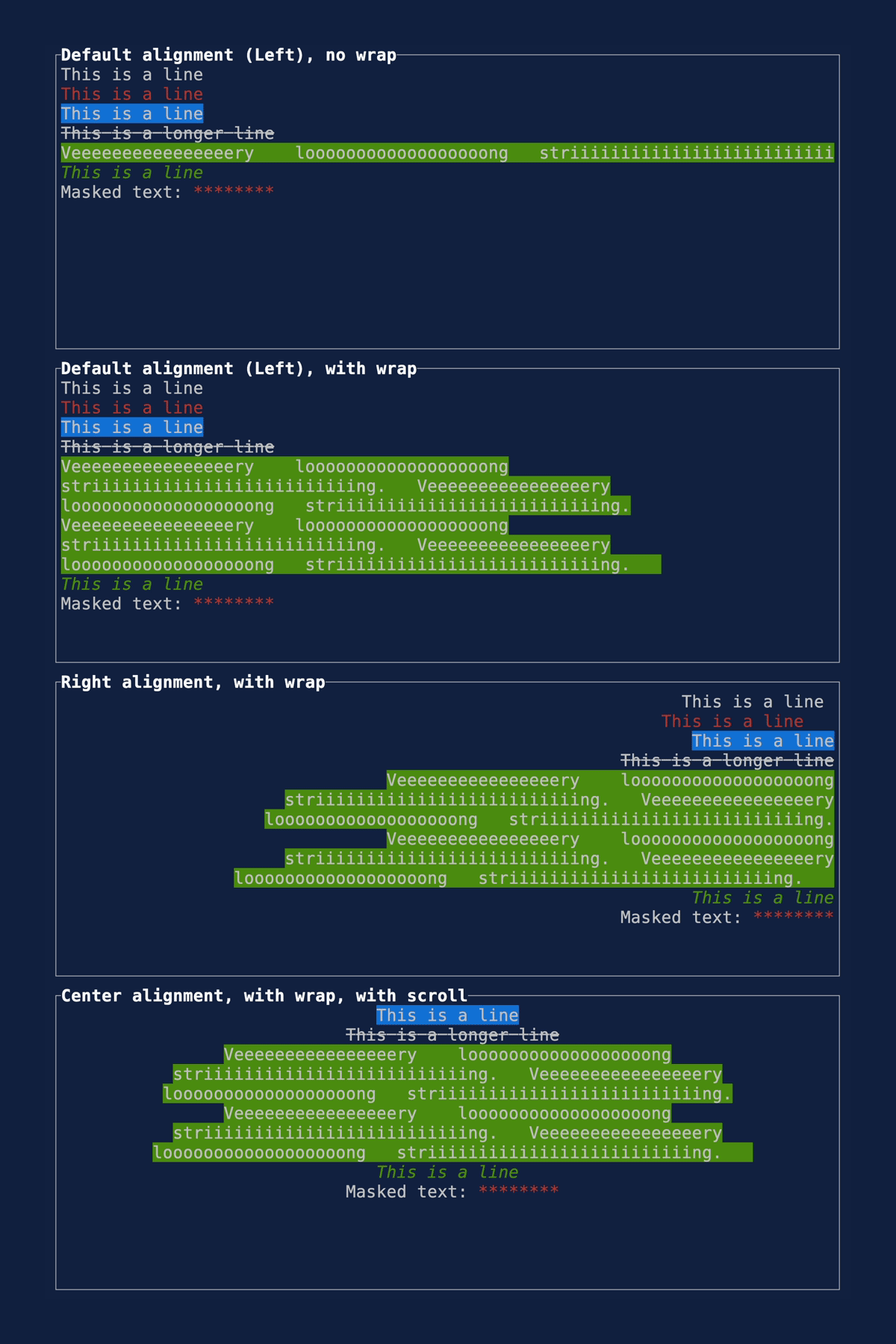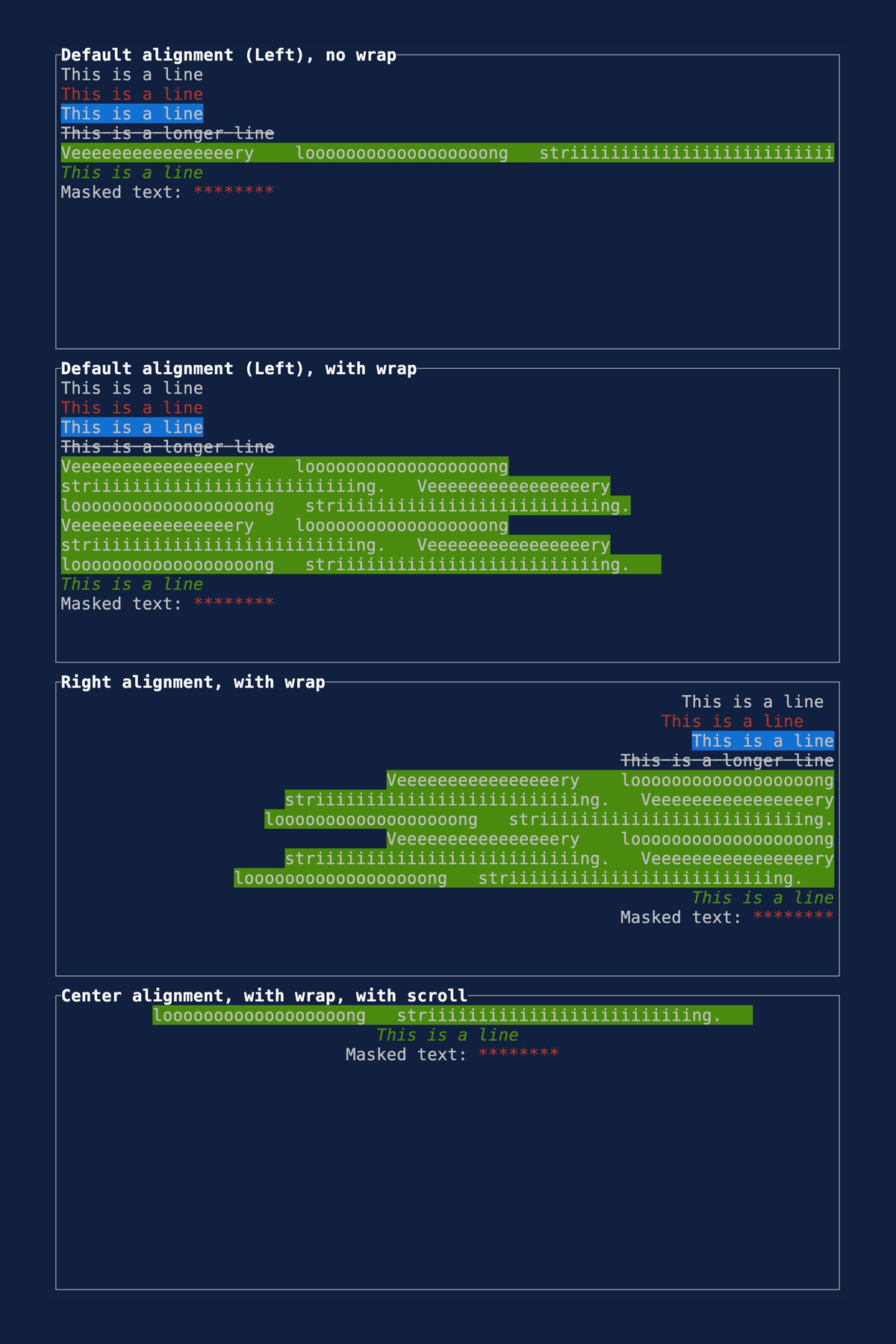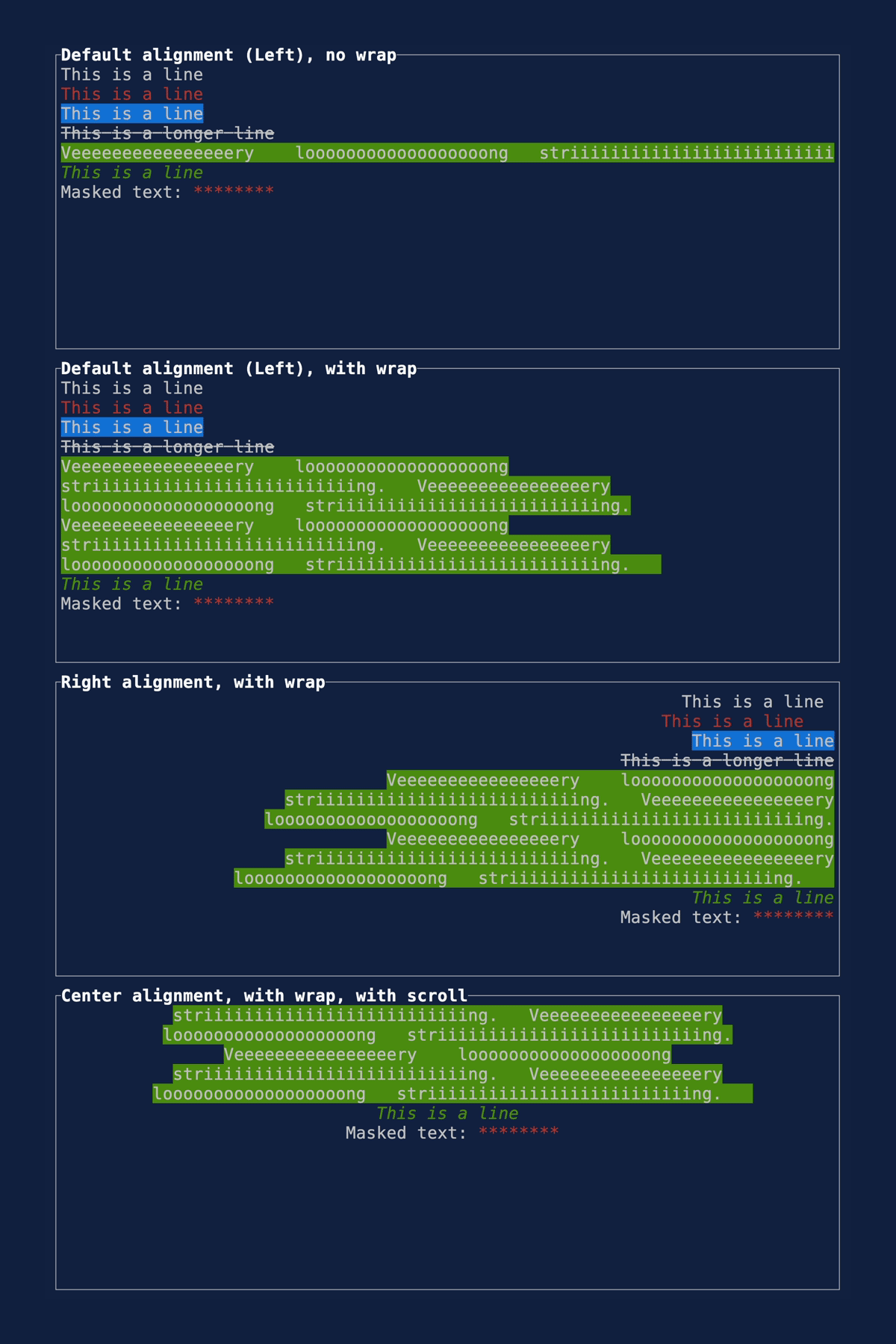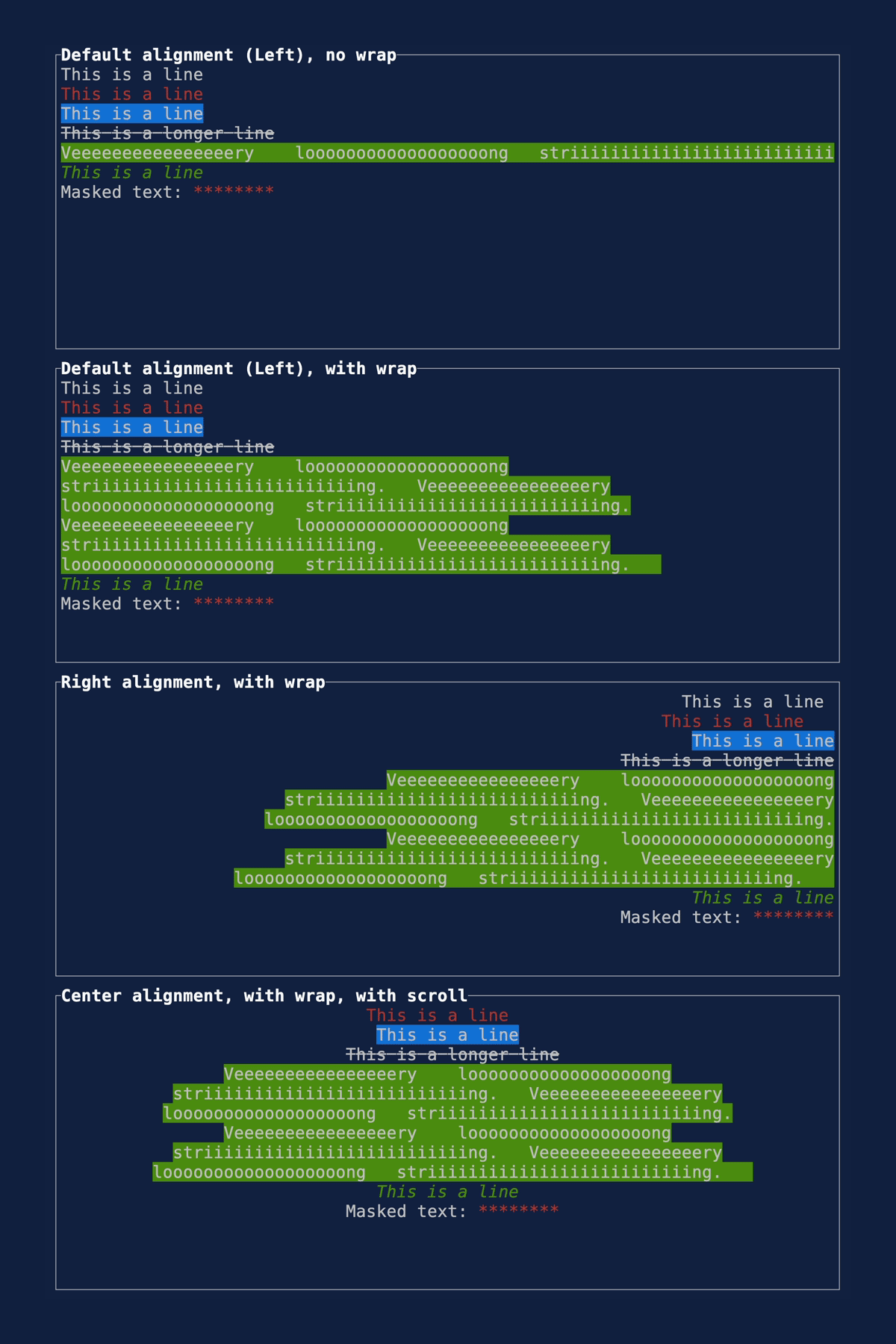
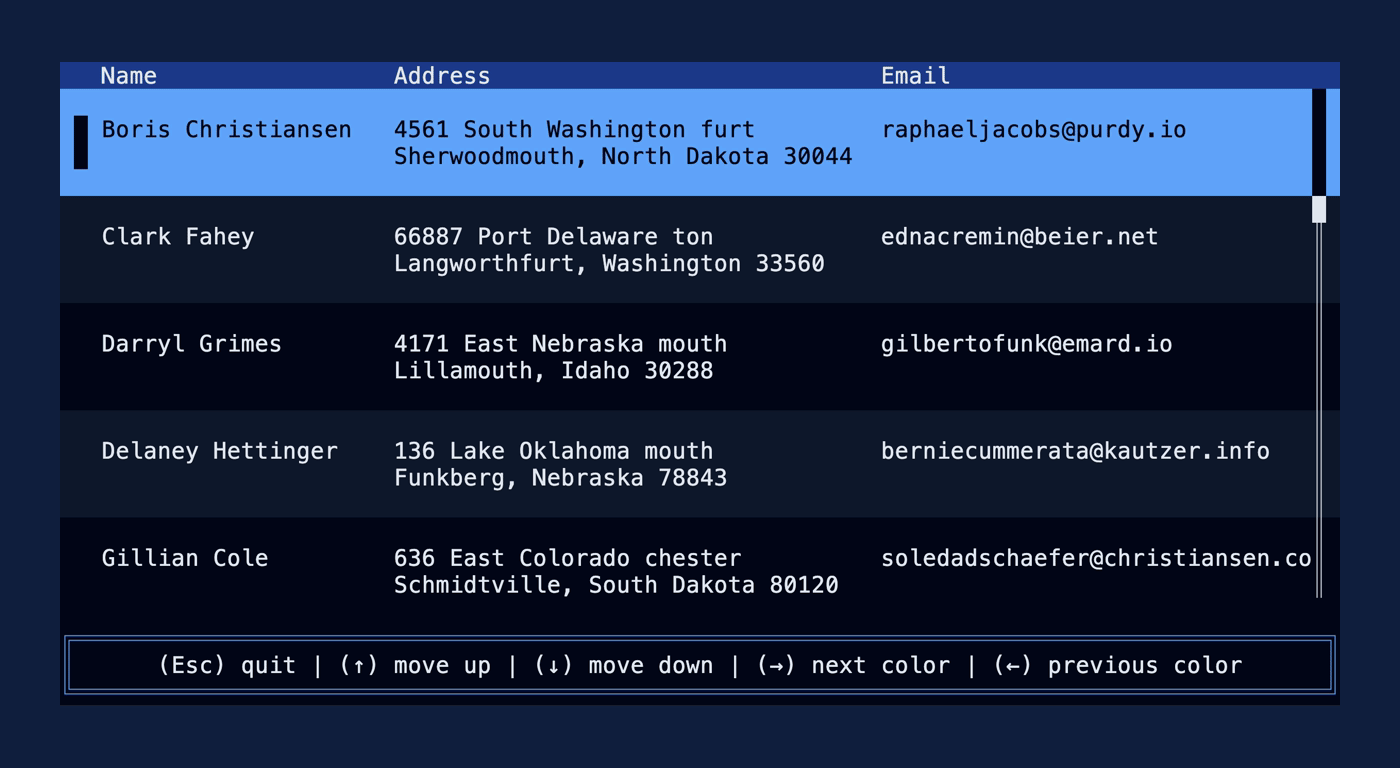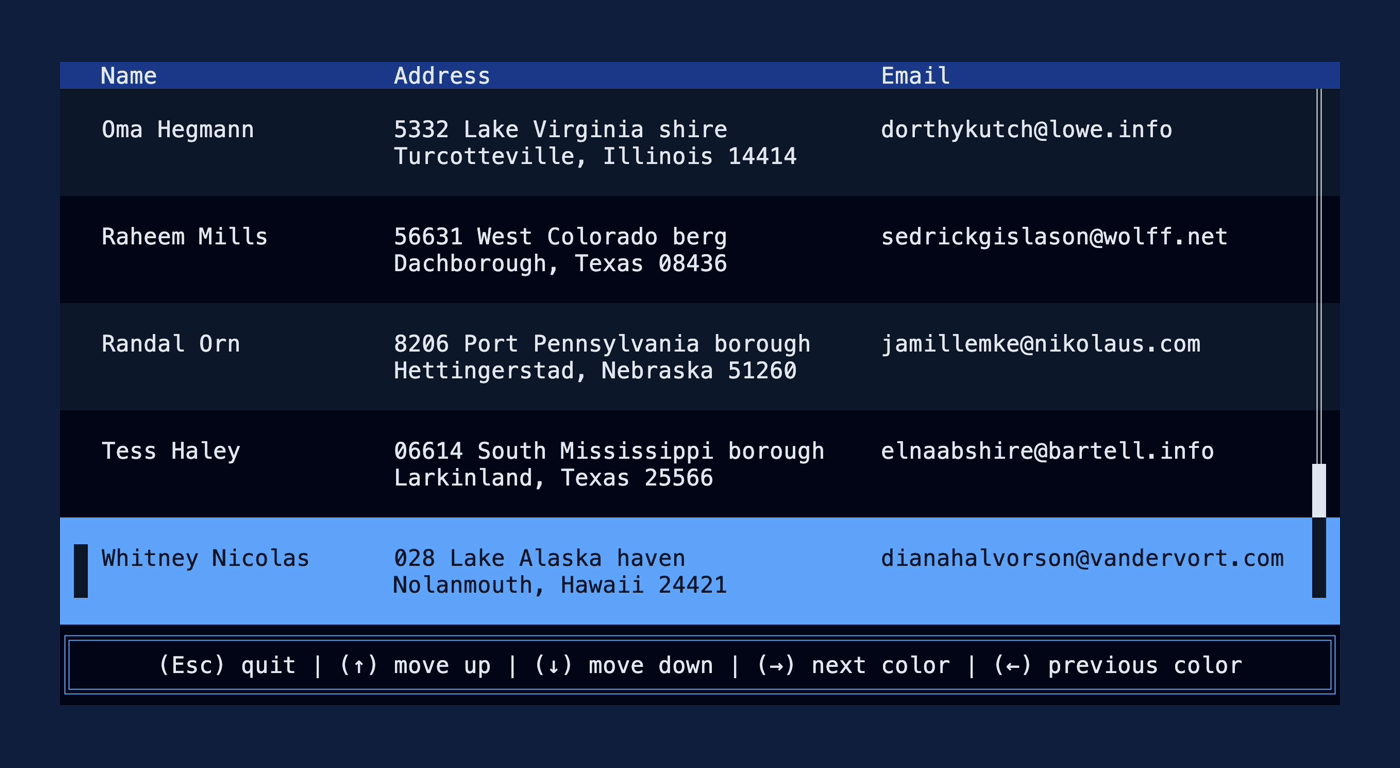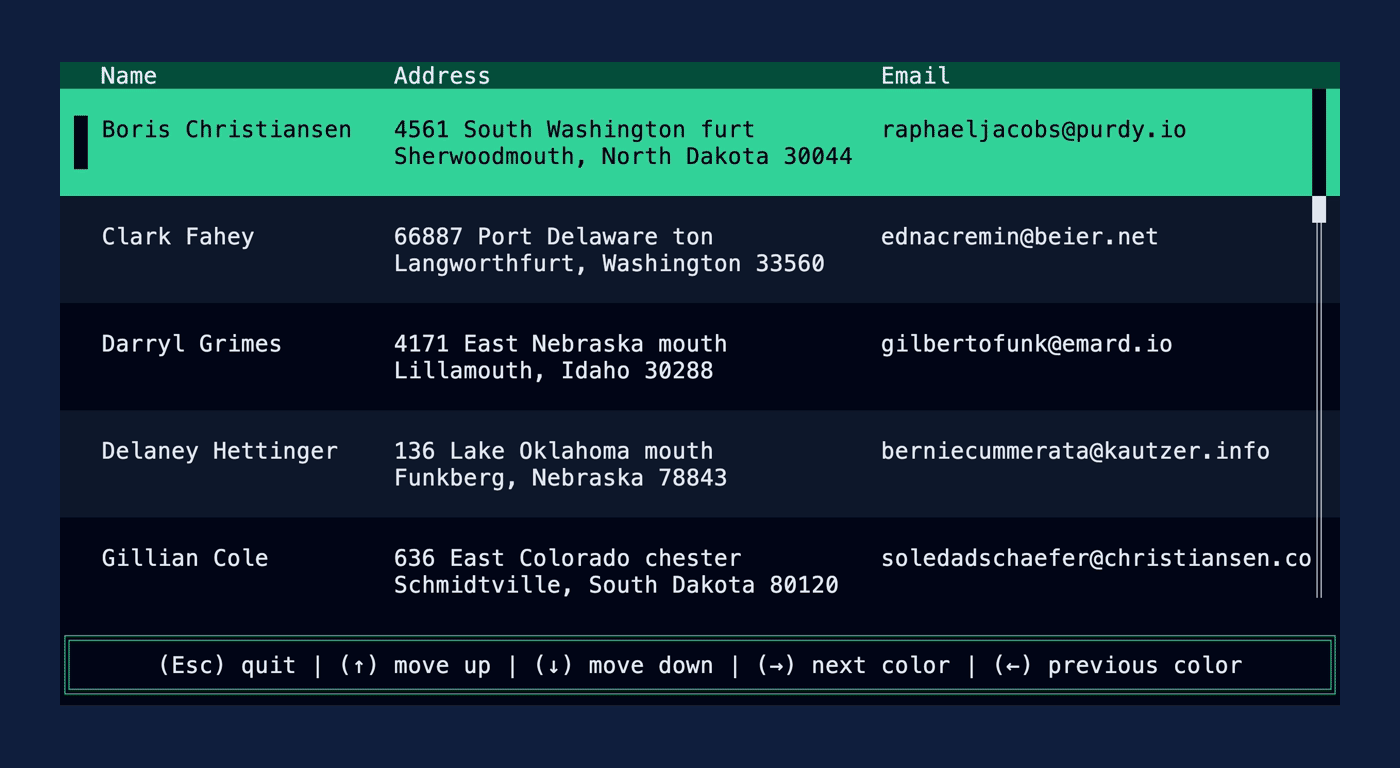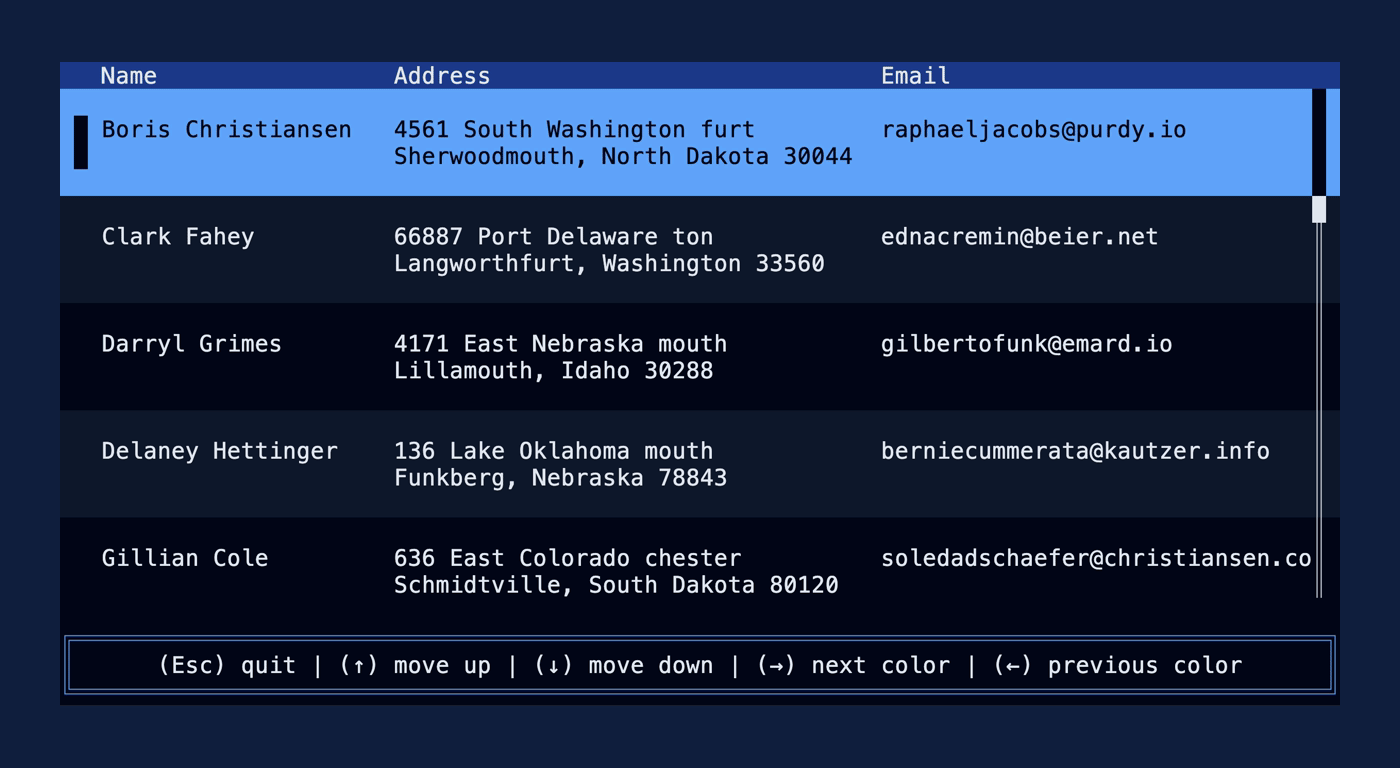
This PR makes a number of simplifications to the layout and constraint features that were added after v0.25.0. For users upgrading from v0.25.0, the net effect of this PR (along with the other PRs) is the following: - New `Flex` modes have been added. - `Flex::Start` (new default) - `Flex::Center` - `Flex::End` - `Flex::SpaceAround` - `Flex::SpaceBetween` - `Flex::Legacy` (old default) - `Min(v)` grows to allocate excess space in all `Flex` modes instead of shrinking (except in `Flex::Legacy` where it retains old behavior). - `Fill(1)` grows to allocate excess space, growing equally with `Min(v)`. --- The following contains a summary of the changes in this PR and the motivation behind them. **`Flex`** - Removes `Flex::Stretch` - Renames `Flex::StretchLast` to `Flex::Legacy` **`Constraint`** - Removes `Fixed` - Makes `Min(v)` grow as much as possible everywhere (except `Flex::Legacy` where it retains the old behavior) - Makes `Min(v)` grow equally as `Fill(1)` while respecting `Min` lower bounds. When `Fill` and `Min` are used together, they both fill excess space equally. Allowing `Min(v)` to grow still allows users to build the same layouts as before with `Flex::Start` with no breaking changes to the behavior. This PR also removes the unstable feature `SegmentSize`. This is a breaking change to the behavior of constraints. If users want old behavior, they can use `Flex::Legacy`. ```rust Layout::vertical([Length(25), Length(25)]).flex(Flex::Legacy) ``` Users that have constraint that exceed the available space will probably not see any difference or see an improvement in their layouts. Any layout with `Min` will be identical in `Flex::Start` and `Flex::Legacy` so any layout with `Min` will not be breaking. Previously, `Table` used `EvenDistribution` internally by default, but with that gone the default is now `Flex::Start`. This changes the behavior of `Table` (for the better in most cases). The only way for users to get exactly the same as the old behavior is to change their constraints. I imagine most users will be happier out of the box with the new Table default. Resolves https://github.com/ratatui-org/ratatui/issues/843 Thanks to @joshka for the direction |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| demo | ||
| demo2 | ||
| vhs | ||
| barchart.rs | ||
| block.rs | ||
| calendar.rs | ||
| canvas.rs | ||
| chart.rs | ||
| colors.rs | ||
| colors_rgb.rs | ||
| constraints.rs | ||
| custom_widget.rs | ||
| docsrs.rs | ||
| flex.rs | ||
| gauge.rs | ||
| hello_world.rs | ||
| inline.rs | ||
| layout.rs | ||
| list.rs | ||
| modifiers.rs | ||
| panic.rs | ||
| paragraph.rs | ||
| popup.rs | ||
| ratatui-logo.rs | ||
| README.md | ||
| scrollbar.rs | ||
| sparkline.rs | ||
| table.rs | ||
| tabs.rs | ||
| user_input.rs | ||
Examples
This folder contains unreleased code. View the examples for the latest release (0.25.0) instead.
Warning
There are backwards incompatible changes in these examples, as they are designed to compile against the
mainbranch.There are a few workaround for this problem:
- View the examples as they were when the latest version was release by selecting the tag that matches that version. E.g. https://github.com/ratatui-org/ratatui/tree/v0.25.0/examples. There is a combo box at the top of this page which allows you to select any previous tagged version.
- To view the code locally, checkout the tag using
git switch --detach v0.25.0.- Use the latest alpha version of Ratatui. These are released weekly on Saturdays.
- Compile your code against the main branch either locally by adding e.g.
path = "../ratatui"to the dependency, or remotely by addinggit = "https://github.com/ratatui-org/ratatui"For a list of unreleased breaking changes, see BREAKING-CHANGES.md.
We don't keep the CHANGELOG updated with unreleased changes, check the git commit history or run
git-cliff -uagainst a cloned version of this repository.
Demo2
This is the demo example from the main README and crate page. Source: demo2.
cargo run --example=demo2 --features="crossterm widget-calendar"
Demo
This is the previous demo example from the main README. It is available for each of the backends. Source: demo.rs.
cargo run --example=demo --features=crossterm
cargo run --example=demo --no-default-features --features=termion
cargo run --example=demo --no-default-features --features=termwiz
Hello World
This is a pretty boring example, but it contains some good documentation on writing tui apps. Source: hello_world.rs.
cargo run --example=hello_world --features=crossterm
Barchart
Demonstrates the BarChart
widget. Source: barchart.rs.
cargo run --example=barchart --features=crossterm
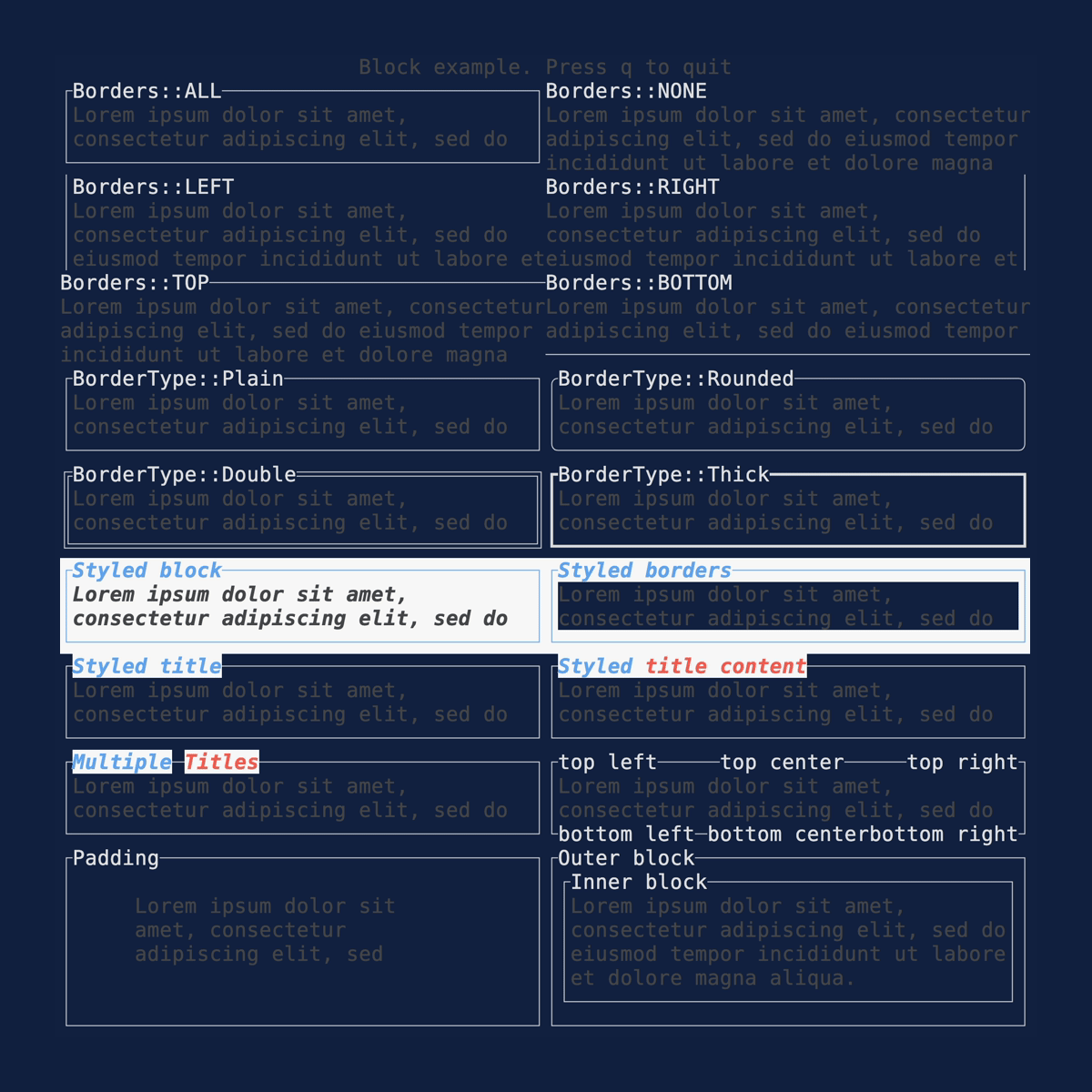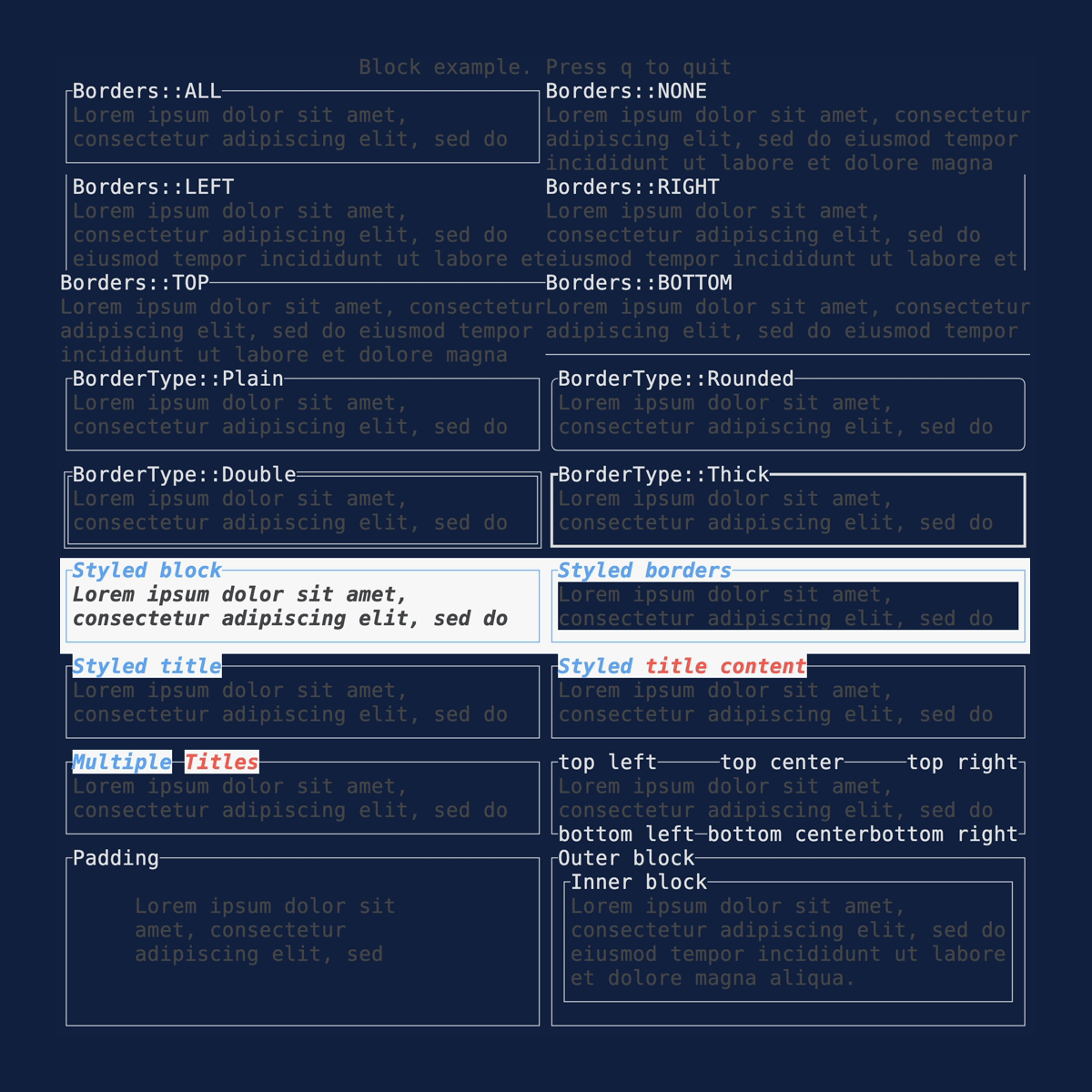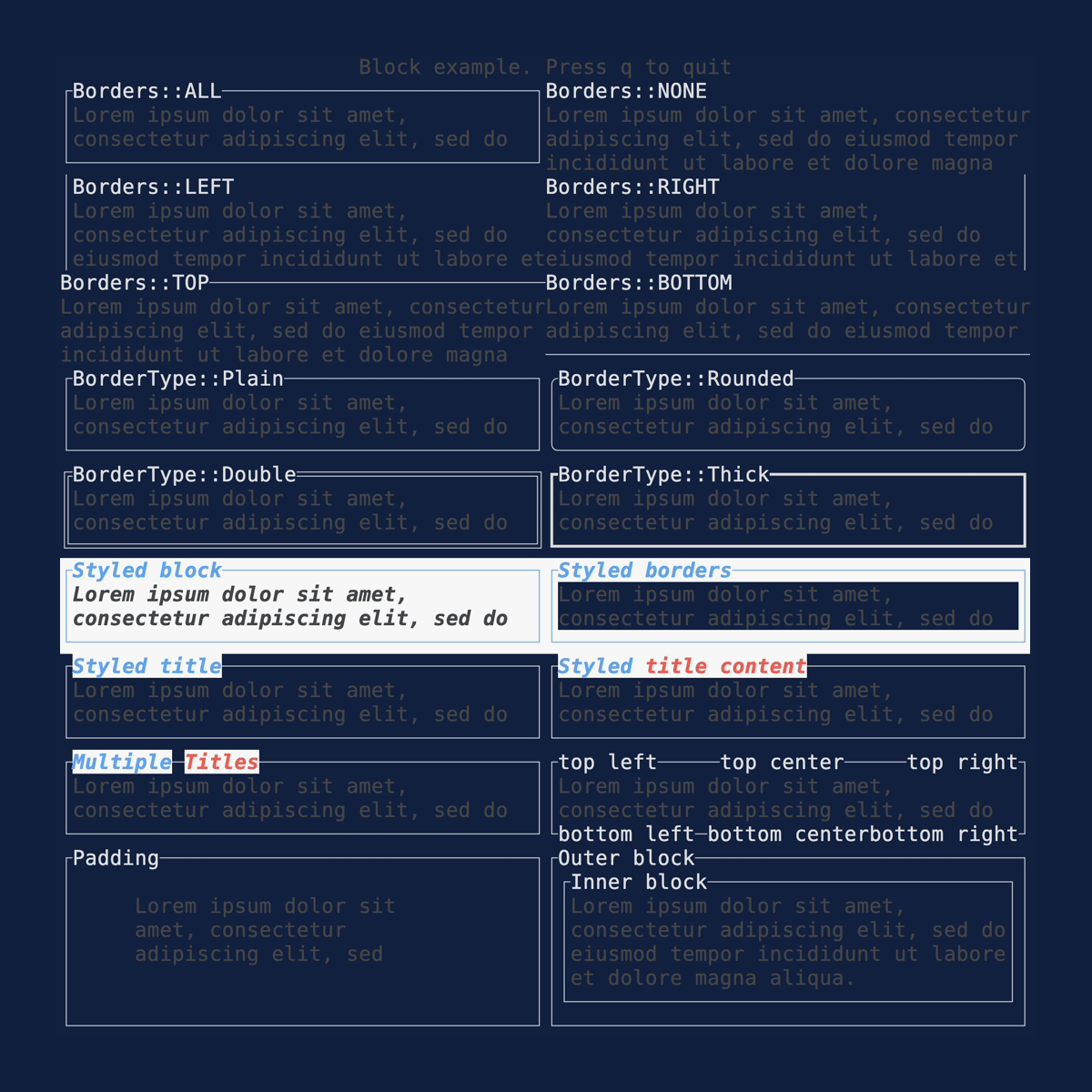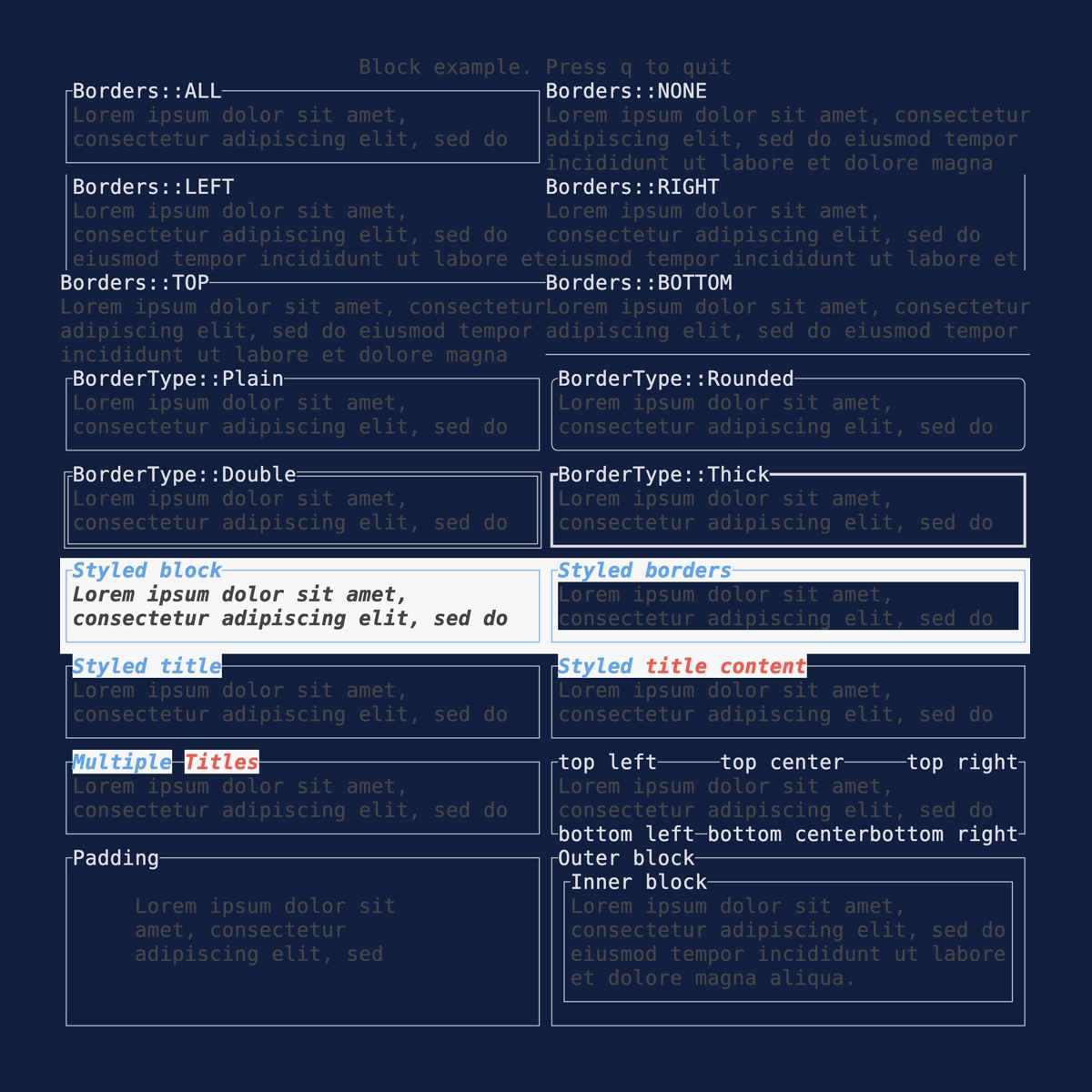
Block
Demonstrates the Block
widget. Source: block.rs.
cargo run --example=block --features=crossterm
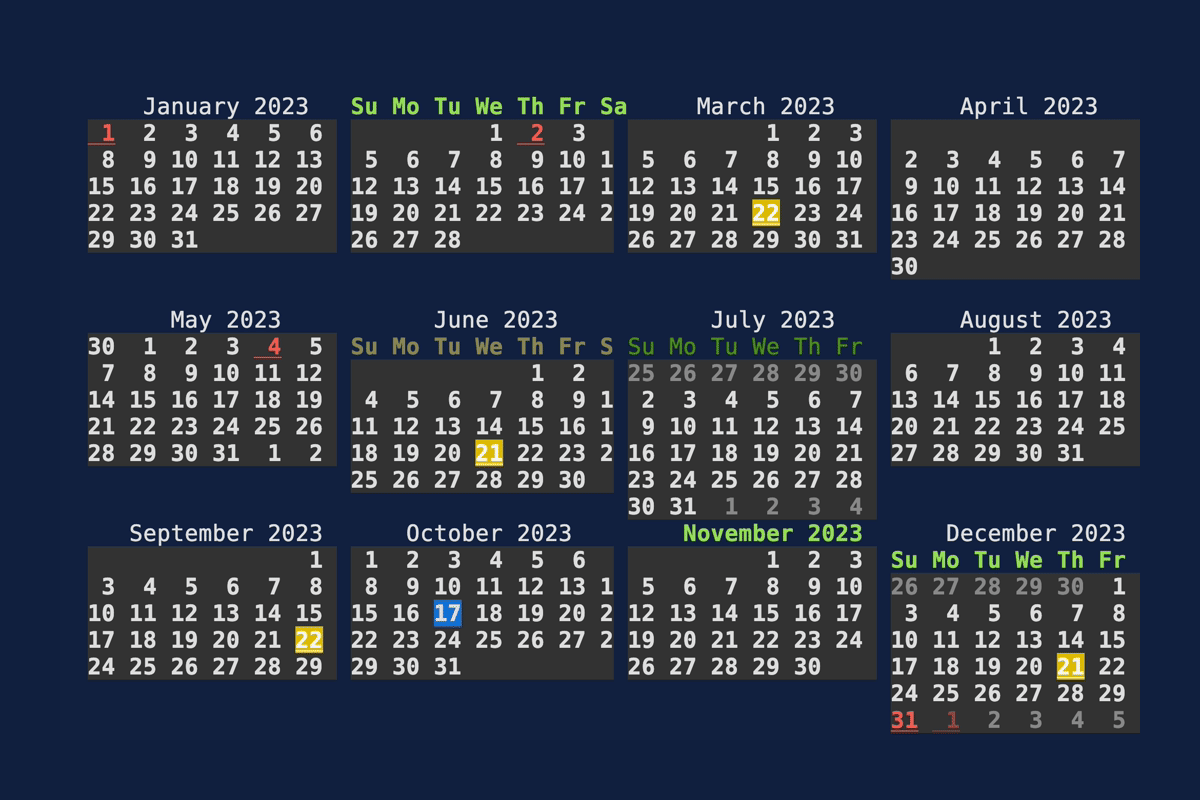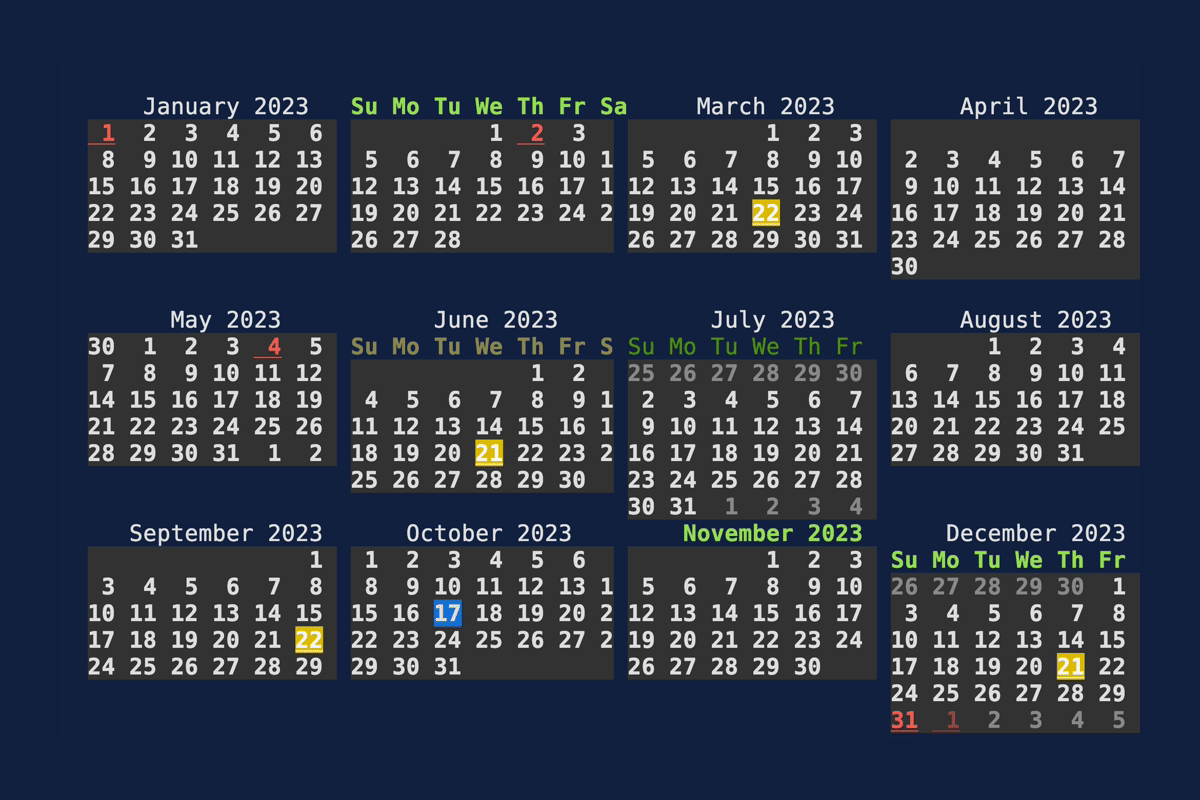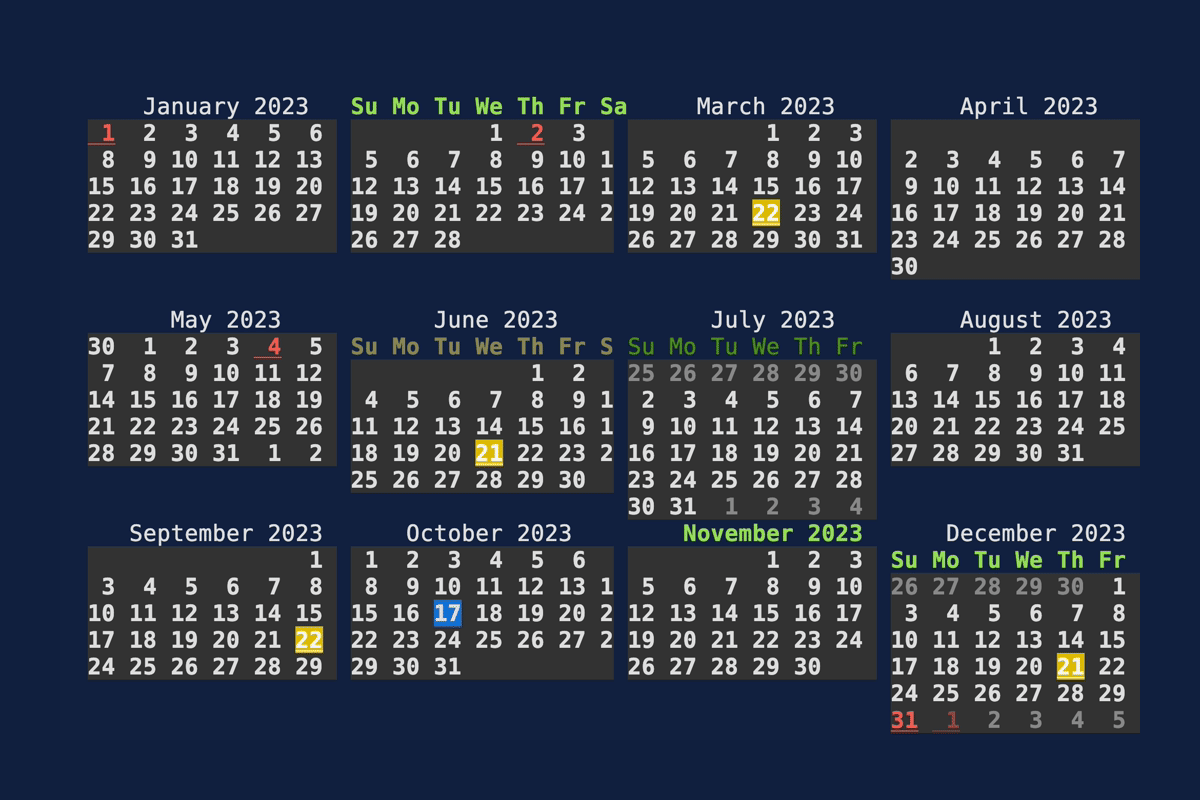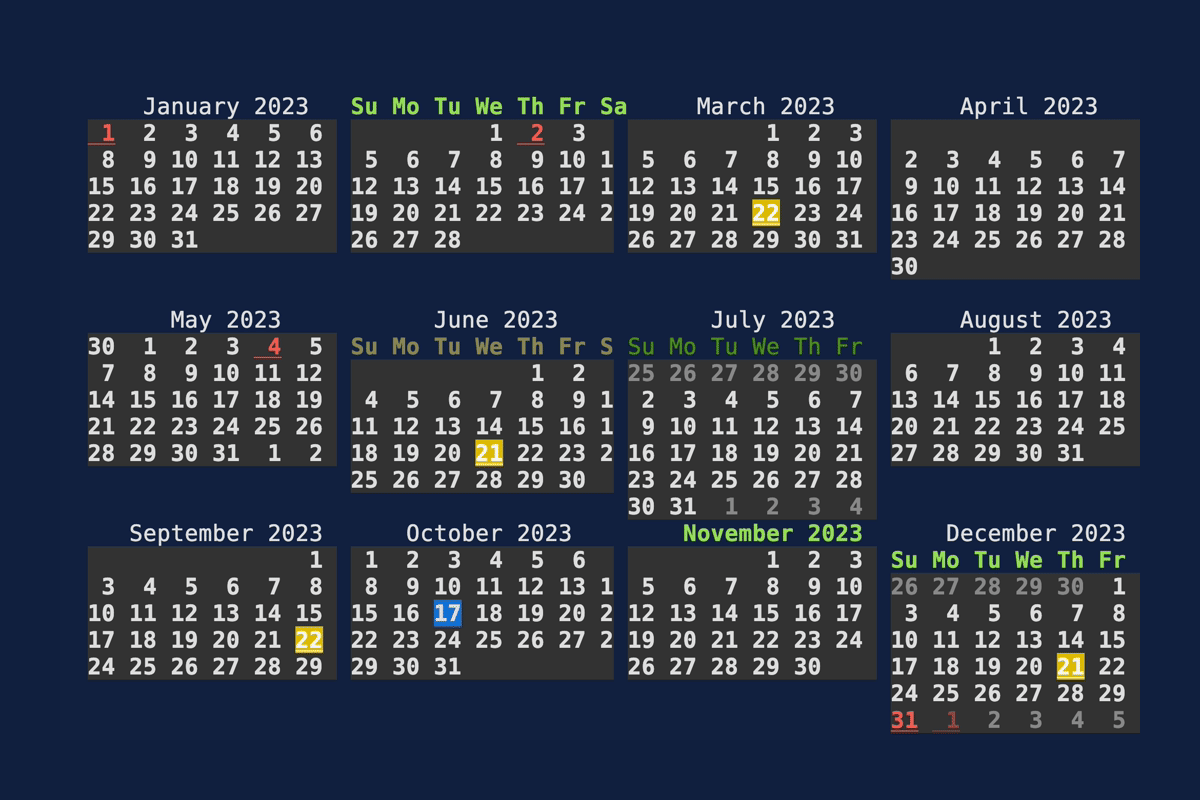
Calendar
Demonstrates the Calendar
widget. Source: calendar.rs.
cargo run --example=calendar --features="crossterm widget-calendar"
Canvas
Demonstrates the Canvas widget
and related shapes in the
canvas module. Source:
canvas.rs.
cargo run --example=canvas --features=crossterm
Chart
Demonstrates the Chart widget.
Source: chart.rs.
cargo run --example=chart --features=crossterm
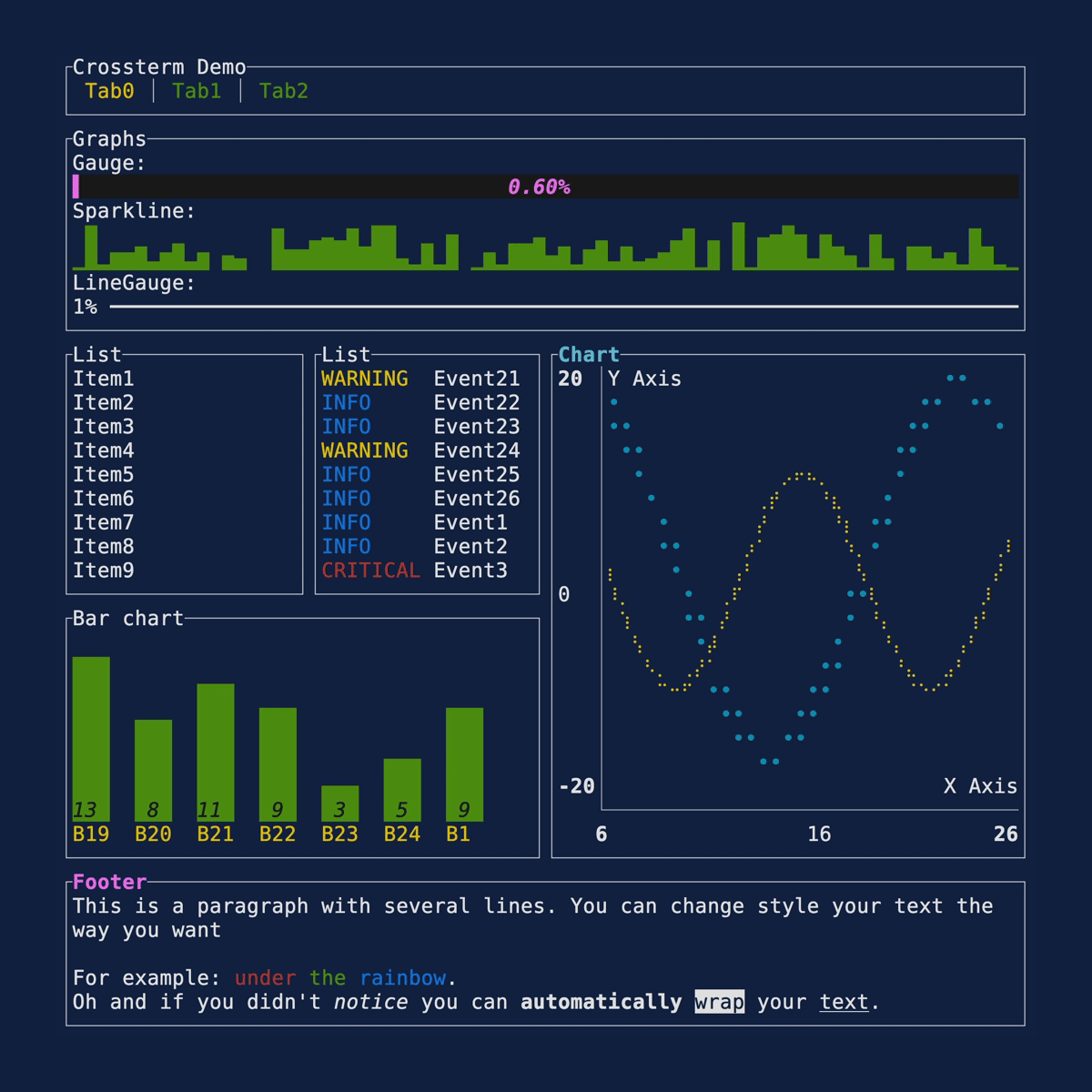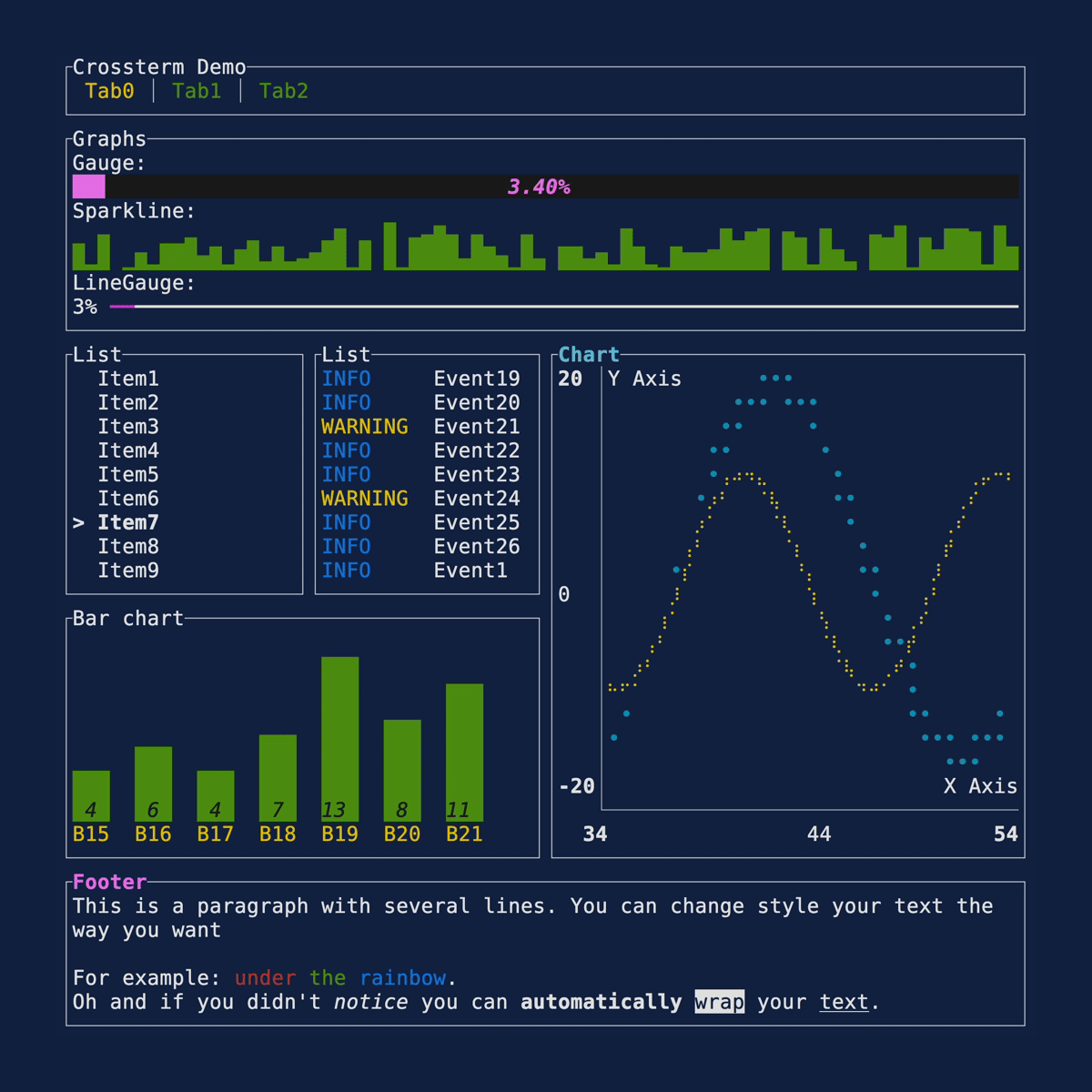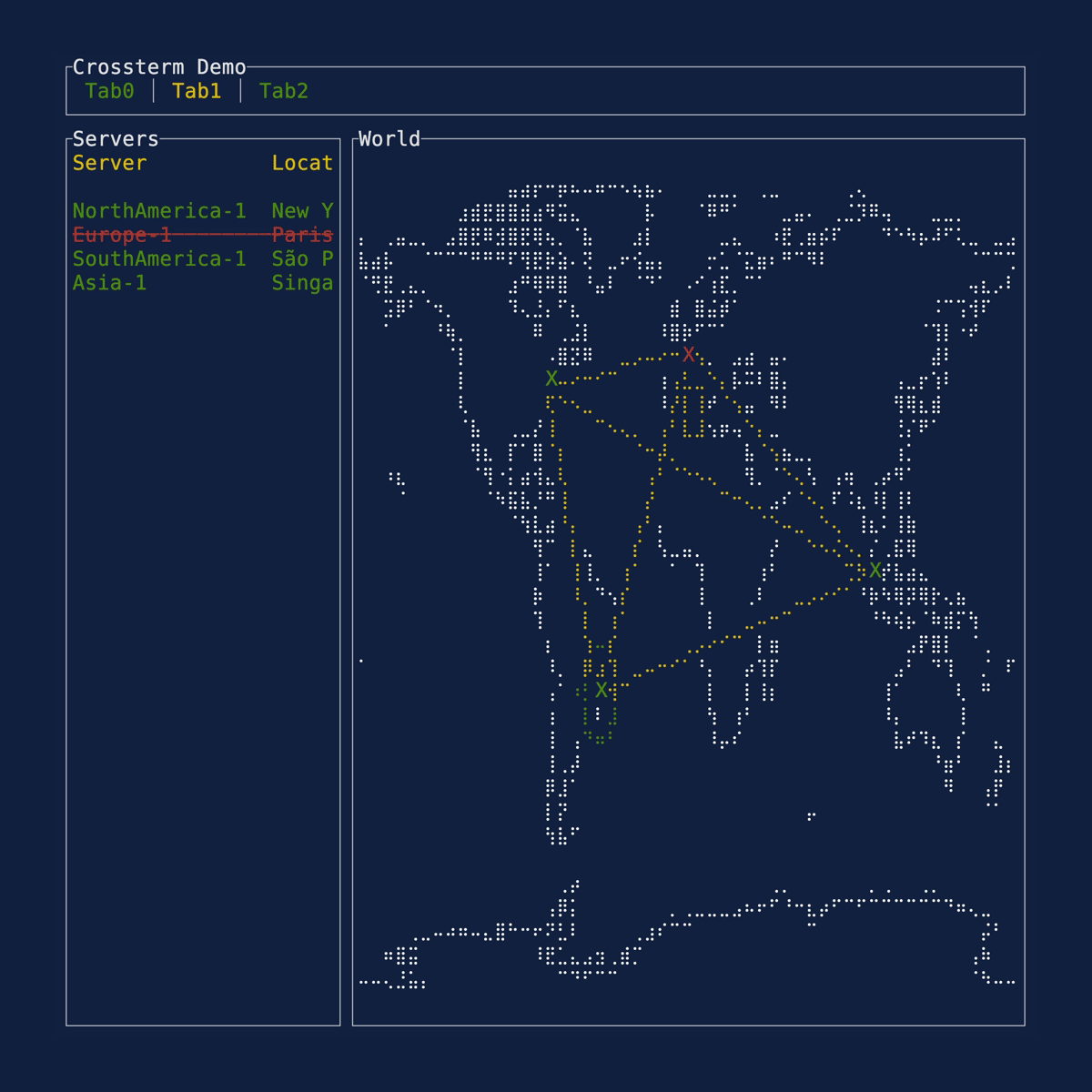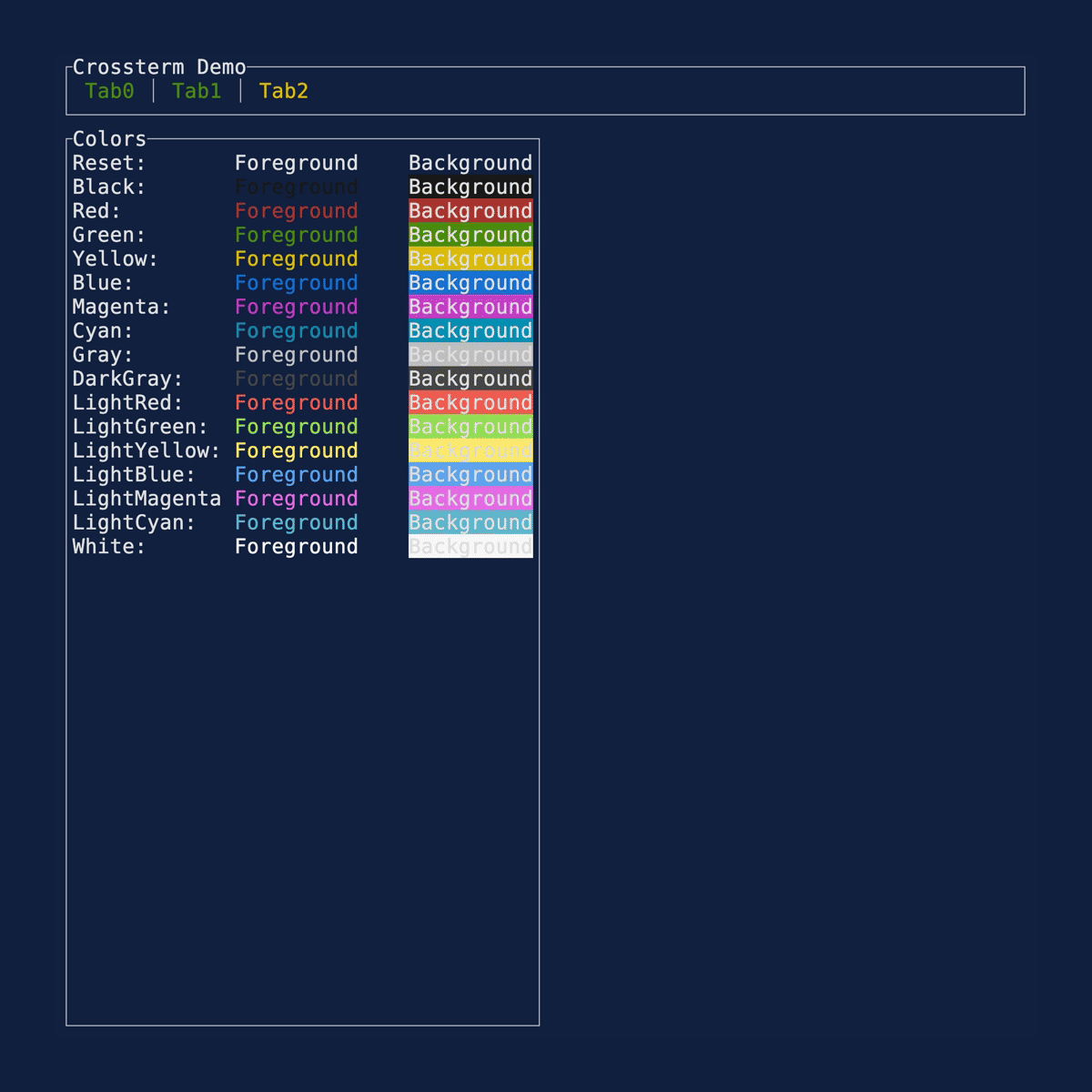
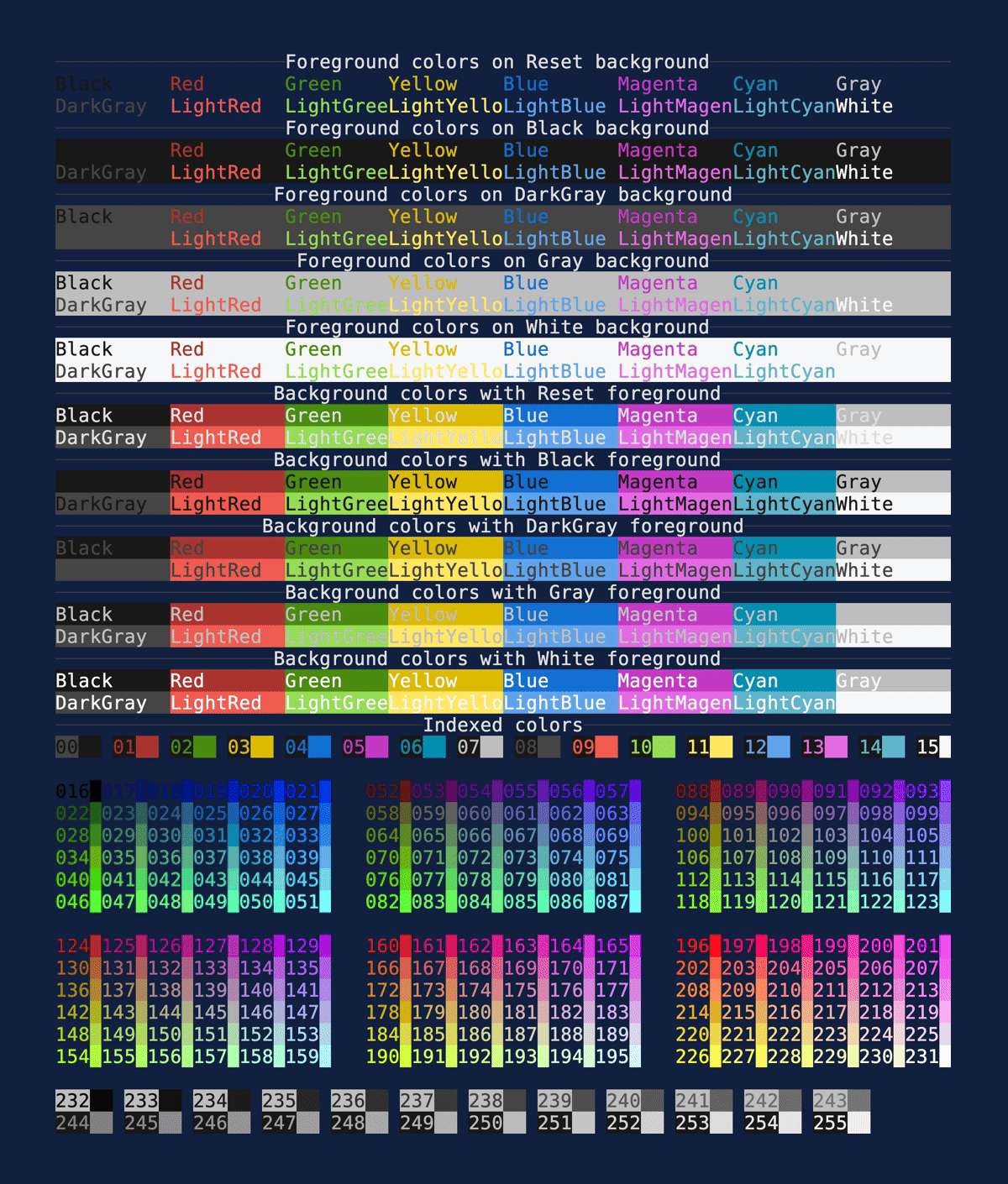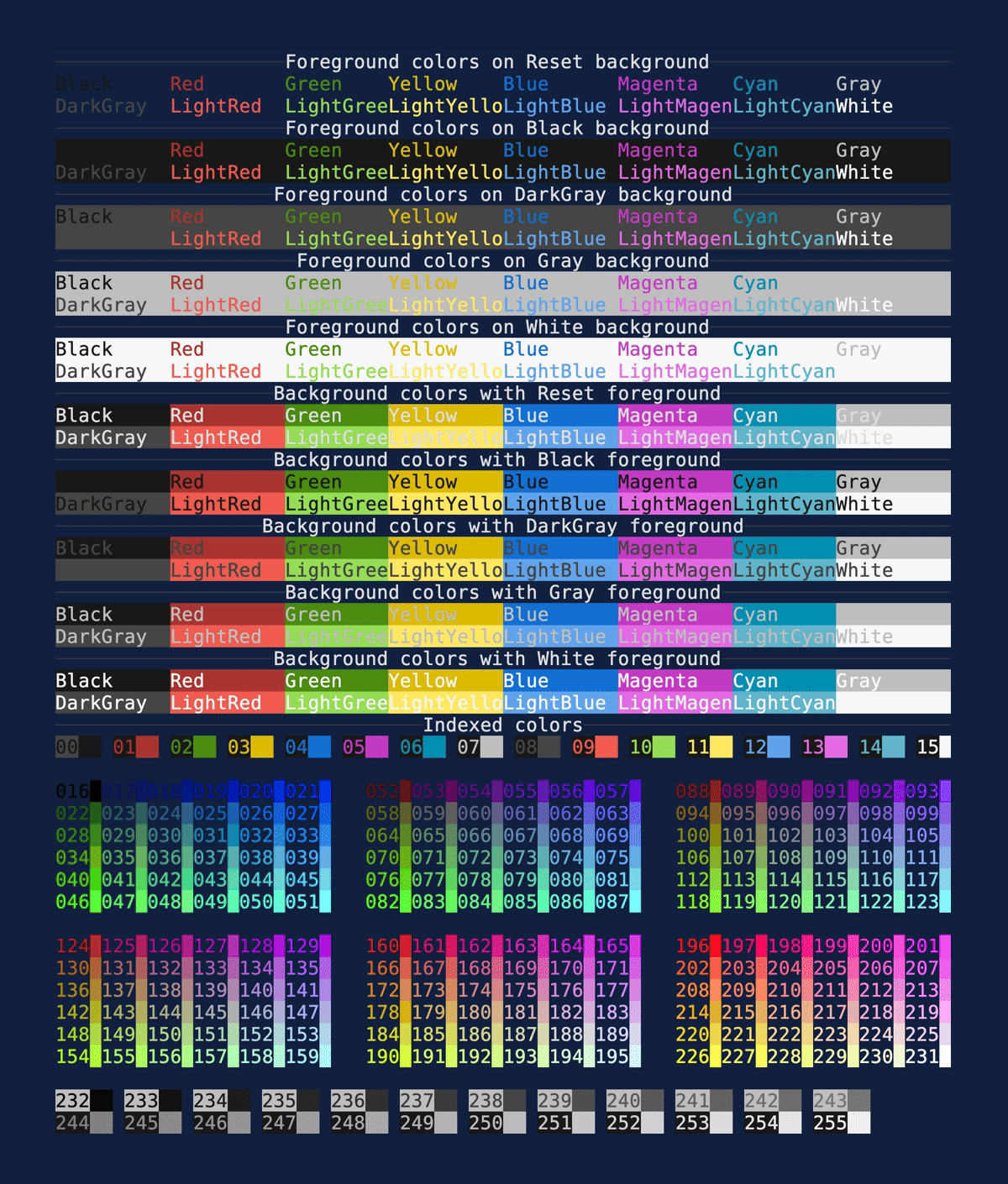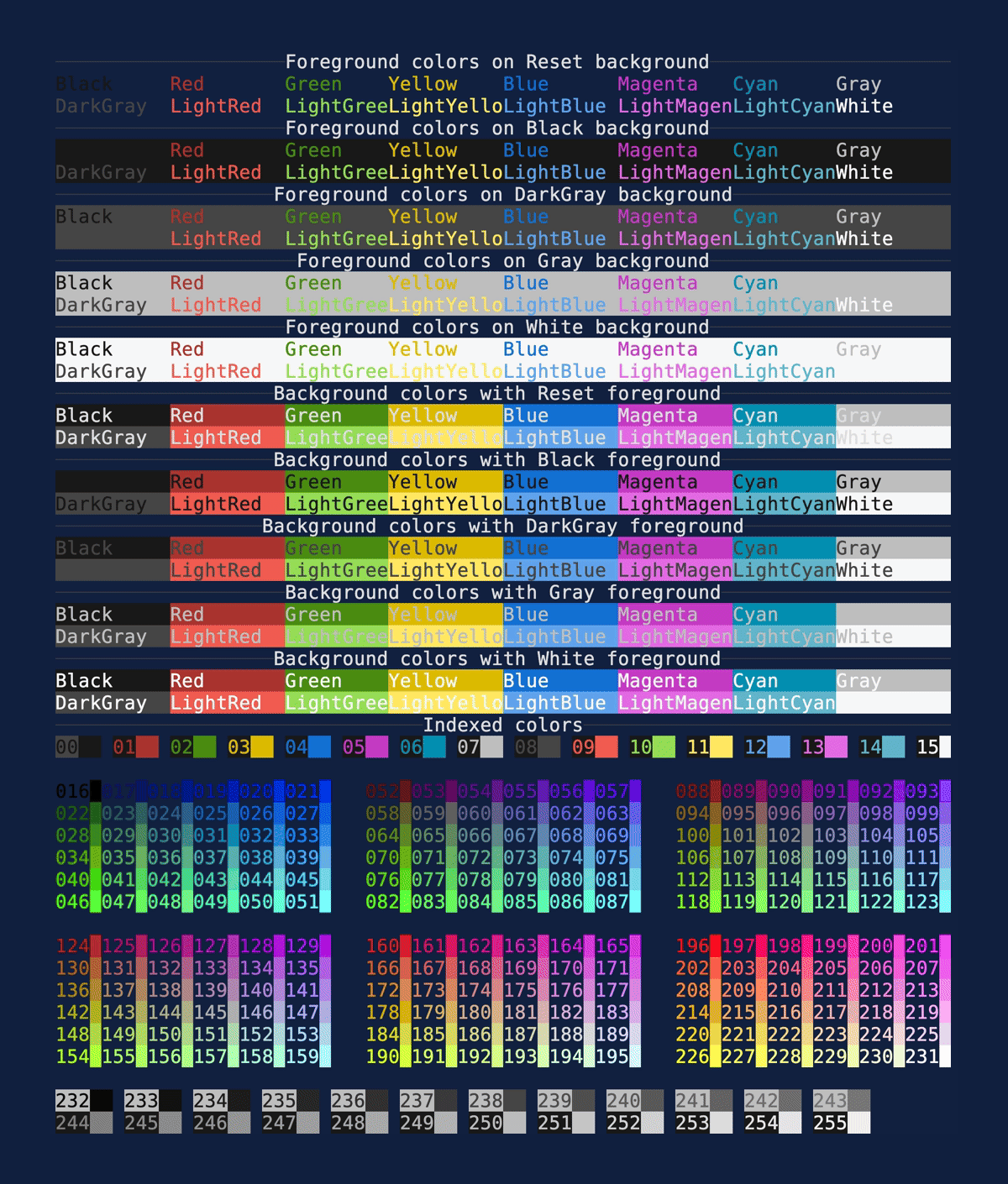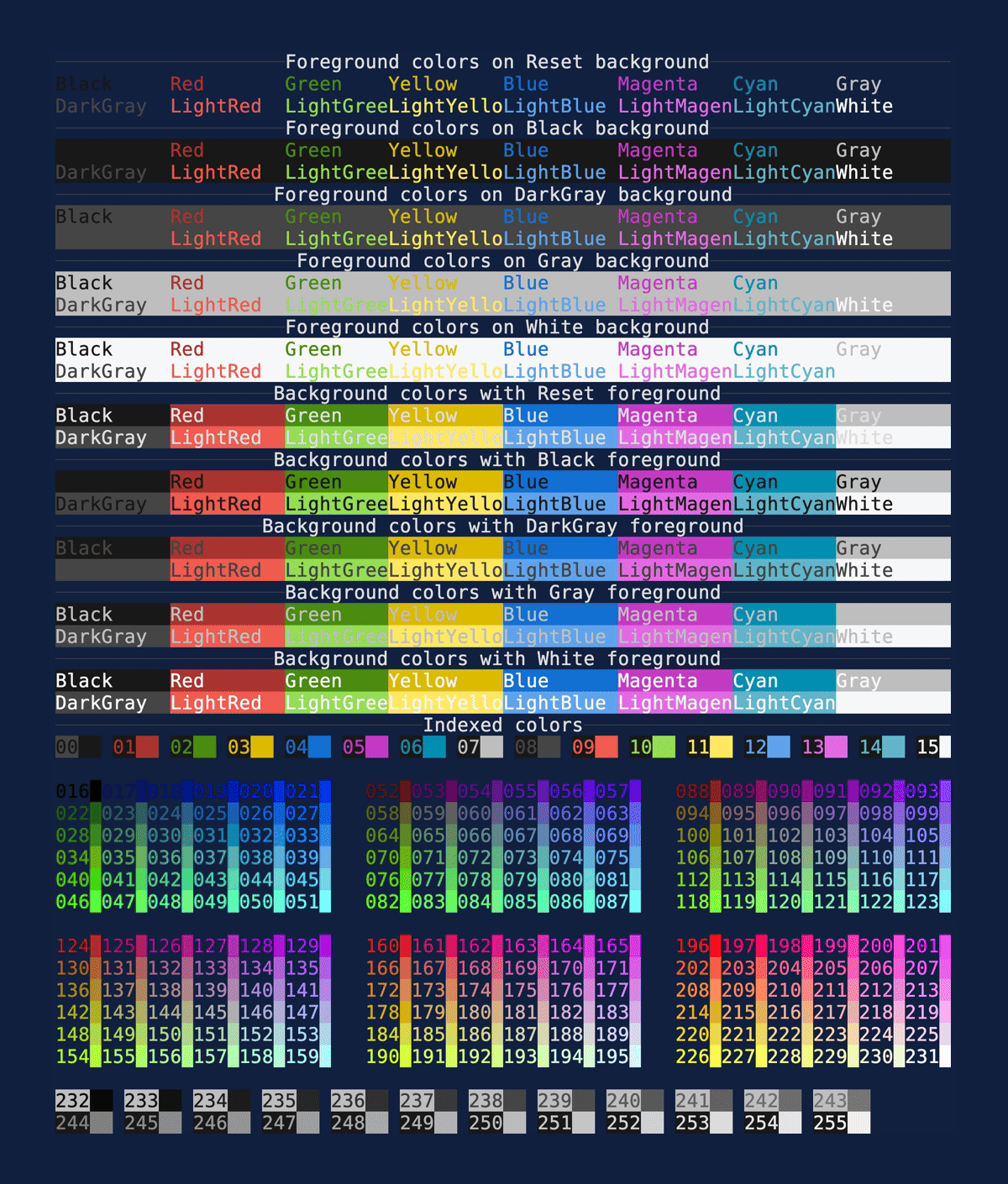
Colors
Demonstrates the available Color
options. These can be used in any style field. Source: colors.rs.
cargo run --example=colors --features=crossterm
Colors (RGB)
Demonstrates the available RGB
Color options. These can be used
in any style field. Source: colors_rgb.rs. Uses a half block technique to render
two square-ish pixels in the space of a single rectangular terminal cell.
cargo run --example=colors_rgb --features=crossterm
Note: VHs renders full screen animations poorly, so this is a screen capture rather than the output of the VHS tape.
https://github.com/ratatui-org/ratatui/assets/381361/485e775a-e0b5-4133-899b-1e8aeb56e774
Custom Widget
Demonstrates how to implement the
Widget trait. Also shows mouse
interaction. Source: custom_widget.rs.
cargo run --example=custom_widget --features=crossterm
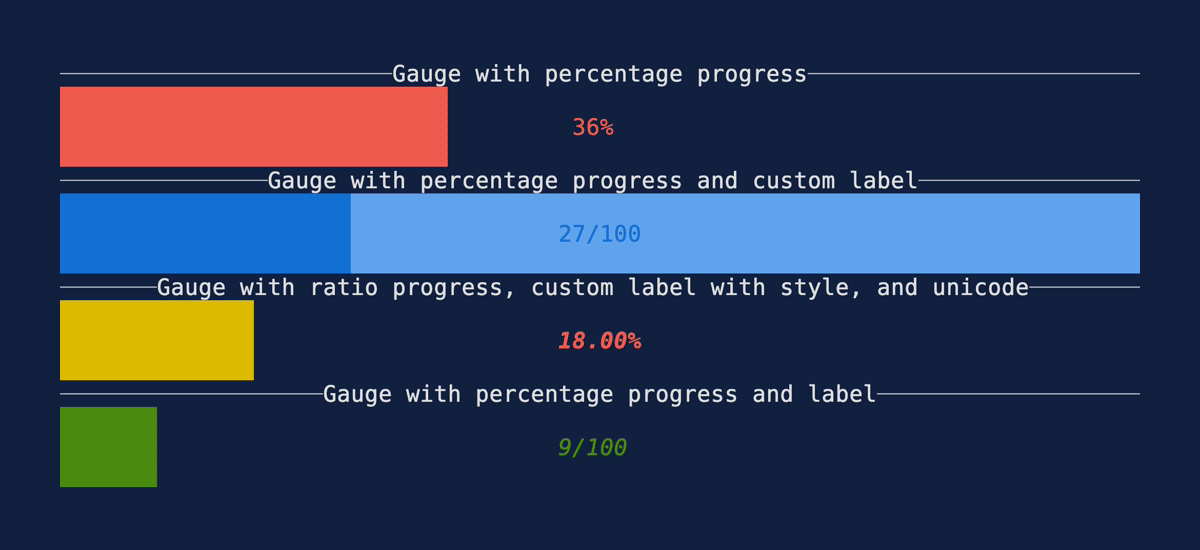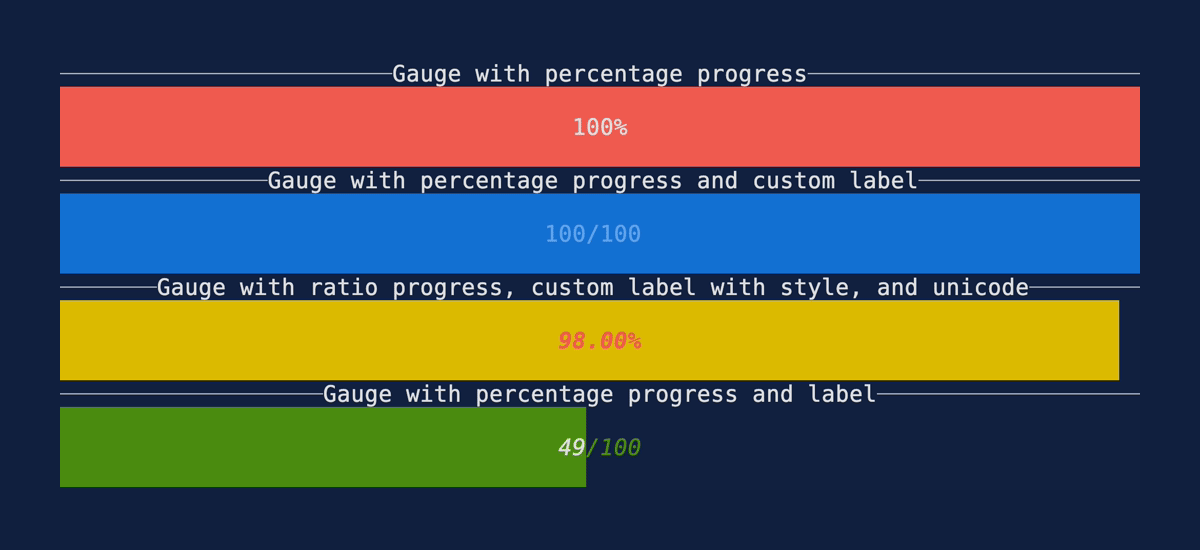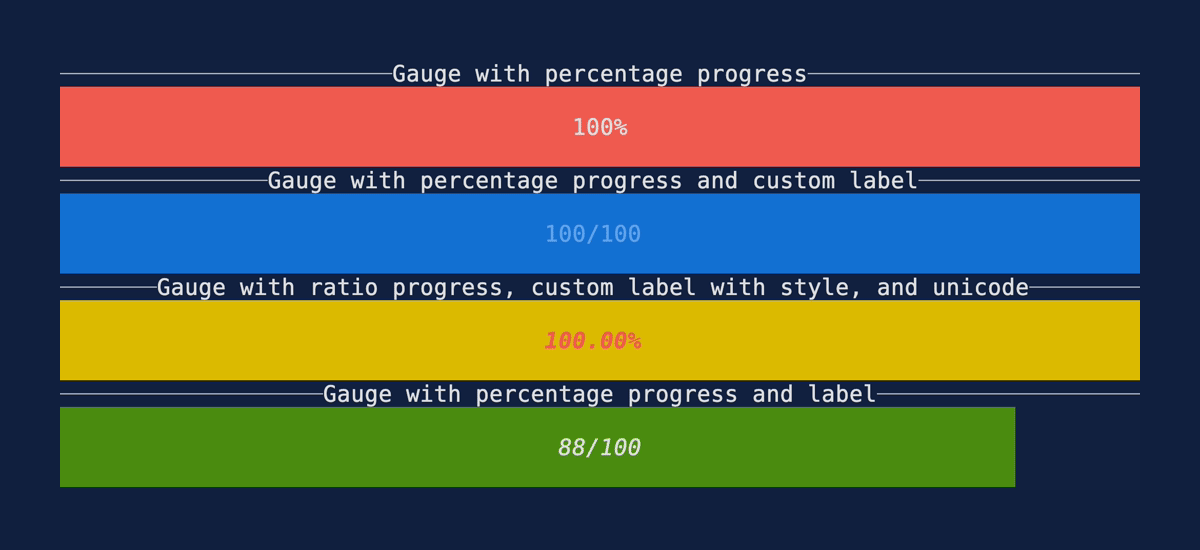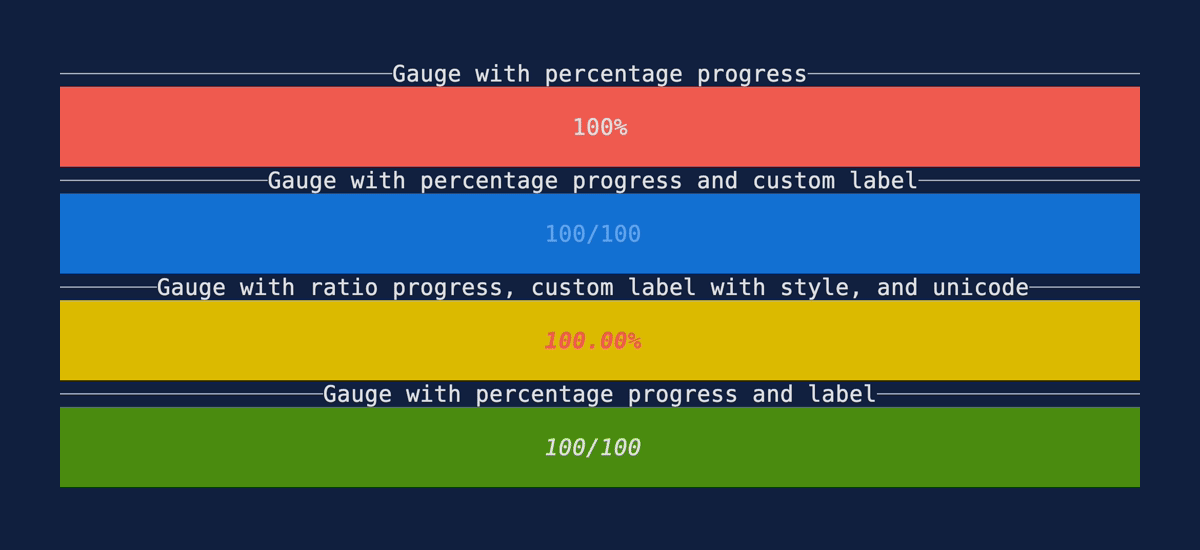
Gauge
Demonstrates the Gauge widget.
Source: gauge.rs.
cargo run --example=gauge --features=crossterm
Inline
Demonstrates how to use the
Inline
Viewport mode for ratatui apps. Source: inline.rs.
cargo run --example=inline --features=crossterm
Layout
Demonstrates the Layout and
interaction between each constraint. Source: layout.rs.
cargo run --example=layout --features=crossterm
List
Demonstrates the List widget.
Source: list.rs.
cargo run --example=list --features=crossterm
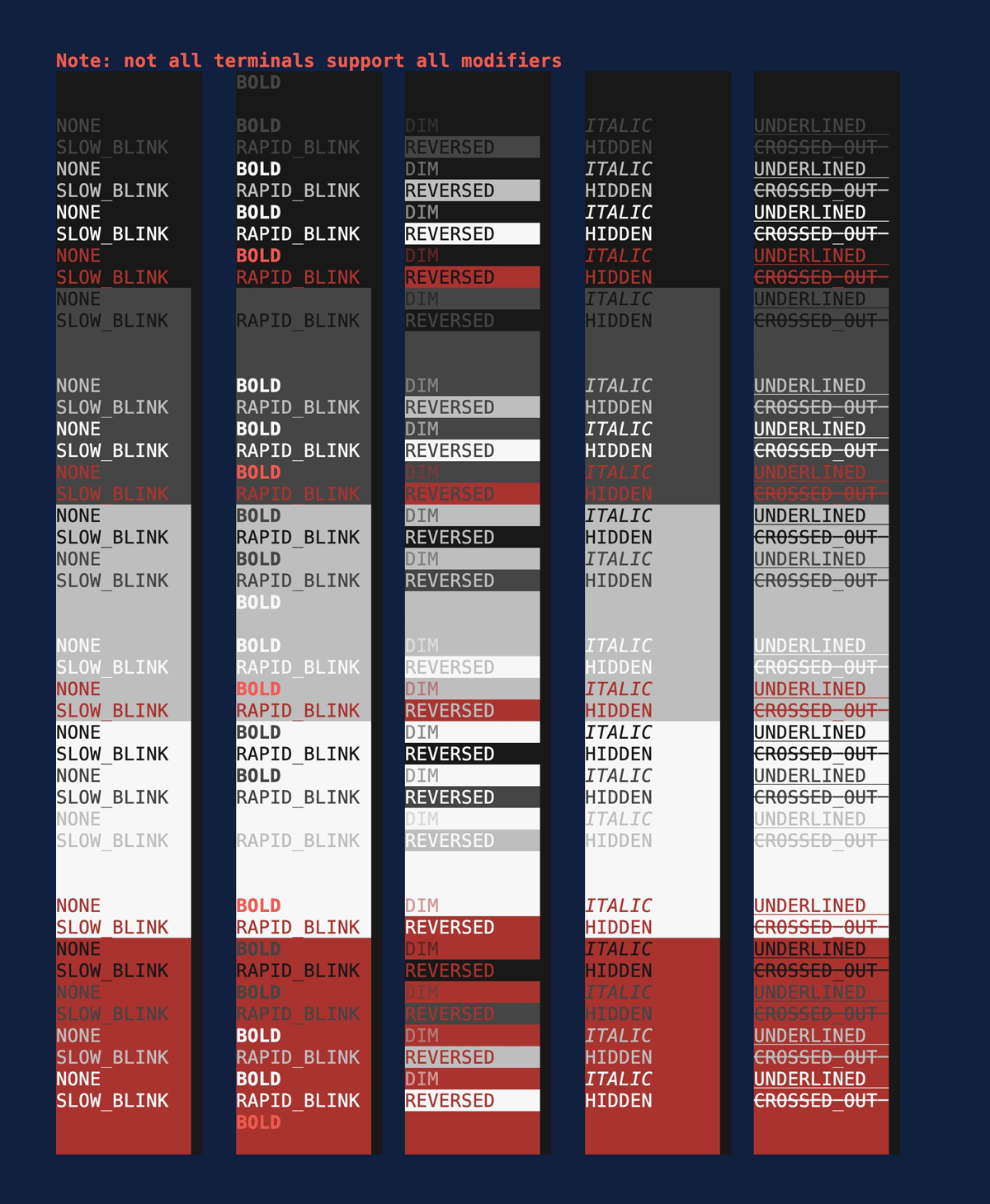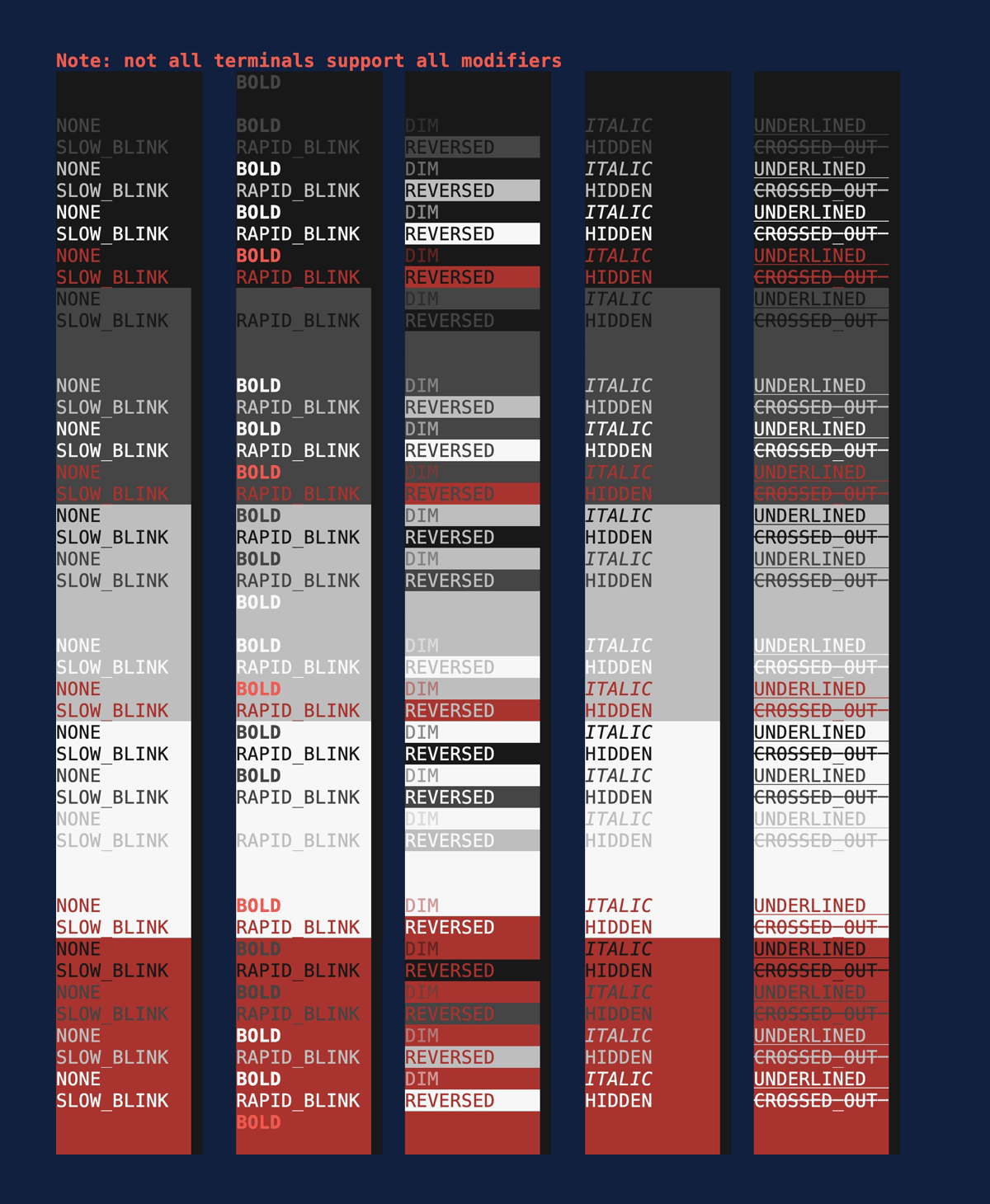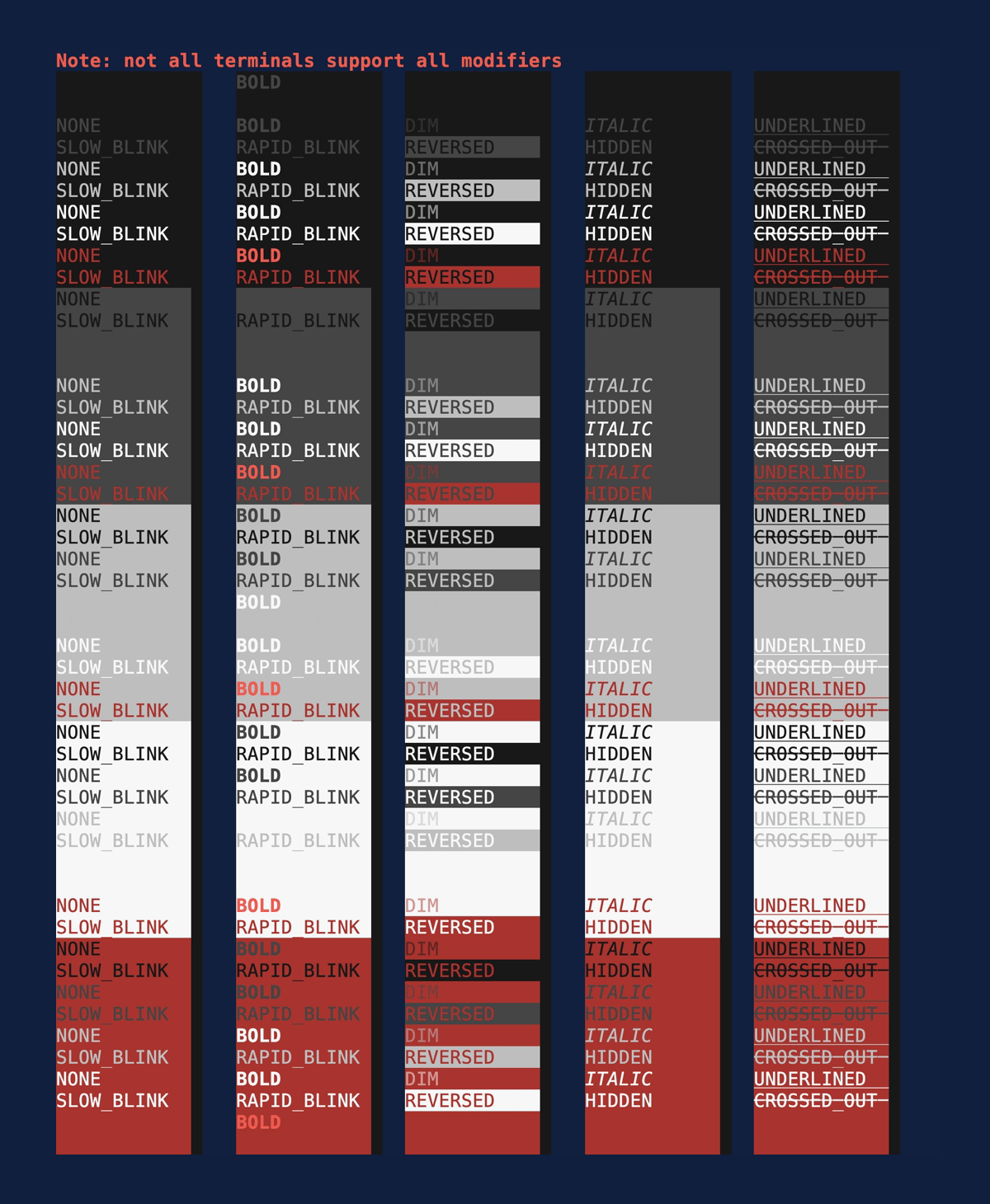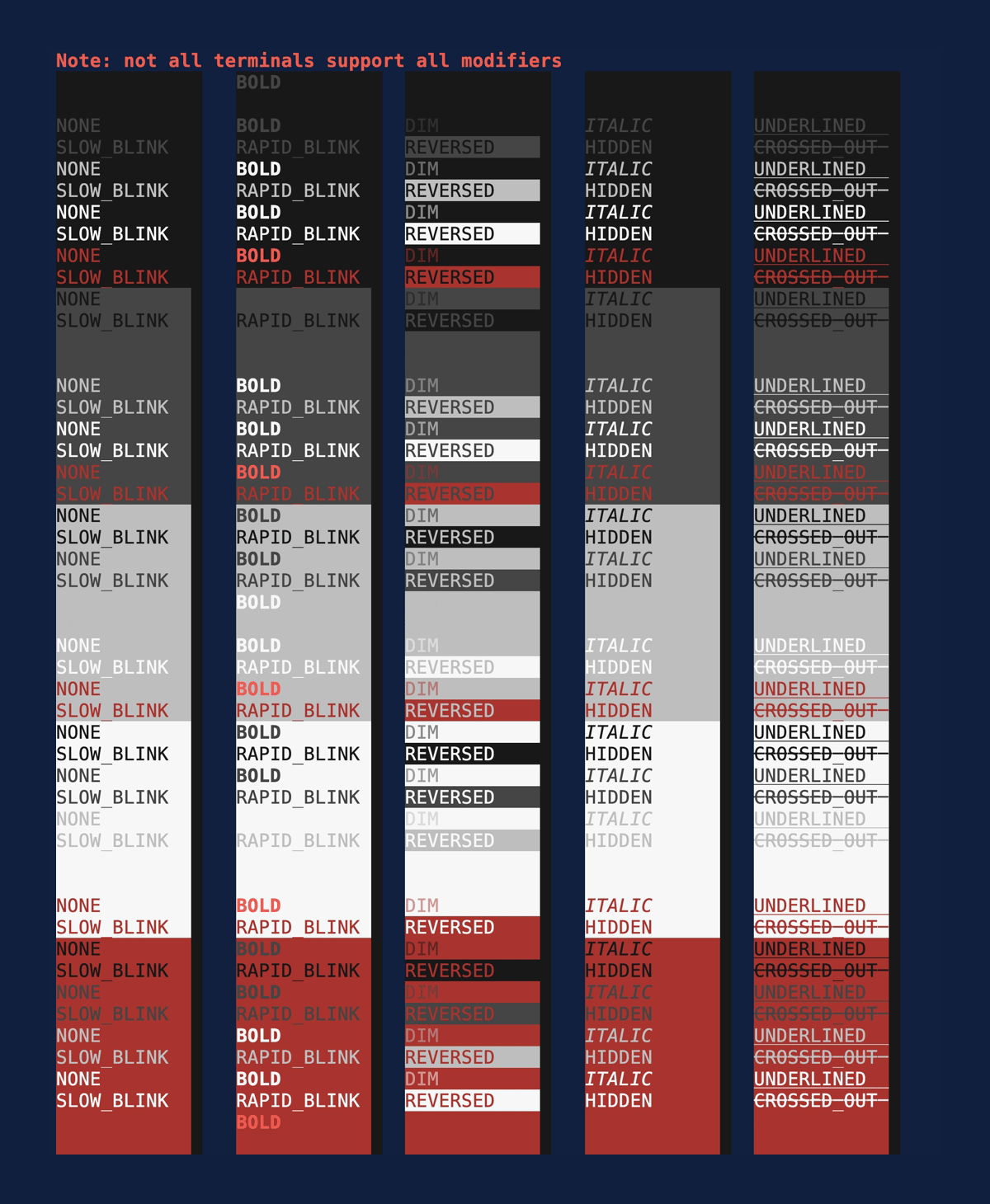
Modifiers
Demonstrates the style
Modifiers. Source:
modifiers.rs.
cargo run --example=modifiers --features=crossterm
Panic
Demonstrates how to handle panics by ensuring that panic messages are written correctly to the screen. Source: panic.rs.
cargo run --example=panic --features=crossterm
Paragraph
Demonstrates the Paragraph
widget. Source: paragraph.rs
cargo run --example=paragraph --features=crossterm
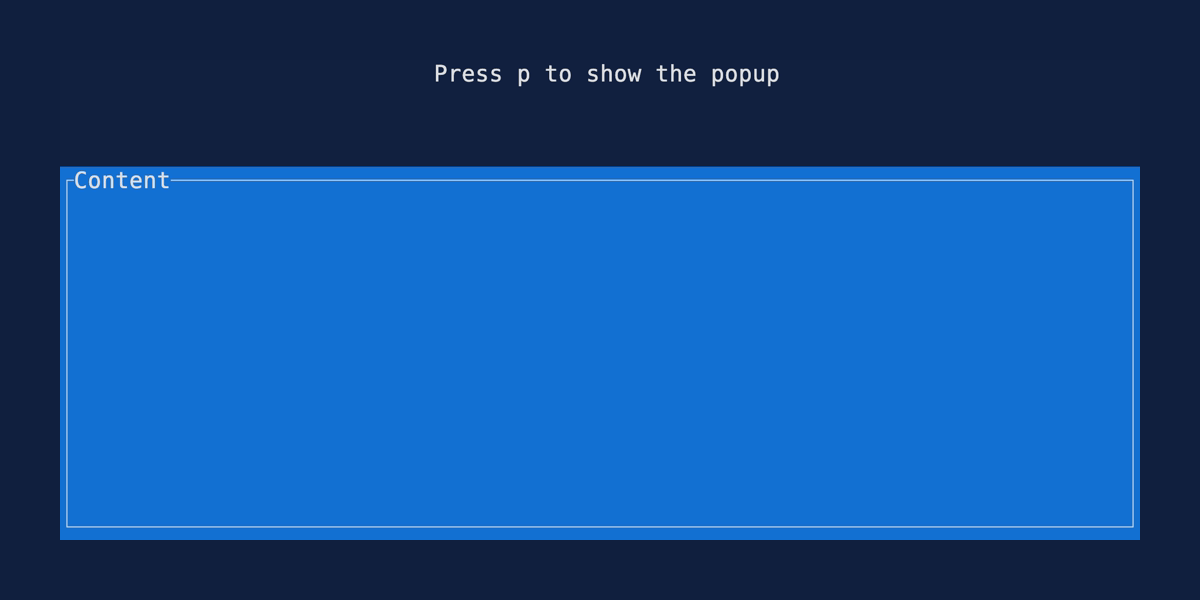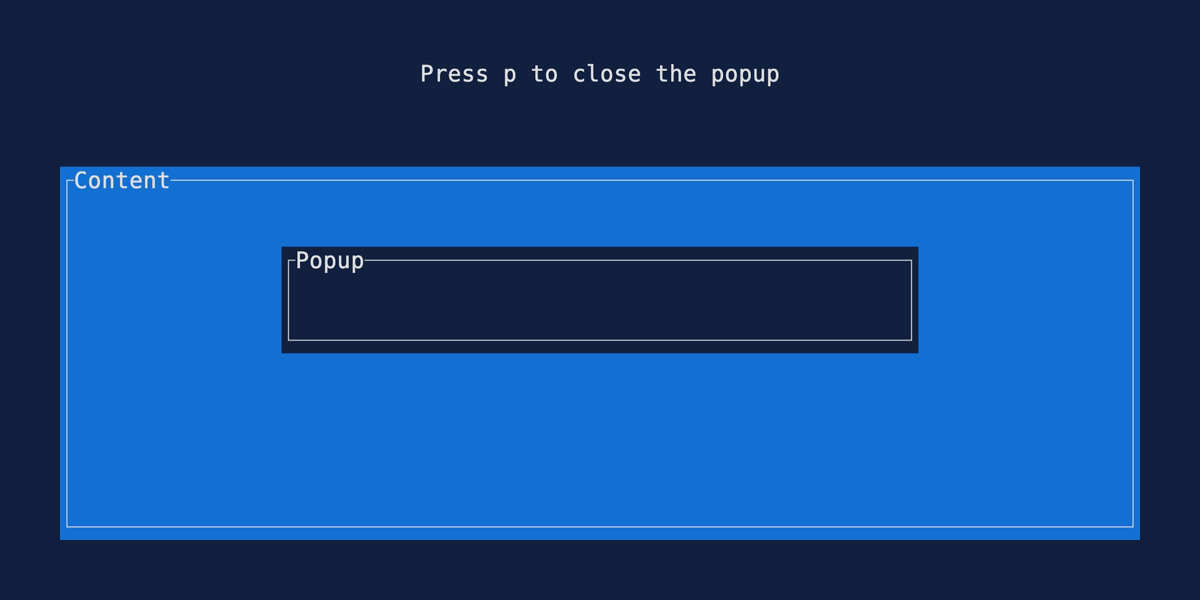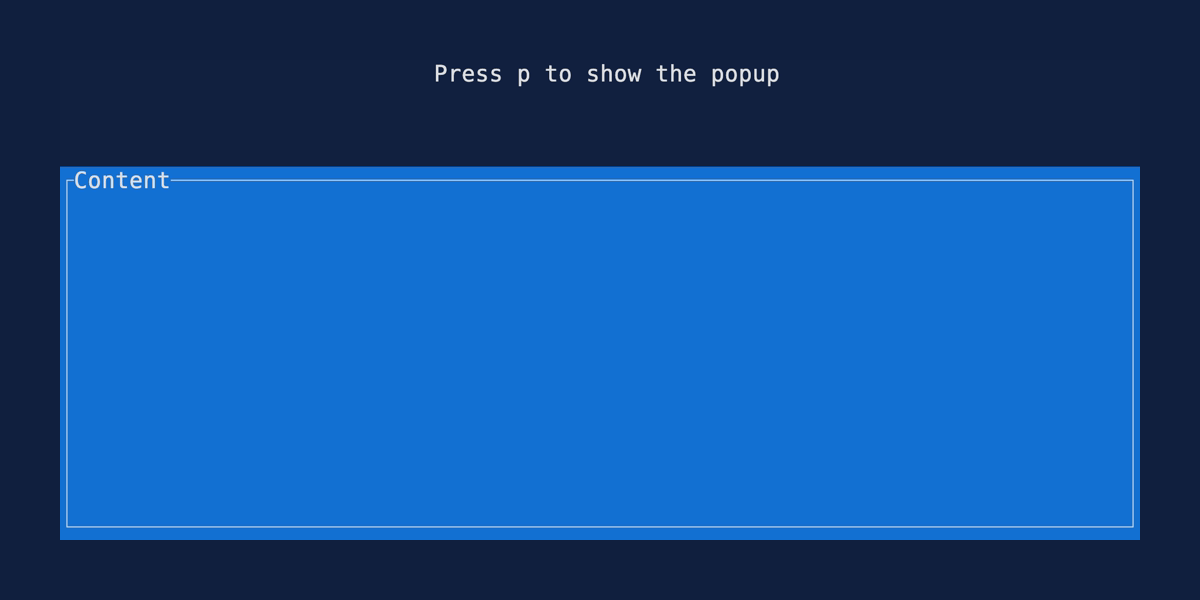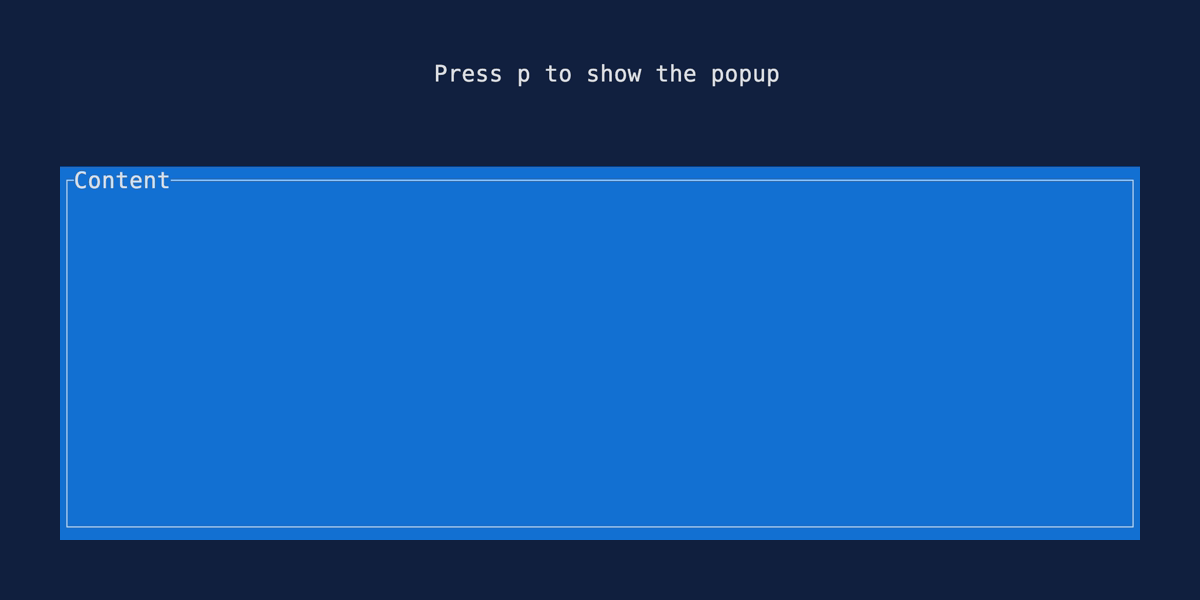
Popup
Demonstrates how to render a widget over the top of previously rendered widgets using the
Clear widget. Source:
popup.rs.
cargo run --example=popup --features=crossterm
Ratatui-logo
A fun example of using half blocks to render graphics Source: ratatui-logo.rs.
cargo run --example=ratatui-logo --features=crossterm
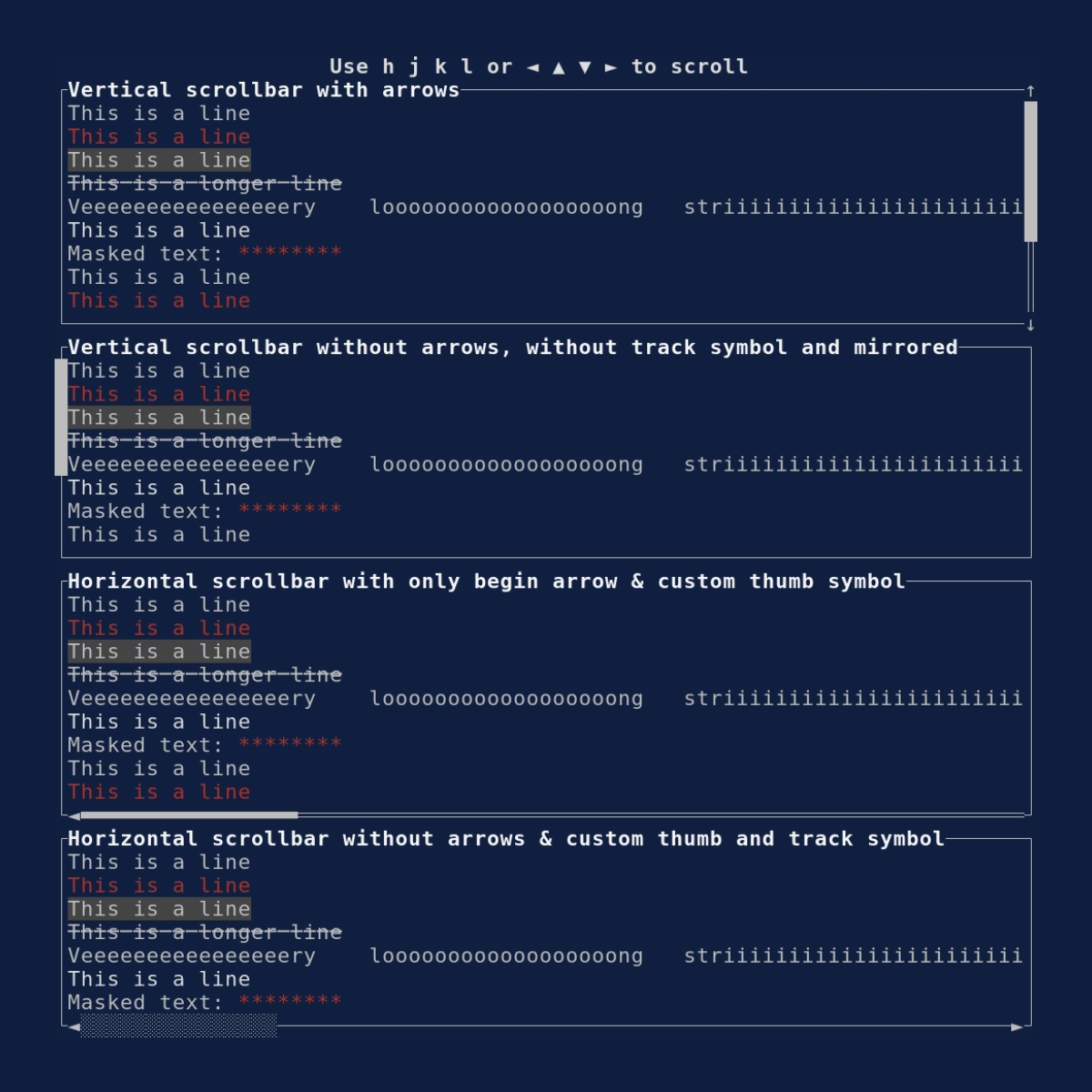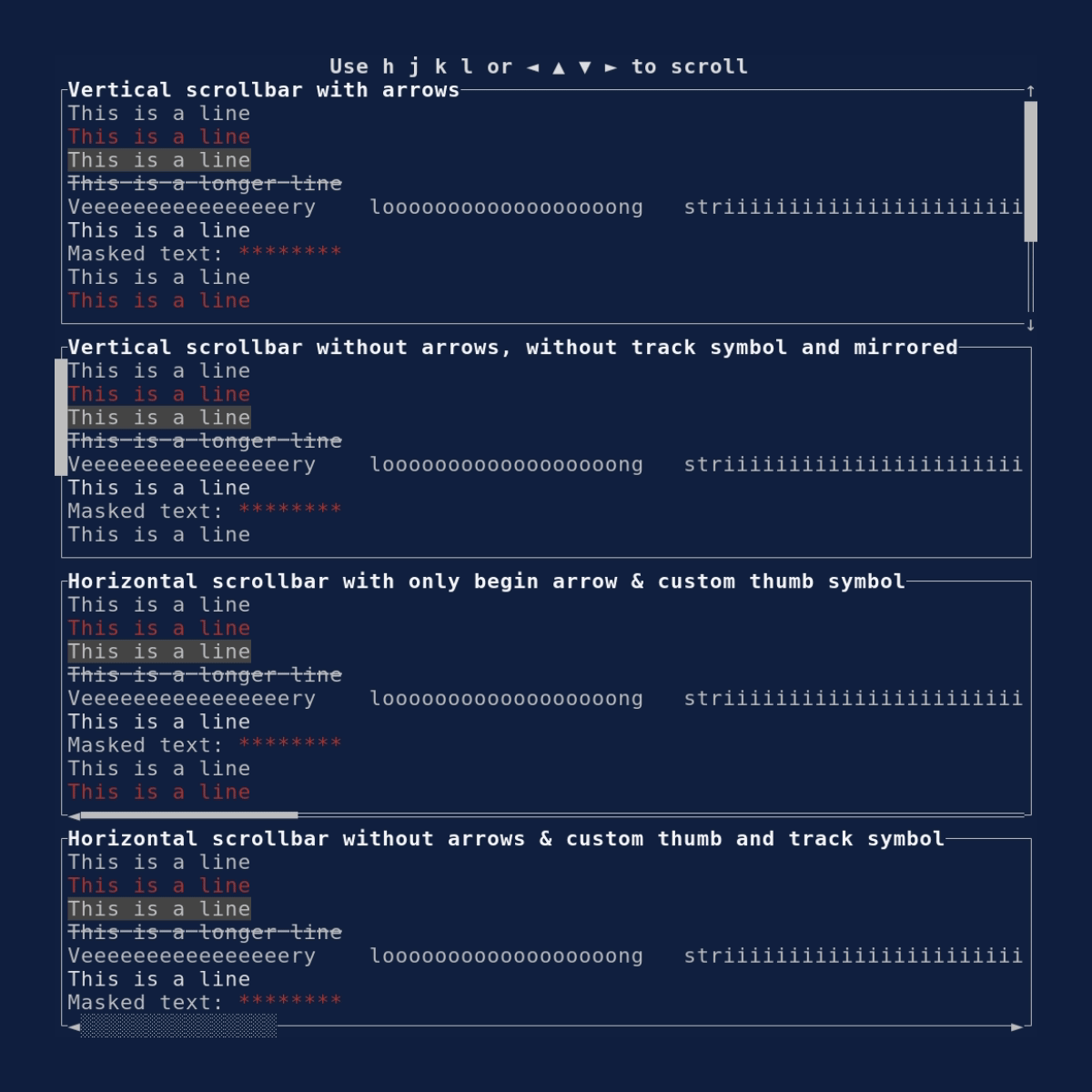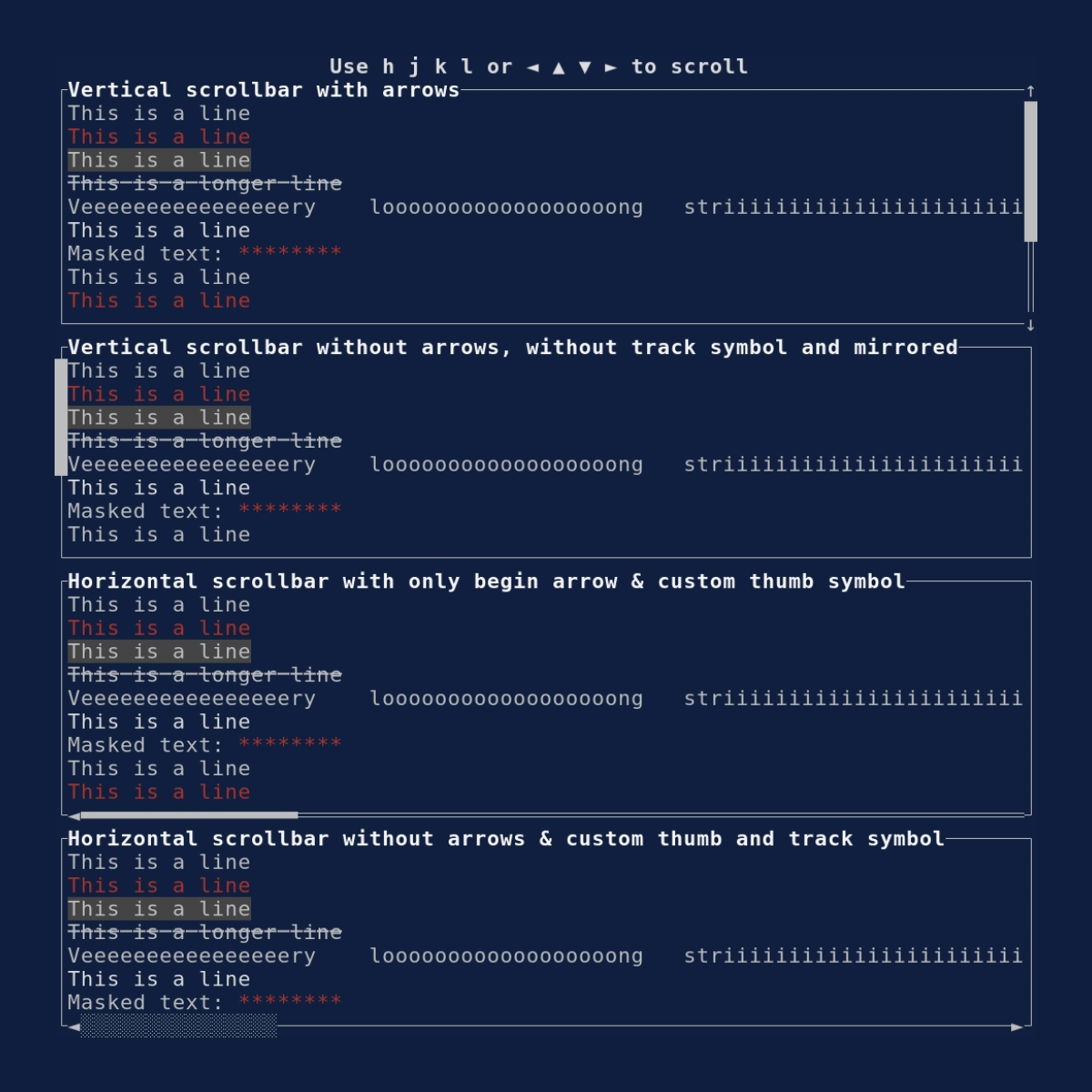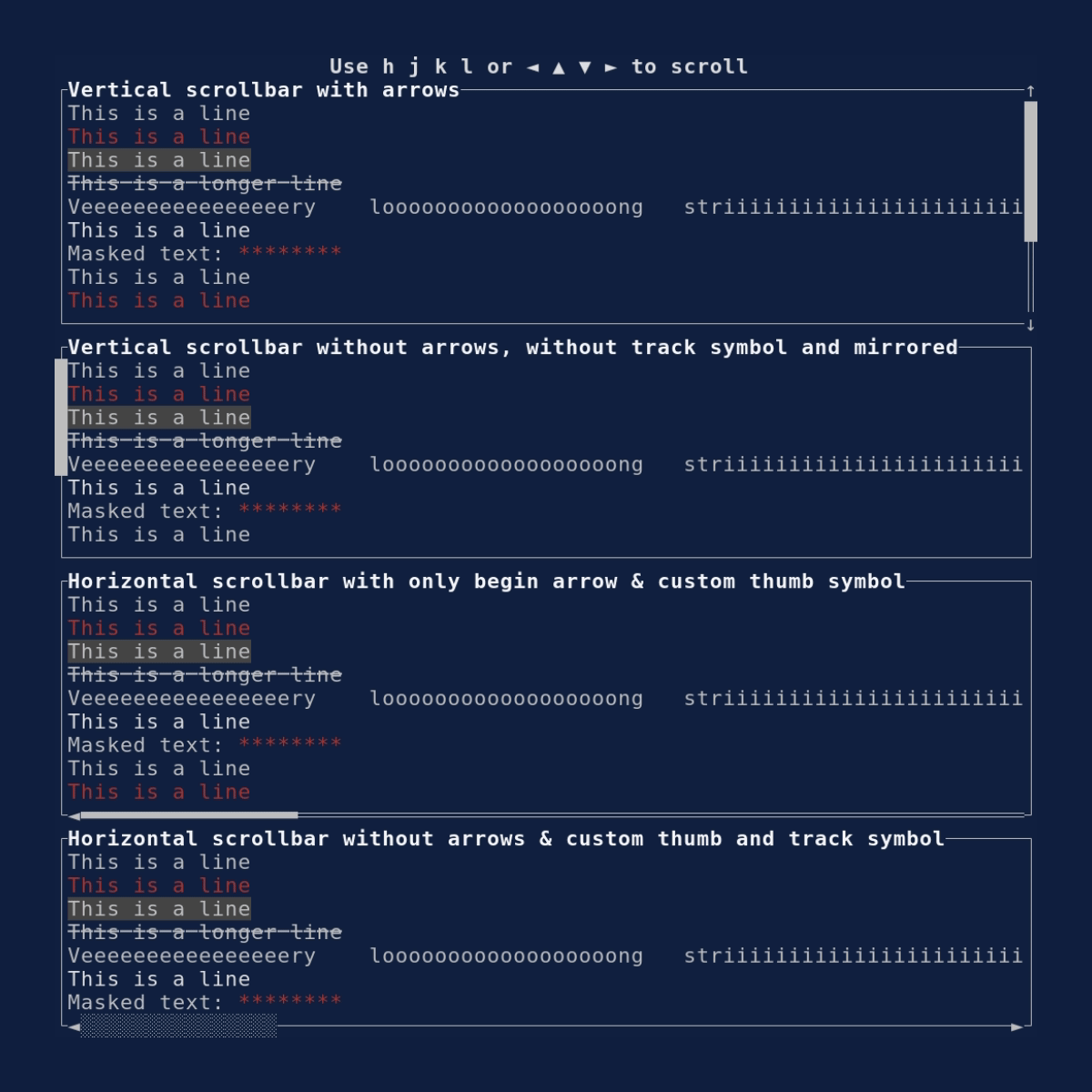
Scrollbar
Demonstrates the Scrollbar
widget. Source: scrollbar.rs.
cargo run --example=scrollbar --features=crossterm
Sparkline
Demonstrates the Sparkline
widget. Source: sparkline.rs.
cargo run --example=sparkline --features=crossterm
Table
Demonstrates the Table widget.
Source: table.rs.
cargo run --example=table --features=crossterm
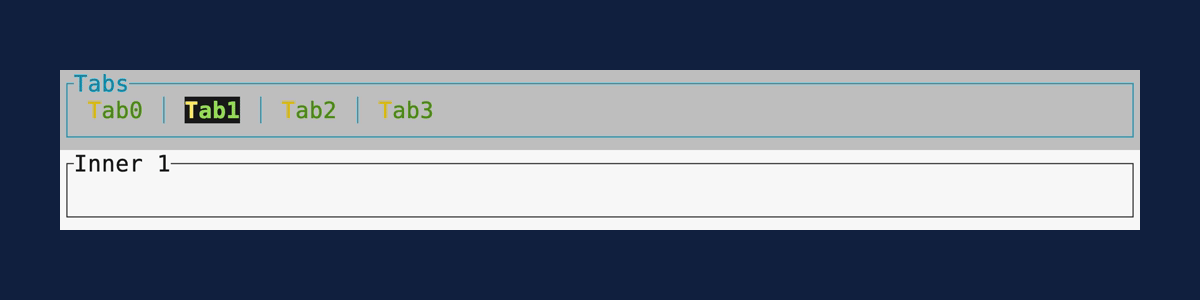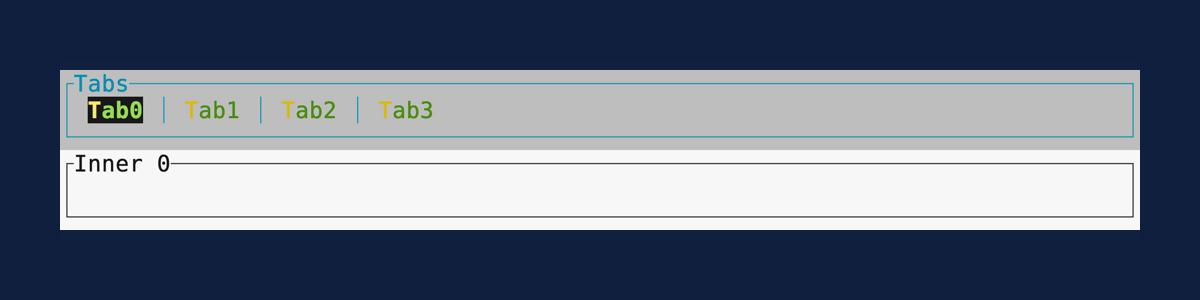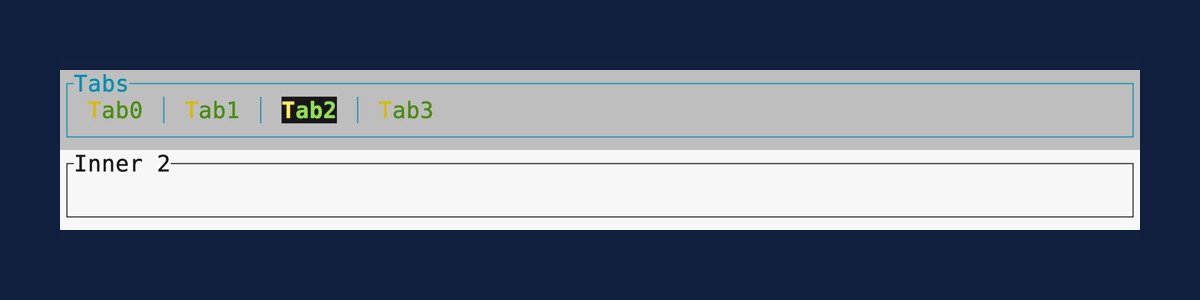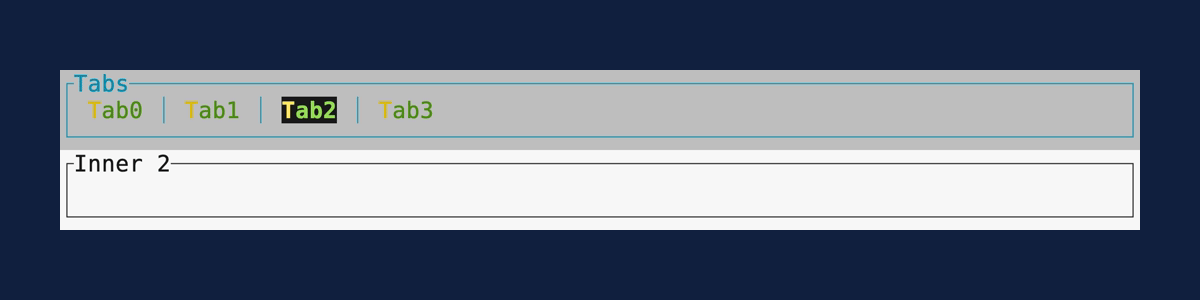
Tabs
Demonstrates the Tabs widget.
Source: tabs.rs.
cargo run --example=tabs --features=crossterm
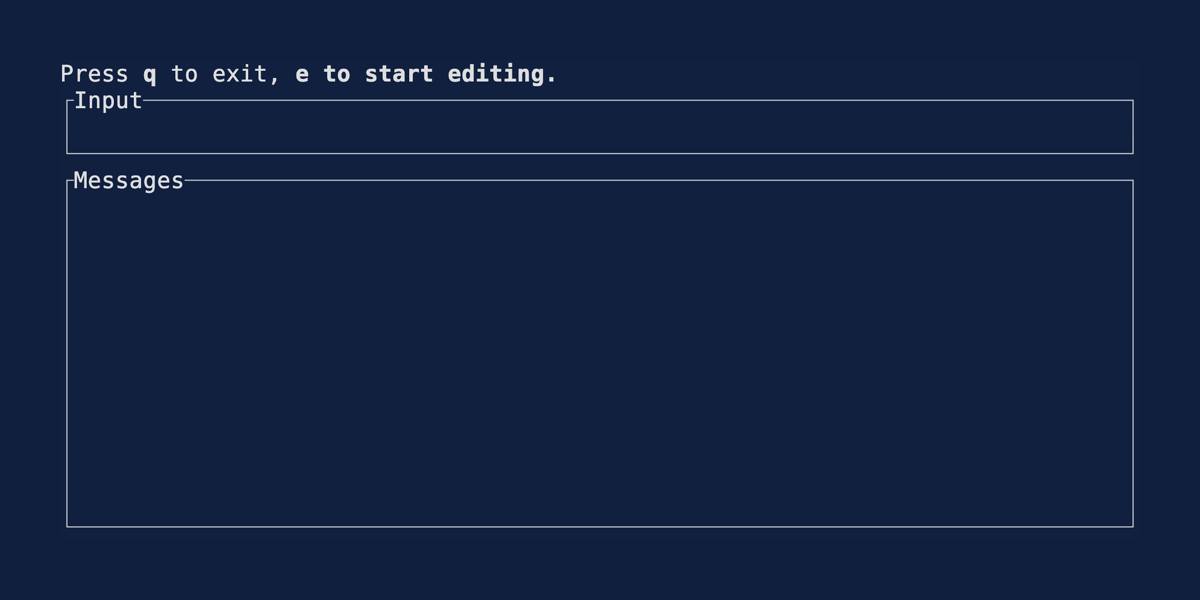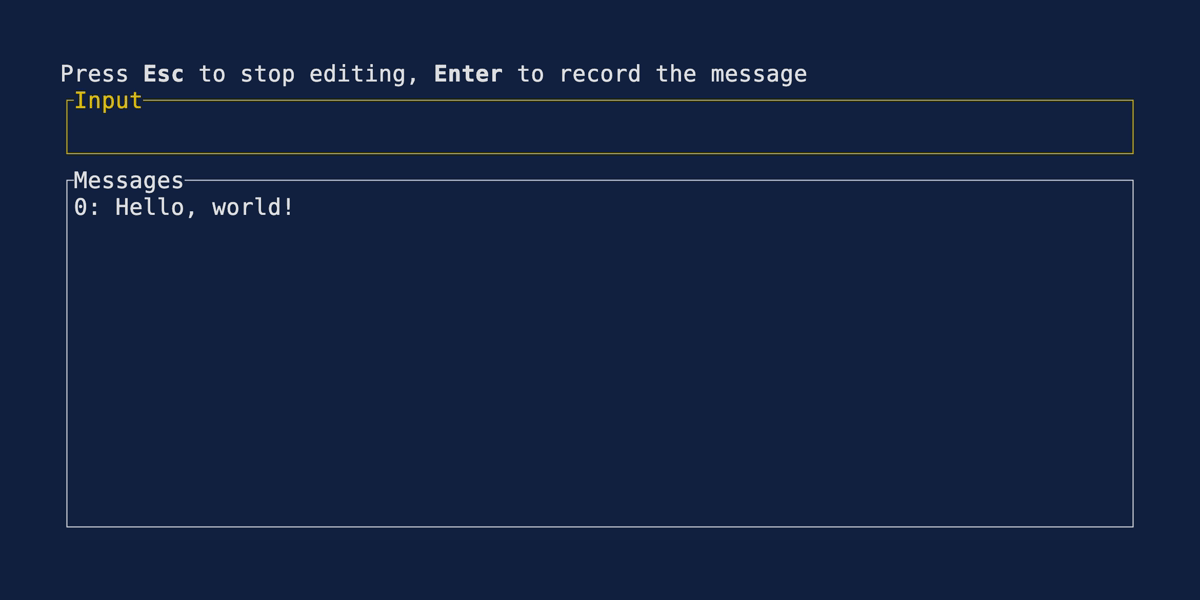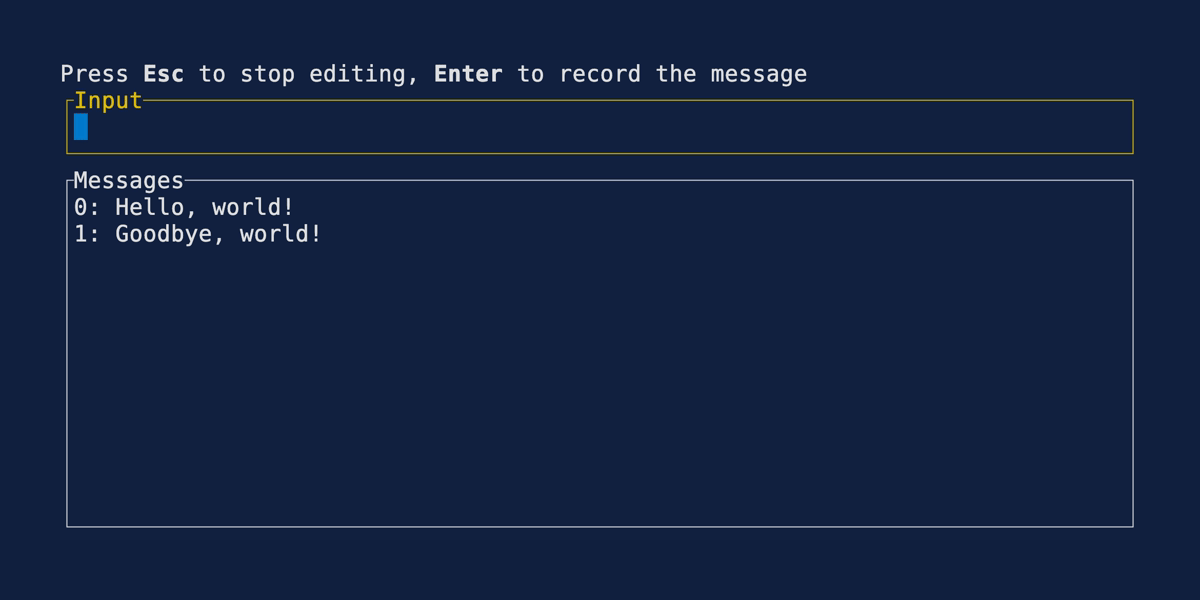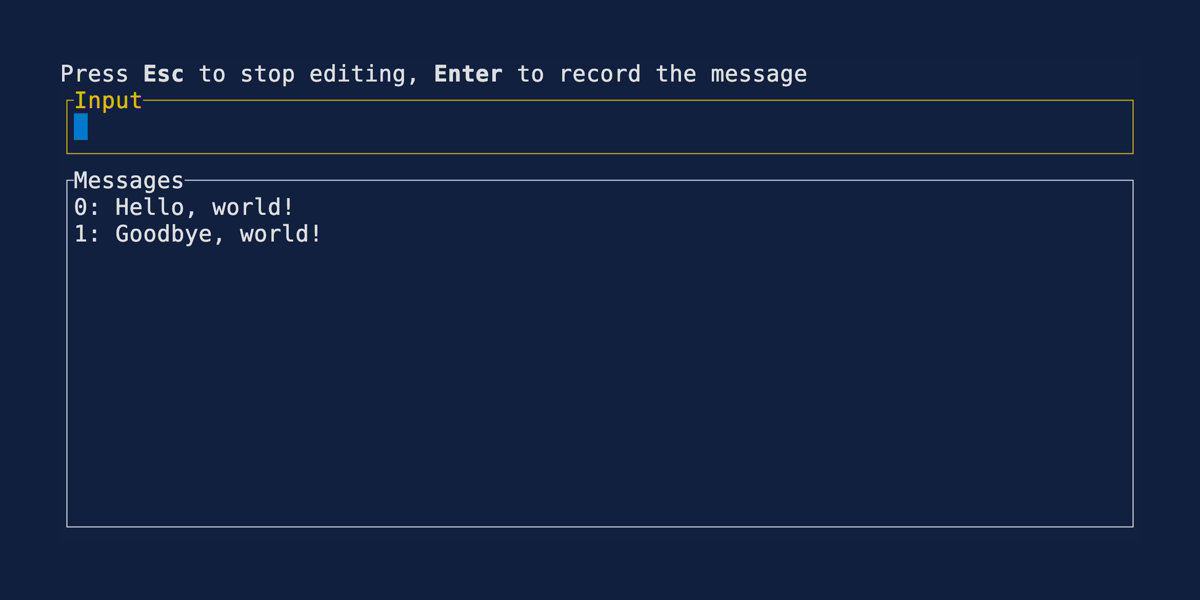
User Input
Demonstrates one approach to accepting user input. Source user_input.rs.
Note
Consider using
tui-textareaortui-inputcrates for more functional text entry UIs.
cargo run --example=user_input --features=crossterm
How to update these examples
These gifs were created using VHS. Each example has a
corresponding .tape file that holds instructions for how to generate the images. Note that the
images themselves are stored in a separate images git branch to avoid bloating the main
repository.