2022-04-11 18:18:46 +00:00
|
|
|
use crate::tests::{fail_test, run_test, run_test_with_env, TestResult};
|
|
|
|
|
use std::collections::HashMap;
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-01-22 18:24:47 +00:00
|
|
|
use super::run_test_contains;
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn env_shorthand() -> TestResult {
|
2022-03-03 00:55:03 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test("FOO=BAR if false { 3 } else { 4 }", "4")
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn subcommand() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("def foo [] {}; def \"foo bar\" [] {3}; foo bar", "3")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn alias_1() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("def foo [$x] { $x + 10 }; alias f = foo; f 100", "110")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-01-15 15:03:57 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn ints_with_underscores() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("1_0000_0000_0000 + 10", "1000000000010")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn floats_with_underscores() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("3.1415_9265_3589_793 * 2", "6.283185307179586")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn bin_ints_with_underscores() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("0b_10100_11101_10010", "21426")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn oct_ints_with_underscores() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("0o2443_6442_7652_0044", "90422533333028")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn hex_ints_with_underscores() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("0x68__9d__6a", "6856042")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn alias_2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
"def foo [$x $y] { $x + $y + 10 }; alias f = foo 33; f 100",
|
|
|
|
|
"143",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn alias_2_multi_word() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"def "foo bar" [$x $y] { $x + $y + 10 }; alias f = foo bar 33; f 100"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"143",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Re-implement aliases (#8123)
# Description
This PR adds an alternative alias implementation. Old aliases still work
but you need to use `old-alias` instead of `alias`.
Instead of replacing spans in the original code and re-parsing, which
proved to be extremely error-prone and a constant source of panics, the
new implementation creates a new command that references the old
command. Consider the new alias defined as `alias ll = ls -l`. The
parser creates a new command called `ll` and remembers that it is
actually a `ls` command called with the `-l` flag. Then, when the parser
sees the `ll` command, it will translate it to `ls -l` and passes to it
any parameters that were passed to the call to `ll`. It works quite
similar to how known externals defined with `extern` are implemented.
The new alias implementation should work the same way as the old
aliases, including exporting from modules, referencing both known and
unknown externals. It seems to preserve custom completions and pipeline
metadata. It is quite robust in most cases but there are some rough
edges (see later).
Fixes https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7648,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/8026,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7512,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/5780,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7754
No effect: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/8122 (we might
revisit the completions code after this PR)
Should use custom command instead:
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/6048
# User-Facing Changes
Since aliases are now basically commands, it has some new implications:
1. `alias spam = "spam"` (requires command call)
* **workaround**: use `alias spam = echo "spam"`
2. `def foo [] { 'foo' }; alias foo = ls -l` (foo defined more than
once)
* **workaround**: use different name (commands also have this
limitation)
4. `alias ls = (ls | sort-by type name -i)`
* **workaround**: Use custom command. _The common issue with this is
that it is currently not easy to pass flags through custom commands and
command referencing itself will lead to stack overflow. Both of these
issues are meant to be addressed._
5. TODO: Help messages, `which` command, `$nu.scope.aliases`, etc.
* Should we treat the aliases as commands or should they be separated
from regular commands?
6. Needs better error message and syntax highlight for recursed alias
(`alias f = f`)
7. Can't create alias with the same name as existing command (`alias ls
= ls -a`)
* Might be possible to add support for it (not 100% sure)
8. Standalone `alias` doesn't list aliases anymore
9. Can't alias parser keywords (e.g., stuff like `alias ou = overlay
use` won't work)
* TODO: Needs a better error message when attempting to do so
# Tests + Formatting
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used -A
clippy::needless_collect` to check that you're using the standard code
style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass
# After Submitting
If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
2023-02-27 07:44:05 +00:00
|
|
|
#[ignore = "TODO: Allow alias to alias existing command with the same name"]
|
2022-02-15 22:36:24 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn alias_recursion() -> TestResult {
|

Re-implement aliases (#8123)
# Description
This PR adds an alternative alias implementation. Old aliases still work
but you need to use `old-alias` instead of `alias`.
Instead of replacing spans in the original code and re-parsing, which
proved to be extremely error-prone and a constant source of panics, the
new implementation creates a new command that references the old
command. Consider the new alias defined as `alias ll = ls -l`. The
parser creates a new command called `ll` and remembers that it is
actually a `ls` command called with the `-l` flag. Then, when the parser
sees the `ll` command, it will translate it to `ls -l` and passes to it
any parameters that were passed to the call to `ll`. It works quite
similar to how known externals defined with `extern` are implemented.
The new alias implementation should work the same way as the old
aliases, including exporting from modules, referencing both known and
unknown externals. It seems to preserve custom completions and pipeline
metadata. It is quite robust in most cases but there are some rough
edges (see later).
Fixes https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7648,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/8026,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7512,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/5780,
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/7754
No effect: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/8122 (we might
revisit the completions code after this PR)
Should use custom command instead:
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/6048
# User-Facing Changes
Since aliases are now basically commands, it has some new implications:
1. `alias spam = "spam"` (requires command call)
* **workaround**: use `alias spam = echo "spam"`
2. `def foo [] { 'foo' }; alias foo = ls -l` (foo defined more than
once)
* **workaround**: use different name (commands also have this
limitation)
4. `alias ls = (ls | sort-by type name -i)`
* **workaround**: Use custom command. _The common issue with this is
that it is currently not easy to pass flags through custom commands and
command referencing itself will lead to stack overflow. Both of these
issues are meant to be addressed._
5. TODO: Help messages, `which` command, `$nu.scope.aliases`, etc.
* Should we treat the aliases as commands or should they be separated
from regular commands?
6. Needs better error message and syntax highlight for recursed alias
(`alias f = f`)
7. Can't create alias with the same name as existing command (`alias ls
= ls -a`)
* Might be possible to add support for it (not 100% sure)
8. Standalone `alias` doesn't list aliases anymore
9. Can't alias parser keywords (e.g., stuff like `alias ou = overlay
use` won't work)
* TODO: Needs a better error message when attempting to do so
# Tests + Formatting
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used -A
clippy::needless_collect` to check that you're using the standard code
style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass
# After Submitting
If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
2023-02-27 07:44:05 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test_contains(r#"alias ls = ls -a; ls"#, " ")
|
2022-02-15 22:36:24 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn block_param1() -> TestResult {
|
2022-02-17 11:40:24 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test("[3] | each { |it| $it + 10 } | get 0", "13")
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn block_param2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("[3] | each { |y| $y + 10 } | get 0", "13")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn block_param3_list_iteration() -> TestResult {
|
2022-02-17 11:40:24 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test("[1,2,3] | each { |it| $it + 10 } | get 1", "12")
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn block_param4_list_iteration() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("[1,2,3] | each { |y| $y + 10 } | get 2", "13")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn range_iteration1() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("1..4 | each { |y| $y + 10 } | get 0", "11")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn range_iteration2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test("4..1 | each { |y| $y + 100 } | get 3", "101")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn simple_value_iteration() -> TestResult {
|
2022-02-17 11:40:24 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test("4 | each { |it| $it + 10 }", "14")
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn comment_multiline() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"def foo [] {
|
|
|
|
|
let x = 1 + 2 # comment
|
|
|
|
|
let y = 3 + 4 # another comment
|
|
|
|
|
$x + $y
|
|
|
|
|
}; foo"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"10",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn comment_skipping_1() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"let x = {
|
|
|
|
|
y: 20
|
|
|
|
|
# foo
|
|
|
|
|
}; $x.y"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"20",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn comment_skipping_2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"let x = {
|
|
|
|
|
y: 20
|
|
|
|
|
# foo
|
|
|
|
|
z: 40
|
|
|
|
|
}; $x.z"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"40",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn bad_var_name() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"let $"foo bar" = 4"#, "can't contain")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-07-27 02:08:54 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn bad_var_name2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"let $foo-bar = 4"#, "valid variable")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn long_flag() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
2023-02-02 22:59:58 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"([a, b, c] | enumerate | each --keep-empty { |e| if $e.index != 1 { 100 }}).1 | to nuon"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"null",
|
2021-12-25 19:39:42 +00:00
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-27 03:04:22 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn let_not_statement() -> TestResult {
|
2022-01-15 15:26:52 +00:00
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"let x = "hello" | str length"#, "used in pipeline")
|
2021-12-27 03:04:22 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-27 20:04:48 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn for_in_missing_var_name() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test("for in", "missing")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-02 05:27:58 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn multiline_pipe_in_block() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"do {
|
|
|
|
|
echo hello |
|
|
|
|
|
str length
|
|
|
|
|
}"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"5",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-06 21:06:54 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn bad_short_flag() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"def foo3 [-l?:int] { $l }"#, "short flag")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-10 02:52:01 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn alias_with_error_doesnt_panic() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"alias s = shells
|
|
|
|
|
s ."#,
|
|
|
|
|
"extra positional",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-19 14:58:12 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn quotes_with_equals() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"let query_prefix = "https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=repo:nushell/"; $query_prefix"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=repo:nushell/",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_interp_with_equals() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"let query_prefix = $"https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=repo:nushell/"; $query_prefix"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=repo:nushell/",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-21 16:39:55 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn recursive_parse() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"def c [] { c }; echo done"#, "done")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-22 18:24:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn commands_have_usage() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test_contains(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"
|
|
|
|
|
# This is a test
|
|
|
|
|
#
|
|
|
|
|
# To see if I have cool usage
|
|
|
|
|
def foo [] {}
|
|
|
|
|
help foo"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"cool usage",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-01-27 01:20:12 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn equals_separates_long_flag() -> TestResult {
|
2022-11-09 22:19:02 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test(
|

A `fill` command to replace `str lpad` and `str rpad` (#7846)
# Description
The point of this command is to allow you to be able to format ints,
floats, filesizes, and strings with an alignment, padding, and a fill
character, as strings. It's meant to take the place of `str lpad` and
`str rpad`.
```
> help fill
Fill and Align
Search terms: display, render, format, pad, align
Usage:
> fill {flags}
Flags:
-h, --help - Display the help message for this command
-w, --width <Int> - The width of the output. Defaults to 1
-a, --alignment <String> - The alignment of the output. Defaults to Left (Left(l), Right(r), Center(c/m), MiddleRight(cr/mr))
-c, --character <String> - The character to fill with. Defaults to ' ' (space)
Signatures:
<number> | fill -> <string>
<string> | fill -> <string>
Examples:
Fill a string on the left side to a width of 15 with the character '─'
> 'nushell' | fill -a l -c '─' -w 15
Fill a string on the right side to a width of 15 with the character '─'
> 'nushell' | fill -a r -c '─' -w 15
Fill a string on both sides to a width of 15 with the character '─'
> 'nushell' | fill -a m -c '─' -w 15
Fill a number on the left side to a width of 5 with the character '0'
> 1 | fill --alignment right --character 0 --width 5
Fill a filesize on the left side to a width of 5 with the character '0'
> 1kib | fill --alignment middle --character 0 --width 10
```
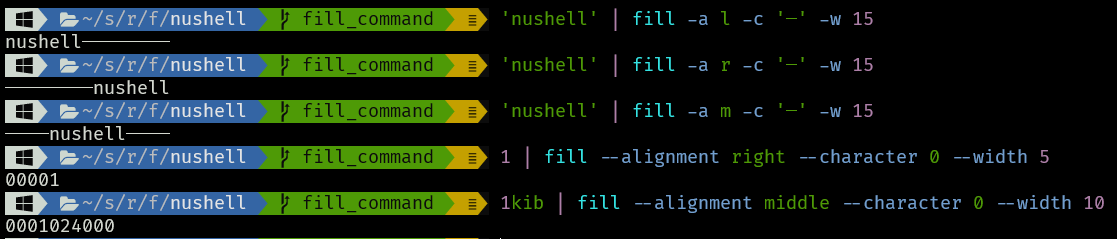
# User-Facing Changes
Deprecated `str lpad` and `str rpad`.
# Tests + Formatting
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used -A
clippy::needless_collect` to check that you're using the standard code
style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass
# After Submitting
If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
2023-02-09 20:56:52 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"'nushell' | fill --alignment right --width=10 --character='-'"#,
|
2022-11-09 22:19:02 +00:00
|
|
|
"---nushell",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
2022-01-27 01:20:12 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-09 18:41:41 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn let_env_expressions() -> TestResult {
|
2022-04-11 18:18:46 +00:00
|
|
|
let env = HashMap::from([("VENV_OLD_PATH", "Foobar"), ("Path", "Quux")]);
|
|
|
|
|
run_test_with_env(
|
2023-03-01 08:20:00 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"let-env Path = if ($env | columns | "VENV_OLD_PATH" in $in) { $env.VENV_OLD_PATH } else { $env.Path }; echo $env.Path"#,
|
2022-04-11 18:18:46 +00:00
|
|
|
"Foobar",
|
|
|
|
|
&env,
|
2022-02-09 18:41:41 +00:00
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-10 16:09:08 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_interpolation_paren_test() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"('(')(')')""#, "()")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_interpolation_paren_test2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"('(')test(')')""#, "(test)")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_interpolation_paren_test3() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"('(')("test")test(')')""#, "(testtest)")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-03-15 16:09:30 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_interpolation_escaping() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"hello\nworld" | lines | length"#, "2")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn capture_multiple_commands() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"
|
|
|
|
|
let CONST_A = 'Hello'
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'say-hi' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo (call-me)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'call-me' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo $CONST_A
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
[(say-hi) (call-me)] | str join
|
2022-02-21 13:38:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"HelloHello",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn capture_multiple_commands2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"
|
|
|
|
|
let CONST_A = 'Hello'
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'call-me' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo $CONST_A
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'say-hi' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo (call-me)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
[(say-hi) (call-me)] | str join
|
2022-02-21 13:38:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"HelloHello",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn capture_multiple_commands3() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"
|
|
|
|
|
let CONST_A = 'Hello'
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'say-hi' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo (call-me)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'call-me' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo $CONST_A
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
[(call-me) (say-hi)] | str join
|
2022-02-21 13:38:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"HelloHello",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn capture_multiple_commands4() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"
|
|
|
|
|
let CONST_A = 'Hello'
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'call-me' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo $CONST_A
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
def 'say-hi' [] {
|
|
|
|
|
echo (call-me)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
[(call-me) (say-hi)] | str join
|
2022-02-21 13:38:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-02-10 23:15:15 +00:00
|
|
|
"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"HelloHello",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-11 12:37:10 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn capture_row_condition() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"let name = "foo"; [foo] | where $'($name)' =~ $it | str join"#,
|
2022-02-11 12:37:10 +00:00
|
|
|
"foo",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-14 17:33:47 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-04-01 18:35:46 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn starts_with_operator_succeeds() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"[Moe Larry Curly] | where $it starts-with L | str join"#,
|
2022-04-01 18:35:46 +00:00
|
|
|
"Larry",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-05-02 08:02:38 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn ends_with_operator_succeeds() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
2022-09-11 08:48:27 +00:00
|
|
|
r#"[Moe Larry Curly] | where $it ends-with ly | str join"#,
|
2022-05-02 08:02:38 +00:00
|
|
|
"Curly",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-02-14 17:33:47 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn proper_missing_param() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"def foo [x y z w] { }; foo a b c"#, "missing w")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-02-17 11:40:24 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn block_arity_check1() -> TestResult {
|
2023-01-01 10:26:51 +00:00
|
|
|
fail_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"ls | each { |x, y, z| 1}"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"expected 2 closure parameters",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
2022-02-17 11:40:24 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2022-03-03 18:14:03 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-01-28 20:25:53 +00:00
|
|
|
// deprecating former support for escapes like `/uNNNN`, dropping test.
|
2022-03-03 18:14:03 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
2023-01-28 20:25:53 +00:00
|
|
|
fn string_escape_unicode_extended() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#""\u{015B}\u{1f10b}""#, "ś🄋")
|
2022-03-03 18:14:03 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_escape_interpolation() -> TestResult {
|
2023-01-28 20:25:53 +00:00
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"\u{015B}(char hamburger)abc""#, "ś≡abc")
|
2022-03-03 18:14:03 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2022-03-07 16:44:27 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-03-26 23:52:09 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn string_escape_interpolation2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"$"2 + 2 is \(2 + 2)""#, "2 + 2 is (2 + 2)")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-03-07 16:44:27 +00:00
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn proper_rest_types() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"def foo [--verbose(-v): bool, # my test flag
|
|
|
|
|
...rest: int # my rest comment
|
|
|
|
|
] { if $verbose { print "verbose!" } else { print "not verbose!" } }; foo"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"not verbose!",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-04-02 22:41:36 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn single_value_row_condition() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"[[a, b]; [true, false], [true, true]] | where a | length"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"2",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-04-06 19:10:25 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_1() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"not false"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"not (false)"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_3() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"(not false)"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_4() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"if not false { "hello" } else { "world" }"#, "hello")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_5() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"if not not not not false { "hello" } else { "world" }"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"world",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unary_not_6() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(
|
|
|
|
|
r#"[[name, present]; [abc, true], [def, false]] | where not present | get name.0"#,
|
|
|
|
|
"def",
|
|
|
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-04-07 06:02:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn date_literal() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"2022-09-10 | date to-record | get day"#, "10")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-04-22 19:14:31 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn and_and_or() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"true and false or true"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2022-11-26 16:02:37 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn and_and_xor() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
// Assumes the precedence NOT > AND > XOR > OR
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"true and true xor true and false"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn or_and_xor() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
// Assumes the precedence NOT > AND > XOR > OR
|
|
|
|
|
run_test(r#"true or false xor true or false"#, "true")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2023-01-24 08:05:46 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unbalanced_delimiter() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"{a:{b:5}}}"#, "unbalanced { and }")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2023-03-10 20:26:14 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unbalanced_delimiter2() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"{}#.}"#, "unbalanced { and }")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2023-03-17 02:19:23 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn unbalanced_delimiter3() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"{"#, "Unexpected end of code")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2023-04-08 20:04:57 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn register_with_string_literal() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(r#"register 'nu-plugin-math'"#, "File not found")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn register_with_string_constant() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
let input = "\
|
|
|
|
|
const file = 'nu-plugin-math'
|
|
|
|
|
register $file
|
|
|
|
|
";
|
|
|
|
|
// should not fail with `not a constant`
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(input, "File not found")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn register_with_string_variable() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
let input = "\
|
|
|
|
|
let file = 'nu-plugin-math'
|
|
|
|
|
register $file
|
|
|
|
|
";
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(input, "Value is not a parse-time constant")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
|
|
|
fn register_with_non_string_constant() -> TestResult {
|
|
|
|
|
let input = "\
|
|
|
|
|
const file = 6
|
|
|
|
|
register $file
|
|
|
|
|
";
|
|
|
|
|
fail_test(input, "expected string, found int")
|
|
|
|
|
}
|