| .github | ||
| alfred | ||
| scripts | ||
| shell | ||
| src | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| Cargo.lock | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
navi 


An interactive cheatsheet tool for the command-line and application launchers.
navi allows you to browse through cheatsheets (that you may write yourself or download from maintainers) and execute commands. Argument suggestions are prompted to you.
Pros
- it will make you type less;
- it will spare you from knowing CLIs by heart;
- it will teach you new one-liners.
It uses fzf, skim, or Alfred under the hood and it can be either used as a command or as a shell widget (à la Ctrl-R).
Table of contents
- Installation
- Usage
- Trying out online
- Cheatsheets
- Cheatsheet syntax
- List customization
- Related projects
- Etymology
Installation
Using Homebrew or Linuxbrew
brew install navi
Using nix
nix-env -iA nixpkgs.navi
Using cargo
cargo install navi
Using install script
bash <(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/denisidoro/navi/master/scripts/install)
# alternatively, to set directories:
# SOURCE_DIR=/opt/navi BIN_DIR=/usr/local/bin bash <(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/denisidoro/navi/master/scripts/install)
Downloading pre-compiled binaries
You can download binaries here.
Building from source
git clone https://github.com/denisidoro/navi ~/.navi
cd ~/.navi
make install
# alternatively, to set install directory:
# make BIN_DIR=/usr/local/bin install
Other package managers
You can find navi for more package managers by clicking on the image below:
Feel free to be the maintainer of navi for any package manager you'd like!
Usage
By running navi for the first time, you'll be suggested to download some cheatsheets. By running navi again, these cheatsheets will appear.
Shell widget
You can use navi as a widget to your shell. This way, your history is correctly populated and you can edit the command as you wish before executing it. To set it up, add this line to your .bashrc-like file:
# bash
source <(echo "$(navi widget bash)")
# zsh
source <(echo "$(navi widget zsh)")
# fish
navi widget fish | source
By default, Ctrl+G is assigned to launching navi.
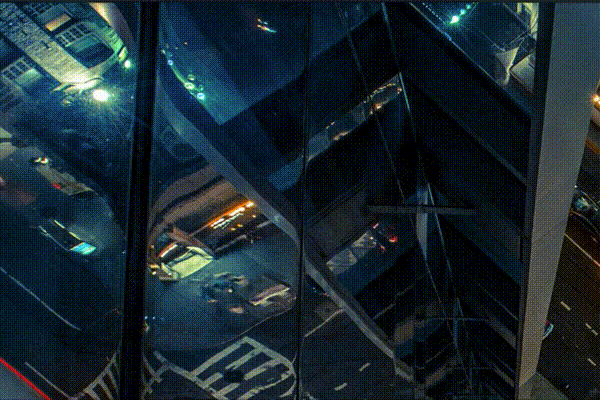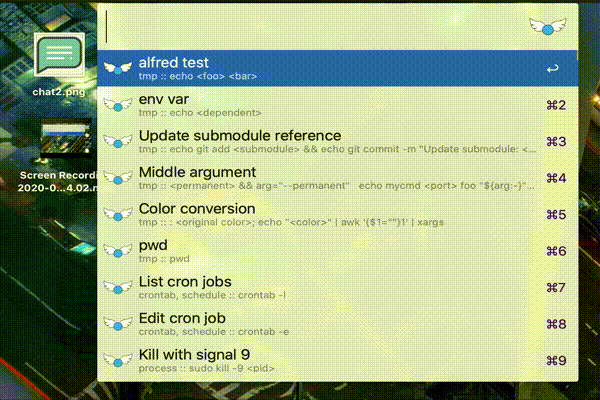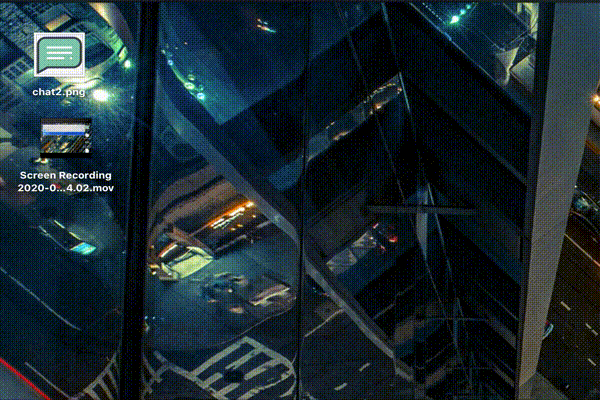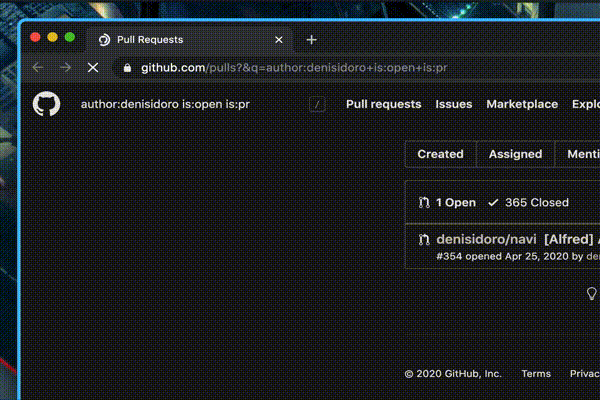
Alfred
This is experimental. If you face any issues, please report the issue here.
- make sure you have Alfred Powerpack;
- make sure navi is up to date;
- make sure that the
navibinary is in the$PATHdetermined by~/.bashrc; - download and install the
.alfredworkflowfor the latest release.
More options
Please refer to navi --help for more details.
Trying out online
If you don't have access to a Unix shell at the moment and you want to live preview navi, head to this playground. It'll start a docker container with instructions for you to install and use the tool. Note: login required.
Cheatsheets
Importing cheatsheets
You can find cheatsheet repositories with:
navi repo browse
In addition, you can import cheatsheets from any git repository:
navi repo add https://github.com/denisidoro/cheats
Adding your own cheatsheets
You can either start a git repo with cheatsheets and import it as described above or you can add them directly to data_dir/navi.
Submitting cheatsheets
The main repository for cheatsheets is denisidoro/cheats. Feel free to open a PR there for me to include your contributions.
In order to add your own repository as a featured cheatsheet repo, please edit this file. This list will be displayed when navi repo browse is run.
Cheatsheet syntax
Cheatsheets are described in .cheat files that look like this:
% git, code
# Change branch
git checkout <branch>
$ branch: git branch | awk '{print $NF}'
Syntax overview
- lines starting with
%determine the start of a new cheatsheet and should contain tags, useful for searching; - lines starting with
#should be descriptions of commands; - lines starting with
;are ignored. You can use them for metacomments; - lines starting with
$should contain commands that generate a list of possible values for a given argument; - lines starting with
@should contain tags whose associated cheatsheet you want to base on; - all the other non-empty lines are considered as executable commands.
It's irrelevant how many files are used to store cheatsheets. They can be all in a single file if you wish, as long as you split them accordingly with lines starting with %.
Variables
The interface prompts for variable names inside brackets (eg <branch>).
Variable names should only include alphanumeric characters and _.
If there's a corresponding line starting with $ for a variable, suggestions will be displayed. Otherwise, the user will be able to type any value for it.
If you hit <tab> the query typed will be prefered. If you hit <enter> the selection will be prefered.
Advanced variable options
For lines starting with $ you can use --- to customize the behavior of fzf or how the value is going to be used:
# This will pick the 3rd column and use the first line as header
docker rmi <image_id>
# Even though "false/true" is displayed, this will print "0/1"
echo <mapped>
$ image_id: docker images --- --column 3 --header-lines 1 --delimiter '\s\s+'
$ mapped: echo 'false true' | tr ' ' '\n' --- --map "[[ $0 == t* ]] && echo 1 || echo 0"
The supported parameters are:
--prevent-extra(experimental): limits the user to select one of the suggestions;--column <number>: extracts a single column from the selected result;--map <bash_code>(experimental): applies a map function to the selected variable value;
In addition, it's possible to forward the following parameters to fzf:
--multi;--header-lines <number>;--delimiter <regex>;--query <text>;--filter <text>;--header <text>;--preview <bash_code>;--preview-window <text>.
Variable dependency
The command for generating possible inputs can implicitly refer other variables by using the <varname> syntax:
# Should print /my/pictures/wallpapers
echo "<wallpaper_folder>"
$ pictures_folder: echo "/my/pictures"
$ wallpaper_folder: echo "<pictures_folder>/wallpapers"
If you want to make dependencies explicit, you can use the $varname syntax:
# If you select "hello" for <x>, the possible values of <y> will be "hello foo" and "hello bar"
echo <x> <y>
# If you want to ignore the contents of <x> and only print <y>
: <x>; echo <y>
$ x: echo "hello hi" | tr ' ' '\n'
$ y: echo "$x foo;$x bar" | tr ';' '\n'
Extending cheatsheets
With the @ same tags from other cheatsheet syntax you can reuse the same variable in multiple cheatsheets.
% dirs, common
$ pictures_folder: echo "/my/pictures"
% wallpapers
@ dirs, common
# Should print /my/pictures/wallpapers
echo "<pictures_folder>/wallpapers"
% screenshots
@ dirs, common
# Should print /my/pictures/screenshots
echo "<pictures_folder>/screenshots"
Multiline snippets
Commands may be multiline:
# This will output "foo\nyes"
echo foo
true \
&& echo yes \
|| echo no
Variable as multiple arguments
# This will result into: cat "file1.json" "file2.json"
jsons=($(echo "<jsons>"))
cat "${jsons[@]}"
$ jsons: find . -iname '*.json' -type f -print --- --multi
List customization
Lists can be stylized with the $FZF_DEFAULT_OPTS environment variable or similar variables/parameters (please refer to navi --help). This way, you can change the color scheme, for example.
Related projects
There are many similar projects out there (bro, eg, cheat.sh, tldr, cmdmenu, cheat, beavr, how2 and howdoi, to name a few).
Most of them provide excellent cheatsheet repositories, but lack a nice UI and argument suggestions.
Etymology
In The Legend of Zelda Ocarina of Time, navi is a character that provides Link with a variety of clues to help him solve puzzles and progress in his quest.