|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| ci | ||
| doc | ||
| src | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .release.toml | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| build.rs | ||
| Cargo.lock | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| CODEOWNERS | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
LSD (LSDeluxe)
Table of Contents
- Description
- Screenshot
- Installation
- Configuration
- External Configurations
- F.A.Q.
- Contributors
- Credits
Description
This project is heavily inspired by the super colorls project but with some little differences. For example it is written in rust and not in ruby which makes it much faster.
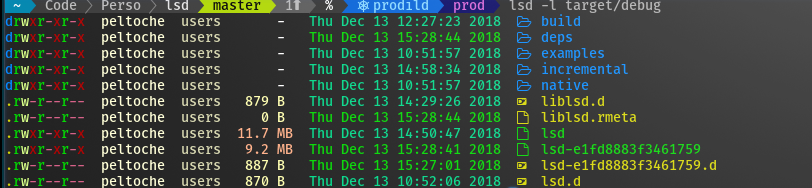
Screenshot
Installation
Prerequisites
Install the patched fonts of powerline nerd-font and/or font-awesome. Have a look at the Nerd Font README for more installation instructions. Don't forget to setup your terminal in order to use the correct font.
See this issue comment for detailed instructions on how to configure iTerm2 font settings correctly.
On Archlinux
pacman -S lsd
On Fedora
dnf install lsd
On Ubuntu
... and other Debian-based Linux distributions
Download the latest .deb package from the release page and install it via:
sudo dpkg -i lsd_0.20.1_amd64.deb # adapt version number and architecture
On Gentoo
sudo emerge sys-apps/lsd
(Ebuild maintained by Georgy Yakovlev)
On macOS
via Homebrew:
brew install lsd
or MacPorts:
sudo port install lsd
On NixOS/From nix
nix-env -iA nixos.lsd
Or add lsd to your configuration.nix like so:
# ...
environment.systemPackages = with pkgs; [
# other packages ...
lsd
];
# ...
On FreeBSD
pkg install lsd
On NetBSD
... and other platforms using pkgsrc
Using the package manager:
pkgin install lsd
Building from source:
cd /usr/pkgsrc/sysutils/lsd
make install
On Windows
Install with Scoop:
scoop install lsd
On Android (via Termux)
pkg install lsd
From Sources
With Rust's package manager cargo, you can install lsd via:
cargo install lsd
If you want to install the latest master branch commit:
cargo install --git https://github.com/Peltoche/lsd.git --branch master
From Binaries
The release page includes precompiled binaries for Linux and macOS.
Configuration
lsd can be configured with a configuration file to set the default options.
Check Config file content for details.
Config file location
Non-Windows
On non-Windows systems lsd follows the
XDG Base Directory Specification
convention for the location of the configuration file. The configuration dir
lsd uses is itself named lsd. In that directory it looks first for a file
called config.yaml.
For most people it should be enough to put their config file at
~/.config/lsd/config.yaml.
Windows
On Windows systems lsd only looks for the config.yaml files in one location:
%APPDATA%\lsd\
Custom
You can also provide a configuration file from a non standard location:
lsd --config-file [PATH]
Config file content
This is an example config file with the default values and some additional remarks.
# == Classic ==
# This is a shorthand to override some of the options to be backwards compatible
# with `ls`. It affects the "color"->"when", "sorting"->"dir-grouping", "date"
# and "icons"->"when" options.
# Possible values: false, true
classic: false
# == Blocks ==
# This specifies the columns and their order when using the long and the tree
# layout.
# Possible values: permission, user, group, size, size_value, date, name, inode
blocks:
- permission
- user
- group
- size
- date
- name
# == Color ==
# This has various color options. (Will be expanded in the future.)
color:
# When to colorize the output.
# When "classic" is set, this is set to "never".
# Possible values: never, auto, always
when: auto
# How to colorize the output.
# When "classic" is set, this is set to "no-color".
# Possible values: default, <theme-file-name>
# when specifying <theme-file-name>, lsd will look up theme file
# XDG Base Directory if relative, e.g. ~/.config/lsd/themes/<theme-file-name>.yaml,
# The file path if absolute
theme: default
# == Date ==
# This specifies the date format for the date column. The freeform format
# accepts an strftime like string.
# When "classic" is set, this is set to "date".
# Possible values: date, relative, '+<date_format>'
# `date_format` will be a `strftime` formatted value. e.g. `date: '+%d %b %y %X'` will give you a date like this: 17 Jun 21 20:14:55
date: date
# == Dereference ==
# Whether to dereference symbolic links.
# Possible values: false, true
dereference: false
# == Display ==
# What items to display. Do not specify this for the default behavior.
# Possible values: all, almost-all, directory-only
# display: all
# == Icons ==
icons:
# When to use icons.
# When "classic" is set, this is set to "never".
# Possible values: always, auto, never
when: auto
# Which icon theme to use.
# Possible values: fancy, unicode
theme: fancy
# Separator between icon and the name
# Default to 1 space
separator: ' '
# == Ignore Globs ==
# A list of globs to ignore when listing.
# ignore-globs:
# - .git
# == Indicators ==
# Whether to add indicator characters to certain listed files.
# Possible values: false, true
indicators: false
# == Layout ==
# Which layout to use. "oneline" might be a bit confusing here and should be
# called "one-per-line". It might be changed in the future.
# Possible values: grid, tree, oneline
layout: grid
# == Recursion ==
recursion:
# Whether to enable recursion.
# Possible values: false, true
enabled: false
# How deep the recursion should go. This has to be a positive integer. Leave
# it unspecified for (virtually) infinite.
# depth: 3
# == Size ==
# Specifies the format of the size column.
# Possible values: default, short, bytes
size: default
# == Sorting ==
sorting:
# Specify what to sort by.
# Possible values: extension, name, time, size, version
column: name
# Whether to reverse the sorting.
# Possible values: false, true
reverse: false
# Whether to group directories together and where.
# When "classic" is set, this is set to "none".
# Possible values: first, last, none
dir-grouping: none
# == No Symlink ==
# Whether to omit showing symlink targets
# Possible values: false, true
no-symlink: false
# == Total size ==
# Whether to display the total size of directories.
# Possible values: false, true
total-size: false
# == Symlink arrow ==
# Specifies how the symlink arrow display, chars in both ascii and utf8
symlink-arrow: ⇒
Theme
lsd can be configured with a theme file to set the colors.
Theme can be configured in the configuration file(color.theme), The valid theme configurations are:
default: the default color scheme shipped inlsd- theme-file-name(yaml): use the theme file to specify colors(without the
yamlextension)
when configured with the theme-file-name which is a yaml file,
lsd will look up the theme file in the following way:
- relative name: check the themes under XDG Base Directory, e.g. ~/.config/lsd/themes/.yaml
- absolute name: use the file path and name to find theme file
Check Theme file content for details.
Filename coloring
lsd use both LS_COLORS and this theme feature to
colorize the filename, lsd will use the color and format option defined in LS_COLORS,
and then the theme configurations if no LS_COLOR are found.
Theme file content
Theme file use the crossterm configure the colors, check crossterm for the supported colors.
Color table: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/15/Xterm_256color_chart.svg
Please notice that color value would ignore case, both lowercase and UPPERCASE is supported.
This is the default theme scheme shipped with lsd.
user: 230
group: 187
permissions:
read: Green
write: Yellow
exec: Red
exec-sticky: 5
no-access: 245
file-type:
file:
exec-uid: 40
uid-no-exec: 184
exec-no-uid: 40
no-exec-no-uid: 184
dir:
uid: 33
no-uid: 33
pipe: 44
symlink:
default: 44
broken: 124
block-device: 44
char-device: 172
socket: 44
special: 44
modified:
hour-old: 40
day-old: 42
older: 36
size:
none: 245
small: 229
medium: 216
large: 172
inode:
valid: 13
invalid: 245
links:
valid: 13
invalid: 245
tree-edge: 245
External Configurations
Required
Enable nerd fonts for your terminal, URxvt for example:
.Xresources
URxvt*font: xft:Hack Nerd Font:style=Regular:size=11
Optional
In order to use lsd when entering the ls command, you need to add this to your shell
configuration file (~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, etc.):
alias ls='lsd'
Some further examples of useful aliases:
alias l='ls -l'
alias la='ls -a'
alias lla='ls -la'
alias lt='ls --tree'
F.A.Q
Default Colors
In the future the possibility to customize the colors might be implemented. For now, the default colors are:
UTF-8 Chars
lsd will try to display the UTF-8 chars in file name, A U+FFFD REPLACEMENT CHARACTER(<28>) is used to represent the invalid UTF-8 chars.
Contributors
Everyone can contribute to this project, improving the code or adding functions. If anyone wants something to be added we will try to do it.
As this is being updated regularly, don't forget to rebase your fork before creating a pull-request.
Credits
Special thanks to:
- meain for all his contributions and reviews
- danieldulaney for the Windows integration
- sharkdp and his superb fd from which I have stolen a lot of CI stuff.
- athityakumar for the project colorls
- All the other contributors