| .. | ||
| enrolling-devices-in-other-organisations.md | ||
| README.md | ||
MacOS MDM
Basics
What is MDM (Mobile Device Management)?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a technology commonly used to administer end-user computing devices such as mobile phones, laptops, desktops and tablets. In the case of Apple platforms like iOS, macOS and tvOS, it refers to a specific set of features, APIs and techniques used by administrators to manage these devices. Management of devices via MDM requires a compatible commercial or open-source MDM server that implements support for the MDM Protocol.
- A way to achieve centralized device management
- Requires an MDM server which implements support for the MDM protocol
- MDM server can send MDM commands, such as remote wipe or “install this config”
Basics What is DEP (Device Enrolment Program)?
The Device Enrollment Program (DEP) is a service offered by Apple that simplifies Mobile Device Management (MDM) enrollment by offering zero-touch configuration of iOS, macOS, and tvOS devices. Unlike more traditional deployment methods, which require the end-user or administrator to take action to configure a device, or manually enroll with an MDM server, DEP aims to bootstrap this process, allowing the user to unbox a new Apple device and have it configured for use in the organization almost immediately.
Administrators can leverage DEP to automatically enroll devices in their organization’s MDM server. Once a device is enrolled, in many cases it is treated as a “trusted” device owned by the organization, and could receive any number of certificates, applications, WiFi passwords, VPN configurations and so on.
- Allows a device to automatically enroll in pre-configured MDM server the first time it’s powered on
- Most useful when the device is brand new
- Can also be useful for reprovisioning workflows (wiped with fresh install of the OS)
{% hint style="danger" %} Unfortunately, if an organization has not taken additional steps to** protect their MDM enrollment**, a simplified end-user enrollment process through DEP can also mean a simplified process for** attackers to enroll a device of their choosing in the organization’s MDM** server, assuming the "identity" of a corporate device. {% endhint %}
Basics What is SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrolment Protocol)?
- A relatively old protocol, created before TLS and HTTPS were widespread.
- Gives clients a standardized way of sending a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for the purpose of being granted a certificate. The client will ask the server to give him a signed certificate.
What are Configuration Profiles (aka mobileconfigs)?
- Apple’s official way of setting/enforcing system configuration.
- File format that can contain multiple payloads.
- Based on property lists (the XML kind).
- “can be signed and encrypted to validate their origin, ensure their integrity, and protect their contents.” Basics — Page 70, iOS Security Guide, January 2018.
Protocols
MDM
- Combination of APNs (Apple servers) + RESTful API (MDM vendor servers)
- Communication occurs between a device and a server associated with a device management product
- Commands delivered from the MDM to the device in plist-encoded dictionaries
- All over HTTPS. MDM servers can be (and are usually) pinned.
- Apple grants the MDM vendor an APNs certificate for authentication
DEP
- 3 APIs: 1 for resellers, 1 for MDM vendors, 1 for device identity (undocumented):
- The so-called DEP "cloud service" API. This is used by MDM servers to associate DEP profiles with specific devices.
- The DEP API used by Apple Authorized Resellers to enroll devices, check enrollment status, and check transaction status.
- The undocumented private DEP API. This is used by Apple Devices to request their DEP profile. On macOS, the
cloudconfigurationdbinary is responsible for communicating over this API.
- More modern and JSON based (vs. plist)
- Apple grants an OAuth token to the MDM vendor
DEP "cloud service" API
- RESTful
- sync device records from Apple to the MDM server
- sync “DEP profiles” to Apple from the MDM server (delivered by Apple to the device later on)
- A DEP “profile” contains:
- MDM vendor server URL
- Additional trusted certificates for server URL (optional pinning)
- Extra settings (e.g. which screens to skip in Setup Assistant)
Steps for enrolment and management
- Device record creation (Reseller, Apple): The record for the new device is created
- Device record assignment (Customer): The device is assigned to a MDM server
- Device record sync (MDM vendor): MDM sync the device records and push the DEP profiles to Apple
- DEP check-in (Device): Device gets his DEP profile
- Profile retrieval (Device)
- Profile installation (Device) a. incl. MDM, SCEP and root CA payloads
- MDM command issuance (Device)
The file /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX10.15.sdk/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/ConfigurationProfiles.framework/ConfigurationProfiles.tbd exports functions that can be considered high-level "steps" of the enrolment process.
Step 4: DEP check-in - Getting the Activation Record
This part of the process occurs when a user boots a Mac for the first time (or after a complete wipe)
or when executing sudo profiles show -type enrollment
- Determine whether device is DEP enabled
- Activation Record is the internal name for DEP “profile”
- Begins as soon as the device is connected to Internet
- Driven by
CPFetchActivationRecord - Implemented by
cloudconfigurationdvia XPC. The "Setup Assistant" (when the device is firstly booted) or theprofilescommand will contact this daemon to retrieve the activation record.- LaunchDaemon (always runs as root)
It follows a few steps to get the Activation Record performed by MCTeslaConfigurationFetcher. This process uses an encryption called Absinthe
- Retrieve certificate
- Initialize state from certificate (
NACInit)- Uses various device-specific data (i.e. Serial Number via
IOKit)
- Uses various device-specific data (i.e. Serial Number via
- Retrieve session key
- Establish the session (
NACKeyEstablishment) - Make the request
- POST to https://iprofiles.apple.com/macProfile sending the data
{ "action": "RequestProfileConfiguration", "sn": "" } - The JSON payload is encrypted using Absinthe (
NACSign) - All requests over HTTPs, built-in root certificates are used
- POST to https://iprofiles.apple.com/macProfile sending the data
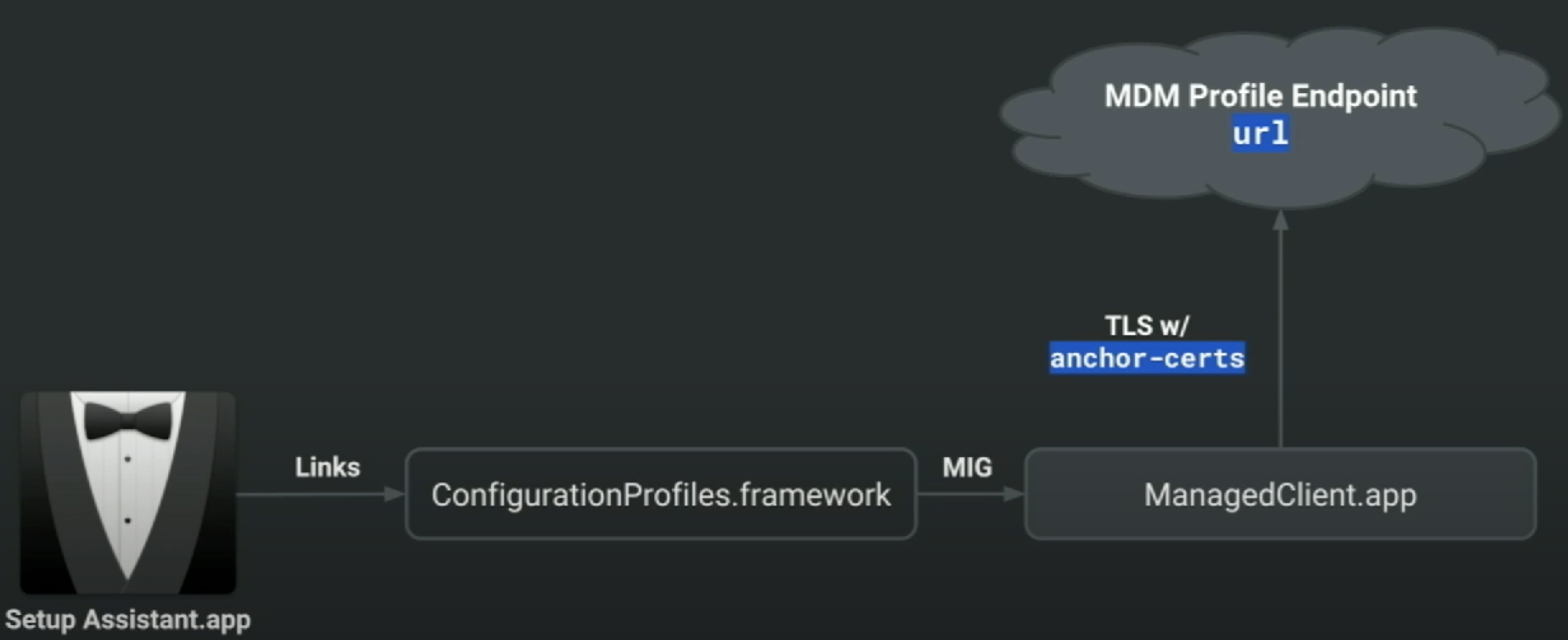
The response is a JSON dictionary with some important data like:
- url: URL of the MDM vendor host for the activation profile
- anchor-certs: Array of DER certificates used as trusted anchors
Step 5: Profile Retrieval
- Request sent to url provided in DEP profile.
- Anchor certificates are used to evaluate trust if provided.
- Reminder: the anchor_certs property of the DEP profile
- Request is a simple .plist with device identification
- Examples: UDID, OS version.
- CMS-signed, DER-encoded
- Signed using the device identity certificate (from APNS)
- Certificate chain includes expired Apple iPhone Device CA
Step 6: Profile Installation
- Once retrieved, profile is stored on the system
- This step begins automatically (if in setup assistant)
- Driven by
CPInstallActivationProfile - Implemented by mdmclient over XPC
- LaunchDaemon (as root) or LaunchAgent (as user), depending on context
- Configuration profiles have multiple payloads to install
- Framework has a plugin-based architecture for installing profiles
- Each payload type is associated with a plugin
- Can be XPC (in framework) or classic Cocoa (in ManagedClient.app)
- Example:
- Certificate Payloads use CertificateService.xpc
Typically, activation profile provided by an MDM vendor will include the following payloads:
com.apple.mdm: to enroll the device in MDMcom.apple.security.scep: to securely provide a client certificate to the device.com.apple.security.pem: to install trusted CA certificates to the device’s System Keychain.- Installing the MDM payload equivalent to MDM check-in in the documentation
- Payload contains key properties:
- MDM Check-In URL (
CheckInURL) - MDM Command Polling URL (
ServerURL) + APNs topic to trigger it - To install MDM payload, request is sent to
CheckInURL - Implemented in
mdmclient - MDM payload can depend on other payloads
- Allows requests to be pinned to specific certificates:
- Property:
CheckInURLPinningCertificateUUIDs - Property:
ServerURLPinningCertificateUUIDs - Delivered via PEM payload
- Property:
- Allows device to be attributed with an identity certificate:
- Property: IdentityCertificateUUID
- Delivered via SCEP payload
Step 7: Listening for MDM commands
- After MDM check-in is complete, vendor can issue push notifications using APNs
- Upon receipt, handled by
mdmclient - To poll for MDM commands, request is sent to ServerURL
- Makes use of previously installed MDM payload:
ServerURLPinningCertificateUUIDsfor pinning requestIdentityCertificateUUIDfor TLS client certificate
Attacks
Enrolling Devices in Other Organisations
As previously commented, in order to try to enrol a device into an organization only a Serial Number belonging to that Organization is needed. Once the device is enrolled, several organizations will install sensitive data on the new device: certificates, applications, WiFi passwords, VPN configurations and so on.
Therefore, this could be a dangerous entrypoint for attackers if the enrolment process isn't correctly protected:
{% content-ref url="enrolling-devices-in-other-organisations.md" %} enrolling-devices-in-other-organisations.md {% endcontent-ref %}