# SpEL - Spring Expression Language
**POST COPIED FROM** [**https://medium.com/@xvnpw/hacking-spel-part-1-d2ff2825f62a**](https://medium.com/@xvnpw/hacking-spel-part-1-d2ff2825f62a)\*\*\*\*
This story will explain how to find and exploit SpEL parser in web applications based on Java language.
What is SpEL ? From Spring documentation: _The Spring Expression Language \(SpEL for short\) is a powerful expression language that supports querying and manipulating an object graph at runtime._
Where is it used ?
1. Spring Framework: Security, Data, …
2. **Any place developers use it by SpEL API**
3. For languages it can be used in Java, Kotlin, Scala, and other JVM based technologies.
First point is known by issues in past like: [CVE-2018–1273](https://tanzu.vmware.com/security/cve-2018-1273), [CVE-2017–8046](https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2017-8046) or CVE-2011–2730. I will not talk about them, I will focus on point number two.
### SpEL API
Most common use cases for SpEL that I have seen in web applications:
* complex expressions using custom function calls: `fun1("some string") ? "text" : fun2("some other string")`
* dynamic code evaluation: `T(org.springframework.util.StreamUtils).copy(T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec`…
Any of user input can be part of expression. Also input can be expression as a whole. Those above use cases are good indicators what to look for in web apps. Key words: **expression**, **mapping**, **dynamic** 😃
### Payloads
From you have already see I bet you know what is coming. If developers are using SpEL with user input, we need to create payload with injection. Let’s check one that allow remote code execution \(RCE\). It was created as part of exploit for [CVE-2017–8046](https://github.com/m3ssap0/SpringBreakVulnerableApp).

It consist of 3 parts:
* black color — copy result of command execution directly to output stream of HTTP request
* red color — get Java Runtime and execute command in system
* blue color — String containing command: `cmd /c dir`. To make it more robust individual characters of command are decoded from numbers.
Result of executing it:
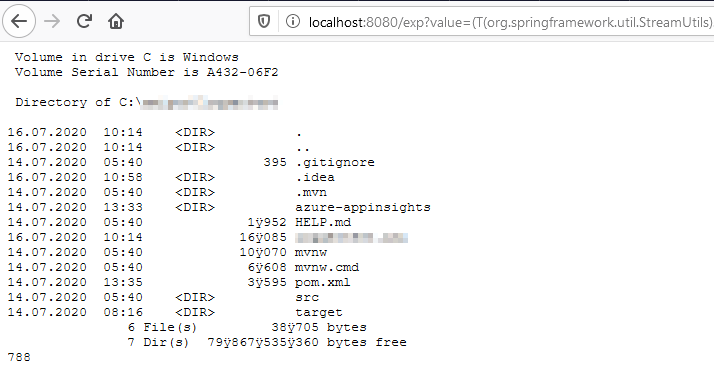

Code of intentionally vulnerable web application:
Keep in mind:
* payload is working in some of Blind scenarios — always copy result to HTTP response
* can be tune to work on Linux — just remove `cmd /c` and it should work out-of-box
* in real world you will need probably first break out of string to inject this or do other tricks that are common for injection attacks
* it can be used with multiple versions of String Framework and Java
Here is payload to copy:
The other interesting payload is this one:

It’s far less complicated but short and powerful. It’s also not using `T(...)` syntax and no constructor is used. It’s just executing methods and accessing properties. I will show in next part why it does matter.
Check more payloads for SpEL in my repository: [https://github.com/marcin33/hacking/blob/master/payloads/spel-injections.txt](https://github.com/marcin33/hacking/blob/master/payloads/spel-injections.txt)
### Summary
That will be all for this part. I have explained what is SpEL API and how to exploit it. In next part I will deep dive into Spring source code to show how exactly it works.