mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2025-01-25 03:15:20 +00:00
28 commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
15826d6019 |
bevy_reflect: Reflect enums (#4761)
# Objective
> This is a revival of #1347. Credit for the original PR should go to @Davier.
Currently, enums are treated as `ReflectRef::Value` types by `bevy_reflect`. Obviously, there needs to be better a better representation for enums using the reflection API.
## Solution
Based on prior work from @Davier, an `Enum` trait has been added as well as the ability to automatically implement it via the `Reflect` derive macro. This allows enums to be expressed dynamically:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
enum Foo {
A,
B(usize),
C { value: f32 },
}
let mut foo = Foo::B(123);
assert_eq!("B", foo.variant_name());
assert_eq!(1, foo.field_len());
let new_value = DynamicEnum::from(Foo::C { value: 1.23 });
foo.apply(&new_value);
assert_eq!(Foo::C{value: 1.23}, foo);
```
### Features
#### Derive Macro
Use the `#[derive(Reflect)]` macro to automatically implement the `Enum` trait for enum definitions. Optionally, you can use `#[reflect(ignore)]` with both variants and variant fields, just like you can with structs. These ignored items will not be considered as part of the reflection and cannot be accessed via reflection.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
enum TestEnum {
A,
// Uncomment to ignore all of `B`
// #[reflect(ignore)]
B(usize),
C {
// Uncomment to ignore only field `foo` of `C`
// #[reflect(ignore)]
foo: f32,
bar: bool,
},
}
```
#### Dynamic Enums
Enums may be created/represented dynamically via the `DynamicEnum` struct. The main purpose of this struct is to allow enums to be deserialized into a partial state and to allow dynamic patching. In order to ensure conversion from a `DynamicEnum` to a concrete enum type goes smoothly, be sure to add `FromReflect` to your derive macro.
```rust
let mut value = TestEnum::A;
// Create from a concrete instance
let dyn_enum = DynamicEnum::from(TestEnum::B(123));
value.apply(&dyn_enum);
assert_eq!(TestEnum::B(123), value);
// Create a purely dynamic instance
let dyn_enum = DynamicEnum::new("TestEnum", "A", ());
value.apply(&dyn_enum);
assert_eq!(TestEnum::A, value);
```
#### Variants
An enum value is always represented as one of its variants— never the enum in its entirety.
```rust
let value = TestEnum::A;
assert_eq!("A", value.variant_name());
// Since we are using the `A` variant, we cannot also be the `B` variant
assert_ne!("B", value.variant_name());
```
All variant types are representable within the `Enum` trait: unit, struct, and tuple.
You can get the current type like:
```rust
match value.variant_type() {
VariantType::Unit => println!("A unit variant!"),
VariantType::Struct => println!("A struct variant!"),
VariantType::Tuple => println!("A tuple variant!"),
}
```
> Notice that they don't contain any values representing the fields. These are purely tags.
If a variant has them, you can access the fields as well:
```rust
let mut value = TestEnum::C {
foo: 1.23,
bar: false
};
// Read/write specific fields
*value.field_mut("bar").unwrap() = true;
// Iterate over the entire collection of fields
for field in value.iter_fields() {
println!("{} = {:?}", field.name(), field.value());
}
```
#### Variant Swapping
It might seem odd to group all variant types under a single trait (why allow `iter_fields` on a unit variant?), but the reason this was done ~~is to easily allow *variant swapping*.~~ As I was recently drafting up the **Design Decisions** section, I discovered that other solutions could have been made to work with variant swapping. So while there are reasons to keep the all-in-one approach, variant swapping is _not_ one of them.
```rust
let mut value: Box<dyn Enum> = Box::new(TestEnum::A);
value.set(Box::new(TestEnum::B(123))).unwrap();
```
#### Serialization
Enums can be serialized and deserialized via reflection without needing to implement `Serialize` or `Deserialize` themselves (which can save thousands of lines of generated code). Below are the ways an enum can be serialized.
> Note, like the rest of reflection-based serialization, the order of the keys in these representations is important!
##### Unit
```json
{
"type": "my_crate::TestEnum",
"enum": {
"variant": "A"
}
}
```
##### Tuple
```json
{
"type": "my_crate::TestEnum",
"enum": {
"variant": "B",
"tuple": [
{
"type": "usize",
"value": 123
}
]
}
}
```
<details>
<summary>Effects on Option</summary>
This ends up making `Option` look a little ugly:
```json
{
"type": "core::option::Option<usize>",
"enum": {
"variant": "Some",
"tuple": [
{
"type": "usize",
"value": 123
}
]
}
}
```
</details>
##### Struct
```json
{
"type": "my_crate::TestEnum",
"enum": {
"variant": "C",
"struct": {
"foo": {
"type": "f32",
"value": 1.23
},
"bar": {
"type": "bool",
"value": false
}
}
}
}
```
## Design Decisions
<details>
<summary><strong>View Section</strong></summary>
This section is here to provide some context for why certain decisions were made for this PR, alternatives that could have been used instead, and what could be improved upon in the future.
### Variant Representation
One of the biggest decisions was to decide on how to represent variants. The current design uses a "all-in-one" design where unit, tuple, and struct variants are all simultaneously represented by the `Enum` trait. This is not the only way it could have been done, though.
#### Alternatives
##### 1. Variant Traits
One way of representing variants would be to define traits for each variant, implementing them whenever an enum featured at least one instance of them. This would allow us to define variants like:
```rust
pub trait Enum: Reflect {
fn variant(&self) -> Variant;
}
pub enum Variant<'a> {
Unit,
Tuple(&'a dyn TupleVariant),
Struct(&'a dyn StructVariant),
}
pub trait TupleVariant {
fn field_len(&self) -> usize;
// ...
}
```
And then do things like:
```rust
fn get_tuple_len(foo: &dyn Enum) -> usize {
match foo.variant() {
Variant::Tuple(tuple) => tuple.field_len(),
_ => panic!("not a tuple variant!")
}
}
```
The reason this PR does not go with this approach is because of the fact that variants are not separate types. In other words, we cannot implement traits on specific variants— these cover the *entire* enum. This means we offer an easy footgun:
```rust
let foo: Option<i32> = None;
let my_enum = Box::new(foo) as Box<dyn TupleVariant>;
```
Here, `my_enum` contains `foo`, which is a unit variant. However, since we need to implement `TupleVariant` for `Option` as a whole, it's possible to perform such a cast. This is obviously wrong, but could easily go unnoticed. So unfortunately, this makes it not a good candidate for representing variants.
##### 2. Variant Structs
To get around the issue of traits necessarily needing to apply to both the enum and its variants, we could instead use structs that are created on a per-variant basis. This was also considered but was ultimately [[removed](
|
||
|
|
4d05eb19be |
bevy_reflect: remove glam from a test which is active without the glam feature (#5195)
# Objective
`glam` is an optional feature in `bevy_reflect` and there is a separate `mod test { #[cfg(feature = "glam")] mod glam { .. }}`.
The `reflect_downcast` test is not in that module and doesn't depend on glam, which breaks `cargo test -p bevy_reflect` without the `glam` feature.
## Solution
- Remove the glam types from the test, they're not relevant to it
|
||
|
|
5498ef81fb |
bevy_reflect: support map insertion (#5173)
# Objective This is a rebase of #3701 which is currently scheduled for 0.8 but is marked for adoption. > Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/3609 ## Solution > - add an `insert_boxed()` method on the `Map` trait > - implement it for `HashMap` using a new `FromReflect` generic bound > - add a `map_apply()` helper method to implement `Map::apply()`, that inserts new values instead of ignoring them --- ## Changelog TODO Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com> |
||
|
|
33f9b3940d |
Updated glam to 0.21. (#5142)
Removed `const_vec2`/`const_vec3` and replaced with equivalent `.from_array`. # Objective Fixes #5112 ## Solution - `encase` needs to update to `glam` as well. See teoxoy/encase#4 on progress on that. - `hexasphere` also needs to be updated, see OptimisticPeach/hexasphere#12. |
||
|
|
c27a3cff6d |
Make Reflect safe to implement (#5010)
# Objective Currently, `Reflect` is unsafe to implement because of a contract in which `any` and `any_mut` must return `self`, or `downcast` will cause UB. This PR makes `Reflect` safe, makes `downcast` not use unsafe, and eliminates this contract. ## Solution This PR adds a method to `Reflect`, `any`. It also renames the old `any` to `as_any`. `any` now takes a `Box<Self>` and returns a `Box<dyn Any>`. --- ## Changelog ### Added: - `any()` method - `represents()` method ### Changed: - `Reflect` is now a safe trait - `downcast()` is now safe - The old `any` is now called `as_any`, and `any_mut` is now `as_mut_any` ## Migration Guide - Reflect derives should not have to change anything - Manual reflect impls will need to remove the `unsafe` keyword, add `any()` implementations, and rename the old `any` and `any_mut` to `as_any` and `as_mut_any`. - Calls to `any`/`any_mut` must be changed to `as_any`/`as_mut_any` ## Points of discussion: - Should renaming `any` be avoided and instead name the new method `any_box`? - ~~Could there be a performance regression from avoiding the unsafe? I doubt it, but this change does seem to introduce redundant checks.~~ - ~~Could/should `is` and `type_id()` be implemented differently? For example, moving `is` onto `Reflect` as an `fn(&self, TypeId) -> bool`~~ Co-authored-by: PROMETHIA-27 <42193387+PROMETHIA-27@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
218b0fd3b6 |
bevy_reflect: put serialize into external ReflectSerialize type (#4782)
builds on top of #4780 # Objective `Reflect` and `Serialize` are currently very tied together because `Reflect` has a `fn serialize(&self) -> Option<Serializable<'_>>` method. Because of that, we can either implement `Reflect` for types like `Option<T>` with `T: Serialize` and have `fn serialize` be implemented, or without the bound but having `fn serialize` return `None`. By separating `ReflectSerialize` into a separate type (like how it already is for `ReflectDeserialize`, `ReflectDefault`), we could separately `.register::<Option<T>>()` and `.register_data::<Option<T>, ReflectSerialize>()` only if the type `T: Serialize`. This PR does not change the registration but allows it to be changed in a future PR. ## Solution - add the type ```rust struct ReflectSerialize { .. } impl<T: Reflect + Serialize> FromType<T> for ReflectSerialize { .. } ``` - remove `#[reflect(Serialize)]` special casing. - when serializing reflect value types, look for `ReflectSerialize` in the `TypeRegistry` instead of calling `value.serialize()` |
||
|
|
ab72c8368f |
Fix ron deprecation (#5021)
# Objective - Update to fix `ron` deprecation |
||
|
|
e6f34ba47f |
bevy_reflect: Add statically available type info for reflected types (#4042)
# Objective > Resolves #4504 It can be helpful to have access to type information without requiring an instance of that type. Especially for `Reflect`, a lot of the gathered type information is known at compile-time and should not necessarily require an instance. ## Solution Created a dedicated `TypeInfo` enum to store static type information. All types that derive `Reflect` now also implement the newly created `Typed` trait: ```rust pub trait Typed: Reflect { fn type_info() -> &'static TypeInfo; } ``` > Note: This trait was made separate from `Reflect` due to `Sized` restrictions. If you only have access to a `dyn Reflect`, just call `.get_type_info()` on it. This new trait method on `Reflect` should return the same value as if you had called it statically. If all you have is a `TypeId` or type name, you can get the `TypeInfo` directly from the registry using the `TypeRegistry::get_type_info` method (assuming it was registered). ### Usage Below is an example of working with `TypeInfo`. As you can see, we don't have to generate an instance of `MyTupleStruct` in order to get this information. ```rust #[derive(Reflect)] struct MyTupleStruct(usize, i32, MyStruct); let info = MyTupleStruct::type_info(); if let TypeInfo::TupleStruct(info) = info { assert!(info.is::<MyTupleStruct>()); assert_eq!(std::any::type_name::<MyTupleStruct>(), info.type_name()); assert!(info.field_at(1).unwrap().is::<i32>()); } else { panic!("Expected `TypeInfo::TupleStruct`"); } ``` ### Manual Implementations It's not recommended to manually implement `Typed` yourself, but if you must, you can use the `TypeInfoCell` to automatically create and manage the static `TypeInfo`s for you (which is very helpful for blanket/generic impls): ```rust use bevy_reflect::{Reflect, TupleStructInfo, TypeInfo, UnnamedField}; use bevy_reflect::utility::TypeInfoCell; struct Foo<T: Reflect>(T); impl<T: Reflect> Typed for Foo<T> { fn type_info() -> &'static TypeInfo { static CELL: TypeInfoCell = TypeInfoCell::generic(); CELL.get_or_insert::<Self, _>(|| { let fields = [UnnamedField:🆕:<T>()]; let info = TupleStructInfo:🆕:<Self>(&fields); TypeInfo::TupleStruct(info) }) } } ``` ## Benefits One major benefit is that this opens the door to other serialization methods. Since we can get all the type info at compile time, we can know how to properly deserialize something like: ```rust #[derive(Reflect)] struct MyType { foo: usize, bar: Vec<String> } // RON to be deserialized: ( type: "my_crate::MyType", // <- We now know how to deserialize the rest of this object value: { // "foo" is a value type matching "usize" "foo": 123, // "bar" is a list type matching "Vec<String>" with item type "String" "bar": ["a", "b", "c"] } ) ``` Not only is this more compact, but it has better compatibility (we can change the type of `"foo"` to `i32` without having to update our serialized data). Of course, serialization/deserialization strategies like this may need to be discussed and fully considered before possibly making a change. However, we will be better equipped to do that now that we can access type information right from the registry. ## Discussion Some items to discuss: 1. Duplication. There's a bit of overlap with the existing traits/structs since they require an instance of the type while the type info structs do not (for example, `Struct::field_at(&self, index: usize)` and `StructInfo::field_at(&self, index: usize)`, though only `StructInfo` is accessible without an instance object). Is this okay, or do we want to handle it in another way? 2. Should `TypeInfo::Dynamic` be removed? Since the dynamic types don't have type information available at runtime, we could consider them `TypeInfo::Value`s (or just even just `TypeInfo::Struct`). The intention with `TypeInfo::Dynamic` was to keep the distinction from these dynamic types and actual structs/values since users might incorrectly believe the methods of the dynamic type's info struct would map to some contained data (which isn't possible statically). 4. General usefulness of this change, including missing/unnecessary parts. 5. Possible changes to the scene format? (One possible issue with changing it like in the example above might be that we'd have to be careful when handling generic or trait object types.) ## Compile Tests I ran a few tests to compare compile times (as suggested [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4042#discussion_r876408143)). I toggled `Reflect` and `FromReflect` derive macros using `cfg_attr` for both this PR ( |
||
|
|
fb813a3a64 |
bevy_reflect: Add #[reflect(default)] attribute for FromReflect (#4140)
# Objective Currently, `FromReflect` makes a couple assumptions: * Ignored fields must implement `Default` * Active fields must implement `FromReflect` * The reflected must be fully populated for active fields (can't use an empty `DynamicStruct`) However, one or both of these requirements might be unachievable, such as for external types. In these cases, it might be nice to tell `FromReflect` to use a custom default. ## Solution Added the `#[reflect(default)]` derive helper attribute. This attribute can be applied to any field (ignored or not) and will allow a default value to be specified in place of the regular `from_reflect()` call. It takes two forms: `#[reflect(default)]` and `#[reflect(default = "some_func")]`. The former specifies that `Default::default()` should be used while the latter specifies that `some_func()` should be used. This is pretty much [how serde does it](https://serde.rs/field-attrs.html#default). ### Example ```rust #[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)] struct MyStruct { // Use `Default::default()` #[reflect(default)] foo: String, // Use `get_bar_default()` #[reflect(default = "get_bar_default")] #[reflect(ignore)] bar: usize, } fn get_bar_default() -> usize { 123 } ``` ### Active Fields As an added benefit, this also allows active fields to be completely missing from their dynamic object. This is because the attribute tells `FromReflect` how to handle missing active fields (it still tries to use `from_reflect` first so the `FromReflect` trait is still required). ```rust let dyn_struct = DynamicStruct::default(); // We can do this without actually including the active fields since they have `#[reflect(default)]` let my_struct = <MyStruct as FromReflect>::from_reflect(&dyn_struct); ``` ### Container Defaults Also, with the addition of #3733, people will likely start adding `#[reflect(Default)]` to their types now. Just like with the fields, we can use this to mark the entire container as "defaultable". This grants us the ability to completely remove the field markers altogether if our type implements `Default` (and we're okay with fields using that instead of their own `Default` impls): ```rust #[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)] #[reflect(Default)] struct MyStruct { foo: String, #[reflect(ignore)] bar: usize, } impl Default for MyStruct { fn default() -> Self { Self { foo: String::from("Hello"), bar: 123, } } } // Again, we can now construct this from nothing pretty much let dyn_struct = DynamicStruct::default(); let my_struct = <MyStruct as FromReflect>::from_reflect(&dyn_struct); ``` Now if _any_ field is missing when using `FromReflect`, we simply fallback onto the container's `Default` implementation. This behavior can be completely overridden on a per-field basis, of course, by simply defining those same field attributes like before. ### Related * #3733 * #1395 * #2377 --- ## Changelog * Added `#[reflect(default)]` field attribute for `FromReflect` * Allows missing fields to be given a default value when using `FromReflect` * `#[reflect(default)]` - Use the field's `Default` implementation * `#[reflect(default = "some_fn")]` - Use a custom function to get the default value * Allow `#[reflect(Default)]` to have a secondary usage as a container attribute * Allows missing fields to be given a default value based on the container's `Default` impl when using `FromReflect` Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
2f5591ff8c |
bevy_reflect: Improve debug formatting for reflected types (#4218)
# Objective
Debugging reflected types can be somewhat frustrating since all `dyn Reflect` trait objects return something like `Reflect(core::option::Option<alloc::string::String>)`.
It would be much nicer to be able to see the actual value— or even use a custom `Debug` implementation.
## Solution
Added `Reflect::debug` which allows users to customize the debug output. It sets defaults for all `ReflectRef` subtraits and falls back to `Reflect(type_name)` if no `Debug` implementation was registered.
To register a custom `Debug` impl, users can add `#[reflect(Debug)]` like they can with other traits.
### Example
Using the following structs:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
pub struct Foo {
a: usize,
nested: Bar,
#[reflect(ignore)]
_ignored: NonReflectedValue,
}
#[derive(Reflect)]
pub struct Bar {
value: Vec2,
tuple_value: (i32, String),
list_value: Vec<usize>,
// We can't determine debug formatting for Option<T> yet
unknown_value: Option<String>,
custom_debug: CustomDebug
}
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(Debug)]
struct CustomDebug;
impl Debug for CustomDebug {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {
write!(f, "This is a custom debug!")
}
}
pub struct NonReflectedValue {
_a: usize,
}
```
We can do:
```rust
let value = Foo {
a: 1,
_ignored: NonReflectedValue { _a: 10 },
nested: Bar {
value: Vec2::new(1.23, 3.21),
tuple_value: (123, String::from("Hello")),
list_value: vec![1, 2, 3],
unknown_value: Some(String::from("World")),
custom_debug: CustomDebug
},
};
let reflected_value: &dyn Reflect = &value;
println!("{:#?}", reflected_value)
```
Which results in:
```rust
Foo {
a: 2,
nested: Bar {
value: Vec2(
1.23,
3.21,
),
tuple_value: (
123,
"Hello",
),
list_value: [
1,
2,
3,
],
unknown_value: Reflect(core::option::Option<alloc::string::String>),
custom_debug: This is a custom debug!,
},
}
```
Notice that neither `Foo` nor `Bar` implement `Debug`, yet we can still deduce it. This might be a concern if we're worried about leaking internal values. If it is, we might want to consider a way to exclude fields (possibly with a `#[reflect(hide)]` macro) or make it purely opt in (as opposed to the default implementation automatically handled by ReflectRef subtraits).
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
|
||
|
|
acbee7795d |
bevy_reflect: Reflect arrays (#4701)
# Objective > ℹ️ **Note**: This is a rebased version of #2383. A large portion of it has not been touched (only a few minor changes) so that any additional discussion may happen here. All credit should go to @NathanSWard for their work on the original PR. - Currently reflection is not supported for arrays. - Fixes #1213 ## Solution * Implement reflection for arrays via the `Array` trait. * Note, `Array` is different from `List` in the way that you cannot push elements onto an array as they are statically sized. * Now `List` is defined as a sub-trait of `Array`. --- ## Changelog * Added the `Array` reflection trait * Allows arrays up to length 32 to be reflected via the `Array` trait ## Migration Guide * The `List` trait now has the `Array` supertrait. This means that `clone_dynamic` will need to specify which version to use: ```rust // Before let cloned = my_list.clone_dynamic(); // After let cloned = List::clone_dynamic(&my_list); ``` * All implementers of `List` will now need to implement `Array` (this mostly involves moving the existing methods to the `Array` impl) Co-authored-by: NathanW <nathansward@comcast.net> Co-authored-by: MrGVSV <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
3d8d922566 |
bevy_reflect_derive: Tidying up the code (#4712)
# Objective The `bevy_reflect_derive` crate is not the cleanest or easiest to follow/maintain. The `lib.rs` file is especially difficult with over 1000 lines of code written in a confusing order. This is just a result of growth within the crate and it would be nice to clean it up for future work. ## Solution Split `bevy_reflect_derive` into many more submodules. The submodules include: * `container_attributes` - Code relating to container attributes * `derive_data` - Code relating to reflection-based derive metadata * `field_attributes` - Code relating to field attributes * `impls` - Code containing actual reflection implementations * `reflect_value` - Code relating to reflection-based value metadata * `registration` - Code relating to type registration * `utility` - General-purpose utility functions This leaves the `lib.rs` file to contain only the public macros, making it much easier to digest (and fewer than 200 lines). By breaking up the code into smaller modules, we make it easier for future contributors to find the code they're looking for or identify which module best fits their own additions. ### Metadata Structs This cleanup also adds two big metadata structs: `ReflectFieldAttr` and `ReflectDeriveData`. The former is used to store all attributes for a struct field (if any). The latter is used to store all metadata for struct-based derive inputs. Both significantly reduce code duplication and make editing these macros much simpler. The tradeoff is that we may collect more metadata than needed. However, this is usually a small thing (such as checking for attributes when they're not really needed or creating a `ReflectFieldAttr` for every field regardless of whether they actually have an attribute). We could try to remove these tradeoffs and squeeze some more performance out, but doing so might come at the cost of developer experience. Personally, I think it's much nicer to create a `ReflectFieldAttr` for every field since it means I don't have to do two `Option` checks. Others may disagree, though, and so we can discuss changing this either in this PR or in a future one. ### Out of Scope _Some_ documentation has been added or improved, but ultimately good docs are probably best saved for a dedicated PR. ## 🔍 Focus Points (for reviewers) I know it's a lot to sift through, so here is a list of **key points for reviewers**: - The following files contain code that was mostly just relocated: - `reflect_value.rs` - `registration.rs` - `container_attributes.rs` was also mostly moved but features some general cleanup (reducing nesting, removing hardcoded strings, etc.) and lots of doc comments - Most impl logic was moved from `lib.rs` to `impls.rs`, but they have been significantly modified to use the new `ReflectDeriveData` metadata struct in order to reduce duplication. - `derive_data.rs` and `field_attributes.rs` contain almost entirely new code and should probably be given the most attention. - Likewise, `from_reflect.rs` saw major changes using `ReflectDeriveData` so it should also be given focus. - There was no change to the `lib.rs` exports so the end-user API should be the same. ## Prior Work This task was initially tackled by @NathanSWard in #2377 (which was closed in favor of this PR), so hats off to them for beating me to the punch by nearly a year! --- ## Changelog * **[INTERNAL]** Split `bevy_reflect_derive` into smaller submodules * **[INTERNAL]** Add `ReflectFieldAttr` * **[INTERNAL]** Add `ReflectDeriveData` * Add `BevyManifest::get_path_direct()` method (`bevy_macro_utils`) Co-authored-by: MrGVSV <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
aced6aff04 |
Add macro to implement reflect for struct types and migrate glam types (#4540)
# Objective Relevant issue: #4474 Currently glam types implement Reflect as a value, which is problematic for reflection, making scripting/editor work much more difficult. This PR re-implements them as structs. ## Solution Added a new proc macro, `impl_reflect_struct`, which replaces `impl_reflect_value` and `impl_from_reflect_value` for glam types. This macro could also be used for other types, but I don't know of any that would require it. It's specifically useful for foreign types that cannot derive Reflect normally. --- ## Changelog ### Added - `impl_reflect_struct` proc macro ### Changed - Glam reflect impls have been replaced with `impl_reflect_struct` - from_reflect's `impl_struct` altered to take an optional custom constructor, allowing non-default non-constructible foreign types to use it - Calls to `impl_struct` altered to conform to new signature - Altered glam types (All vec/mat combinations) have a different serialization structure, as they are reflected differently now. ## Migration Guide This will break altered glam types serialized to RON scenes, as they will expect to be serialized/deserialized as structs rather than values now. A future PR to add custom serialization for non-value types is likely on the way to restore previous behavior. Additionally, calls to `impl_struct` must add a `None` parameter to the end of the call to restore previous behavior. Co-authored-by: PROMETHIA-27 <42193387+PROMETHIA-27@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
2b6e67f4cb |
add #[reflect(Default)] to create default value for reflected types (#3733)
### Problem
It currently isn't possible to construct the default value of a reflected type. Because of that, it isn't possible to use `add_component` of `ReflectComponent` to add a new component to an entity because you can't know what the initial value should be.
### Solution
1. add `ReflectDefault` type
```rust
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct ReflectDefault {
default: fn() -> Box<dyn Reflect>,
}
impl ReflectDefault {
pub fn default(&self) -> Box<dyn Reflect> {
(self.default)()
}
}
impl<T: Reflect + Default> FromType<T> for ReflectDefault {
fn from_type() -> Self {
ReflectDefault {
default: || Box::new(T::default()),
}
}
}
```
2. add `#[reflect(Default)]` to all component types that implement `Default` and are user facing (so not `ComputedSize`, `CubemapVisibleEntities` etc.)
This makes it possible to add the default value of a component to an entity without any compile-time information:
```rust
fn main() {
let mut app = App::new();
app.register_type::<Camera>();
let type_registry = app.world.get_resource::<TypeRegistry>().unwrap();
let type_registry = type_registry.read();
let camera_registration = type_registry.get(std::any::TypeId::of::<Camera>()).unwrap();
let reflect_default = camera_registration.data::<ReflectDefault>().unwrap();
let reflect_component = camera_registration
.data::<ReflectComponent>()
.unwrap()
.clone();
let default = reflect_default.default();
drop(type_registry);
let entity = app.world.spawn().id();
reflect_component.add_component(&mut app.world, entity, &*default);
let camera = app.world.entity(entity).get::<Camera>().unwrap();
dbg!(&camera);
}
```
### Open questions
- should we have `ReflectDefault` or `ReflectFromWorld` or both?
|
||
|
|
3d36ec41dc |
re-enable #[derive(TypeUuid)] for generics (#4118)
Support for deriving `TypeUuid` for types with generics was initially added in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2044 but later reverted https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2204 because it lead to `MyStruct<A>` and `MyStruct<B>` having the same type uuid. This PR fixes this by generating code like ```rust #[derive(TypeUuid)] #[uuid = "69b09733-a21a-4dab-a444-d472986bd672"] struct Type<T>(T); impl<T: TypeUuid> TypeUuid for Type<T> { const TYPE_UUID: TypeUuid = generate_compound_uuid(Uuid::from_bytes([/* 69b0 uuid */]), T::TYPE_UUID); } ``` where `generate_compound_uuid` will XOR the non-metadata bits of the two UUIDs. Co-authored-by: XBagon <xbagon@outlook.de> Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de> |
||
|
|
5047e1f08e |
bevy_reflect: Add as_reflect and as_reflect_mut (#4350)
# Objective
Trait objects that have `Reflect` as a supertrait cannot be upcast to a `dyn Reflect`.
Attempting something like:
```rust
trait MyTrait: Reflect {
// ...
}
fn foo(value: &dyn MyTrait) {
let reflected = value as &dyn Reflect; // Error!
// ...
}
```
Results in `error[E0658]: trait upcasting coercion is experimental`.
The reason this is important is that a lot of `bevy_reflect` methods require a `&dyn Reflect`. This is trivial with concrete types, but if we don't know the concrete type (we only have the trait object), we can't use these methods. For example, we couldn't create a `ReflectSerializer` for the type since it expects a `&dyn Reflect` value— even though we should be able to.
## Solution
Add `as_reflect` and `as_reflect_mut` to `Reflect` to allow upcasting to a `dyn Reflect`:
```rust
trait MyTrait: Reflect {
// ...
}
fn foo(value: &dyn MyTrait) {
let reflected = value.as_reflect();
// ...
}
```
## Alternatives
We could defer this type of logic to the crate/user. They can add these methods to their trait in the same exact way we do here. The main benefit of doing it ourselves is it makes things convenient for them (especially when using the derive macro).
We could also create an `AsReflect` trait with a blanket impl over all reflected types, however, I could not get that to work for trait objects since they aren't sized.
---
## Changelog
- Added trait method `Reflect::as_reflect(&self)`
- Added trait method `Reflect::as_reflect_mut(&mut self)`
## Migration Guide
- Manual implementors of `Reflect` will need to add implementations for the methods above (this should be pretty easy as most cases just need to return `self`)
|
||
|
|
06d9384447 |
Add FromReflect trait to convert dynamic types to concrete types (#1395)
Dynamic types (`DynamicStruct`, `DynamicTupleStruct`, `DynamicTuple`, `DynamicList` and `DynamicMap`) are used when deserializing scenes, but currently they can only be applied to existing concrete types. This leads to issues when trying to spawn non trivial deserialized scene. For components, the issue is avoided by requiring that reflected components implement ~~`FromResources`~~ `FromWorld` (or `Default`). When spawning, a new concrete type is created that way, and the dynamic type is applied to it. Unfortunately, some components don't have any valid implementation of these traits. In addition, any `Vec` or `HashMap` inside a component will panic when a dynamic type is pushed into it (for instance, `Text` panics when adding a text section). To solve this issue, this PR adds the `FromReflect` trait that creates a concrete type from a dynamic type that represent it, derives the trait alongside the `Reflect` trait, drops the ~~`FromResources`~~ `FromWorld` requirement on reflected components, ~~and enables reflection for UI and Text bundles~~. It also adds the requirement that fields ignored with `#[reflect(ignore)]` implement `Default`, since we need to initialize them somehow. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
e018ac838d |
Add readme as docs to relevant crates. (#2575)
Fixes #2566 Fixes #3005 There are only READMEs in the 4 crates here (with the exception of bevy itself). Those 4 crates are ecs, reflect, tasks, and transform. These should each now include their respective README files. Co-authored-by: Hoidigan <57080125+Hoidigan@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Daniel Nelsen <57080125+Hoidigan@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
653c10371e |
Use bevy_reflect as path in case of no direct references (#1875)
Fixes #1844 Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
b1ed28e17e |
Hide re-exported docs (#1985)
Solves #1957 Co-authored-by: caelumLaron <caelum.laron@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
faeccd7a09 |
Reflection cleanup (#1536)
This is an effort to provide the correct `#[reflect_value(...)]` attributes where they are needed. Supersedes #1533 and resolves #1528. --- I am working under the following assumptions (thanks to @bjorn3 and @Davier for advice here): - Any `enum` that derives `Reflect` and one or more of { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } needs a `#[reflect_value(...)]` attribute containing the same subset of { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } that is present on the derive. - Same as above for `struct` and `#[reflect(...)]`, respectively. - If a `struct` is used as a component, it should also have `#[reflect(Component)]` - All reflected types should be registered in their plugins I treated the following as components (added `#[reflect(Component)]` if necessary): - `bevy_render` - `struct RenderLayers` - `bevy_transform` - `struct GlobalTransform` - `struct Parent` - `struct Transform` - `bevy_ui` - `struct Style` Not treated as components: - `bevy_math` - `struct Size<T>` - `struct Rect<T>` - Note: The updates for `Size<T>` and `Rect<T>` in `bevy::math::geometry` required using @Davier's suggestion to add `+ PartialEq` to the trait bound. I then registered the specific types used over in `bevy_ui` such as `Size<Val>`, etc. in `bevy_ui`'s plugin, since `bevy::math` does not contain a plugin. - `bevy_render` - `struct Color` - `struct PipelineSpecialization` - `struct ShaderSpecialization` - `enum PrimitiveTopology` - `enum IndexFormat` Not Addressed: - I am not searching for components in Bevy that are _not_ reflected. So if there are components that are not reflected that should be reflected, that will need to be figured out in another PR. - I only added `#[reflect(...)]` or `#[reflect_value(...)]` entries for the set of four traits { `Serialize`, `Deserialize`, `PartialEq`, `Hash` } _if they were derived via `#[derive(...)]`_. I did not look for manual trait implementations of the same set of four, nor did I consider any traits outside the four. Are those other possibilities something that needs to be looked into? |
||
|
|
3a2a68852c |
Bevy ECS V2 (#1525)
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes #1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor:🆕:<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)
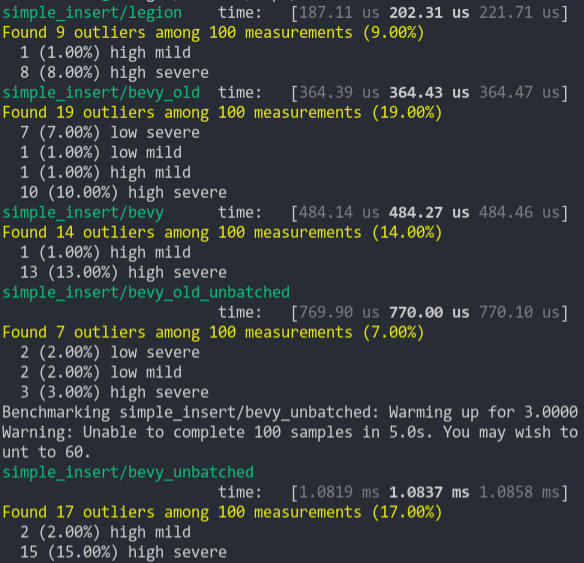
### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
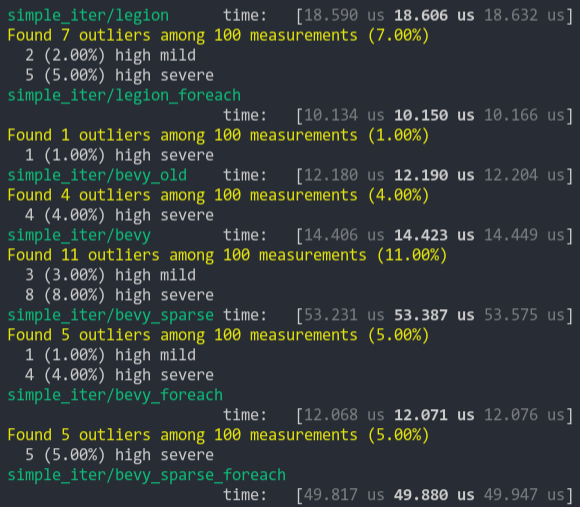
### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
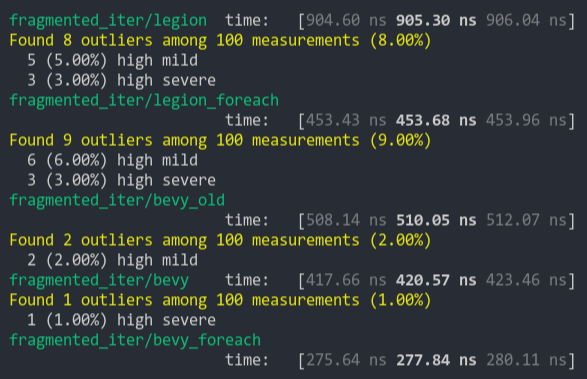
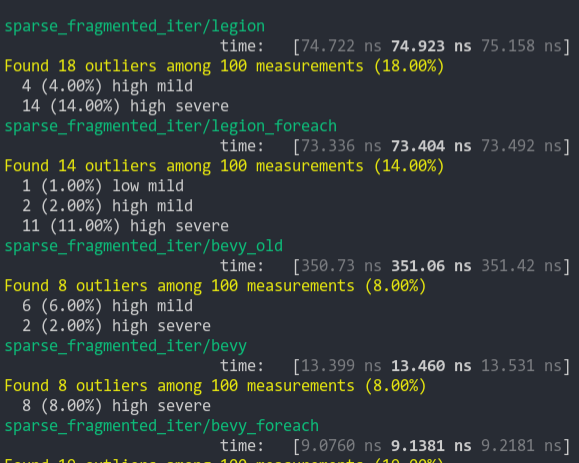
### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes
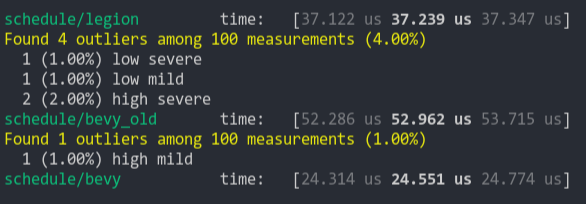
### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)
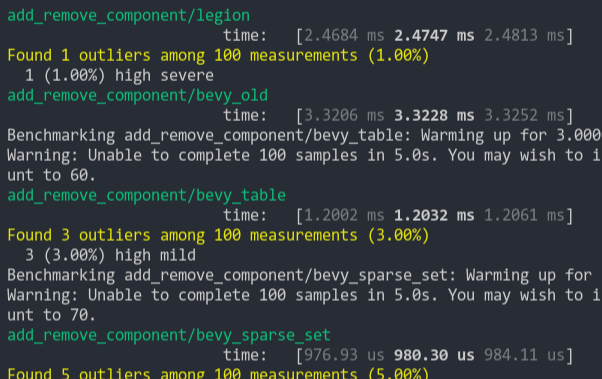
### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)
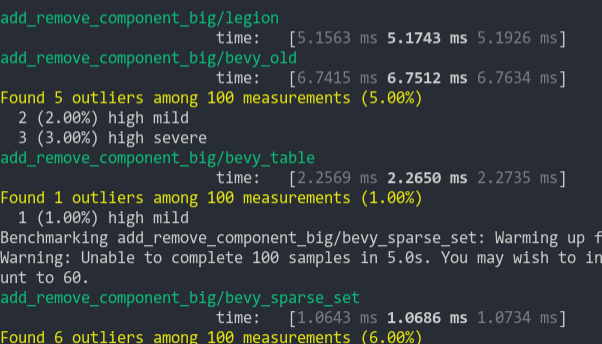
### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed
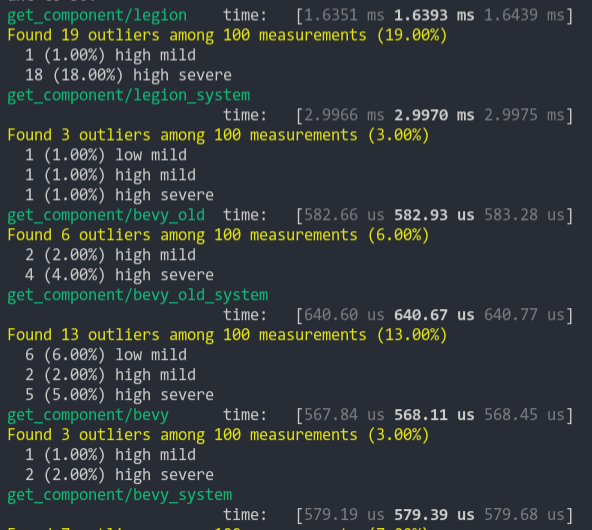
### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times
|
||
|
|
13b602ee3f |
Xtask CI (#1387)
This PR is easiest to review commit by commit. Followup on https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1309#issuecomment-767310084 - [x] Switch from a bash script to an xtask rust workspace member. - Results in ~30s longer CI due to compilation of the xtask itself - Enables Bevy contributors on any platform to run `cargo ci` to run linting -- if the default available Rust is the same version as on CI, then the command should give an identical result. - [x] Use the xtask from official CI so there's only one place to update. - [x] Bonus: Run clippy on the _entire_ workspace (existing CI setup was missing the `--workspace` flag - [x] Clean up newly-exposed clippy errors ~#1388 builds on this to clean up newly discovered clippy errors -- I thought it might be nicer as a separate PR.~ Nope, merged it into this one so CI would pass. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
5b115397ba
|
Fix Reflect serialization of tuple structs (#1366)
* Fix DynamicTupleStruct::type_name() * Fix type_name() for DynamicList, DynamicMap and DynamicTuple |
||
|
|
5e7456115a
|
Implement Reflect for tuples up to length 12 (#1218)
Add Reflect impls for tuples up to length 12 |
||
|
|
9f4c8b1b9a
|
Fix errors and panics to typical Rust conventions (#968)
Fix errors and panics to typical Rust conventions |
||
|
|
3cee95e59a
|
Rename reflect 'hash' method to 'reflect_hash' and partial_eq to reflect_partial_eq (#954)
* Rename reflect 'hash' method to 'reflect_hash' to avoid colliding with std:#️⃣:Hash::hash to resolve #943. * Rename partial_eq to reflect_partial_eq to avoid collisions with implementations of PartialEq on primitives. |
||
|
|
72b2fc9843
|
Bevy Reflection (#926)
Bevy Reflection |