mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2025-01-12 13:18:55 +00:00
5 commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
2ae5a21009
|
Implement percentage-closer soft shadows (PCSS). (#13497)
[*Percentage-closer soft shadows*] are a technique from 2004 that allow shadows to become blurrier farther from the objects that cast them. It works by introducing a *blocker search* step that runs before the normal shadow map sampling. The blocker search step detects the difference between the depth of the fragment being rasterized and the depth of the nearby samples in the depth buffer. Larger depth differences result in a larger penumbra and therefore a blurrier shadow. To enable PCSS, fill in the `soft_shadow_size` value in `DirectionalLight`, `PointLight`, or `SpotLight`, as appropriate. This shadow size value represents the size of the light and should be tuned as appropriate for your scene. Higher values result in a wider penumbra (i.e. blurrier shadows). When using PCSS, temporal shadow maps (`ShadowFilteringMethod::Temporal`) are recommended. If you don't use `ShadowFilteringMethod::Temporal` and instead use `ShadowFilteringMethod::Gaussian`, Bevy will use the same technique as `Temporal`, but the result won't vary over time. This produces a rather noisy result. Doing better would likely require downsampling the shadow map, which would be complex and slower (and would require PR #13003 to land first). In addition to PCSS, this commit makes the near Z plane for the shadow map configurable on a per-light basis. Previously, it had been hardcoded to 0.1 meters. This change was necessary to make the point light shadow map in the example look reasonable, as otherwise the shadows appeared far too aliased. A new example, `pcss`, has been added. It demonstrates the percentage-closer soft shadow technique with directional lights, point lights, spot lights, non-temporal operation, and temporal operation. The assets are my original work. Both temporal and non-temporal shadows are rather noisy in the example, and, as mentioned before, this is unavoidable without downsampling the depth buffer, which we can't do yet. Note also that the shadows don't look particularly great for point lights; the example simply isn't an ideal scene for them. Nevertheless, I felt that the benefits of the ability to do a side-by-side comparison of directional and point lights outweighed the unsightliness of the point light shadows in that example, so I kept the point light feature in. Fixes #3631. [*Percentage-closer soft shadows*]: https://developer.download.nvidia.com/shaderlibrary/docs/shadow_PCSS.pdf ## Changelog ### Added * Percentage-closer soft shadows (PCSS) are now supported, allowing shadows to become blurrier as they stretch away from objects. To use them, set the `soft_shadow_size` field in `DirectionalLight`, `PointLight`, or `SpotLight`, as applicable. * The near Z value for shadow maps is now customizable via the `shadow_map_near_z` field in `DirectionalLight`, `PointLight`, and `SpotLight`. ## Screenshots PCSS off:  PCSS on:  --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
83d6600267
|
Implement minimal reflection probes (fixed macOS, iOS, and Android). (#11366)
This pull request re-submits #10057, which was backed out for breaking macOS, iOS, and Android. I've tested this version on macOS and Android and on the iOS simulator. # Objective This pull request implements *reflection probes*, which generalize environment maps to allow for multiple environment maps in the same scene, each of which has an axis-aligned bounding box. This is a standard feature of physically-based renderers and was inspired by [the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]. ## Solution This is a minimal implementation of reflection probes that allows artists to define cuboid bounding regions associated with environment maps. For every view, on every frame, a system builds up a list of the nearest 4 reflection probes that are within the view's frustum and supplies that list to the shader. The PBR fragment shader searches through the list, finds the first containing reflection probe, and uses it for indirect lighting, falling back to the view's environment map if none is found. Both forward and deferred renderers are fully supported. A reflection probe is an entity with a pair of components, *LightProbe* and *EnvironmentMapLight* (as well as the standard *SpatialBundle*, to position it in the world). The *LightProbe* component (along with the *Transform*) defines the bounding region, while the *EnvironmentMapLight* component specifies the associated diffuse and specular cubemaps. A frequent question is "why two components instead of just one?" The advantages of this setup are: 1. It's readily extensible to other types of light probes, in particular *irradiance volumes* (also known as ambient cubes or voxel global illumination), which use the same approach of bounding cuboids. With a single component that applies to both reflection probes and irradiance volumes, we can share the logic that implements falloff and blending between multiple light probes between both of those features. 2. It reduces duplication between the existing *EnvironmentMapLight* and these new reflection probes. Systems can treat environment maps attached to cameras the same way they treat environment maps applied to reflection probes if they wish. Internally, we gather up all environment maps in the scene and place them in a cubemap array. At present, this means that all environment maps must have the same size, mipmap count, and texture format. A warning is emitted if this restriction is violated. We could potentially relax this in the future as part of the automatic mipmap generation work, which could easily do texture format conversion as part of its preprocessing. An easy way to generate reflection probe cubemaps is to bake them in Blender and use the `export-blender-gi` tool that's part of the [`bevy-baked-gi`] project. This tool takes a `.blend` file containing baked cubemaps as input and exports cubemap images, pre-filtered with an embedded fork of the [glTF IBL Sampler], alongside a corresponding `.scn.ron` file that the scene spawner can use to recreate the reflection probes. Note that this is intentionally a minimal implementation, to aid reviewability. Known issues are: * Reflection probes are basically unsupported on WebGL 2, because WebGL 2 has no cubemap arrays. (Strictly speaking, you can have precisely one reflection probe in the scene if you have no other cubemaps anywhere, but this isn't very useful.) * Reflection probes have no falloff, so reflections will abruptly change when objects move from one bounding region to another. * As mentioned before, all cubemaps in the world of a given type (diffuse or specular) must have the same size, format, and mipmap count. Future work includes: * Blending between multiple reflection probes. * A falloff/fade-out region so that reflected objects disappear gradually instead of vanishing all at once. * Irradiance volumes for voxel-based global illumination. This should reuse much of the reflection probe logic, as they're both GI techniques based on cuboid bounding regions. * Support for WebGL 2, by breaking batches when reflection probes are used. These issues notwithstanding, I think it's best to land this with roughly the current set of functionality, because this patch is useful as is and adding everything above would make the pull request significantly larger and harder to review. --- ## Changelog ### Added * A new *LightProbe* component is available that specifies a bounding region that an *EnvironmentMapLight* applies to. The combination of a *LightProbe* and an *EnvironmentMapLight* offers *reflection probe* functionality similar to that available in other engines. [the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/eevee/light_probes/reflection_cubemaps.html [`bevy-baked-gi`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/bevy-baked-gi [glTF IBL Sampler]: https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-IBL-Sampler |
||
|
|
3d996639a0
|
Revert "Implement minimal reflection probes. (#10057)" (#11307)
# Objective - Fix working on macOS, iOS, Android on main - Fixes #11281 - Fixes #11282 - Fixes #11283 - Fixes #11299 ## Solution - Revert #10057 |
||
|
|
54a943d232
|
Implement minimal reflection probes. (#10057)
# Objective This pull request implements *reflection probes*, which generalize environment maps to allow for multiple environment maps in the same scene, each of which has an axis-aligned bounding box. This is a standard feature of physically-based renderers and was inspired by [the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]. ## Solution This is a minimal implementation of reflection probes that allows artists to define cuboid bounding regions associated with environment maps. For every view, on every frame, a system builds up a list of the nearest 4 reflection probes that are within the view's frustum and supplies that list to the shader. The PBR fragment shader searches through the list, finds the first containing reflection probe, and uses it for indirect lighting, falling back to the view's environment map if none is found. Both forward and deferred renderers are fully supported. A reflection probe is an entity with a pair of components, *LightProbe* and *EnvironmentMapLight* (as well as the standard *SpatialBundle*, to position it in the world). The *LightProbe* component (along with the *Transform*) defines the bounding region, while the *EnvironmentMapLight* component specifies the associated diffuse and specular cubemaps. A frequent question is "why two components instead of just one?" The advantages of this setup are: 1. It's readily extensible to other types of light probes, in particular *irradiance volumes* (also known as ambient cubes or voxel global illumination), which use the same approach of bounding cuboids. With a single component that applies to both reflection probes and irradiance volumes, we can share the logic that implements falloff and blending between multiple light probes between both of those features. 2. It reduces duplication between the existing *EnvironmentMapLight* and these new reflection probes. Systems can treat environment maps attached to cameras the same way they treat environment maps applied to reflection probes if they wish. Internally, we gather up all environment maps in the scene and place them in a cubemap array. At present, this means that all environment maps must have the same size, mipmap count, and texture format. A warning is emitted if this restriction is violated. We could potentially relax this in the future as part of the automatic mipmap generation work, which could easily do texture format conversion as part of its preprocessing. An easy way to generate reflection probe cubemaps is to bake them in Blender and use the `export-blender-gi` tool that's part of the [`bevy-baked-gi`] project. This tool takes a `.blend` file containing baked cubemaps as input and exports cubemap images, pre-filtered with an embedded fork of the [glTF IBL Sampler], alongside a corresponding `.scn.ron` file that the scene spawner can use to recreate the reflection probes. Note that this is intentionally a minimal implementation, to aid reviewability. Known issues are: * Reflection probes are basically unsupported on WebGL 2, because WebGL 2 has no cubemap arrays. (Strictly speaking, you can have precisely one reflection probe in the scene if you have no other cubemaps anywhere, but this isn't very useful.) * Reflection probes have no falloff, so reflections will abruptly change when objects move from one bounding region to another. * As mentioned before, all cubemaps in the world of a given type (diffuse or specular) must have the same size, format, and mipmap count. Future work includes: * Blending between multiple reflection probes. * A falloff/fade-out region so that reflected objects disappear gradually instead of vanishing all at once. * Irradiance volumes for voxel-based global illumination. This should reuse much of the reflection probe logic, as they're both GI techniques based on cuboid bounding regions. * Support for WebGL 2, by breaking batches when reflection probes are used. These issues notwithstanding, I think it's best to land this with roughly the current set of functionality, because this patch is useful as is and adding everything above would make the pull request significantly larger and harder to review. --- ## Changelog ### Added * A new *LightProbe* component is available that specifies a bounding region that an *EnvironmentMapLight* applies to. The combination of a *LightProbe* and an *EnvironmentMapLight* offers *reflection probe* functionality similar to that available in other engines. [the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/eevee/light_probes/reflection_cubemaps.html [`bevy-baked-gi`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/bevy-baked-gi [glTF IBL Sampler]: https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-IBL-Sampler |
||
|
|
dd4299bcf9 |
EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)  (After)  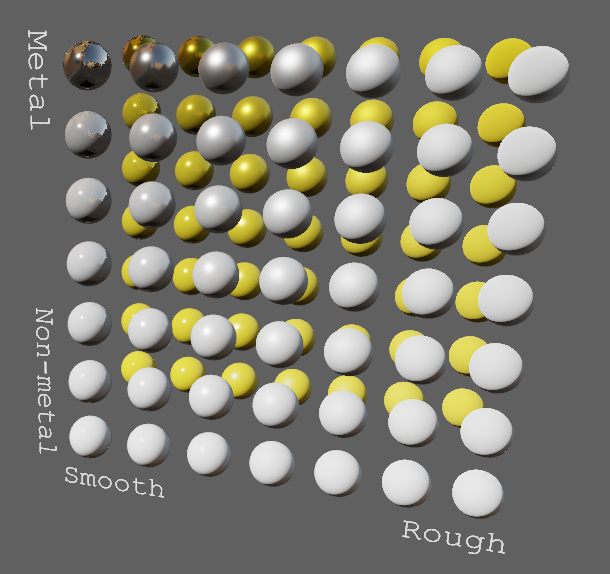 # Objective - Improve lighting; especially reflections. - Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581. ## Solution - Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light. - Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament. - Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular. - Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels. - Added `FallbackImageCubemap`. ## Implementation - IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl. - It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation. - For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation. - Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy. --- ## Changelog - Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene. - StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct. - Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting. - Added `FallbackImageCubemap`. Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com> Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com> |