# Objective
- @mockersf identified a performance regression of about 25% longer frame times introduced by #7784 in a complex scene with the Amazon Lumberyard bistro scene with both exterior and interior variants and a number of point lights with shadow mapping enabled
- The additional time seemed to be spent in the `ShadowPassNode`
- `ShadowPassNode` encodes the draw commands for the shadow phase. Roughly the same numbers of entities were having draw commands encoded, so something about the way they were being encoded had changed.
- One thing that definitely changed was that the pipeline used will be different depending on the alpha mode, and the scene has lots entities with opaque and blend materials. This suggested that maybe the pipeline was changing a lot so I tried a quick hack to see if it was the problem.
## Solution
- Sort the shadow phase items by their pipeline id
- This groups phase items by their pipeline id, which significantly reduces pipeline rebinding required to the point that the performance regression was gone.
# Objective
- Currently, https://github.com/vleue/bevy_bistro_playground crashes when enabling shadows, because this allocates a new buffer for the view uniforms, but the `TonemappingNode` uses a cached bind group that doesn't reference the new uniform buffer.
## Solution
- Check if the buffer id of the view uniforms buffer has changed and create a new bind group if it did.
# Objective
Fixes#7757
New function `Color::as_lcha` was added and `Color::as_lch_f32` changed name to `Color::as_lcha_f32`.
----
As a side note I did it as in every other Color function, that is I created very simillar code in `as_lcha` as was in `as_lcha_f32`. However it is totally possible to avoid this code duplication in LCHA and other color variants by doing something like :
```
pub fn as_lcha(self: &Color) -> Color {
let (lightness, chroma, hue, alpha) = self.as_lcha_f32();
return Color::Lcha { lightness, chroma, hue, alpha };
}
```
This is maybe slightly less efficient but it avoids copy-pasting this huge match expression which is error prone. Anyways since it is my first commit here I wanted to be consistent with the rest of code but can refactor all variants in separate PR if somebody thinks it is good idea.
# Objective
revert combining pipelines for AlphaMode::Blend and AlphaMode::Premultiplied & Add
the recent blend state pr changed `AlphaMode::Blend` to use a blend state of `Blend::PREMULTIPLIED_ALPHA_BLENDING`, and recovered the original behaviour by multiplying colour by alpha in the standard material's fragment shader.
this had some advantages (specifically it means more material instances can be batched together in future), but this also means that custom materials that specify `AlphaMode::Blend` now get a premultiplied blend state, so they must also multiply colour by alpha.
## Solution
revert that combination to preserve 0.9 behaviour for custom materials with AlphaMode::Blend.
This produces more accurate results for the `EmissiveStrengthTest` glTF test case.
(Requires manually setting the emission, for now)
Before: <img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-03-04 at 18 21 25" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/222929455-c7363d52-7133-4d4e-9d6a-562098f6bbe8.png">
After: <img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-03-04 at 18 20 57" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/222929454-3ea20ecb-0773-4aad-978c-3832353b6871.png">
Tagging @JMS55 as a co-author, since this fix is based on their experiments with emission.
# Objective
- Have more accurate results for the `EmissiveStrengthTest` glTF test case.
## Solution
- Make sure we send the emissive color as linear instead of sRGB.
---
## Changelog
- Emission strength is now correctly interpreted by the `StandardMaterial` as linear instead of sRGB.
## Migration Guide
- If you have previously manually specified emissive values with `Color::rgb()` and would like to retain the old visual results, you must now use `Color::rgb_linear()` instead;
- If you have previously manually specified emissive values with `Color::rgb_linear()` and would like to retain the old visual results, you'll need to apply a one-time gamma calculation to your channels manually to get the _actual_ linear RGB value:
- For channel values greater than `0.0031308`, use `(1.055 * value.powf(1.0 / 2.4)) - 0.055`;
- For channel values lower than or equal to `0.0031308`, use `value * 12.92`;
- Otherwise, the results should now be more consistent with other tools/engines.
# Objective
Current `Node` doc comment:
```rust
/// The size of the node as width and height in pixels
/// automatically calculated by [`super::flex::flex_node_system`]
```
It should be changed to make it clear that `Node` stores the size in logical pixels, not physical.
# Objective
- Example `transparent_window` doesn't display a transparent window on macOS
- Fixes#6330
## Solution
- Set the `composite_alpha_mode` of the window to the correct value
- Update docs
# Objective
Upgrade to Taffy 0.3.3
Fixes: #7712
## Solution
Upgrade to Taffy 0.3.3 with the `grid` feature disabled.
---
## Changelog
* Changed Taffy version to 0.3.3 and disabled its `grid` feature.
* Added the `Start` and `End` variants to `AlignItems`, `AlignSelf`, `AlignContent` and `JustifyContent`.
* Added the `SpaceEvenly` variant to `AlignContent`.
* Updated `from_style` for Taffy 0.3.3.
# Objective
the current depth bias only adjusts ordering, so it doesn't work for opaque meshes vs alpha-blend meshes, and it doesn't help when two meshes are infinitesimally offset from one another.
## Solution
pass the material's depth bias into the pipeline depth stencil `constant` field.
# Objective
Simple text pipeline benchmark. It's quite expensive but current examples don't capture the performance of `queue_text` as it only runs on changes to the text.
# Objective
- Fixes#7889.
## Solution
- Change the glTF loader to insert a `Camera3dBundle` instead of a manually constructed bundle. This might prevent future issues when new components are required for a 3D Camera to work correctly.
- Register the `ColorGrading` type because `bevy_scene` was complaining about it.
Huge credit to @StarLederer, who did almost all of the work on this. We're just reusing this PR to keep everything in one place.
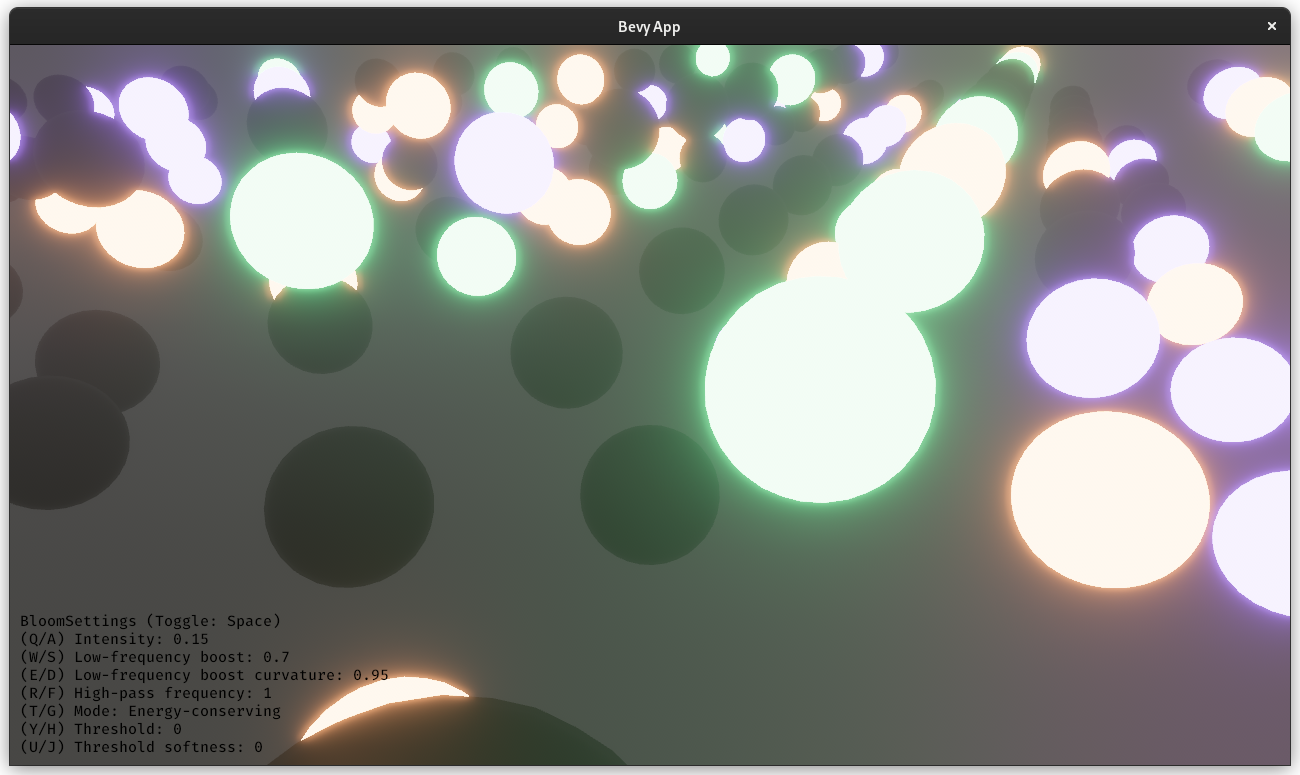
# Objective
1. Make bloom more physically based.
1. Improve artistic control.
1. Allow to use bloom as screen blur.
1. Fix#6634.
1. Address #6655 (although the author makes incorrect conclusions).
## Solution
1. Set the default threshold to 0.
2. Lerp between bloom textures when `composite_mode: BloomCompositeMode::EnergyConserving`.
1. Use [a parametric function](https://starlederer.github.io/bloom) to control blend levels for each bloom texture. In the future this can be controlled per-pixel for things like lens dirt.
3. Implement BloomCompositeMode::Additive` for situations where the old school look is desired.
## Changelog
* Bloom now looks different.
* Added `BloomSettings:lf_boost`, `BloomSettings:lf_boost_curvature`, `BloomSettings::high_pass_frequency` and `BloomSettings::composite_mode`.
* `BloomSettings::scale` removed.
* `BloomSettings::knee` renamed to `BloomPrefilterSettings::softness`.
* `BloomSettings::threshold` renamed to `BloomPrefilterSettings::threshold`.
* The bloom example has been renamed to bloom_3d and improved. A bloom_2d example was added.
## Migration Guide
* Refactor mentions of `BloomSettings::knee` and `BloomSettings::threshold` as `BloomSettings::prefilter_settings` where knee is now `softness`.
* If defined without `..default()` add `..default()` to definitions of `BloomSettings` instances or manually define missing fields.
* Adapt to Bloom looking visually different (if needed).
Co-authored-by: Herman Lederer <germans.lederers@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Update `glam` to the latest version.
## Solution
- Update `glam` to version `0.23`.
Since the breaking change in `glam` only affects the `scalar-math` feature, this should cause no issues.
# Objective
- Make cubic splines more flexible and more performant
- Remove the existing spline implementation that is generic over many degrees
- This is a potential performance footgun and adds type complexity for negligible gain.
- Add implementations of:
- Bezier splines
- Cardinal splines (inc. Catmull-Rom)
- B-Splines
- Hermite splines
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/221780519-495d1b20-ab46-45b4-92a3-32c46da66034.mp4https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/221780524-2b154016-699f-404f-9c18-02092f589b04.mp4https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/221780525-f934f99d-9ad4-4999-bae2-75d675f5644f.mp4
## Solution
- Implements the concept that splines are curve generators (e.g. https://youtu.be/jvPPXbo87ds?t=3488) via the `CubicGenerator` trait.
- Common splines are bespoke data types that implement this trait. This gives us flexibility to add custom spline-specific methods on these types, while ultimately all generating a `CubicCurve`.
- All splines generate `CubicCurve`s, which are a chain of precomputed polynomial coefficients. This means that all splines have the same evaluation cost, as the calculations for determining position, velocity, and acceleration are all identical. In addition, `CubicCurve`s are simply a list of `CubicSegment`s, which are evaluated from t=0 to t=1. This also means cubic splines of different type can be chained together, as ultimately they all are simply a collection of `CubicSegment`s.
- Because easing is an operation on a singe segment of a Bezier curve, we can simply implement easing on `Beziers` that use the `Vec2` type for points. Higher level crates such as `bevy_ui` can wrap this in a more ergonomic interface as needed.
### Performance
Measured on a desktop i5 8600K (6-year-old CPU):
- easing: 2.7x faster (19ns)
- cubic vec2 position sample: 1.5x faster (1.8ns)
- cubic vec3 position sample: 1.5x faster (2.6ns)
- cubic vec3a position sample: 1.9x faster (1.4ns)
On a laptop i7 11800H:
- easing: 16ns
- cubic vec2 position sample: 1.6ns
- cubic vec3 position sample: 2.3ns
- cubic vec3a position sample: 1.2ns
---
## Changelog
- Added a generic cubic curve trait, and implementation for Cardinal splines (including Catmull-Rom), B-Splines, Beziers, and Hermite Splines. 2D cubic curve segments also implement easing functionality for animation.
# Objective
Unfortunately, there are three issues with my changes introduced by #7784.
1. The changes left some dead code. This is already taken care of here: #7875.
2. Disabling prepass causes failures because the shadow mapping relies on the `PrepassPlugin` now.
3. Custom materials use the `prepass.wgsl` shader, but this does not always define a fragment entry point.
This PR fixes 2. and 3. and resolves#7879.
## Solution
- Add a regression test with disabled prepass.
- Split `PrepassPlugin` into two plugins:
- `PrepassPipelinePlugin` contains the part that is required for the shadow mapping to work and is unconditionally added.
- `PrepassPlugin` now only adds the systems and resources required for the "real" prepasses.
- Add a noop fragment entry point to `prepass.wgsl`, used if `NORMAL_PASS` is not defined.
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
# Objective
#7863 introduced a potential footgun. When trying to incorrectly add a user-defined type using `in_base_set`, the compiler will suggest that the user implement `BaseSystemSet` for their type. This is a reasonable-sounding suggestion, however this is not the correct way to make a base set, and will lead to a confusing panic message when a marker trait is implemented for the wrong type.
## Solution
Rewrite the documentation for these traits, making it more clear that `BaseSystemSet` is a marker for types that are already base sets, and not a way to define a base set.
# Objective
- Fixes#7874.
- The `bevy_text` dependency is optional for `bevy_ui`, but the `accessibility` module depended on it.
## Solution
- Guard the `accessibility` module behind the `bevy_text` feature and only add the plugin when it's enabled.