When I was upgrading to 0.9 noticed there were some changes to the timer, mainly the `TimerMode`. When switching from the old `is_repeating()` and `set_repeating()` to the new `mode()` and `set_mode()` noticed the docs still had the old description.
# Objective
Right now, the `TaskPool` implementation allows panics to permanently kill worker threads upon panicking. This is currently non-recoverable without using a `std::panic::catch_unwind` in every scheduled task. This is poor ergonomics and even poorer developer experience. This is exacerbated by #2250 as these threads are global and cannot be replaced after initialization.
Removes the need for temporary fixes like #4998. Fixes#4996. Fixes#6081. Fixes#5285. Fixes#5054. Supersedes #2307.
## Solution
The current solution is to wrap `Executor::run` in `TaskPool` with a `catch_unwind`, and discarding the potential panic. This was taken straight from [smol](404c7bcc0a/src/spawn.rs (L44))'s current implementation. ~~However, this is not entirely ideal as:~~
- ~~the signaled to the awaiting task. We would need to change `Task<T>` to use `async_task::FallibleTask` internally, and even then it doesn't signal *why* it panicked, just that it did.~~ (See below).
- ~~no error is logged of any kind~~ (See below)
- ~~it's unclear if it drops other tasks in the executor~~ (it does not)
- ~~This allows the ECS parallel executor to keep chugging even though a system's task has been dropped. This inevitably leads to deadlock in the executor.~~ Assuming we don't catch the unwind in ParallelExecutor, this will naturally kill the main thread.
### Alternatives
A final solution likely will incorporate elements of any or all of the following.
#### ~~Log and Ignore~~
~~Log the panic, drop the task, keep chugging. This only addresses the discoverability of the panic. The process will continue to run, probably deadlocking the executor. tokio's detatched tasks operate in this fashion.~~
Panics already do this by default, even when caught by `catch_unwind`.
#### ~~`catch_unwind` in `ParallelExecutor`~~
~~Add another layer catching system-level panics into the `ParallelExecutor`. How the executor continues when a core dependency of many systems fails to run is up for debate.~~
`async_task::Task` bubbles up panics already, this will transitively push panics all the way to the main thread.
#### ~~Emulate/Copy `tokio::JoinHandle` with `Task<T>`~~
~~`tokio::JoinHandle<T>` bubbles up the panic from the underlying task when awaited. This can be transitively applied across other APIs that also use `Task<T>` like `Query::par_for_each` and `TaskPool::scope`, bubbling up the panic until it's either caught or it reaches the main thread.~~
`async_task::Task` bubbles up panics already, this will transitively push panics all the way to the main thread.
#### Abort on Panic
The nuclear option. Log the error, abort the entire process on any thread in the task pool panicking. Definitely avoids any additional infrastructure for passing the panic around, and might actually lead to more efficient code as any unwinding is optimized out. However gives the developer zero options for dealing with the issue, a seemingly poor choice for debuggability, and prevents graceful shutdown of the process. Potentially an option for handling very low-level task management (a la #4740). Roughly takes the shape of:
```rust
struct AbortOnPanic;
impl Drop for AbortOnPanic {
fn drop(&mut self) {
abort!();
}
}
let guard = AbortOnPanic;
// Run task
std::mem::forget(AbortOnPanic);
```
---
## Changelog
Changed: `bevy_tasks::TaskPool`'s threads will no longer terminate permanently when a task scheduled onto them panics.
Changed: `bevy_tasks::Task` and`bevy_tasks::Scope` will propagate panics in the spawned tasks/scopes to the parent thread.
This reverts commit 53d387f340.
# Objective
Reverts #6448. This didn't have the intended effect: we're now getting bevy::prelude shown in the docs again.
Co-authored-by: Alejandro Pascual <alejandro.pascual.pozo@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Right now re-exports are completely hidden in prelude docs.
- Fixes#6433
## Solution
- We could show the re-exports without inlining their documentation.
# Objective
- Time have `Reflect`, but doesn't have `FromReflect`.
## Solution
- Add it for `Timer`, `Stopwatch` and `TimerMode`.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `FromReflect` derive for `Timer`, `Stopwatch` and `TimerMode`.
# Objective
- Some tests are very flaky on a m1
- m1 currently have a 41 ns precision
## Solution
- Do not run tests that compare a `Duration` or a `f64` on a m1 (and m2)
# Objective
- Make `Time` API more consistent.
- Support time accel/decel/pause.
## Solution
This is just the `Time` half of #3002. I was told that part isn't controversial.
- Give the "delta time" and "total elapsed time" methods `f32`, `f64`, and `Duration` variants with consistent naming.
- Implement accelerating / decelerating the passage of time.
- Implement stopping time.
---
## Changelog
- Changed `time_since_startup` to `elapsed` because `time.time_*` is just silly.
- Added `relative_speed` and `set_relative_speed` methods.
- Added `is_paused`, `pause`, `unpause` , and methods. (I'd prefer `resume`, but `unpause` matches `Timer` API.)
- Added `raw_*` variants of the "delta time" and "total elapsed time" methods.
- Added `first_update` method because there's a non-zero duration between startup and the first update.
## Migration Guide
- `time.time_since_startup()` -> `time.elapsed()`
- `time.seconds_since_startup()` -> `time.elapsed_seconds_f64()`
- `time.seconds_since_startup_wrapped_f32()` -> `time.elapsed_seconds_wrapped()`
If you aren't sure which to use, most systems should continue to use "scaled" time (e.g. `time.delta_seconds()`). The realtime "unscaled" time measurements (e.g. `time.raw_delta_seconds()`) are mostly for debugging and profiling.
# Objective
Fixes#6244
## Solution
Uses derive to implement `Serialize` and `Deserialize` for `Timer` and `Stopwatch`
### Things to consider
- Should fields such as `finished` and `times_finished_this_tick` in `Timer` be serialized?
- Does `Countdown` and `PrintOnCompletionTimer` need to be serialized and deserialized?
## Changelog
Added `Serialize` and `Deserialize` implementations to `Timer` and `Stopwatch`, `Countdown`.
As mentioned in #2926, it's better to have an explicit type that clearly communicates the intent of the timer mode rather than an opaque boolean, which can be only understood when knowing the signature or having to look up the documentation.
This also opens up a way to merge different timers, such as `Stopwatch`, and possibly future ones, such as `DiscreteStopwatch` and `DiscreteTimer` from #2683, into one struct.
Signed-off-by: Lena Milizé <me@lvmn.org>
# Objective
Fixes#2926.
## Solution
Introduce `TimerMode` which replaces the `bool` argument of `Timer` constructors. A `Default` value for `TimerMode` is `Once`.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `TimerMode` enum, along with variants `TimerMode::Once` and `TimerMode::Repeating`
### Changed
- Replace `bool` argument of `Timer::new` and `Timer::from_seconds` with `TimerMode`
- Change `repeating: bool` field of `Timer` with `mode: TimerMode`
## Migration Guide
- Replace `Timer::new(duration, false)` with `Timer::new(duration, TimerMode::Once)`.
- Replace `Timer::new(duration, true)` with `Timer::new(duration, TimerMode::Repeating)`.
- Replace `Timer::from_seconds(seconds, false)` with `Timer::from_seconds(seconds, TimerMode::Once)`.
- Replace `Timer::from_seconds(seconds, true)` with `Timer::from_seconds(seconds, TimerMode::Repeating)`.
- Change `timer.repeating()` to `timer.mode() == TimerMode::Repeating`.
# Objective
The [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) involves allowing exclusive systems to be referenced and ordered relative to parallel systems. We've agreed that unifying systems under `System` is the right move.
This is an alternative to #4166 (see rationale in the comments I left there). Note that this builds on the learnings established there (and borrows some patterns).
## Solution
This unifies parallel and exclusive systems under the shared `System` trait, removing the old `ExclusiveSystem` trait / impls. This is accomplished by adding a new `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` impl similar to `FunctionSystem`. It is backed by `ExclusiveSystemParam`, which is similar to `SystemParam`. There is a new flattened out SystemContainer api (which cuts out a lot of trait and type complexity).
This means you can remove all cases of `exclusive_system()`:
```rust
// before
commands.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system());
// after
commands.add_system(some_system);
```
I've also implemented `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `&mut QueryState` and `&mut SystemState`, which makes this possible in exclusive systems:
```rust
fn some_exclusive_system(
world: &mut World,
transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>,
state: &mut SystemState<(Res<Time>, Query<&Player>)>,
) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
println!("{transform:?}");
}
let (time, players) = state.get(world);
for player in players.iter() {
println!("{player:?}");
}
}
```
Note that "exclusive function systems" assume `&mut World` is present (and the first param). I think this is a fair assumption, given that the presence of `&mut World` is what defines the need for an exclusive system.
I added some targeted SystemParam `static` constraints, which removed the need for this:
``` rust
fn some_exclusive_system(state: &mut SystemState<(Res<'static, Time>, Query<&'static Player>)>) {}
```
## Related
- #2923
- #3001
- #3946
## Changelog
- `ExclusiveSystem` trait (and implementations) has been removed in favor of sharing the `System` trait.
- `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveSystemParam` were added, enabling flexible exclusive function systems
- `&mut SystemState` and `&mut QueryState` now implement `ExclusiveSystemParam`
- Exclusive and parallel System configuration is now done via a unified `SystemDescriptor`, `IntoSystemDescriptor`, and `SystemContainer` api.
## Migration Guide
Calling `.exclusive_system()` is no longer required (or supported) for converting exclusive system functions to exclusive systems:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system.exclusive_system());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system);
```
Converting "normal" parallel systems to exclusive systems is done by calling the exclusive ordering apis:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system().at_end());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_system.at_end());
```
Query state in exclusive systems can now be cached via ExclusiveSystemParams, which should be preferred for clarity and performance reasons:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
fn some_system(world: &mut World) {
let mut transforms = world.query::<&Transform>();
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
// New (0.9)
fn some_system(world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
```
# Objective
- Sometimes, like when using shaders, you can only use a time value in `f32`. Unfortunately this suffers from floating precision issues pretty quickly. The standard approach to this problem is to wrap the time after a given period
- This is necessary for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5409
## Solution
- Add a `seconds_since_last_wrapping_period` method on `Time` that returns a `f32` that is the `seconds_since_startup` modulo the `max_wrapping_period`
---
## Changelog
Added `seconds_since_last_wrapping_period` to `Time`
## Additional info
I'm very opened to hearing better names. I don't really like the current naming, I just went with something descriptive.
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#5963
## Solution
Add remaining fn in Timer class, this function only minus total duration with elapsed time.
Co-authored-by: Sergi-Ferrez <61662926+Sergi-Ferrez@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
While coding in bevy I needed to get the elapsed time of a stopwatch as f64.
I found it quite odd there are functions on Timer to get time as f64 but not on the Stopwatch.
## Solution
- added a function that returns the `Stopwatch` elapsed time as `f64`
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added a function to get `Stopwatch` elapsed time as `f64`
### Fixed
- The Stopwatch elapsed function had a wrong docs link
# Objective
I'm build a UI system for bevy. In this UI system there is a concept of a system per UI entity. I had an issue where change detection wasn't working how I would expect and it's because when a function system is ran the `last_change_tick` is updated with the latest tick(from world). In my particular case I want to "wait" to update the `last_change_tick` until after my system runs for each entity.
## Solution
Initially I thought bypassing the change detection all together would be a good fix, but on talking to some users in discord a simpler fix is to just expose `last_change_tick` to the end users. This is achieved by adding the following to the `System` trait:
```rust
/// Allows users to get the system's last change tick.
fn get_last_change_tick(&self) -> u32;
/// Allows users to set the system's last change tick.
fn set_last_change_tick(&mut self, last_change_tick: u32);
```
This causes a bit of weirdness with two implementors of `System`. `FixedTimestep` and `ChainSystem` both implement system and thus it's required that some sort of implementation be given for the new functions. I solved this by outputting a warning and not doing anything for these systems.
I think it's important to understand why I can't add the new functions only to the function system and not to the `System` trait. In my code I store the systems generically as `Box<dyn System<...>>`. I do this because I have differing parameters that are being passed in depending on the UI widget's system. As far as I can tell there isn't a way to take a system trait and cast it into a specific type without knowing what those parameters are.
In my own code this ends up looking something like:
```rust
// Runs per entity.
let old_tick = widget_system.get_last_change_tick();
should_update_children = widget_system.run((widget_tree.clone(), entity.0), world);
widget_system.set_last_change_tick(old_tick);
// later on after all the entities have been processed:
for system in context.systems.values_mut() {
system.set_last_change_tick(world.read_change_tick());
}
```
## Changelog
- Added `get_last_change_tick` and `set_last_change_tick` to `System`'s.
# Objective
- While generating https://github.com/jakobhellermann/bevy_reflect_ts_type_export/blob/main/generated/types.ts, I noticed that some types that implement `Reflect` did not register themselves
- `Viewport` isn't reflect but can be (there's a TODO)
## Solution
- register all reflected types
- derive `Reflect` for `Viewport`
## Changelog
- more types are not registered in the type registry
- remove `Serialize`, `Deserialize` impls from `Viewport`
I also decided to remove the `Serialize, Deserialize` from the `Viewport`, since they were (AFAIK) only used for reflection, which now is done without serde. So this is technically a breaking change for people who relied on that impl directly.
Personally I don't think that every bevy type should implement `Serialize, Deserialize`, as that would lead to a ton of code generation that mostly isn't necessary because we can do the same with `Reflect`, but if this is deemed controversial I can remove it from this PR.
## Migration Guide
- `KeyCode` now implements `Reflect` not as `reflect_value`, but with proper struct reflection. The `Serialize` and `Deserialize` impls were removed, now that they are no longer required for scene serialization.
# Objective
The reflection impls on `Option<T>` have the bound `T: Reflect + Clone`. This means that using `FromReflect` requires `Clone` even though we can normally get away with just `FromReflect`.
## Solution
Update the bounds on `Option<T>` to match that of `Vec<T>`, where `T: FromReflect`.
This helps remove a `Clone` implementation that may be undesired but added for the sole purpose of getting the code to compile.
---
## Changelog
* Reflection on `Option<T>` now has `T` bound by `FromReflect` rather than `Reflect + Clone`
* Added a `FromReflect` impl for `Instant`
## Migration Guide
If using `Option<T>` with Bevy's reflection API, `T` now needs to implement `FromReflect` rather than just `Clone`. This can be achieved easily by simply deriving `FromReflect`:
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect, Clone)]
struct Foo;
let reflected: Box<dyn Reflect> = Box::new(Some(Foo));
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct Foo;
let reflected: Box<dyn Reflect> = Box::new(Some(Foo));
```
> Note: You can still derive `Clone`, but it's not required in order to compile.
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Some generic types like `Option<T>`, `Vec<T>` and `HashMap<K, V>` implement `Reflect` when where their generic types `T`/`K`/`V` implement `Serialize + for<'de> Deserialize<'de>`.
This is so that in their `GetTypeRegistration` impl they can insert the `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` type data structs.
This has the annoying side effect that if your struct contains a `Option<NonSerdeStruct>` you won't be able to derive reflect (https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4054).
## Solution
- remove the `Serialize + Deserialize` bounds on wrapper types
- this means that `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` will no longer be inserted even for `.register::<Option<DoesImplSerde>>()`
- add `register_type_data<T, D>` shorthand for `registry.get_mut(T).insert(D::from_type<T>())`
- require users to register their specific generic types **and the serde types** separately like
```rust
.register_type::<Option<String>>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectSerialize>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectDeserialize>()
```
I believe this is the best we can do for extensibility and convenience without specialization.
## Changelog
- `.register_type` for generic types like `Option<T>`, `Vec<T>`, `HashMap<K, V>` will no longer insert `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` type data. Instead you need to register it separately for concrete generic types like so:
```rust
.register_type::<Option<String>>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectSerialize>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectDeserialize>()
```
TODO: more docs and tweaks to the scene example to demonstrate registering generic types.
# Objective
- The time update is currently done in the wrong part of the schedule. For a single frame the current order of things is update input, update time (First stage), other stages, render stage (frame presentation). So when we update the time it includes the input processing of the current frame and the frame presentation of the previous frame. This is a problem when vsync is on. When input processing takes a longer amount of time for a frame, the vsync wait time gets shorter. So when these are not paired correctly we can potentially have a long input processing time added to the normal vsync wait time in the previous frame. This leads to inaccurate frame time reporting and more variance of the time than actually exists. For more details of why this is an issue see the linked issue below.
- Helps with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4669
- Supercedes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728 and https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4735. This PR should be less controversial than those because it doesn't add to the API surface.
## Solution
- The most accurate frame time would come from hardware. We currently don't have access to that for multiple reasons, so the next best thing we can do is measure the frame time as close to frame presentation as possible. This PR gets the Instant::now() for the time immediately after frame presentation in the render system and then sends that time to the app world through a channel.
- implements suggestion from @aevyrie from here https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728#discussion_r872010606
## Statistics
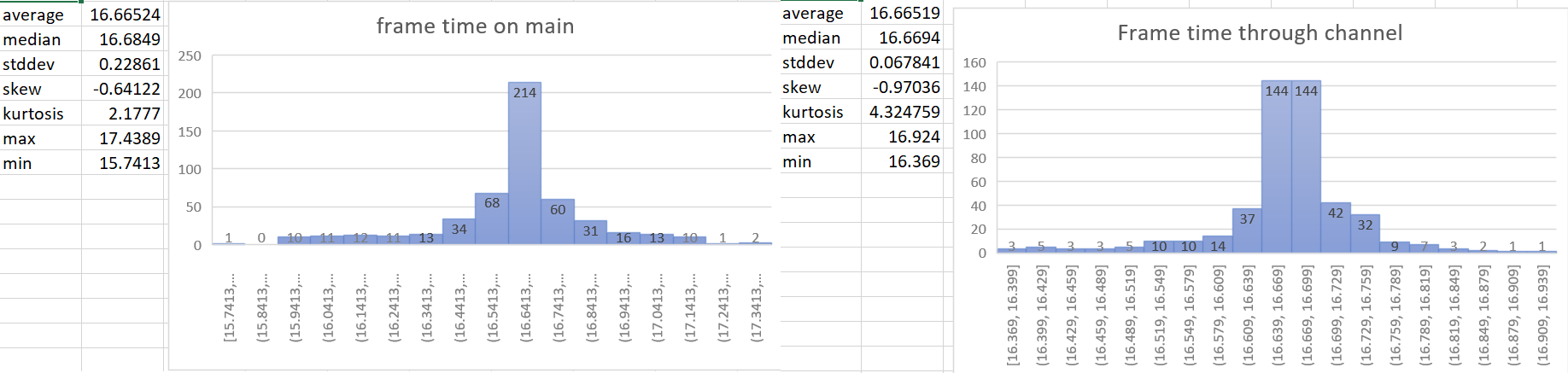
---
## Changelog
- Make frame time reporting more accurate.
## Migration Guide
`time.delta()` now reports zero for 2 frames on startup instead of 1 frame.
# Objective
`SAFETY` comments are meant to be placed before `unsafe` blocks and should contain the reasoning of why in this case the usage of unsafe is okay. This is useful when reading the code because it makes it clear which assumptions are required for safety, and makes it easier to spot possible unsoundness holes. It also forces the code writer to think of something to write and maybe look at the safety contracts of any called unsafe methods again to double-check their correct usage.
There's a clippy lint called `undocumented_unsafe_blocks` which warns when using a block without such a comment.
## Solution
- since clippy expects `SAFETY` instead of `SAFE`, rename those
- add `SAFETY` comments in more places
- for the last remaining 3 places, add an `#[allow()]` and `// TODO` since I wasn't comfortable enough with the code to justify their safety
- add ` #![warn(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` to `bevy_ecs`
### Note for reviewers
The first commit only renames `SAFETY` to `SAFE` so it doesn't need a thorough review.
cb042a416e..55cef2d6fa is the diff for all other changes.
### Safety comments where I'm not too familiar with the code
774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/entity/mod.rs (L540-L546)774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L249-L252)
### Locations left undocumented with a `TODO` comment
5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/executor_parallel.rs (L196-L199)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L287-L289)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L413-L415)
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
Reduce the catch-all grab-bag of functionality in bevy_core by minimally splitting off time functionality into bevy_time. Functionality like that provided by #3002 would increase the complexity of bevy_time, so this is a good candidate for pulling into its own unit.
A step in addressing #2931 and splitting bevy_core into more specific locations.
## Solution
Pull the time module of bevy_core into a new crate, bevy_time.
# Migration guide
- Time related types (e.g. `Time`, `Timer`, `Stopwatch`, `FixedTimestep`, etc.) should be imported from `bevy::time::*` rather than `bevy::core::*`.
- If you were adding `CorePlugin` manually, you'll also want to add `TimePlugin` from `bevy::time`.
- The `bevy::core::CorePlugin::Time` system label is replaced with `bevy::time::TimeSystem`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>