# Objective
The `States::variants` method was once used to construct `OnExit` and
`OnEnter` schedules for every possible value of a given `States` type.
[Since the switch to lazily initialized
schedules](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8028/files#diff-b2fba3a0c86e496085ce7f0e3f1de5960cb754c7d215ed0f087aa556e529f97f),
we no longer need to track every possible value.
This also opens the door to `States` types that aren't enums.
## Solution
- Remove the unused `States::variants` method and its associated type.
- Remove the enum-only restriction on derived States types.
---
## Changelog
- Removed `States::variants` and its associated type.
- Derived `States` can now be datatypes other than enums.
## Migration Guide
- `States::variants` no longer exists. If you relied on this function,
consider using a library that provides enum iterators.
# Objective
I was wondering whether to use `Timer::finished` or
`Timer::just_finished` for my repeating timer. This PR clarifies their
difference (or rather, lack thereof).
## Solution
More docs & examples.
# Objective
- There were a few typos in the project.
- This PR fixes these typos.
## Solution
- Fixing the typos.
Signed-off-by: SADIK KUZU <sadikkuzu@hotmail.com>
# Objective
In order to derive `Asset`s (v2), `TypePath` must also be implemented.
`TypePath` is not currently in the prelude, but given it is *required*
when deriving something that *is* in the prelude, I think it deserves to
be added.
## Solution
Add `TypePath` to `bevy_reflect::prelude`.
# Objective
Text bounds are computed by the layout algorithm using the text's
measurefunc so that text will only wrap after it's used the maximum
amount of available horizontal space.
When the layout size is returned the layout coordinates are rounded and
this sometimes results in the final size of the Node not matching the
size computed with the measurefunc. This means that the text may no
longer fit the horizontal available space and instead wrap onto a new
line. However, no glyphs will be generated for this new line because no
vertical space for the extra line was allocated.
fixes#9874
## Solution
Store both the rounded and unrounded node sizes in `Node`.
Rounding is used to eliminate pixel-wide gaps between nodes that should
be touching edge to edge, but this isn't necessary for text nodes as
they don't have solid edges.
## Changelog
* Added the `rounded_size: Vec2` field to `Node`.
* `text_system` uses the unrounded node size when computing a text
layout.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
Improve compatibility with macOS Sonoma and Xcode 15.0.
## Solution
- Adds the workaround by @ptxmac to ignore the invalid window sizes
provided by `winit` on macOS 14.0
- This still provides a slightly wrong content size when resizing (it
fails to account for the window title bar, so some content gets clipped
at the bottom) but it's _much better_ than crashing.
- Adds docs on how to work around the `bindgen` bug on Xcode 15.0.
## Related Issues:
- https://github.com/RustAudio/coreaudio-sys/issues/85
- https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/2876
---
## Changelog
- Added a workaround for a `winit`-related crash under macOS Sonoma
(14.0)
---------
Co-authored-by: Peter Kristensen <peter@ptx.dk>
# Objective
- Improve rendering performance, particularly by avoiding the large
system commands costs of using the ECS in the way that the render world
does.
## Solution
- Define `EntityHasher` that calculates a hash from the
`Entity.to_bits()` by `i | (i.wrapping_mul(0x517cc1b727220a95) << 32)`.
`0x517cc1b727220a95` is something like `u64::MAX / N` for N that gives a
value close to π and that works well for hashing. Thanks for @SkiFire13
for the suggestion and to @nicopap for alternative suggestions and
discussion. This approach comes from `rustc-hash` (a.k.a. `FxHasher`)
with some tweaks for the case of hashing an `Entity`. `FxHasher` and
`SeaHasher` were also tested but were significantly slower.
- Define `EntityHashMap` type that uses the `EntityHashser`
- Use `EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` for render world entity storage,
including:
- `RenderMaterialInstances` - contains the `AssetId<M>` of the material
associated with the entity. Also for 2D.
- `RenderMeshInstances` - contains mesh transforms, flags and properties
about mesh entities. Also for 2D.
- `SkinIndices` and `MorphIndices` - contains the skin and morph index
for an entity, respectively
- `ExtractedSprites`
- `ExtractedUiNodes`
## Benchmarks
All benchmarks have been conducted on an M1 Max connected to AC power.
The tests are run for 1500 frames. The 1000th frame is captured for
comparison to check for visual regressions. There were none.
### 2D Meshes
`bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d`
#### `--ordered-z`
This test spawns the 2D meshes with z incrementing back to front, which
is the ideal arrangement allocation order as it matches the sorted
render order which means lookups have a high cache hit rate.
<img width="1112" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 50 45"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/e140bc98-7091-4a3b-8ae1-ab75d16d2ccb">
-39.1% median frame time.
#### Random
This test spawns the 2D meshes with random z. This not only makes the
batching and transparent 2D pass lookups get a lot of cache misses, it
also currently means that the meshes are almost certain to not be
batchable.
<img width="1108" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 51 28"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/29c2e813-645a-43ce-982a-55df4bf7d8c4">
-7.2% median frame time.
### 3D Meshes
`many_cubes --benchmark`
<img width="1112" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 51 57"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/1a729673-3254-4e2a-9072-55e27c69f0fc">
-7.7% median frame time.
### Sprites
**NOTE: On `main` sprites are using `SparseSet<Entity, T>`!**
`bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode sprite`
#### `--ordered-z`
This test spawns the sprites with z incrementing back to front, which is
the ideal arrangement allocation order as it matches the sorted render
order which means lookups have a high cache hit rate.
<img width="1116" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 52 31"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/bc8eab90-e375-4d31-b5cd-f55f6f59ab67">
+13.0% median frame time.
#### Random
This test spawns the sprites with random z. This makes the batching and
transparent 2D pass lookups get a lot of cache misses.
<img width="1109" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 53 01"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/22073f5d-99a7-49b0-9584-d3ac3eac3033">
+0.6% median frame time.
### UI
**NOTE: On `main` UI is using `SparseSet<Entity, T>`!**
`many_buttons`
<img width="1111" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-27 at 07 53 26"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/66afd56d-cbe4-49e7-8b64-2f28f6043d85">
+15.1% median frame time.
## Alternatives
- Cart originally suggested trying out `SparseSet<Entity, T>` and indeed
that is slightly faster under ideal conditions. However,
`PassHashMap<Entity, T>` has better worst case performance when data is
randomly distributed, rather than in sorted render order, and does not
have the worst case memory usage that `SparseSet`'s dense `Vec<usize>`
that maps from the `Entity` index to sparse index into `Vec<T>`. This
dense `Vec` has to be as large as the largest Entity index used with the
`SparseSet`.
- I also tested `PassHashMap<u32, T>`, intending to use `Entity.index()`
as the key, but this proved to sometimes be slower and mostly no
different.
- The only outstanding approach that has not been implemented and tested
is to _not_ clear the render world of its entities each frame. That has
its own problems, though they could perhaps be solved.
- Performance-wise, if the entities and their component data were not
cleared, then they would incur table moves on spawn, and should not
thereafter, rather just their component data would be overwritten.
Ideally we would have a neat way of either updating data in-place via
`&mut T` queries, or inserting components if not present. This would
likely be quite cumbersome to have to remember to do everywhere, but
perhaps it only needs to be done in the more performance-sensitive
systems.
- The main problem to solve however is that we want to both maintain a
mapping between main world entities and render world entities, be able
to run the render app and world in parallel with the main app and world
for pipelined rendering, and at the same time be able to spawn entities
in the render world in such a way that those Entity ids do not collide
with those spawned in the main world. This is potentially quite
solvable, but could well be a lot of ECS work to do it in a way that
makes sense.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Component data for entities to be drawn are no longer stored
on entities in the render world. Instead, data is stored in a
`EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` in various resources. This brings significant
performance benefits due to the way the render app clears entities every
frame. Resources of most interest are `RenderMeshInstances` and
`RenderMaterialInstances`, and their 2D counterparts.
## Migration Guide
Previously the render app extracted mesh entities and their component
data from the main world and stored them as entities and components in
the render world. Now they are extracted into essentially
`EntityHashMap<Entity, T>` where `T` are structs containing an
appropriate group of data. This means that while extract set systems
will continue to run extract queries against the main world they will
store their data in hash maps. Also, systems in later sets will either
need to look up entities in the available resources such as
`RenderMeshInstances`, or maintain their own `EntityHashMap<Entity, T>`
for their own data.
Before:
```rust
fn queue_custom(
material_meshes: Query<(Entity, &MeshTransforms, &Handle<Mesh>), With<InstanceMaterialData>>,
) {
...
for (entity, mesh_transforms, mesh_handle) in &material_meshes {
...
}
}
```
After:
```rust
fn queue_custom(
render_mesh_instances: Res<RenderMeshInstances>,
instance_entities: Query<Entity, With<InstanceMaterialData>>,
) {
...
for entity in &instance_entities {
let Some(mesh_instance) = render_mesh_instances.get(&entity) else { continue; };
// The mesh handle in `AssetId<Mesh>` form, and the `MeshTransforms` can now
// be found in `mesh_instance` which is a `RenderMeshInstance`
...
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Complete the documentation for `bevy_window`.
## Solution
The `warn(missing_doc)` attribute was only applying to the `cursor`
module as it was declared as an inner attribute. I switched it to an
outer attribute and documented the remaining items.
# Objective
Fixes: #9898
## Solution
Make morph behave like other keyframes, lerping first between start and
end, and then between the current state and the result.
## Changelog
Fixed jerky morph targets
---------
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: CGMossa <cgmossa@gmail.com>
# Objective
The scetion for guides about flexbox has a link to grid and the section
for grid has a link to a guide about flexbox.
## Solution
Swapped links for flexbox and grid.
---
This is a duplicate of #9632, it was created since I forgot to make a
new branch when I first made this PR, so I was having trouble resolving
merge conflicts, meaning I had to rebuild my PR.
# Objective
- Allow other plugins to create the renderer resources. An example of
where this would be required is my [OpenXR
plugin](https://github.com/awtterpip/bevy_openxr)
## Solution
- Changed the bevy RenderPlugin to optionally take precreated render
resources instead of a configuration.
## Migration Guide
The `RenderPlugin` now takes a `RenderCreation` enum instead of
`WgpuSettings`. `RenderSettings::default()` returns
`RenderSettings::Automatic(WgpuSettings::default())`. `RenderSettings`
also implements `From<WgpuSettings>`.
```rust
// before
RenderPlugin {
wgpu_settings: WgpuSettings {
...
},
}
// now
RenderPlugin {
render_creation: RenderCreation::Automatic(WgpuSettings {
...
}),
}
// or
RenderPlugin {
render_creation: WgpuSettings {
...
}.into(),
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Malek <pocmalek@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Some beginners spend time trying to manually set the position of a
`TextBundle`, without realizing that `Text2dBundle` exists.
## Solution
Mention `Text2dBundle` in the documentation of `TextBundle`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#9625
## Solution
Adds `async-io` as an optional dependency of `bevy_tasks`. When enabled,
this causes calls to `futures_lite::future::block_on` to be replaced
with calls to `async_io::block_on`.
---
## Changelog
- Added a new `async-io` feature to `bevy_tasks`. When enabled, this
causes `bevy_tasks` to use `async-io`'s implemention of `block_on`
instead of `futures-lite`'s implementation. You should enable this if
you use `async-io` in your application.
# Objective
This is a minimally disruptive version of #8340. I attempted to update
it, but failed due to the scope of the changes added in #8204.
Fixes#8307. Partially addresses #4642. As seen in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8284, we're actually copying
data twice in Prepare stage systems. Once into a CPU-side intermediate
scratch buffer, and once again into a mapped buffer. This is inefficient
and effectively doubles the time spent and memory allocated to run these
systems.
## Solution
Skip the scratch buffer entirely and use
`wgpu::Queue::write_buffer_with` to directly write data into mapped
buffers.
Separately, this also directly uses
`wgpu::Limits::min_uniform_buffer_offset_alignment` to set up the
alignment when writing to the buffers. Partially addressing the issue
raised in #4642.
Storage buffers and the abstractions built on top of
`DynamicUniformBuffer` will need to come in followup PRs.
This may not have a noticeable performance difference in this PR, as the
only first-party systems affected by this are view related, and likely
are not going to be particularly heavy.
---
## Changelog
Added: `DynamicUniformBuffer::get_writer`.
Added: `DynamicUniformBufferWriter`.
derive `Reflect` to `GlyphAtlasInfo`,`PositionedGlyph` and
`TextLayoutInfo`.
# Objective
- I need reflection gets all components of the `TextBundle` and
`clone_value` it
## Solution
- registry it
# Objective
mesh.rs is infamously large. We could split off unrelated code.
## Solution
Morph targets are very similar to skinning and have their own module. We
move skinned meshes to an independent module like morph targets and give
the systems similar names.
### Open questions
Should the skinning systems and structs stay public?
---
## Migration Guide
Renamed skinning systems, resources and components:
- extract_skinned_meshes -> extract_skins
- prepare_skinned_meshes -> prepare_skins
- SkinnedMeshUniform -> SkinUniform
- SkinnedMeshJoints -> SkinIndex
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: vero <email@atlasdostal.com>
# Objective
Scheduling low cost systems has significant overhead due to task pool
contention and the extra machinery to schedule and run them. Event
update systems are the prime example of a low cost system, requiring a
guaranteed O(1) operation, and there are a *lot* of them.
## Solution
Add a run condition to every event system so they only run when there is
an event in either of it's two internal Vecs.
---
## Changelog
Changed: Event update systems will not run if there are no events to
process.
## Migration Guide
`Events<T>::update_system` has been split off from the the type and can
be found at `bevy_ecs::event::event_update_system`.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#9707
## Solution
- At large translations (a few thousand units), the precision of
calculating the ray direction from the fragment world position and
camera world position seems to break down. Sampling the cubemap only
needs the ray direction. As such we can use the view space fragment
position, normalise it, rotate it to world space, and use that.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: Jittery skybox at large translations.
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7609 broke Android support
```
8721 8770 I event crates/bevy_winit/src/system.rs:55: Creating new window "App" (0v0)
8721 8769 I RustStdoutStderr: thread '<unnamed>' panicked at 'Cannot get the native window, it's null and will always be null before Event::Resumed and after Event::Suspended. Make sure you only call this function between those events.', winit-0.28.6/src/platform_impl/android/mod.rs:1058:13
```
## Solution
- Don't create windows on `StartCause::Init` as it's too early
# Objective
- Make it possible to write APIs that require a type or homogenous
storage for both `Children` & `Parent` that is agnostic to edge
direction.
## Solution
- Add a way to get the `Entity` from `Parent` as a slice.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Implement the foundations of automatic batching/instancing of draw
commands as the next step from #89
- NOTE: More performance improvements will come when more data is
managed and bound in ways that do not require rebinding such as mesh,
material, and texture data.
## Solution
- The core idea for batching of draw commands is to check whether any of
the information that has to be passed when encoding a draw command
changes between two things that are being drawn according to the sorted
render phase order. These should be things like the pipeline, bind
groups and their dynamic offsets, index/vertex buffers, and so on.
- The following assumptions have been made:
- Only entities with prepared assets (pipelines, materials, meshes) are
queued to phases
- View bindings are constant across a phase for a given draw function as
phases are per-view
- `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` is the only system that performs this
batching and has sole responsibility for preparing the per-object data.
As such the mesh binding and dynamic offsets are assumed to only vary as
a result of the `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` system, e.g. due to
having to split data across separate uniform bindings within the same
buffer due to the maximum uniform buffer binding size.
- Implement `GpuArrayBuffer` for `Mesh2dUniform` to store Mesh2dUniform
in arrays in GPU buffers rather than each one being at a dynamic offset
in a uniform buffer. This is the same optimisation that was made for 3D
not long ago.
- Change batch size for a range in `PhaseItem`, adding API for getting
or mutating the range. This is more flexible than a size as the length
of the range can be used in place of the size, but the start and end can
be otherwise whatever is needed.
- Add an optional mesh bind group dynamic offset to `PhaseItem`. This
avoids having to do a massive table move just to insert
`GpuArrayBufferIndex` components.
## Benchmarks
All tests have been run on an M1 Max on AC power. `bevymark` and
`many_cubes` were modified to use 1920x1080 with a scale factor of 1. I
run a script that runs a separate Tracy capture process, and then runs
the bevy example with `--features bevy_ci_testing,trace_tracy` and
`CI_TESTING_CONFIG=../benchmark.ron` with the contents of
`../benchmark.ron`:
```rust
(
exit_after: Some(1500)
)
```
...in order to run each test for 1500 frames.
The recent changes to `many_cubes` and `bevymark` added reproducible
random number generation so that with the same settings, the same rng
will occur. They also added benchmark modes that use a fixed delta time
for animations. Combined this means that the same frames should be
rendered both on main and on the branch.
The graphs compare main (yellow) to this PR (red).
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark`
<img width="1411" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 42 10"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/2088716a-c918-486c-8129-090b26fd2bc4">
The mesh and material are the same for all instances. This is basically
the best case for the initial batching implementation as it results in 1
draw for the ~11.7k visible meshes. It gives a ~30% reduction in median
frame time.
The 1000th frame is identical using the flip tool:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4615 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1404" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 45 18"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/5ee9c447-5bd2-45c6-9706-ac5ff8916daf">
This run uses 10 different materials by varying their textures. The
materials are randomly selected, and there is no sorting by material
bind group for opaque 3D so any batching is 'random'. The PR produces a
~5% reduction in median frame time. If we were to sort the opaque phase
by the material bind group, then this should be a lot faster. This
produces about 10.5k draws for the 11.7k visible entities. This makes
sense as randomly selecting from 10 materials gives a chance that two
adjacent entities randomly select the same material and can be batched.
The 1000th frame is identical in flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4537 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1394" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 48 44"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/f02a816b-a444-4c18-a96a-63b5436f3b7f">
This run varies the material data per instance by randomly-generating
its colour. This is the worst case for batching and that it performs
about the same as `main` is a good thing as it demonstrates that the
batching has minimal overhead when dealing with ~11k visible mesh
entities.
The 1000th frame is identical according to flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4568 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d`
<img width="1412" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 59 56"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/cb02ae07-237b-4646-ae9f-fda4dafcbad4">
This spawns 160 waves of 1000 quad meshes that are shaded with
ColorMaterial. Each wave has a different material so 160 waves currently
should result in 160 batches. This results in a 50% reduction in median
frame time.
Capturing a screenshot of the 1000th frame main vs PR gives:

```
Mean: 0.001222
Weighted median: 0.750432
1st weighted quartile: 0.453494
3rd weighted quartile: 0.969758
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.990296
Evaluation time: 0.4255 seconds
```
So they seem to produce the same results. I also double-checked the
number of draws. `main` does 160000 draws, and the PR does 160, as
expected.
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 09 22"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/4358da2e-ce32-4134-82df-3ab74c40849c">
This generates 10 textures and generates materials for each of those and
then selects one material per wave. The median frame time is reduced by
50%. Similar to the plain run above, this produces 160 draws on the PR
and 160000 on `main` and the 1000th frame is identical (ignoring the fps
counter text overlay).

```
Mean: 0.002877
Weighted median: 0.964980
1st weighted quartile: 0.668871
3rd weighted quartile: 0.982749
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.992377
Evaluation time: 0.4301 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 13 53"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/b2198b18-3439-47ad-919a-cdabe190facb">
This creates unique materials per instance by randomly-generating the
material's colour. This is the worst case for 2D batching. Somehow, this
PR manages a 7% reduction in median frame time. Both main and this PR
issue 160000 draws.
The 1000th frame is the same:

```
Mean: 0.001214
Weighted median: 0.937499
1st weighted quartile: 0.635467
3rd weighted quartile: 0.979085
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.988971
Evaluation time: 0.4462 seconds
```
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 21 12"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/8b31e915-d6be-4cac-abf5-c6a4da9c3d43">
This just spawns 160 waves of 1000 sprites. There should be and is no
notable difference between main and the PR.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1389" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 36 08"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/45fe8d6d-c901-4062-a349-3693dd044413">
This spawns the sprites selecting a texture at random per instance from
the 10 generated textures. This has no significant change vs main and
shouldn't.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1401" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 29 52"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/762c5c60-352e-471f-8dbe-bbf10e24ebd6">
This sets the sprite colour as being unique per instance. This can still
all be drawn using one batch. There should be no difference but the PR
produces median frame times that are 4% higher. Investigation showed no
clear sources of cost, rather a mix of give and take that should not
happen. It seems like noise in the results.
### Summary
| Benchmark | % change in median frame time |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| many_cubes | 🟩 -30% |
| many_cubes 10 materials | 🟩 -5% |
| many_cubes unique materials | 🟩 ~0% |
| bevymark mesh2d | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d 10 materials | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d unique materials | 🟩 -7% |
| bevymark sprite | 🟥 2% |
| bevymark sprite 10 materials | 🟥 0.6% |
| bevymark sprite unique materials | 🟥 4.1% |
---
## Changelog
- Added: 2D and 3D mesh entities that share the same mesh and material
(same textures, same data) are now batched into the same draw command
for better performance.
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nico@nicopap.ch>
# Objective
Improve code-gen for `QueryState::validate_world` and
`SystemState::validate_world`.
## Solution
* Move panics into separate, non-inlined functions, to reduce the code
size of the outer methods.
* Mark the panicking functions with `#[cold]` to help the compiler
optimize for the happy path.
* Mark the functions with `#[track_caller]` to make debugging easier.
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Fix a performance regression in the "[bevy vs
pixi](https://github.com/SUPERCILEX/bevy-vs-pixi)" benchmark.
This benchmark seems to have a slightly pathological distribution of `z`
values -- Sprites are spawned with a random `z` value with a child
sprite at `f32::EPSILON` relative to the parent.
See discussion here:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8100#issuecomment-1726978633
## Solution
Use `radsort` for sorting `Transparent2d` `PhaseItem`s.
Use random `z` values in bevymark to stress the phase sort. Add an
`--ordered-z` option to `bevymark` that uses the old behavior.
## Benchmarks
mac m1 max
| benchmark | fps before | fps after | diff |
| - | - | - | - |
| bevymark --waves 120 --per-wave 1000 --random-z | 42.16 | 47.06 | 🟩
+11.6% |
| bevymark --waves 120 --per-wave 1000 | 52.50 | 52.29 | 🟥 -0.4% |
| bevymark --waves 120 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d --random-z | 9.64 |
10.24 | 🟩 +6.2% |
| bevymark --waves 120 --per-wave 1000 --mode mesh2d | 15.83 | 15.59 | 🟥
-1.5% |
| bevy-vs-pixi | 39.71 | 59.88 | 🟩 +50.1% |
## Discussion
It's possible that `TransparentUi` should also change. We could probably
use `slice::sort_unstable_by_key` with the current sort key though, as
its items are always sorted and unique. I'd prefer to follow up later to
look into that.
Here's a survey of sorts used by other `PhaseItem`s
#### slice::sort_by_key
`Transparent2d`, `TransparentUi`
#### radsort
`Opaque3d`, `AlphaMask3d`, `Transparent3d`, `Opaque3dPrepass`,
`AlphaMask3dPrepass`, `Shadow`
I also tried `slice::sort_unstable_by_key` with a compound sort key
including `Entity`, but it didn't seem as promising and I didn't test it
as thoroughly.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Some rendering system did heavy use of `if let`, and could be improved
by using `let else`.
## Solution
- Reduce rightward drift by using let-else over if-let
- Extract value-to-key mappings to their own functions so that the
system is less bloated, easier to understand
- Use a `let` binding instead of untupling in closure argument to reduce
indentation
## Note to reviewers
Enable the "no white space diff" for easier viewing.
In the "Files changed" view, click on the little cog right of the "Jump
to" text, on the row where the "Review changes" button is. then enable
the "Hide whitespace" checkbox and click reload.
# Objective
Rename the `num_font_atlases` method of `FontAtlasSet` to `len`.
All the function does is return the number of entries in its hashmap and
the unnatural naming only makes it harder to discover.
---
## Changelog
* Renamed the `num_font_atlases` method of `FontAtlasSet` to `len`.
## Migration Guide
The `num_font_atlases` method of `FontAtlasSet` has been renamed to
`len`.
# Objective
Occasionally, it is useful to pull `ComponentInfo` or
`ComponentDescriptor` out of the `Components` collection so that they
can be inspected without borrowing the whole `World`.
## Solution
Make `ComponentInfo` and `ComponentDescriptor` `Clone`, so that
reflection-heavy code can store them in a side table.
---
## Changelog
- Implement `Clone` for `ComponentInfo` and `ComponentDescriptor`
# Objective
- I spoke with some users in the ECS channel of bevy discord today and
they suggested that I implement a fallible form of .insert for
components.
- In my opinion, it would be nice to have a fallible .insert like
.try_insert (or to just make insert be fallible!) because it was causing
a lot of panics in my game. In my game, I am spawning terrain chunks and
despawning them in the Update loop. However, this was causing bevy_xpbd
to panic because it was trying to .insert some physics components on my
chunks and a race condition meant that its check to see if the entity
exists would pass but then the next execution step it would not exist
and would do an .insert and then panic. This means that there is no way
to avoid a panic with conditionals.
Luckily, bevy_xpbd does not care about inserting these components if the
entity is being deleted and so if there were a .try_insert, like this PR
provides it could use that instead in order to NOT panic.
( My interim solution for my own game has been to run the entity despawn
events in the Last schedule but really this is just a hack and I should
not be expected to manage the scheduling of despawns like this - it
should just be easy and simple. IF it just so happened that bevy_xpbd
ran .inserts in the Last schedule also, this would be an untenable soln
overall )
## Solution
- Describe the solution used to achieve the objective above.
Add a new command named TryInsert (entitycommands.try_insert) which
functions exactly like .insert except if the entity does not exist it
will not panic. Instead, it will log to info. This way, crates that are
attaching components in ways which they do not mind that the entity no
longer exists can just use try_insert instead of insert.
---
## Changelog
## Additional Thoughts
In my opinion, NOT panicing should really be the default and having an
.insert that does panic should be the odd edgecase but removing the
panic! from .insert seems a bit above my paygrade -- although i would
love to see it. My other thought is it would be good for .insert to
return an Option AND not panic but it seems it uses an event bus right
now so that seems to be impossible w the current architecture.
# Objective
- Fixes#9876
## Solution
- Reverted commit `5012a0fd57748ab6f146776368b4cf988bba1eaa` to restore
the previous default values for `OrthographicProjection`.
---
## Migration Guide
- Migration guide steps from #9537 should be removed for next release.
# Objective
Fix a typo introduced by #9497. While drafting the PR, the type was
originally called `VisibleInHierarchy` before I renamed it to
`InheritedVisibility`, but this field got left behind due to a typo.
# Objective
- When adding/removing bindings in large binding lists, git would
generate very difficult-to-read diffs
## Solution
- Move the `@group(X) @binding(Y)` into the same line as the binding
type declaration
# Objective
- `check_visibility` system in `bevy_render` had an
`Option<&NoFrustumCulling>` that could be replaced by `Has`, which is
theoretically faster and semantically more correct.
- It also had some awkward indenting due to very large closure argument
lists.
- Some of the tests could be written more concisely
## Solution
Use `Has`, move the tuple destructuring in a `let` binding, create a
function for the tests.
## Note to reviewers
Enable the "no white space diff" in the diff viewer to have a more
meaningful diff in the `check_visibility` system.
In the "Files changed" view, click on the little cog right of the "Jump
to" text, on the row where the "Review changes" button is. then enable
the "Hide whitespace" checkbox and click reload.
---
## Migration Guide
- The `check_visibility` system's `Option<&NoFrustumCulling>` parameter
has been replaced by `Has<NoFrustumCulling>`, if you were calling it
manually, you should change the type to match it
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
Currently, in bevy, it's valid to do `Query<&mut Foo, Changed<Foo>>`.
This assumes that `filter_fetch` and `fetch` are mutually exclusive,
because of the mutable reference to the tick that `Mut<Foo>` implies and
the reference that `Changed<Foo>` implies. However nothing guarantees
that.
## Solution
Documenting this assumption as a safety invariant is the least thing.
# Objective
`single_threaded_task_pool` emitted a warning:
```
warning: use of `default` to create a unit struct
--> crates/bevy_tasks/src/single_threaded_task_pool.rs:22:25
|
22 | Self(PhantomData::default())
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ help: remove this call to `default`
|
= help: for further information visit https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#default_constructed_unit_structs
= note: `#[warn(clippy::default_constructed_unit_structs)]` on by default
```
## Solution
fix the lint
I'm adopting this ~~child~~ PR.
# Objective
- Working with exclusive world access is not always easy: in many cases,
a standard system or three is more ergonomic to write, and more
modularly maintainable.
- For small, one-off tasks (commonly handled with scripting), running an
event-reader system incurs a small but flat overhead cost and muddies
the schedule.
- Certain forms of logic (e.g. turn-based games) want very fine-grained
linear and/or branching control over logic.
- SystemState is not automatically cached, and so performance can suffer
and change detection breaks.
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2192.
- Partial workaround for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/279.
## Solution
- Adds a SystemRegistry resource to the World, which stores initialized
systems keyed by their SystemSet.
- Allows users to call world.run_system(my_system) and
commands.run_system(my_system), without re-initializing or losing state
(essential for change detection).
- Add a Callback type to enable convenient use of dynamic one shot
systems and reduce the mental overhead of working with Box<dyn
SystemSet>.
- Allow users to run systems based on their SystemSet, enabling more
complex user-made abstractions.
## Future work
- Parameterized one-shot systems would improve reusability and bring
them closer to events and commands. The API could be something like
run_system_with_input(my_system, my_input) and use the In SystemParam.
- We should evaluate the unification of commands and one-shot systems
since they are two different ways to run logic on demand over a World.
### Prior attempts
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2234
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2417
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4090
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7999
This PR continues the work done in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7999.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Federico Rinaldi <gisquerin@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alejandro Pascual Pozo <alejandro.pascual.pozo@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Dmytro Banin <banind@cs.washington.edu>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Make `bevy_ui` "root" nodes more intuitive to use/style by:
- Removing the implicit flexbox styling (such as stretch alignment) that
is applied to them, and replacing it with more intuitive CSS Grid
styling (notably with stretch alignment disabled in both axes).
- Making root nodes layout independently of each other. Instead of there
being a single implicit "viewport" node that all root nodes are children
of, there is now an implicit "viewport" node *per root node*. And layout
of each tree is computed separately.
## Solution
- Remove the global implicit viewport node, and instead create an
implicit viewport node for each user-specified root node.
- Keep track of both the user-specified root nodes and the implicit
viewport nodes in a separate `Vec`.
- Use the window's size as the `available_space` parameter to
`Taffy.compute_layout` rather than setting it on the implicit viewport
node (and set the viewport to `height: 100%; width: 100%` to make this
"just work").
---
## Changelog
- Bevy UI now lays out root nodes independently of each other in
separate layout contexts.
- The implicit viewport node (which contains each user-specified root
node) is now `Display::Grid` with `align_items` and `justify_items` both
set to `Start`.
## Migration Guide
- Bevy UI now lays out root nodes independently of each other in
separate layout contexts. If you were relying on your root nodes being
able to affect each other's layouts, then you may need to wrap them in a
single root node.
- The implicit viewport node (which contains each user-specified root
node) is now `Display::Grid` with `align_items` and `justify_items` both
set to `Start`. You may need to add `height: Val::Percent(100.)` to your
root nodes if you were previously relying on being implicitly set.
# Objective
- When initializing the renderer, Bevy currently create a detached task
- This is needed on wasm but not on native
## Solution
- Don't create a detached task on native but block on the future
# Objective
Replace instances of
```rust
for x in collection.iter{_mut}() {
```
with
```rust
for x in &{mut} collection {
```
This also changes CI to no longer suppress this lint. Note that since
this lint only shows up when using clippy in pedantic mode, it was
probably unnecessary to suppress this lint in the first place.
# Objective
- When reading API docs and seeing a reference to `ComponentId`, it
isn't immediately clear how to get one from your `Component`. It could
be made to be more clear.
## Solution
- Improve cross-linking of docs about `ComponentId`
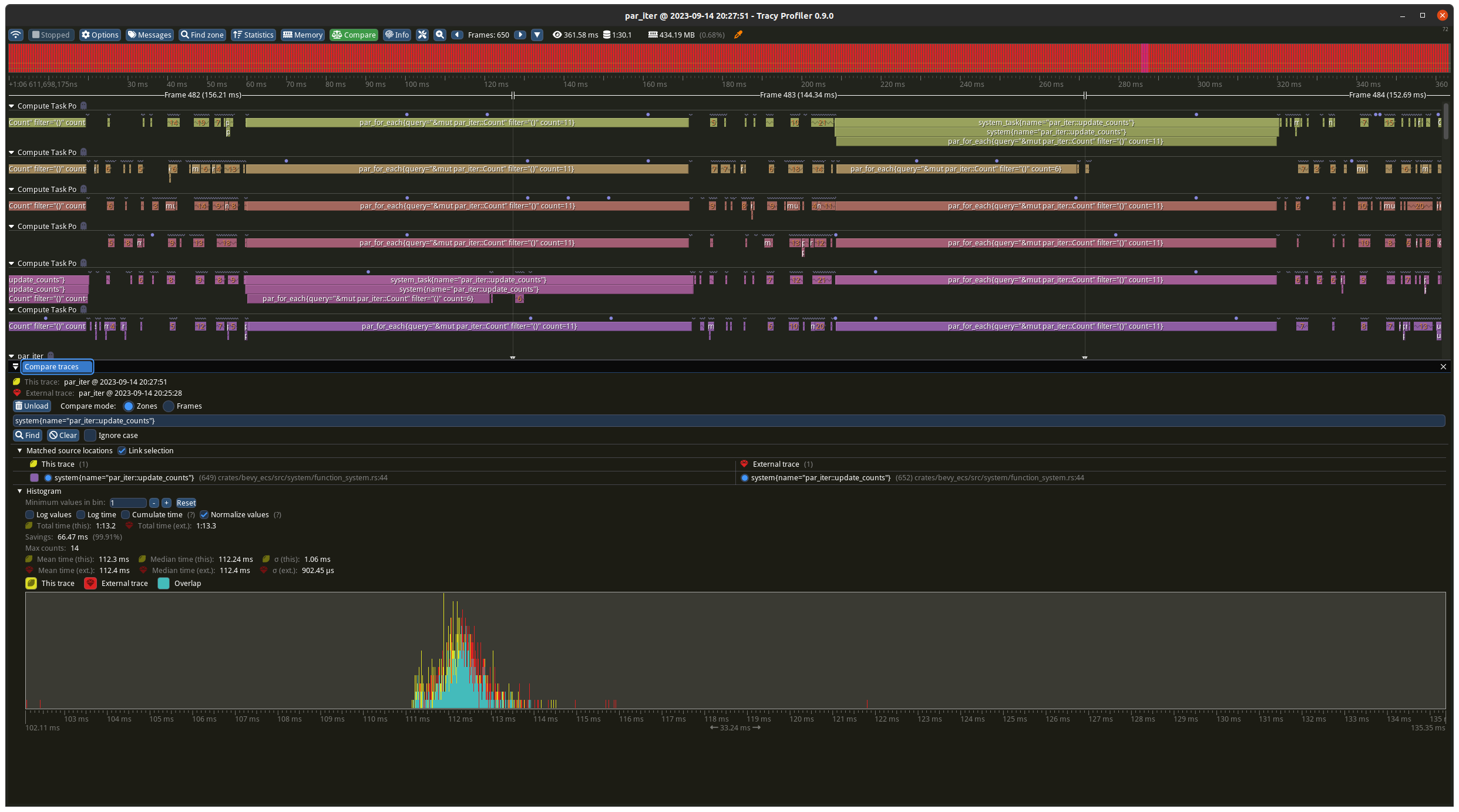
# Objective
The default division for a `usize` rounds down which means the batch
sizes were too small when the `max_size` isn't exactly divisible by the
batch count.
## Solution
Changing the division to round up fixes this which can dramatically
improve performance when using `par_iter`.
I created a small example to proof this out and measured some results. I
don't know if it's worth committing this permanently so I left it out of
the PR for now.
```rust
use std::{thread, time::Duration};
use bevy::{
prelude::*,
window::{PresentMode, WindowPlugin},
};
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins((DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin {
primary_window: Some(Window {
present_mode: PresentMode::AutoNoVsync,
..default()
}),
..default()
}),))
.add_systems(Startup, spawn)
.add_systems(Update, update_counts)
.run();
}
#[derive(Component, Default, Debug, Clone, Reflect)]
pub struct Count(u32);
fn spawn(mut commands: Commands) {
// Worst case
let tasks = bevy::tasks::available_parallelism() * 5 - 1;
// Best case
// let tasks = bevy::tasks::available_parallelism() * 5 + 1;
for _ in 0..tasks {
commands.spawn(Count(0));
}
}
// changing the bounds of the text will cause a recomputation
fn update_counts(mut count_query: Query<&mut Count>) {
count_query.par_iter_mut().for_each(|mut count| {
count.0 += 1;
thread::sleep(Duration::from_millis(10))
});
}
```
## Results
I ran this four times, with and without the change, with best case
(should favour the old maths) and worst case (should favour the new
maths) task numbers.
### Worst case
Before the change the batches were 9 on each thread, plus the 5
remainder ran on one of the threads in addition. With the change its 10
on each thread apart from one which has 9. The results show a decrease
from ~140ms to ~100ms which matches what you would expect from the maths
(`10 * 10ms` vs `(9 + 4) * 10ms`).

### Best case
Before the change the batches were 10 on each thread, plus the 1
remainder ran on one of the threads in addition. With the change its 11
on each thread apart from one which has 5. The results slightly favour
the new change but are basically identical as the total time is
determined by the worse case which is `11 * 10ms` for both tests.
# Objective
according to
[khronos](https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF/issues/1697), gltf nodes
with inverted scales should invert the winding order of the mesh data.
this is to allow negative scale to be used for mirrored geometry.
## Solution
in the gltf loader, create a separate material with `cull_mode` set to
`Face::Front` when the node scale is negative.
note/alternatives:
this applies for nodes where the scale is negative at gltf import time.
that seems like enough for the mentioned use case of mirrored geometry.
it doesn't help when scales dynamically go negative at runtime, but you
can always set double sided in that case.
i don't think there's any practical difference between using front-face
culling and setting a clockwise winding order explicitly, but winding
order is supported by wgpu so we could add the field to
StandardMaterial/StandardMaterialKey and set it directly on the pipeline
descriptor if there's a reason to. it wouldn't help with dynamic scale
adjustments anyway, and would still require a separate material.
fixes#4738, probably fixes#7901.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
The reasoning is similar to #8687.
I'm building a dynamic query. Currently, I store the ReflectFromPtr in
my dynamic `Fetch` type.
[See relevant
code](97ba68ae1e/src/fetches.rs (L14-L17))
However, `ReflectFromPtr` is:
- 16 bytes for TypeId
- 8 bytes for the non-mutable function pointer
- 8 bytes for the mutable function pointer
It's a lot, it adds 32 bytes to my base `Fetch` which is only
`ComponendId` (8 bytes) for a total of 40 bytes.
I only need one function per fetch, reducing the total dynamic fetch
size to 16 bytes.
Since I'm querying the components by the ComponendId associated with the
function pointer I'm using, I don't need the TypeId, it's a redundant
check.
In fact, I've difficulties coming up with situations where checking the
TypeId beforehand is relevant. So to me, if ReflectFromPtr makes sense
as a public API, exposing the function pointers also makes sense.
## Solution
- Make the fields public through methods.
---
## Changelog
- Add `from_ptr` and `from_ptr_mut` methods to `ReflectFromPtr` to
access the underlying function pointers
- `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_ptr` is now `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect`
- `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_ptr_mut` is now
`ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_mut`
## Migration guide
- `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_ptr` is now `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect`
- `ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_ptr_mut` is now
`ReflectFromPtr::as_reflect_mut`