mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2025-02-19 15:38:36 +00:00
13 commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
3dd8b42f72 |
Fix various typos (#7096)
I stumbled across a typo in some docs. Fixed some more while I was in there. |
||
|
|
01aedc8431 |
Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands). ## Solution All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input: ```rust // before: commands .spawn() .insert((A, B, C)); world .spawn() .insert((A, B, C); // after commands.spawn((A, B, C)); world.spawn((A, B, C)); ``` All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api. By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`). This improves spawn performance by over 10%:  To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark. Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main. **Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).** --- ## Changelog - All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input - All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api - World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior. ## Migration Guide ```rust // Old (0.8): commands .spawn() .insert_bundle((A, B, C)); // New (0.9) commands.spawn((A, B, C)); // Old (0.8): commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C)); // New (0.9) commands.spawn((A, B, C)); // Old (0.8): let entity = commands.spawn().id(); // New (0.9) let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id(); // Old (0.8) let entity = world.spawn().id(); // New (0.9) let entity = world.spawn_empty(); ``` |
||
|
|
cd15f0f5be |
Accept Bundles for insert and remove. Deprecate insert/remove_bundle (#6039)
# Objective Take advantage of the "impl Bundle for Component" changes in #2975 / add the follow up changes discussed there. ## Solution - Change `insert` and `remove` to accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World) - Deprecate `insert_bundle`, `remove_bundle`, and `remove_bundle_intersection` - Add `remove_intersection` --- ## Changelog - Change `insert` and `remove` now accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World) - `insert_bundle` and `remove_bundle` are deprecated ## Migration Guide Replace `insert_bundle` with `insert`: ```rust // Old (0.8) commands.spawn().insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default()); // New (0.9) commands.spawn().insert(SomeBundle::default()); ``` Replace `remove_bundle` with `remove`: ```rust // Old (0.8) commands.entity(some_entity).remove_bundle::<SomeBundle>(); // New (0.9) commands.entity(some_entity).remove::<SomeBundle>(); ``` Replace `remove_bundle_intersection` with `remove_intersection`: ```rust // Old (0.8) world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_bundle_intersection::<SomeBundle>(); // New (0.9) world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_intersection::<SomeBundle>(); ``` Consider consolidating as many operations as possible to improve ergonomics and cut down on archetype moves: ```rust // Old (0.8) commands.spawn() .insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default()) .insert(SomeComponent); // New (0.9) - Option 1 commands.spawn().insert(( SomeBundle::default(), SomeComponent, )) // New (0.9) - Option 2 commands.spawn_bundle(( SomeBundle::default(), SomeComponent, )) ``` ## Next Steps Consider changing `spawn` to accept a bundle and deprecate `spawn_bundle`. |
||
|
|
6b073ee412 |
Update shader_material_glsl example to include texture sampling (#5215)
# Objective Add texture sampling to the GLSL shader example, as naga does not support the commonly used sampler2d type. Fixes #5059 ## Solution - Align the shader_material_glsl example behaviour with the shader_material example, as the later includes texture sampling. - Update the GLSL shader to do texture sampling the way naga supports it, and document the way naga does not support it. ## Changelog - The shader_material_glsl example has been updated to demonstrate texture sampling using the GLSL shading language. Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
747b0c69b0 |
Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
|
||
|
|
f487407e07 |
Camera Driven Rendering (#4745)
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier. Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):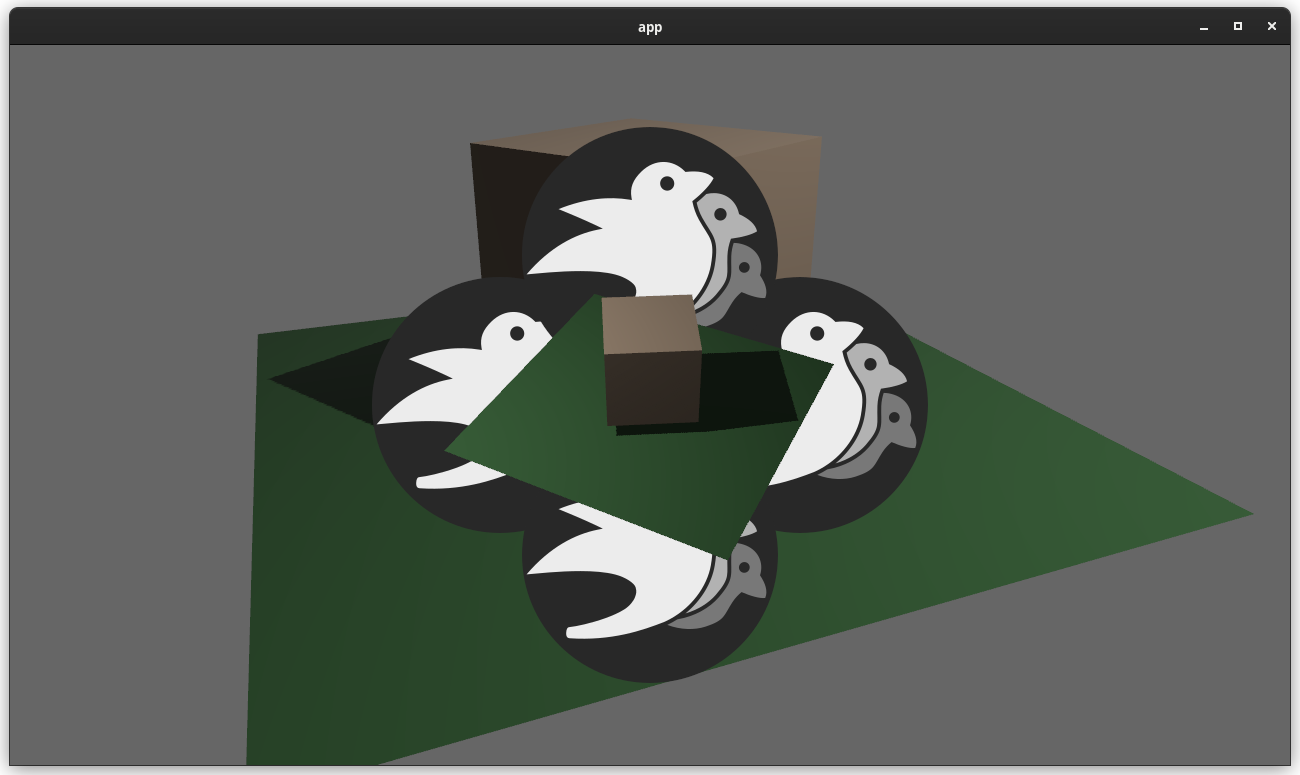  Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work". Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id: ```rust // main camera (main window) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()); // second camera (other window) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id), ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle), ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`). ```rust // main pass camera with a default priority of 0 commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()); commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()), priority: -1, ..default() }, ..default() }); commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle { texture: image_handle, ..default() }) ``` Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()); commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle { camera: Camera { // this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render priority: 1, ..default() }, ..default() }); ``` There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active. Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections. ```rust // old 3d perspective camera commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default()) // new 3d perspective camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()) ``` ```rust // old 2d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d()) // new 2d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default()) ``` ```rust // old 3d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d()) // new 3d orthographic camera commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { projection: OrthographicProjection { scale: 3.0, scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical, ..default() }.into(), ..default() }) ``` Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors. If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name), ..default() }) ``` Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added. Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options: ```rust commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_3d: Camera3d { // overrides the default global clear color clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED), ..default() }, ..default() }) commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle { camera_3d: Camera3d { // disables clearing clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None, ..default() }, ..default() }) ``` Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future. By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component: ```rust commands .spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default()) .insert(CameraUi { is_enabled: false, ..default() }) ``` ## Other Changes * The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr. * I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization. * I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler. * All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr. * Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic. * Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals: 1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs. 2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense. ## Follow Up Work * Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen) * Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor) * Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system). * Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable. * Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home. |
||
|
|
deeaf64897 |
shader examples wording coherence (#4810)
# Objective I noticed different examples descriptions were not using the same structure:  This results in sentences that a reader has to read differently each time, which might result in information being hard to find, especially foreign language users. Original discord discussion: https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/976846499889705020 ## Solution - Use less different words, similar structure and being straight to the point. --- ## Changelog - Examples descriptions more accessible. |
||
|
|
7cb4d3cb43 |
Migrate to encase from crevice (#4339)
# Objective - Unify buffer APIs - Also see #4272 ## Solution - Replace vendored `crevice` with `encase` --- ## Changelog Changed `StorageBuffer` Added `DynamicStorageBuffer` Replaced `UniformVec` with `UniformBuffer` Replaced `DynamicUniformVec` with `DynamicUniformBuffer` ## Migration Guide ### `StorageBuffer` removed `set_body()`, `values()`, `values_mut()`, `clear()`, `push()`, `append()` added `set()`, `get()`, `get_mut()` ### `UniformVec` -> `UniformBuffer` renamed `uniform_buffer()` to `buffer()` removed `len()`, `is_empty()`, `capacity()`, `push()`, `reserve()`, `clear()`, `values()` added `set()`, `get()` ### `DynamicUniformVec` -> `DynamicUniformBuffer` renamed `uniform_buffer()` to `buffer()` removed `capacity()`, `reserve()` Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
1ba7429371 |
Doc/module style doc blocks for examples (#4438)
# Objective Provide a starting point for #3951, or a partial solution. Providing a few comment blocks to discuss, and hopefully find better one in the process. ## Solution Since I am pretty new to pretty much anything in this context, I figured I'd just start with a draft for some file level doc blocks. For some of them I found more relevant details (or at least things I considered interessting), for some others there is less. ## Changelog - Moved some existing comments from main() functions in the 2d examples to the file header level - Wrote some more comment blocks for most other 2d examples TODO: - [x] 2d/sprite_sheet, wasnt able to come up with something good yet - [x] all other example groups... Also: Please let me know if the commit style is okay, or to verbose. I could certainly squash these things, or add more details if needed. I also hope its okay to raise this PR this early, with just a few files changed. Took me long enough and I dont wanted to let it go to waste because I lost motivation to do the whole thing. Additionally I am somewhat uncertain over the style and contents of the commets. So let me know what you thing please. |
||
|
|
c5963b4fd5 |
Use storage buffers for clustered forward point lights (#3989)
# Objective - Make use of storage buffers, where they are available, for clustered forward bindings to support far more point lights in a scene - Fixes #3605 - Based on top of #4079 This branch on an M1 Max can keep 60fps with about 2150 point lights of radius 1m in the Sponza scene where I've been testing. The bottleneck is mostly assigning lights to clusters which grows faster than linearly (I think 1000 lights was about 1.5ms and 5000 was 7.5ms). I have seen papers and presentations leveraging compute shaders that can get this up to over 1 million. That said, I think any further optimisations should probably be done in a separate PR. ## Solution - Add `RenderDevice` to the `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` trait `::key()` functions to allow setting flags on the keys depending on feature/limit availability - Make `GpuPointLights` and `ViewClusterBuffers` into enums containing `UniformVec` and `StorageBuffer` variants. Implement the necessary API on them to make usage the same for both cases, and the only difference is at initialisation time. - Appropriate shader defs in the shader code to handle the two cases ## Context on some decisions / open questions - I'm using `max_storage_buffers_per_shader_stage >= 3` as a check to see if storage buffers are supported. I was thinking about diving into 'binding resource management' but it feels like we don't have enough use cases to understand the problem yet, and it is mostly a separate concern to this PR, so I think it should be handled separately. - Should `ViewClusterBuffers` and `ViewClusterBindings` be merged, duplicating the count variables into the enum variants? Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
b6a647cc01 |
default() shorthand (#4071)
Adds a `default()` shorthand for `Default::default()` ... because life is too short to constantly type `Default::default()`.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
#[derive(Default)]
struct Foo {
bar: usize,
baz: usize,
}
// Normally you would do this:
let foo = Foo {
bar: 10,
..Default::default()
};
// But now you can do this:
let foo = Foo {
bar: 10,
..default()
};
```
The examples have been adapted to use `..default()`. I've left internal crates as-is for now because they don't pull in the bevy prelude, and the ergonomics of each case should be considered individually.
|
||
|
|
e369a8ad51 |
Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
|
||
|
|
b1476015d9 |
add some more pipelined-rendering shader examples (#3041)
based on #3031 Adds some examples showing of how to use the new pipelined rendering for custom shaders. - a minimal shader example which doesn't use render assets - the same but using glsl - an example showing how to render instanced data - a shader which uses the seconds since startup to animate some textures Instancing shader: 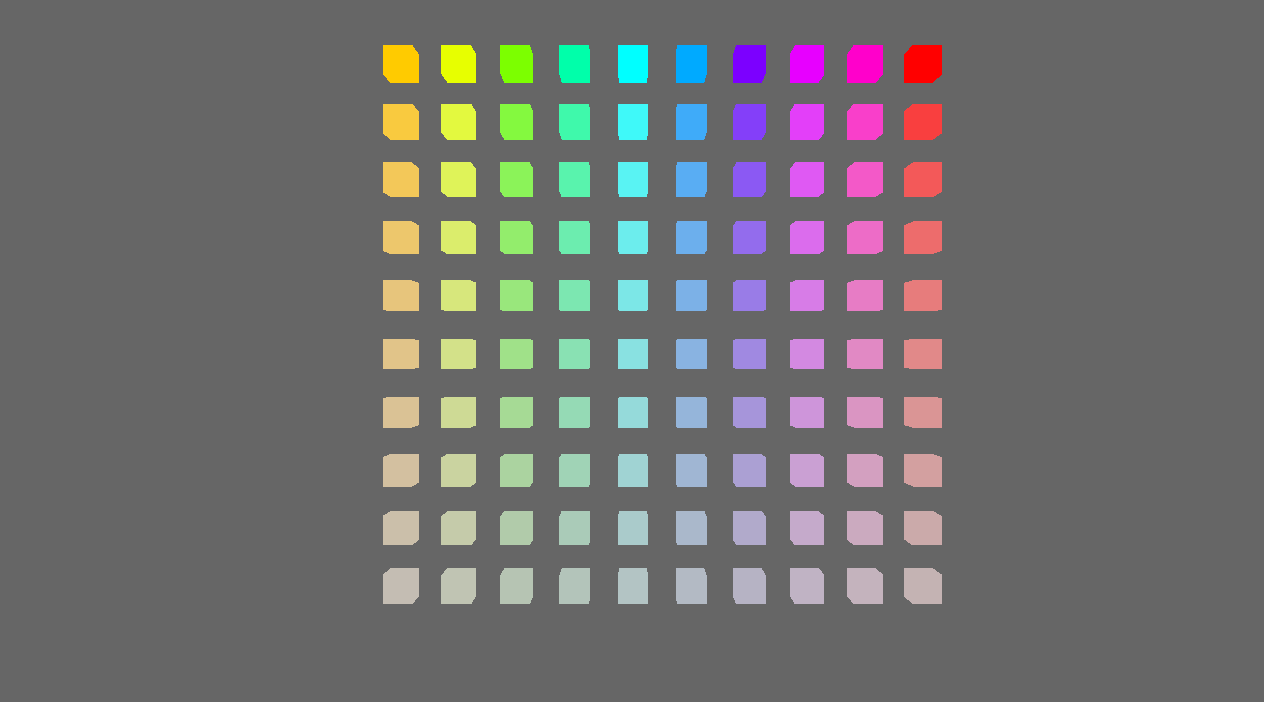 Animated shader: 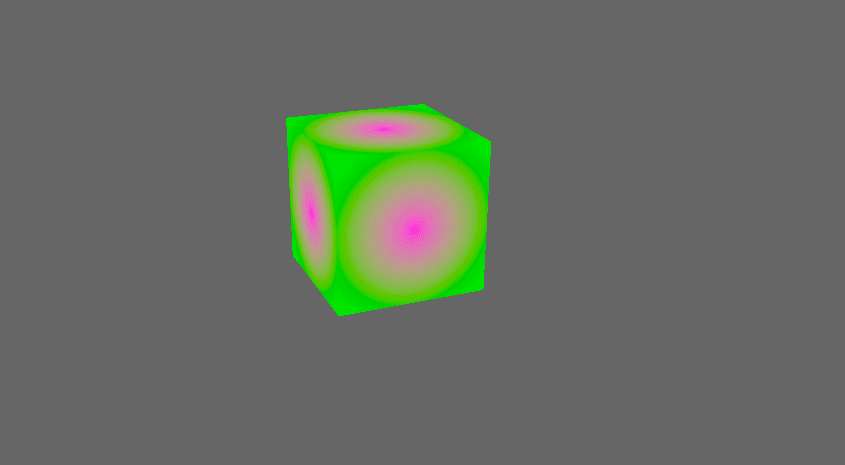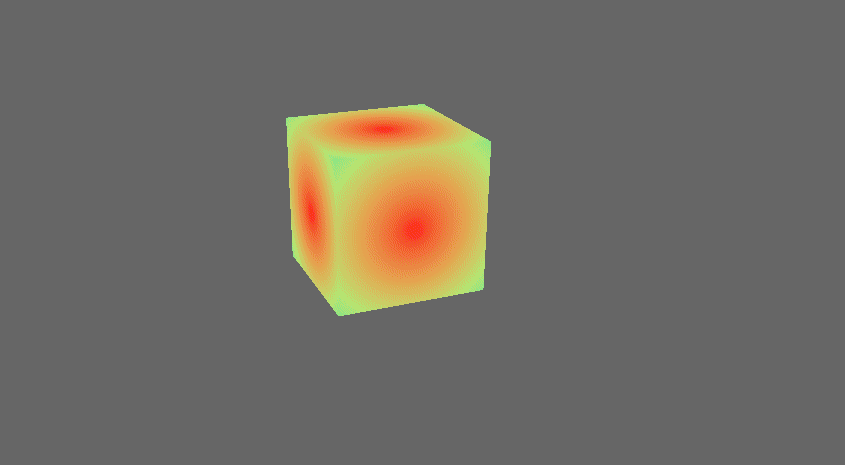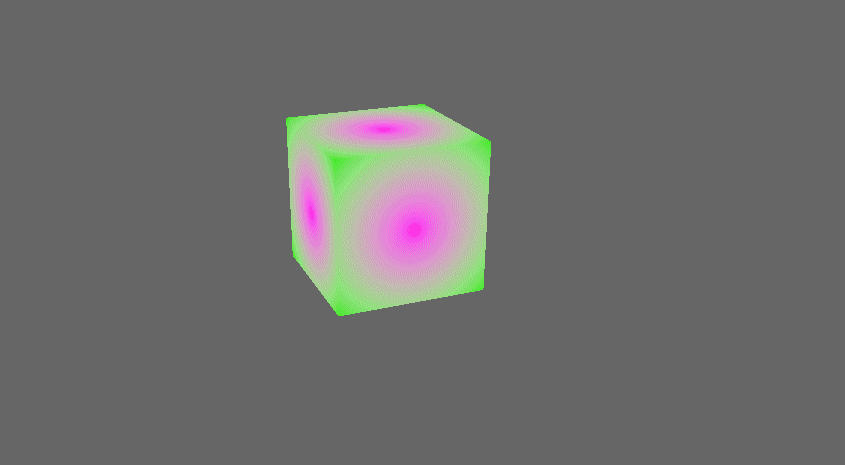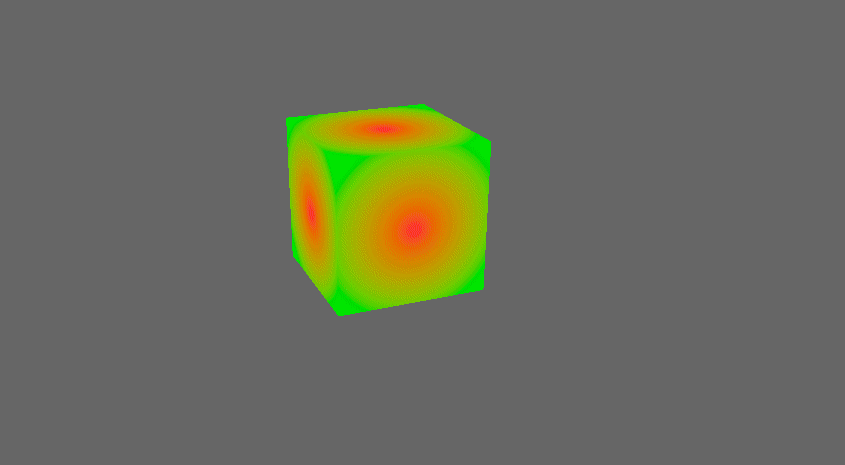 (the gif makes it look a bit ugly) Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |