# Objective
I was about to submit a PR to add these two examples to `bevy-website` and re-discovered the inconsistency.
Although it's not a major issue on the website where only the filenames are shown, this would help to visually distinguish the two examples in the list because the names are very prominent.
This also helps out when fuzzy-searching the codebase for these files.
## Solution
Rename `shapes` to `2d_shapes`. Now the filename matches the example name, and the naming structure matches the 3d example.
## Notes
@Nilirad proposed this in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4613#discussion_r862455631 but it had slipped away from my brain at that time.
# Objective
- Adopted from #3836
- Example showcases how to request a new resolution
- Example showcases how to react to resolution changes
Co-authored-by: Andreas Weibye <13300393+Weibye@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Allow users to change the scaling of the UI
- Adopted from #2808
## Solution
- This is an accessibility feature for fixed-size UI elements, allowing the developer to expose a range of UI scales for the player to set a scale that works for their needs.
> - The user can modify the UiScale struct to change the scaling at runtime. This multiplies the Px values by the scale given, while not touching any others.
> - The example showcases how this even allows for fluid transitions
> Here's how the example looks like:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1631166/132979069-044161a9-8e85-45ab-9e93-fcf8e3852c2b.mp4
---
## Changelog
- Added a `UiScale` which can be used to scale all of UI
Co-authored-by: Andreas Weibye <13300393+Weibye@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix / support KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes#4495 . Supersedes #4514 .
## Solution
- Add `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` to `Image` to enable configuration of the `TextureViewDimension` of a texture.
- This allows users to set `D2Array`, `D3`, `Cube`, `CubeArray` or whatever they need
- Automatically configure this when loading KTX2
- Transcode all layers and faces instead of just one
- Use the UASTC block size of 128 bits, and the number of blocks in x/y for a given mip level in order to determine the offset of the layer and face within the KTX2 mip level data
- `wgpu` wants data ordered as layer 0 mip 0..n, layer 1 mip 0..n, etc. See https://docs.rs/wgpu/latest/wgpu/util/trait.DeviceExt.html#tymethod.create_texture_with_data
- Reorder the data KTX2 mip X layer Y face Z to `wgpu` layer Y face Z mip X order
- Add a `skybox` example to demonstrate / test loading cubemaps from PNG and KTX2, including ASTC 4x4, BC7, and ETC2 compression for support everywhere. Note that you need to enable the `ktx2,zstd` features to be able to load the compressed textures.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes: Validation failure for compressed textures stored in KTX2 where the width/height are not a multiple of the block dimensions.
- Added: `Image` now has an `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` field to enable configuration of the texture view. This is useful for configuring the `TextureViewDimension` when it is not just a plain 2D texture and the loader could/did not identify what it should be.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Add a section to the example's README on how
to reduce generated wasm executable size.
Add a `wasm-release` profile to bevy's `Cargo.toml`
in order to use it when building bevy-website.
Notes:
- We do not recommend `strip = "symbols"` since it breaks bindgen
- see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website/pull/402
# Objective
Bevy need a way to benchmark UI rendering code,
this PR adds a stress test that spawns a lot of buttons.
## Solution
- Add the `many_buttons` stress test.
---
## Changelog
- Add the `many_buttons` stress test.
# Objective
- Showcase how to use a `Material` and `Mesh` to spawn 3d lines
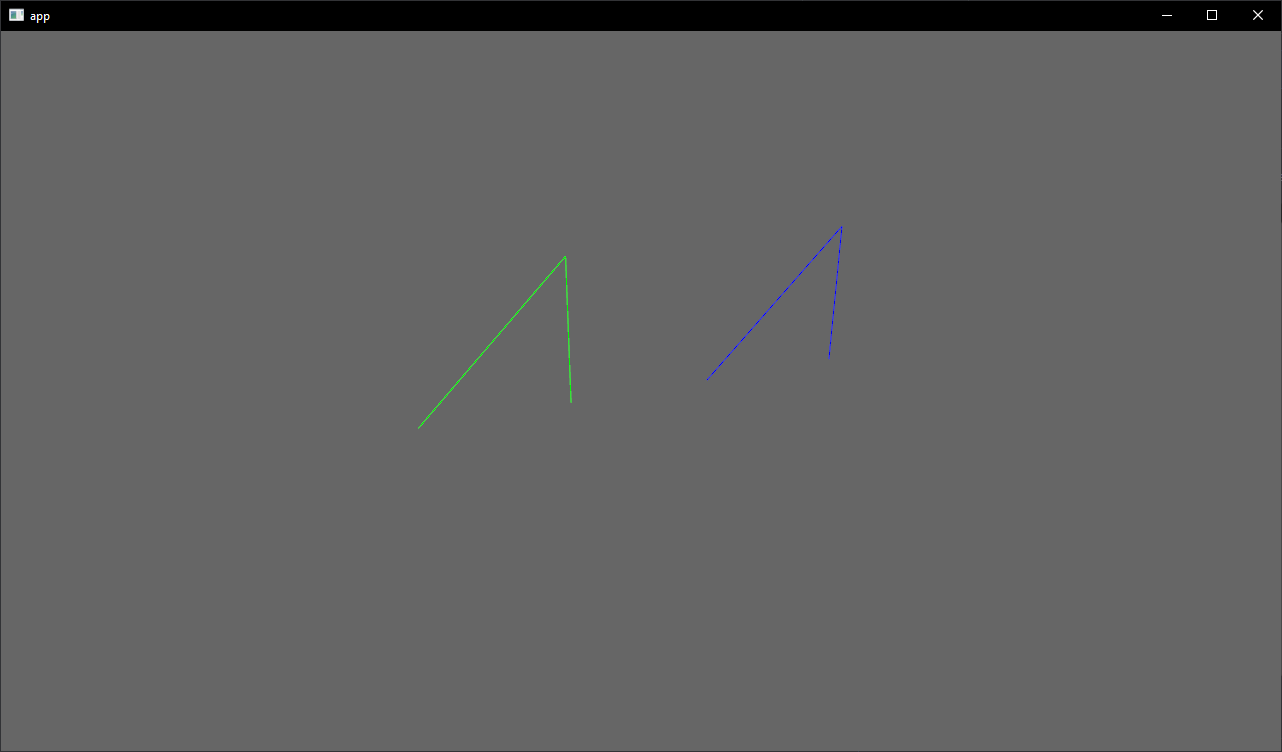
## Solution
- Add an example using a simple `Material` and `Mesh` definition to draw a 3d line
- Shows how to use `LineList` and `LineStrip` in combination with a specialized `Material`
## Notes
This isn't just a primitive shape because it needs a special Material, but I think it's a good showcase of the power of the `Material` and `AsBindGroup` abstractions. All of this is easy to figure out when you know these options are a thing, but I think they are hard to discover which is why I think this should be an example and not shipped with bevy.
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Reduce confusion as the example opens a window and isn't truly "headless"
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5260.
## Solution
- Rename the example and add to the docs that the window is expected.
# Objective
add spotlight support
## Solution / Changelog
- add spotlight angles (inner, outer) to ``PointLight`` struct. emitted light is linearly attenuated from 100% to 0% as angle tends from inner to outer. Direction is taken from the existing transform rotation.
- add spotlight direction (vec3) and angles (f32,f32) to ``GpuPointLight`` struct (60 bytes -> 80 bytes) in ``pbr/render/lights.rs`` and ``mesh_view_bind_group.wgsl``
- reduce no-buffer-support max point light count to 204 due to above
- use spotlight data to attenuate light in ``pbr.wgsl``
- do additional cluster culling on spotlights to minimise cost in ``assign_lights_to_clusters``
- changed one of the lights in the lighting demo to a spotlight
- also added a ``spotlight`` demo - probably not justified but so reviewers can see it more easily
## notes
increasing the size of the GpuPointLight struct on my machine reduces the FPS of ``many_lights -- sphere`` from ~150fps to 140fps.
i thought this was a reasonable tradeoff, and felt better than handling spotlights separately which is possible but would mean introducing a new bind group, refactoring light-assignment code and adding new spotlight-specific code in pbr.wgsl. the FPS impact for smaller numbers of lights should be very small.
the cluster culling strategy reintroduces the cluster aabb code which was recently removed... sorry. the aabb is used to get a cluster bounding sphere, which can then be tested fairly efficiently using the strategy described at the end of https://bartwronski.com/2017/04/13/cull-that-cone/. this works well with roughly cubic clusters (where the cluster z size is close to the same as x/y size), less well for other cases like single Z slice / tiled forward rendering. In the worst case we will end up just keeping the culling of the equivalent point light.
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Intended to close#5073
## Solution
Adds a stress test that use TextureAtlas based on the existing many_sprites test using the animated sprite implementation from the sprite_sheet example.
In order to satisfy the goals described in #5073 the animations are all slightly offset.
Of note is that the original stress test was designed to test fullstrum culling. I kept this test similar as to facilitate easy comparisons between the use of TextureAtlas and without.
# Objective
- Make Bevy work on android
## Solution
- Update android metadata and add a few more
- Set the target sdk to 31 as it will soon (in august) be the minimum sdk level for play store
- Remove the custom code to create an activity and use ndk-glue macro instead
- Delay window creation event on android
- Set the example with compatibility settings for wgpu. Those are needed for Bevy to work on my 2019 android tablet
- Add a few details on how to debug in case of failures
- Fix running the example on emulator. This was failing because of the name of the example
Bevy still doesn't work on android with this, audio features need to be disabled because of an ndk-glue version mismatch: rodio depends on 0.6.2, winit on 0.5.2. You can test with:
```
cargo apk run --release --example android_example --no-default-features --features "bevy_winit,render"
```
# Objective
- Make the reusable PBR shading functionality a little more reusable
- Add constructor functions for `StandardMaterial` and `PbrInput` structs to populate them with default values
- Document unclear `PbrInput` members
- Demonstrate how to reuse the bevy PBR shading functionality
- The final important piece from #3969 as the initial shot at making the PBR shader code reusable in custom materials
## Solution
- Add back and rework the 'old' `array_texture` example from pre-0.6.
- Create a custom shader material
- Use a single array texture binding and sampler for the material bind group
- Use a shader that calls `pbr()` from the `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions` import
- Spawn a row of cubes using the custom material
- In the shader, select the array texture layer to sample by using the world position x coordinate modulo the number of array texture layers
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-06-23 at 12 28 05" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/175278593-2296f519-f577-4ece-81c0-d842283784a1.png">
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Have information about examples only in one place that can be used for the repo and for the website (and remove the need to keep a list of example to build for wasm in the website 75acb73040/generate-wasm-examples/generate_wasm_examples.sh (L92-L99))
## Solution
- Add metadata about examples in `Cargo.toml`
- Build the `examples/README.md` from a template using those metadata. I used tera as the template engine to use the same tech as the website.
- Make CI fail if an example is missing metadata, or if the readme file needs to be updated (the command to update it is displayed in the failed step in CI)
## Remaining To Do
- After the next release with this merged in, the website will be able to be updated to use those metadata too
- I would like to build the examples in wasm and make them available at http://dev-docs.bevyengine.org/ but that will require more design
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website/issues/299 for other ToDos
Co-authored-by: Readme <github-actions@github.com>
# Objective
- Add an example showing a custom post processing effect, done after the first rendering pass.
## Solution
- A simple post processing "chromatic aberration" effect. I mixed together examples `3d/render_to_texture`, and `shader/shader_material_screenspace_texture`
- Reading a bit how https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3430 was done gave me pointers to apply the main pass to the 2d render rather than using a 3d quad.
This work might be or not be relevant to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2724
<details>
<summary> ⚠️ Click for a video of the render ⚠️ I’ve been told it might hurt the eyes 👀 , maybe we should choose another effect just in case ?</summary>
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2290685/169138830-a6dc8a9f-8798-44b9-8d9e-449e60614916.mp4
</details>
# Request for feedbacks
- [ ] Is chromatic aberration effect ok ? (Correct term, not a danger for the eyes ?) I'm open to suggestion to make something different.
- [ ] Is the code idiomatic ? I preferred a "main camera -> **new camera with post processing applied to a quad**" approach to emulate minimum modification to existing code wanting to add global post processing.
---
## Changelog
- Add a full screen post processing shader example
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution
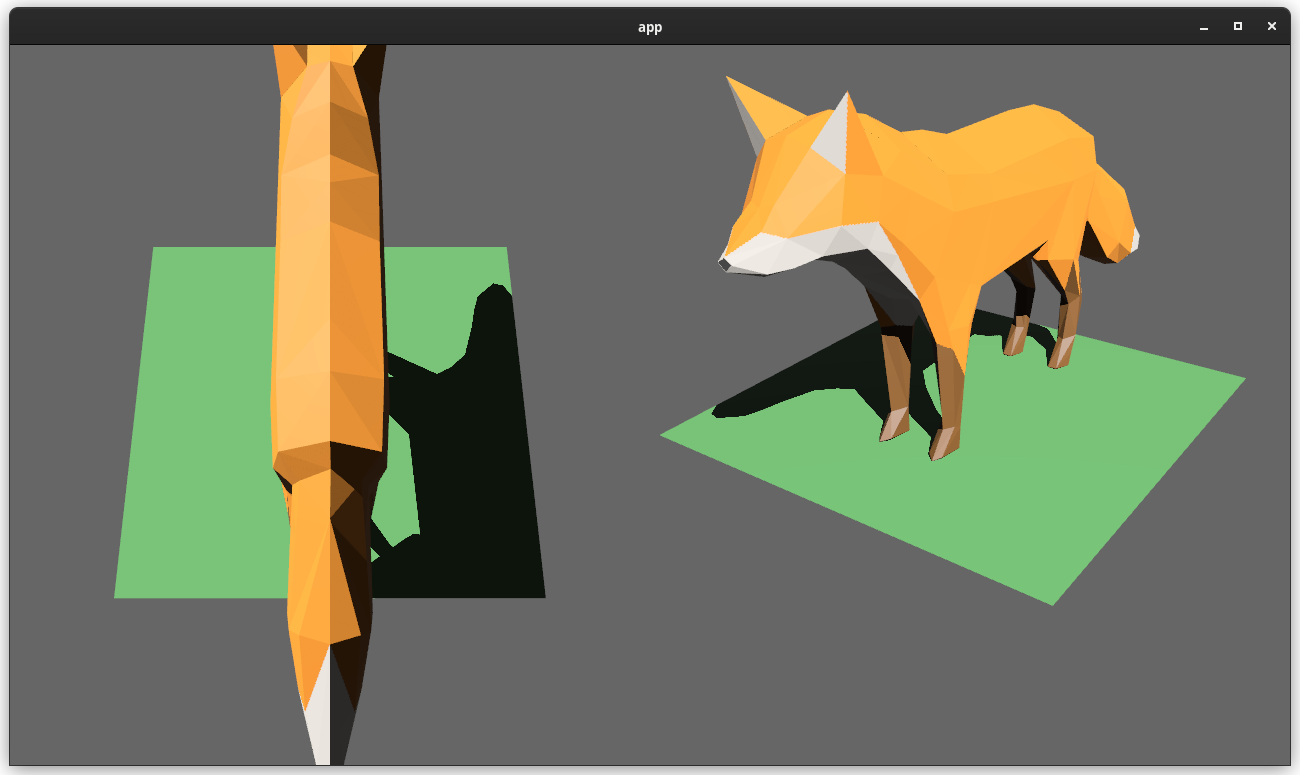
Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier.
Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):

Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work".
Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id:
```rust
// main camera (main window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
// second camera (other window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`).
```rust
// main pass camera with a default priority of 0
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()),
priority: -1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle {
texture: image_handle,
..default()
})
```
Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
// this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render
priority: 1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active.
Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections.
```rust
// old 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default())
// new 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d())
// new 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d())
// new 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
projection: OrthographicProjection {
scale: 3.0,
scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical,
..default()
}.into(),
..default()
})
```
Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors.
If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name),
..default()
})
```
Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added.
Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// overrides the default global clear color
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED),
..default()
},
..default()
})
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// disables clearing
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None,
..default()
},
..default()
})
```
Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future.
By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component:
```rust
commands
.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
.insert(CameraUi {
is_enabled: false,
..default()
})
```
## Other Changes
* The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr.
* I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization.
* I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler.
* All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr.
* Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic.
* Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals:
1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs.
2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense.
## Follow Up Work
* Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen)
* Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor)
* Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system).
* Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable.
* Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home.
# Objective
- Add Vertex Color support to 2D meshes and ColorMaterial. This extends the work from #4528 (which in turn builds on the excellent tangent handling).
## Solution
- Added `#ifdef` wrapped support for vertex colors in the 2D mesh shader and `ColorMaterial` shader.
- Added an example, `mesh2d_vertex_color_texture` to demonstrate it in action.

---
## Changelog
- Added optional (ifdef wrapped) vertex color support to the 2dmesh and color material systems.
# Objective
Provide a starting point for #3951, or a partial solution.
Providing a few comment blocks to discuss, and hopefully find better one in the process.
## Solution
Since I am pretty new to pretty much anything in this context, I figured I'd just start with a draft for some file level doc blocks. For some of them I found more relevant details (or at least things I considered interessting), for some others there is less.
## Changelog
- Moved some existing comments from main() functions in the 2d examples to the file header level
- Wrote some more comment blocks for most other 2d examples
TODO:
- [x] 2d/sprite_sheet, wasnt able to come up with something good yet
- [x] all other example groups...
Also: Please let me know if the commit style is okay, or to verbose. I could certainly squash these things, or add more details if needed.
I also hope its okay to raise this PR this early, with just a few files changed. Took me long enough and I dont wanted to let it go to waste because I lost motivation to do the whole thing. Additionally I am somewhat uncertain over the style and contents of the commets. So let me know what you thing please.
# Objective
Add support for vertex colors
## Solution
This change is modeled after how vertex tangents are handled, so the shader is conditionally compiled with vertex color support if the mesh has the corresponding attribute set.
Vertex colors are multiplied by the base color. I'm not sure if this is the best for all cases, but may be useful for modifying vertex colors without creating a new mesh.
I chose `VertexFormat::Float32x4`, but I'd prefer 16-bit floats if/when support is added.
## Changelog
### Added
- Vertex colors can be specified using the `Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_COLOR` mesh attribute.
# Objective
Bevy users often want to create circles and other simple shapes.
All the machinery is in place to accomplish this, and there are external crates that help. But when writing code for e.g. a new bevy example, it's not really possible to draw a circle without bringing in a new asset, writing a bunch of scary looking mesh code, or adding a dependency.
In particular, this PR was inspired by this interaction in another PR: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3721#issuecomment-1016774535
## Solution
This PR adds `shape::RegularPolygon` and `shape::Circle` (which is just a `RegularPolygon` that defaults to a large number of sides)
## Discussion
There's a lot of ongoing discussion about shapes in <https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/12> and at least one other lingering shape PR (although it seems incomplete).
That RFC currently includes `RegularPolygon` and `Circle` shapes, so I don't think that having working mesh generation code in the engine for those shapes would add much burden to an author of an implementation.
But if we'd prefer not to add additional shapes until after that's sorted out, I'm happy to close this for now.
## Alternatives for users
For any users stumbling on this issue, here are some plugins that will help if you need more shapes.
https://github.com/Nilirad/bevy_prototype_lyonhttps://github.com/johanhelsing/bevy_smudhttps://github.com/Weasy666/bevy_svghttps://github.com/redpandamonium/bevy_more_shapeshttps://github.com/ForesightMiningSoftwareCorporation/bevy_polyline
# Objective
- As requested here: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4520#issuecomment-1109302039
- Make it easier to spot issues with built-in shapes
## Solution
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/200550/165624709-c40dfe7e-0e1e-4bd3-ae52-8ae66888c171.mp4
- Add an example showcasing the built-in 3d shapes with lighting/shadows
- Rotate objects in such a way that all faces are seen by the camera
- Add a UV debug texture
## Discussion
I'm not sure if this is what @alice-i-cecile had in mind, but I adapted the little "torus playground" from the issue linked above to include all built-in shapes.
This exact arrangement might not be particularly scalable if many more shapes are added. Maybe a slow camera pan, or cycling with the keyboard or on a timer, or a sidebar with buttons would work better. If one of the latter options is used, options for showing wireframes or computed flat normals might add some additional utility.
Ideally, I think we'd have a better way of visualizing normals.
Happy to rework this or close it if there's not a consensus around it being useful.
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3499
## Solution
Uses a `HashMap` from `RenderTarget` to sampled textures when preparing `ViewTarget`s to ensure that two passes with the same render target get sampled to the same texture.
This builds on and depends on https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3412, so this will be a draft PR until #3412 is merged. All changes for this PR are in the last commit.
# Objective
- Several examples are useful for qualitative tests of Bevy's performance
- By contrast, these are less useful for learning material: they are often relatively complex and have large amounts of setup and are performance optimized.
## Solution
- Move bevymark, many_sprites and many_cubes into the new stress_tests example folder
- Move contributors into the games folder: unlike the remaining examples in the 2d folder, it is not focused on demonstrating a clear feature.
# Objective
- Make use of storage buffers, where they are available, for clustered forward bindings to support far more point lights in a scene
- Fixes#3605
- Based on top of #4079
This branch on an M1 Max can keep 60fps with about 2150 point lights of radius 1m in the Sponza scene where I've been testing. The bottleneck is mostly assigning lights to clusters which grows faster than linearly (I think 1000 lights was about 1.5ms and 5000 was 7.5ms). I have seen papers and presentations leveraging compute shaders that can get this up to over 1 million. That said, I think any further optimisations should probably be done in a separate PR.
## Solution
- Add `RenderDevice` to the `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` trait `::key()` functions to allow setting flags on the keys depending on feature/limit availability
- Make `GpuPointLights` and `ViewClusterBuffers` into enums containing `UniformVec` and `StorageBuffer` variants. Implement the necessary API on them to make usage the same for both cases, and the only difference is at initialisation time.
- Appropriate shader defs in the shader code to handle the two cases
## Context on some decisions / open questions
- I'm using `max_storage_buffers_per_shader_stage >= 3` as a check to see if storage buffers are supported. I was thinking about diving into 'binding resource management' but it feels like we don't have enough use cases to understand the problem yet, and it is mostly a separate concern to this PR, so I think it should be handled separately.
- Should `ViewClusterBuffers` and `ViewClusterBindings` be merged, duplicating the count variables into the enum variants?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files. Animate meshes.
## Solution
- Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files.
- Added `SkinnedMesh` component and ` SkinnedMeshInverseBindPose` asset
- Added `extract_skinned_meshes` to extract joint matrices.
- Added queue phase systems for enqueuing the buffer writes.
Some notes:
- This ports part of # #2359 to the current main.
- This generates new `BufferVec`s and bind groups every frame. The expectation here is that the number of `Query::get` calls during extract is probably going to be the stronger bottleneck, with up to 256 calls per skinned mesh. Until that is optimized, caching buffers and bind groups is probably a non-concern.
- Unfortunately, due to the uniform size requirements, this means a 16KB buffer is allocated for every skinned mesh every frame. There's probably a few ways to get around this, but most of them require either compute shaders or storage buffers, which are both incompatible with WebGL2.
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
## Objective
There recently was a discussion on Discord about a possible test case for stress-testing transform hierarchies.
## Solution
Create a test case for stress testing transform propagation.
*Edit:* I have scrapped my previous example and built something more functional and less focused on visuals.
There are three test setups:
- `TestCase::Tree` recursively creates a tree with a specified depth and branch width
- `TestCase::NonUniformTree` is the same as `Tree` but omits nodes in a way that makes the tree "lean" towards one side, like this:
<details>
<summary></summary>
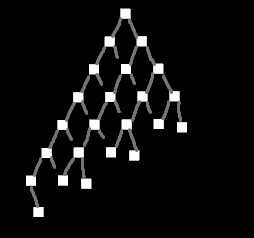
</details>
- `TestCase::Humanoids` creates one or more separate hierarchies based on the structure of common humanoid rigs
- this can both insert `active` and `inactive` instances of the human rig
It's possible to parameterize which parts of the hierarchy get updated (transform change) and which remain unchanged. This is based on @james7132 suggestion:
There's a probability to decide which entities should remain static. On top of that these changes can be limited to a certain range in the hierarchy (min_depth..max_depth).
# Objective
- Allow quick and easy testing of scenes
## Solution
- Add a `scene-viewer` tool based on `load_gltf`.
- Run it with e.g. `cargo run --release --example scene_viewer --features jpeg -- ../some/path/assets/models/Sponza/glTF/Sponza.gltf#Scene0`
- Configure the asset path as pointing to the repo root for convenience (paths specified relative to current working directory)
- Copy over the camera controller from the `shadow_biases` example
- Support toggling the light animation
- Support toggling shadows
- Support adjusting the directional light shadow projection (cascaded shadow maps will remove the need for this later)
I don't want to do too much on it up-front. Rather we can add features over time as we need them.
# Add Transform Examples
- Adding examples for moving/rotating entities (with its own section) to resolve#2400
I've stumbled upon this project and been fiddling around a little. Saw the issue and thought I might just add some examples for the proposed transformations.
Mind to check if I got the gist correctly and suggest anything I can improve?
# Objective
- Reduce power usage for games when not focused.
- Reduce power usage to ~0 when a desktop application is minimized (opt-in).
- Reduce power usage when focused, only updating on a `winit` event, or the user sends a redraw request. (opt-in)
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/156904387-ec47d7de-7f06-4c6f-8aaf-1e952c1153a2.mp4
Note resource usage in the Task Manager in the above video.
## Solution
- Added a type `UpdateMode` that allows users to specify how the winit event loop is updated, without exposing winit types.
- Added two fields to `WinitConfig`, both with the `UpdateMode` type. One configures how the application updates when focused, and the other configures how the application behaves when it is not focused. Users can modify this resource manually to set the type of event loop control flow they want.
- For convenience, two functions were added to `WinitConfig`, that provide reasonable presets: `game()` (default) and `desktop_app()`.
- The `game()` preset, which is used by default, is unchanged from current behavior with one exception: when the app is out of focus the app updates at a minimum of 10fps, or every time a winit event is received. This has a huge positive impact on power use and responsiveness on my machine, which will otherwise continue running the app at many hundreds of fps when out of focus or minimized.
- The `desktop_app()` preset is fully reactive, only updating when user input (winit event) is supplied or a `RedrawRequest` event is sent. When the app is out of focus, it only updates on `Window` events - i.e. any winit event that directly interacts with the window. What this means in practice is that the app uses *zero* resources when minimized or not interacted with, but still updates fluidly when the app is out of focus and the user mouses over the application.
- Added a `RedrawRequest` event so users can force an update even if there are no events. This is useful in an application when you want to, say, run an animation even when the user isn't providing input.
- Added an example `low_power` to demonstrate these changes
## Usage
Configuring the event loop:
```rs
use bevy::winit::{WinitConfig};
// ...
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::desktop_app()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::game()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig{ .. }) // manual
```
Requesting a redraw:
```rs
use bevy:🪟:RequestRedraw;
// ...
fn request_redraw(mut event: EventWriter<RequestRedraw>) {
event.send(RequestRedraw);
}
```
## Other details
- Because we have a single event loop for multiple windows, every time I've mentioned "focused" above, I more precisely mean, "if at least one bevy window is focused".
- Due to a platform bug in winit (https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/1619), we can't simply use `Window::request_redraw()`. As a workaround, this PR will temporarily set the window mode to `Poll` when a redraw is requested. This is then reset to the user's `WinitConfig` setting on the next frame.
# Objective
- Add ways to control how audio is played
## Solution
- playing a sound will return a (weak) handle to an asset that can be used to control playback
- if the asset is dropped, it will detach the sink (same behaviour as now)
# Objective
Will fix#3377 and #3254
## Solution
Use an enum to represent either a `WindowId` or `Handle<Image>` in place of `Camera::window`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Closes#786
- Closes#2252
- Closes#2588
This PR implements a derive macro that allows users to define their queries as structs with named fields.
## Example
```rust
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct NumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
entity: Entity,
u: UNumQuery<'w>,
generic: GenericQuery<'w, T, P>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct UNumQuery<'w> {
u_16: &'w u16,
u_32_opt: Option<&'w u32>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct GenericQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
generic: (&'w T, &'w P),
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(filter)]
struct NumQueryFilter<T: Component, P: Component> {
_u_16: With<u16>,
_u_32: With<u32>,
_or: Or<(With<i16>, Changed<u16>, Added<u32>)>,
_generic_tuple: (With<T>, With<P>),
_without: Without<Option<u16>>,
_tp: PhantomData<(T, P)>,
}
fn print_nums_readonly(query: Query<NumQuery<u64, i64>, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct MutNumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
i_16: &'w mut i16,
i_32_opt: Option<&'w mut i32>,
}
fn print_nums(mut query: Query<MutNumQuery, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter_mut() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
```
## TODOs:
- [x] Add support for `&T` and `&mut T`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for optional types
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `Entity`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for nested `WorldQuery`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for tuples
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for generics
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for query filters
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `PhantomData`
- [x] Test
- [x] Refactor `read_world_query_field_type_info`
- [x] Properly document `readonly` attribute for nested queries and the static assertions that guarantee safety
- [x] Test that we never implement `ReadOnlyFetch` for types that need mutable access
- [x] Test that we insert static assertions for nested `WorldQuery` that a user marked as readonly
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120Fixes#3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
My attempt at fixing #2142. My very first attempt at contributing to Bevy so more than open to any feedback.
I borrowed heavily from the [Bevy Cheatbook page](https://bevy-cheatbook.github.io/patterns/generic-systems.html?highlight=generic#generic-systems).
## Solution
Fairly straightforward example using a clean up system to delete entities that are coupled with app state after exiting that state.
Co-authored-by: B-Janson <brandon@canva.com>
Add two examples on how to communicate with a task that is running either in another thread or in a thread from `AsyncComputeTaskPool`.
Loosely based on https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/1150
## Objective
There is no bevy example that shows how to transform a sprite. At least as its singular purpose. This creates an example of how to use transform.translate to move a sprite up and down. The last pull request had issues that I couldn't fix so I created a new one
### Solution
I created move_sprite example.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Some new bevy users are unfamiliar with quaternions and have trouble working with rotations in 2D.
There has been an [issue](https://github.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/issues/226) raised with glam to add helpers to better support these users, however for now I feel could be better to provide examples of how to do this in Bevy as a starting point for new users.
## Solution
I've added a 2d_rotation example which demonstrates 3 different rotation examples to try help get people started:
- Rotating and translating a player ship based on keyboard input
- An enemy ship type that rotates to face the player ship immediately
- An enemy ship type that rotates to face the player at a fixed angular velocity
I also have a standalone version of this example here https://github.com/bitshifter/bevy-2d-rotation-example but I think it would be more discoverable if it's included with Bevy.