# Objective
- Implement the foundations of automatic batching/instancing of draw
commands as the next step from #89
- NOTE: More performance improvements will come when more data is
managed and bound in ways that do not require rebinding such as mesh,
material, and texture data.
## Solution
- The core idea for batching of draw commands is to check whether any of
the information that has to be passed when encoding a draw command
changes between two things that are being drawn according to the sorted
render phase order. These should be things like the pipeline, bind
groups and their dynamic offsets, index/vertex buffers, and so on.
- The following assumptions have been made:
- Only entities with prepared assets (pipelines, materials, meshes) are
queued to phases
- View bindings are constant across a phase for a given draw function as
phases are per-view
- `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` is the only system that performs this
batching and has sole responsibility for preparing the per-object data.
As such the mesh binding and dynamic offsets are assumed to only vary as
a result of the `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` system, e.g. due to
having to split data across separate uniform bindings within the same
buffer due to the maximum uniform buffer binding size.
- Implement `GpuArrayBuffer` for `Mesh2dUniform` to store Mesh2dUniform
in arrays in GPU buffers rather than each one being at a dynamic offset
in a uniform buffer. This is the same optimisation that was made for 3D
not long ago.
- Change batch size for a range in `PhaseItem`, adding API for getting
or mutating the range. This is more flexible than a size as the length
of the range can be used in place of the size, but the start and end can
be otherwise whatever is needed.
- Add an optional mesh bind group dynamic offset to `PhaseItem`. This
avoids having to do a massive table move just to insert
`GpuArrayBufferIndex` components.
## Benchmarks
All tests have been run on an M1 Max on AC power. `bevymark` and
`many_cubes` were modified to use 1920x1080 with a scale factor of 1. I
run a script that runs a separate Tracy capture process, and then runs
the bevy example with `--features bevy_ci_testing,trace_tracy` and
`CI_TESTING_CONFIG=../benchmark.ron` with the contents of
`../benchmark.ron`:
```rust
(
exit_after: Some(1500)
)
```
...in order to run each test for 1500 frames.
The recent changes to `many_cubes` and `bevymark` added reproducible
random number generation so that with the same settings, the same rng
will occur. They also added benchmark modes that use a fixed delta time
for animations. Combined this means that the same frames should be
rendered both on main and on the branch.
The graphs compare main (yellow) to this PR (red).
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark`
<img width="1411" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 42 10"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/2088716a-c918-486c-8129-090b26fd2bc4">
The mesh and material are the same for all instances. This is basically
the best case for the initial batching implementation as it results in 1
draw for the ~11.7k visible meshes. It gives a ~30% reduction in median
frame time.
The 1000th frame is identical using the flip tool:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4615 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1404" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 45 18"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/5ee9c447-5bd2-45c6-9706-ac5ff8916daf">
This run uses 10 different materials by varying their textures. The
materials are randomly selected, and there is no sorting by material
bind group for opaque 3D so any batching is 'random'. The PR produces a
~5% reduction in median frame time. If we were to sort the opaque phase
by the material bind group, then this should be a lot faster. This
produces about 10.5k draws for the 11.7k visible entities. This makes
sense as randomly selecting from 10 materials gives a chance that two
adjacent entities randomly select the same material and can be batched.
The 1000th frame is identical in flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4537 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1394" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 48 44"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/f02a816b-a444-4c18-a96a-63b5436f3b7f">
This run varies the material data per instance by randomly-generating
its colour. This is the worst case for batching and that it performs
about the same as `main` is a good thing as it demonstrates that the
batching has minimal overhead when dealing with ~11k visible mesh
entities.
The 1000th frame is identical according to flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4568 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d`
<img width="1412" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 59 56"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/cb02ae07-237b-4646-ae9f-fda4dafcbad4">
This spawns 160 waves of 1000 quad meshes that are shaded with
ColorMaterial. Each wave has a different material so 160 waves currently
should result in 160 batches. This results in a 50% reduction in median
frame time.
Capturing a screenshot of the 1000th frame main vs PR gives:

```
Mean: 0.001222
Weighted median: 0.750432
1st weighted quartile: 0.453494
3rd weighted quartile: 0.969758
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.990296
Evaluation time: 0.4255 seconds
```
So they seem to produce the same results. I also double-checked the
number of draws. `main` does 160000 draws, and the PR does 160, as
expected.
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 09 22"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/4358da2e-ce32-4134-82df-3ab74c40849c">
This generates 10 textures and generates materials for each of those and
then selects one material per wave. The median frame time is reduced by
50%. Similar to the plain run above, this produces 160 draws on the PR
and 160000 on `main` and the 1000th frame is identical (ignoring the fps
counter text overlay).

```
Mean: 0.002877
Weighted median: 0.964980
1st weighted quartile: 0.668871
3rd weighted quartile: 0.982749
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.992377
Evaluation time: 0.4301 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 13 53"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/b2198b18-3439-47ad-919a-cdabe190facb">
This creates unique materials per instance by randomly-generating the
material's colour. This is the worst case for 2D batching. Somehow, this
PR manages a 7% reduction in median frame time. Both main and this PR
issue 160000 draws.
The 1000th frame is the same:

```
Mean: 0.001214
Weighted median: 0.937499
1st weighted quartile: 0.635467
3rd weighted quartile: 0.979085
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.988971
Evaluation time: 0.4462 seconds
```
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 21 12"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/8b31e915-d6be-4cac-abf5-c6a4da9c3d43">
This just spawns 160 waves of 1000 sprites. There should be and is no
notable difference between main and the PR.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1389" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 36 08"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/45fe8d6d-c901-4062-a349-3693dd044413">
This spawns the sprites selecting a texture at random per instance from
the 10 generated textures. This has no significant change vs main and
shouldn't.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1401" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 29 52"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/762c5c60-352e-471f-8dbe-bbf10e24ebd6">
This sets the sprite colour as being unique per instance. This can still
all be drawn using one batch. There should be no difference but the PR
produces median frame times that are 4% higher. Investigation showed no
clear sources of cost, rather a mix of give and take that should not
happen. It seems like noise in the results.
### Summary
| Benchmark | % change in median frame time |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| many_cubes | 🟩 -30% |
| many_cubes 10 materials | 🟩 -5% |
| many_cubes unique materials | 🟩 ~0% |
| bevymark mesh2d | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d 10 materials | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d unique materials | 🟩 -7% |
| bevymark sprite | 🟥 2% |
| bevymark sprite 10 materials | 🟥 0.6% |
| bevymark sprite unique materials | 🟥 4.1% |
---
## Changelog
- Added: 2D and 3D mesh entities that share the same mesh and material
(same textures, same data) are now batched into the same draw command
for better performance.
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nico@nicopap.ch>
CI-capable version of #9086
---------
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
I created this manually as Github didn't want to run CI for the
workflow-generated PR. I'm guessing we didn't hit this in previous
releases because we used bors.
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#5432
- Fixes#6680
## Solution
- move code responsible for generating the `impl TypeUuid` from `type_uuid_derive` into a new function, `gen_impl_type_uuid`.
- this allows the new proc macro, `impl_type_uuid`, to call the code for generation.
- added struct `TypeUuidDef` and implemented `syn::Parse` to allow parsing of the input for the new macro.
- finally, used the new macro `impl_type_uuid` to implement `TypeUuid` for the standard library (in `crates/bevy_reflect/src/type_uuid_impl.rs`).
- fixes#6680 by doing a wrapping add of the param's index to its `TYPE_UUID`
Co-authored-by: dis-da-moe <84386186+dis-da-moe@users.noreply.github.com>
Profiles show that in extremely hot loops, like the draw loops in the renderer, invoking the trace! macro has noticeable overhead, even if the trace log level is not enabled.
Solve this by introduce a 'wrapper' detailed_trace macro around trace, that wraps the trace! log statement in a trivially false if statement unless a cargo feature is enabled
# Objective
- Eliminate significant overhead observed with trace-level logging in render hot loops, even when trace log level is not enabled.
- This is an alternative solution to the one proposed in #7223
## Solution
- Introduce a wrapper around the `trace!` macro called `detailed_trace!`. This macro wraps the `trace!` macro with an if statement that is conditional on a new cargo feature, `detailed_trace`. When the feature is not enabled (the default), then the if statement is trivially false and should be optimized away at compile time.
- Convert the observed hot occurrences of trace logging in `TrackedRenderPass` with this new macro.
Testing the results of
```
cargo run --profile stress-test --features bevy/trace_tracy --example many_cubes -- spheres
```
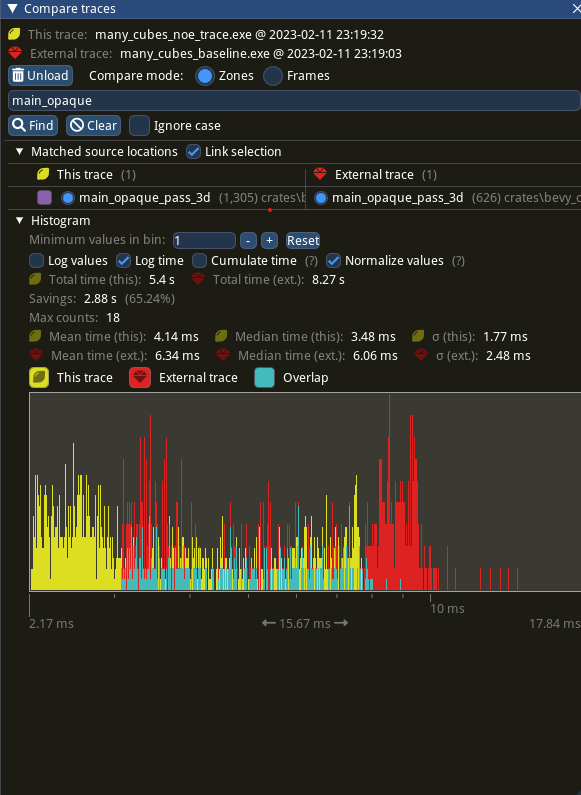
shows significant improvement of the `main_opaque_pass_3d` of the renderer, a median time decrease from 6.0ms to 3.5ms.
---
## Changelog
- For performance reasons, some detailed renderer trace logs now require the use of cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to setting the log level to `TRACE` in order to be shown.
## Migration Guide
- Some detailed bevy trace events now require the use of the cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to enabling `TRACE` level logging to view. Should you wish to see these logs, please compile your code with the bevy feature `detailed_trace`. Currently, the only logs that are affected are the renderer logs pertaining to `TrackedRenderPass` functions
# Objective
Complete the first part of the migration detailed in bevyengine/rfcs#45.
## Solution
Add all the new stuff.
### TODO
- [x] Impl tuple methods.
- [x] Impl chaining.
- [x] Port ambiguity detection.
- [x] Write docs.
- [x] ~~Write more tests.~~(will do later)
- [ ] Write changelog and examples here?
- [x] ~~Replace `petgraph`.~~ (will do later)
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Michael Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
# Objective
I noticed while working on #5366 that the documentation for label types wasn't working correctly. Having experimented with this for a few weeks, I believe that generating docs in macros is more effort than it's worth.
## Solution
Add more boilerplate, copy-paste and edit the docs across types. This also lets us add custom doctests for specific types. Also, we don't need `concat_idents` as a dependency anymore.
# Objective
- Closes#4954
- Reduce the complexity of the `{System, App, *}Label` APIs.
## Solution
For the sake of brevity I will only refer to `SystemLabel`, but everything applies to all of the other label types as well.
- Add `SystemLabelId`, a lightweight, `copy` struct.
- Convert custom types into `SystemLabelId` using the trait `SystemLabel`.
## Changelog
- String literals implement `SystemLabel` for now, but this should be changed with #4409 .
## Migration Guide
- Any previous use of `Box<dyn SystemLabel>` should be replaced with `SystemLabelId`.
- `AsSystemLabel` trait has been modified.
- No more output generics.
- Method `as_system_label` now returns `SystemLabelId`, removing an unnecessary level of indirection.
- If you *need* a label that is determined at runtime, you can use `Box::leak`. Not recommended.
## Questions for later
* Should we generate a `Debug` impl along with `#[derive(*Label)]`?
* Should we rename `as_str()`?
* Should we remove the extra derives (such as `Hash`) from builtin `*Label` types?
* Should we automatically derive types like `Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq`?
* More-ergonomic comparisons between `Label` and `LabelId`.
* Move `Dyn{Eq, Hash,Clone}` somewhere else.
* Some API to make interning dynamic labels easier.
* Optimize string representation
* Empty string for unit structs -- no debug info but faster comparisons
* Don't show enum types -- same tradeoffs as asbove.
# Objective
- Update hashbrown to 0.12
## Solution
- Replace #4004
- As the 0.12 is already in Bevy dependency tree, it shouldn't be an issue to update
- The exception for the 0.11 should be removed once https://github.com/zakarumych/gpu-descriptor/pull/21 is merged and released
- Also removed a few exceptions that weren't needed anymore
# Objective
Fixes#4353. Fixes#4431. Picks up fixes for a panic for `gilrs` when `getGamepads()` is not available.
## Solution
Update the `gilrs` to `v0.9.0`. Changelog can be seen here: dba36f9186
EDIT: Updated `uuid` to 1.1 to avoid duplicate dependencies. Added `nix`'s two dependencies as exceptions until `rodio` updates their deps.
# Objective
Reduce from scratch build time.
## Solution
Reduce the size of the critical path by removing dependencies between crates where not necessary. For `cargo check --no-default-features` this reduced build time from ~51s to ~45s. For some commits I am not completely sure if the tradeoff between build time reduction and convenience caused by the commit is acceptable. If not, I can drop them.
# Objective
- Debug logs are useful in release builds, but `tracing` logs are hard-capped (`release_max_level_info`) at the `info` level by `bevy_utils`.
## Solution
- This PR simply removes the limit in `bevy_utils` with no further actions.
- If any out-of-the box performance regressions arise, the steps to enable this `tracing` feature should be documented in a user guide in the future.
This PR closes#4069 and closes#1206.
## Alternatives considered
- Instruct the user to build with `debug-assertions` enabled: this is just a workaround, as it obviously enables all `debug-assertions` that affect more than logging itself.
- Re-exporting the feature from `tracing` and enabling it by default: I believe it just adds complexity and confusion, the `tracing` feature can also be re-enabled with one line in userland.
---
## Changelog
### Fixed
- Log level is not hard capped at `info` for release builds anymore.
## Migration Guide
- Maximum log levels for release builds is not enforced by Bevy anymore, to omit "debug" and "trace" level logs entirely from release builds, `tracing` must be added as a dependency with its `release_max_level_info` feature enabled in `Cargo.toml`. (`tracing = { version = "0.1", features = ["release_max_level_info"] }`)
For some keys, it is too expensive to hash them on every lookup. Historically in Bevy, we have regrettably done the "wrong" thing in these cases (pre-computing hashes, then re-hashing them) because Rust's built in hashed collections don't give us the tools we need to do otherwise. Doing this is "wrong" because two different values can result in the same hash. Hashed collections generally get around this by falling back to equality checks on hash collisions. You can't do that if the key _is_ the hash. Additionally, re-hashing a hash increase the odds of collision!
#3959 needs pre-hashing to be viable, so I decided to finally properly solve the problem. The solution involves two different changes:
1. A new generalized "pre-hashing" solution in bevy_utils: `Hashed<T>` types, which store a value alongside a pre-computed hash. And `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . `PreHashMap` is just an alias for a normal HashMap that uses `Hashed<T>` as the key and a new `PassHash` implementation as the Hasher.
2. Replacing the `std::collections` re-exports in `bevy_utils` with equivalent `hashbrown` impls. Avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. The latest version of `hashbrown` adds support for the `entity_ref` api, so we can move to that in preparation for an std migration, if thats the direction they seem to be going in. Note that adding hashbrown doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree.
In addition to providing these core tools, I also ported the "table identity hashing" in `bevy_ecs` to `raw_entry_mut`, which was a particularly egregious case.
The biggest outstanding case is `AssetPathId`, which stores a pre-hash. We need AssetPathId to be cheaply clone-able (and ideally Copy), but `Hashed<AssetPath>` requires ownership of the AssetPath, which makes cloning ids way more expensive. We could consider doing `Hashed<Arc<AssetPath>>`, but cloning an arc is still a non-trivial expensive that needs to be considered. I would like to handle this in a separate PR. And given that we will be re-evaluating the Bevy Assets implementation in the very near future, I'd prefer to hold off until after that conversation is concluded.
Objective
During work on #3009 I've found that not all jobs use actions-rs, and therefore, an previous version of Rust is used for them. So while compilation and other stuff can pass, checking markup and Android build may fail with compilation errors.
Solution
This PR adds `action-rs` for any job running cargo, and updates the edition to 2021.
This relicenses Bevy under the dual MIT or Apache-2.0 license. For rationale, see #2373.
* Changes the LICENSE file to describe the dual license. Moved the MIT license to docs/LICENSE-MIT. Added the Apache-2.0 license to docs/LICENSE-APACHE. I opted for this approach over dumping both license files at the root (the more common approach) for a number of reasons:
* Github links to the "first" license file (LICENSE-APACHE) in its license links (you can see this in the wgpu and rust-analyzer repos). People clicking these links might erroneously think that the apache license is the only option. Rust and Amethyst both use COPYRIGHT or COPYING files to solve this problem, but this creates more file noise (if you do everything at the root) and the naming feels way less intuitive.
* People have a reflex to look for a LICENSE file. By providing a single license file at the root, we make it easy for them to understand our licensing approach.
* I like keeping the root clean and noise free
* There is precedent for putting the apache and mit license text in sub folders (amethyst)
* Removed the `Copyright (c) 2020 Carter Anderson` copyright notice from the MIT license. I don't care about this attribution, it might make license compliance more difficult in some cases, and it didn't properly attribute other contributors. We shoudn't replace it with something like "Copyright (c) 2021 Bevy Contributors" because "Bevy Contributors" is not a legal entity. Instead, we just won't include the copyright line (which has precedent ... Rust also uses this approach).
* Updates crates to use the new "MIT OR Apache-2.0" license value
* Removes the old legion-transform license file from bevy_transform. bevy_transform has been its own, fully custom implementation for a long time and that license no longer applies.
* Added a License section to the main readme
* Updated our Bevy Plugin licensing guidelines.
As a follow-up we should update the website to properly describe the new license.
Closes#2373
There are cases where we want an enum variant name. Right now the only way to do that with rust's std is to derive Debug, but this will also print out the variant's fields. This creates the unfortunate situation where we need to manually write out each variant's string name (ex: in #1963), which is both boilerplate-ey and error-prone. Crates such as `strum` exist for this reason, but it includes a lot of code and complexity that we don't need.
This adds a dead-simple `EnumVariantMeta` derive that exposes `enum_variant_index` and `enum_variant_name` functions. This allows us to make cases like #1963 much cleaner (see the second commit). We might also be able to reuse this logic for `bevy_reflect` enum derives.