# Objective
> Part of #6573
`Children` was not being properly deserialized in scenes. This was due to a missing registration on `SmallVec<[Entity; 8]>`, which is used by `Children`.
## Solution
Register `SmallVec<[Entity; 8]>`.
---
## Changelog
- Registered `SmallVec<[Entity; 8]>`
# Objective
Fixes#6030, making ``serde`` optional.
## Solution
This was solved by making a ``serialize`` feature that can activate ``serde``, which is now optional.
When ``serialize`` is deactivated, the ``Plugin`` implementation for ``ScenePlugin`` does nothing.
Co-authored-by: Linus Käll <linus.kall.business@gmail.com>
# Objective
Currently, `Ptr` and `PtrMut` can only be constructed via unsafe code. This means that downgrading a reference to an untyped pointer is very cumbersome, despite being a very simple operation.
## Solution
Define conversions for easily and safely constructing untyped pointers. This is the non-owned counterpart to `OwningPtr::make`.
Before:
```rust
let ptr = unsafe { PtrMut::new(NonNull::from(&mut value).cast()) };
```
After:
```rust
let ptr = PtrMut::from(&mut value);
```
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
I needed a window which is always on top, to create a overlay app.
## Solution
expose the `always_on_top` property of winit in bevy's `WindowDescriptor` as a boolean flag
---
## Changelog
### Added
- add `WindowDescriptor.always_on_top` which configures a window to stay on top.
# Objective
`ScalingMode::Auto` for cameras only targets min_height and min_width, or as the docs say it `Use minimal possible viewport size while keeping the aspect ratio.`
But there is no ScalingMode that targets max_height and Max_width or `Use maximal possible viewport size while keeping the aspect ratio.`
## Solution
Added `ScalingMode::AutoMax` that does the exact opposite of `ScalingMode::Auto`
---
## Changelog
Renamed `ScalingMode::Auto` to `ScalingMode::AutoMin`.
## Migration Guide
just rename `ScalingMode::Auto` to `ScalingMode::AutoMin` if you are using it.
Co-authored-by: Lixou <82600264+DasLixou@users.noreply.github.com>
Add a method to get the focused window.
Use this instead of `WindowFocused` events in `close_on_esc`.
Seems that the OS/window manager might not always send focused events on application startup.
Sadly, not a fix for #5646.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes #3225, Allow for flippable UI Images
## Solution
Add flip_x and flip_y fields to UiImage, and swap the UV coordinates accordingly in ui_prepare_nodes.
## Changelog
* Changes UiImage to a struct with texture, flip_x, and flip_y fields.
* Adds flip_x and flip_y fields to ExtractedUiNode.
* Changes extract_uinodes to extract the flip_x and flip_y values from UiImage.
* Changes prepare_uinodes to swap the UV coordinates as required.
* Changes UiImage derefs to texture field accesses.
# Objective
Fixes#6615.
`BlobVec` does not respect alignment for zero-sized types, which results in UB whenever a ZST with alignment other than 1 is used in the world.
## Solution
Add the fn `bevy_ptr::dangling_with_align`.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the function `dangling_with_align` to `bevy_ptr`, which creates a well-aligned dangling pointer to a type whose alignment is not known at compile time.
# Objective
- Implements removal of entries from a `dyn Map`
- Fixes#6563
## Solution
- Adds a `remove` method to the `Map` trait which takes in a `&dyn Reflect` key and returns the value removed if it was present.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Map::remove`
## Migration Guide
- Implementors of `Map` will need to implement the `remove` method.
Co-authored-by: radiish <thesethskigamer@gmail.com>
# Objective
The [documentation for `ButtonSettingsError`](https://docs.rs/bevy/0.9.0/bevy/input/gamepad/enum.ButtonSettingsError.html) incorrectly describes the valid range of values as `0.0..=2.0`, probably because it was copied from `AxisSettingsError`. The actual range, as seen in the functions that return it and in its own `thiserror` description, is `0.0..=1.0`.
## Solution
Update the doc comments to reflect the correct range.
Co-authored-by: Sol Toder <ajaxgb@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#6548. Most of these methods were already made `const` in #5688. `Entity::to_bits` is the only one that remained.
## Solution
Make it const.
# Objective
- Using the instancing example as reference, I found it was breaking when enabling HDR on the camera. I found that this was because, unlike in internal code, this was not updating the specialization key with `view.hdr`.
## Solution
- Add the missing HDR bit.
# Objective
- Fix#3606
- Fix#4579
- Fix#3380
## Solution
When running on a Linux machine with some AMD or Intel device, when calling
`surface.get_current_texture()`, ignore `wgpu::SurfaceError::Timeout` errors.
## Alternative
An alternative solution found in the `wgpu` examples is:
```rust
let frame = surface
.get_current_texture()
.or_else(|_| {
render_device.configure_surface(surface, &swap_chain_descriptor);
surface.get_current_texture()
})
.expect("Error reconfiguring surface");
window.swap_chain_texture = Some(TextureView::from(frame));
```
See: <94ce76391b/wgpu/examples/framework.rs (L362-L370)>
Veloren [handles the Timeout error the way this PR proposes to handle it](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/1218#issuecomment-1092056971).
The reason I went with this PR's solution is that `configure_surface` seems to be quite an expensive operation, and it would run every frame with the wgpu framework solution, despite the fact it works perfectly fine without `configure_surface`.
I know this looks super hacky with the linux-specific line and the AMD check, but my understanding is that the `Timeout` occurrence is specific to a quirk of some AMD drivers on linux, and if otherwise met should be considered a bug.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Closes#5262
- Fix color banding caused by quantization.
## Solution
- Adds dithering to the tonemapping node from #3425.
- This is inspired by Godot's default "debanding" shader: https://gist.github.com/belzecue/
- Unlike Godot:
- debanding happens after tonemapping. My understanding is that this is preferred, because we are running the debanding at the last moment before quantization (`[f32, f32, f32, f32]` -> `f32`). This ensures we aren't biasing the dithering strength by applying it in a different (linear) color space.
- This code instead uses and reference the origin source, Valve at GDC 2015
## Additional Notes
Real time rendering to standard dynamic range outputs is limited to 8 bits of depth per color channel. Internally we keep everything in full 32-bit precision (`vec4<f32>`) inside passes and 16-bit between passes until the image is ready to be displayed, at which point the GPU implicitly converts our `vec4<f32>` into a single 32bit value per pixel, with each channel (rgba) getting 8 of those 32 bits.
### The Problem
8 bits of color depth is simply not enough precision to make each step invisible - we only have 256 values per channel! Human vision can perceive steps in luma to about 14 bits of precision. When drawing a very slight gradient, the transition between steps become visible because with a gradient, neighboring pixels will all jump to the next "step" of precision at the same time.
### The Solution
One solution is to simply output in HDR - more bits of color data means the transition between bands will become smaller. However, not everyone has hardware that supports 10+ bit color depth. Additionally, 10 bit color doesn't even fully solve the issue, banding will result in coherent bands on shallow gradients, but the steps will be harder to perceive.
The solution in this PR adds noise to the signal before it is "quantized" or resampled from 32 to 8 bits. Done naively, it's easy to add unneeded noise to the image. To ensure dithering is correct and absolutely minimal, noise is adding *within* one step of the output color depth. When converting from the 32bit to 8bit signal, the value is rounded to the nearest 8 bit value (0 - 255). Banding occurs around the transition from one value to the next, let's say from 50-51. Dithering will never add more than +/-0.5 bits of noise, so the pixels near this transition might round to 50 instead of 51 but will never round more than one step. This means that the output image won't have excess variance:
- in a gradient from 49 to 51, there will be a step between each band at 49, 50, and 51.
- Done correctly, the modified image of this gradient will never have a adjacent pixels more than one step (0-255) from each other.
- I.e. when scanning across the gradient you should expect to see:
```
|-band-| |-band-| |-band-|
Baseline: 49 49 49 50 50 50 51 51 51
Dithered: 49 50 49 50 50 51 50 51 51
Dithered (wrong): 49 50 51 49 50 51 49 51 50
```


You can see from above how correct dithering "fuzzes" the transition between bands to reduce distinct steps in color, without adding excess noise.
### HDR
The previous section (and this PR) assumes the final output is to an 8-bit texture, however this is not always the case. When Bevy adds HDR support, the dithering code will need to take the per-channel depth into account instead of assuming it to be 0-255. Edit: I talked with Rob about this and it seems like the current solution is okay. We may need to revisit once we have actual HDR final image output.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- All pipelines now support deband dithering. This is enabled by default in 3D, and can be toggled in the `Tonemapping` component in camera bundles. Banding is a graphical artifact created when the rendered image is crunched from high precision (f32 per color channel) down to the final output (u8 per channel in SDR). This results in subtle gradients becoming blocky due to the reduced color precision. Deband dithering applies a small amount of noise to the signal before it is "crunched", which breaks up the hard edges of blocks (bands) of color. Note that this does not add excess noise to the image, as the amount of noise is less than a single step of a color channel - just enough to break up the transition between color blocks in a gradient.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make the many foxes not unnecessarily bright. Broken since #5666.
- Fixes#6528
## Solution
- In #5666 normalisation of normals was moved from the fragment stage to the vertex stage. However, it was not added to the vertex stage for skinned normals. The many foxes are skinned and their skinned normals were not unit normals. which made them brighter. Normalising the skinned normals fixes this.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: Non-unit length skinned normals are now normalized.
This reverts commit 8429b6d6ca as discussed in #6522.
I tested that the game_menu example works as it should.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Attempting to build `bevy_tasks` produces the following error:
```
error[E0599]: no method named `is_finished` found for struct `async_executor::Task` in the current scope
--> /[...]]/bevy/crates/bevy_tasks/src/task.rs:51:16
|
51 | self.0.is_finished()
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ method not found in `async_executor::Task<T>`
```
It looks like this was introduced along with `Task::is_finished`, which delegates to `async_task::Task::is_finished`. However, the latter was only introduced in `async-task` 4.2.0; `bevy_tasks` does not explicitly depend on `async-task` but on `async-executor` ^1.3.0, which in turn depends on `async-task` ^4.0.0.
## Solution
Add an explicit dependency on `async-task` ^4.2.0.
# Objective
Copy `send_event` and friends from `World` to `WorldCell`.
Clean up `bevy_winit` using `WorldCell::send_event`.
## Changelog
Added `send_event`, `send_event_default`, and `send_event_batch` to `WorldCell`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- it would be useful to inspect these structs using reflection
## Solution
- derive and register reflect
- Note that `#[reflect(Component)]` requires `Default` (or `FromWorld`) until #6060, so I implemented `Default` for `Tonemapping` with `is_enabled: false`
# Objective
The `load_internal_asset` macro is helpful when creating rendering plugins, but it doesn't support load binary assets (like those compiled as spir-v).
## Solution
Add a `load_internal_binary_asset` macro that use `include_bytes!`.
# Objective
Fixes#5393
## Solution
- Add padding to `GlobalsUniform` / `Globals` to make it 16-byte aligned.
Still not super clear on whether this is a `naga` thing or an `encase` thing or what. But now that we're offering `globals` up to users and #5393 is not just breaking an example, maybe we should do this sort of workaround?
* Move the despawn debug log from `World::despawn` to `EntityMut::despawn`.
* Move the despawn non-existent warning log from `Commands::despawn` to `World::despawn`.
This should make logging consistent regardless of which of the three `despawn` methods is used.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Using `Reflect` we can easily switch between a specific reflection trait object, such as a `dyn Struct`, to a `dyn Reflect` object via `Reflect::as_reflect` or `Reflect::as_reflect_mut`.
```rust
fn do_something(value: &dyn Reflect) {/* ... */}
let foo: Box<dyn Struct> = Box::new(Foo::default());
do_something(foo.as_reflect());
```
However, there is no way to convert a _boxed_ reflection trait object to a `Box<dyn Reflect>`.
## Solution
Add a `Reflect::into_reflect` method which allows converting a boxed reflection trait object back into a boxed `Reflect` trait object.
```rust
fn do_something(value: Box<dyn Reflect>) {/* ... */}
let foo: Box<dyn Struct> = Box::new(Foo::default());
do_something(foo.into_reflect());
```
---
## Changelog
- Added `Reflect::into_reflect`
# Objective
Some render plugins, like [bevy-hikari](https://github.com/cryscan/bevy-hikari) require to set `CameraRenderGraph`. In order to switch between render graphs I need to insert a new `CameraRenderGraph` component. It's not very ergonomic.
## Solution
Add `CameraRenderGraph::set` like in [Name](https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/core/struct.Name.html).
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `CameraRenderGraph::set`.
# Objective
There is no way to gen an owned value of `Reflect`.
## Solution
Add it! This was originally a part of #6421, but @MrGVSV asked me to create a separate for it to implement reflect diffing.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `Reflect::reflect_owned` to get an owned version of `Reflect`.
# Objective
`NodeBundle` contains an `image` field, which can be misleading, because if you do supply an image there, nothing will be shown to screen. You need to use an `ImageBundle` instead.
## Solution
* `image` (`UiImage`) field is removed from `NodeBundle`,
* extraction stage queries now make an optional query for `UiImage`, if one is not found, use the image handle that is used as a default by `UiImage`: c019a60b39/crates/bevy_ui/src/ui_node.rs (L464)
* touching up docs for `NodeBundle` to help guide what `NodeBundle` should be used for
* renamed `entity.rs` to `node_bundle.rs` as that gives more of a hint regarding the module's purpose
* separating `camera_config` stuff from the pre-made UI node bundles so that `node_bundle.rs` makes more sense as a module name.
# Objective
- adding a new `.register` should not overwrite old type data
- separate crates should both be able to register the same type
I ran into this while debugging why `register::<Handle<T>>` removed the `ReflectHandle` type data from a prior `register_asset_reflect`.
## Solution
- make `register` do nothing if called again for the same type
- I also removed some unnecessary duplicate registrations
# Objective
- Fix an awkwardly phrased/typoed error message
- Actually tell users which file caused the error
- IMO we don't need to panic
## Solution
- Add a warning including the involved asset path when a non-image is found by `load_folder`
- Note: uses `let else` which is stable now
```
2022-11-03T14:17:59.006861Z WARN texture_atlas: Some(AssetPath { path: "textures/rpg/tiles/whatisthisdoinghere.ogg", label: None }) did not resolve to an `Image` asset.
```
# Objective
When an error causes `debug_checked_unreachable` to be called, the panic message unhelpfully points to the function definition instead of the place that caused the error.
## Solution
Add the `#[track_caller]` attribute in debug mode.
# Objective
Fixes: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/6466
Summary: The UI Scaling example dynamically scales the UI which will dynamically allocate fonts to the font atlas surpassing the protective limit, throwing a panic.
## Solution
- Set TextSettings.allow_dynamic_font_size = true for the UI Scaling example. This is the ideal solution since the dynamic changes to the UI are not continuous yet still discrete.
- Update the panic text to reflect ui scaling as a potential cause
# Objective
#6461 introduced `lto = true` as a profile setting for release builds. This is causing the `run-examples` CI task to timeout.
## Solution
Remove it.
# Objective
Bevy UI (and third party plugins) currently have no good way to position themselves after all post processing effects. They currently use the tonemapping node, but this is not adequate if there is anything after tonemapping (such as FXAA).
## Solution
Add a logical `END_MAIN_PASS_POST_PROCESSING` RenderGraph node that main pass post processing effects position themselves before, and things like UIs can position themselves after.
# Objective
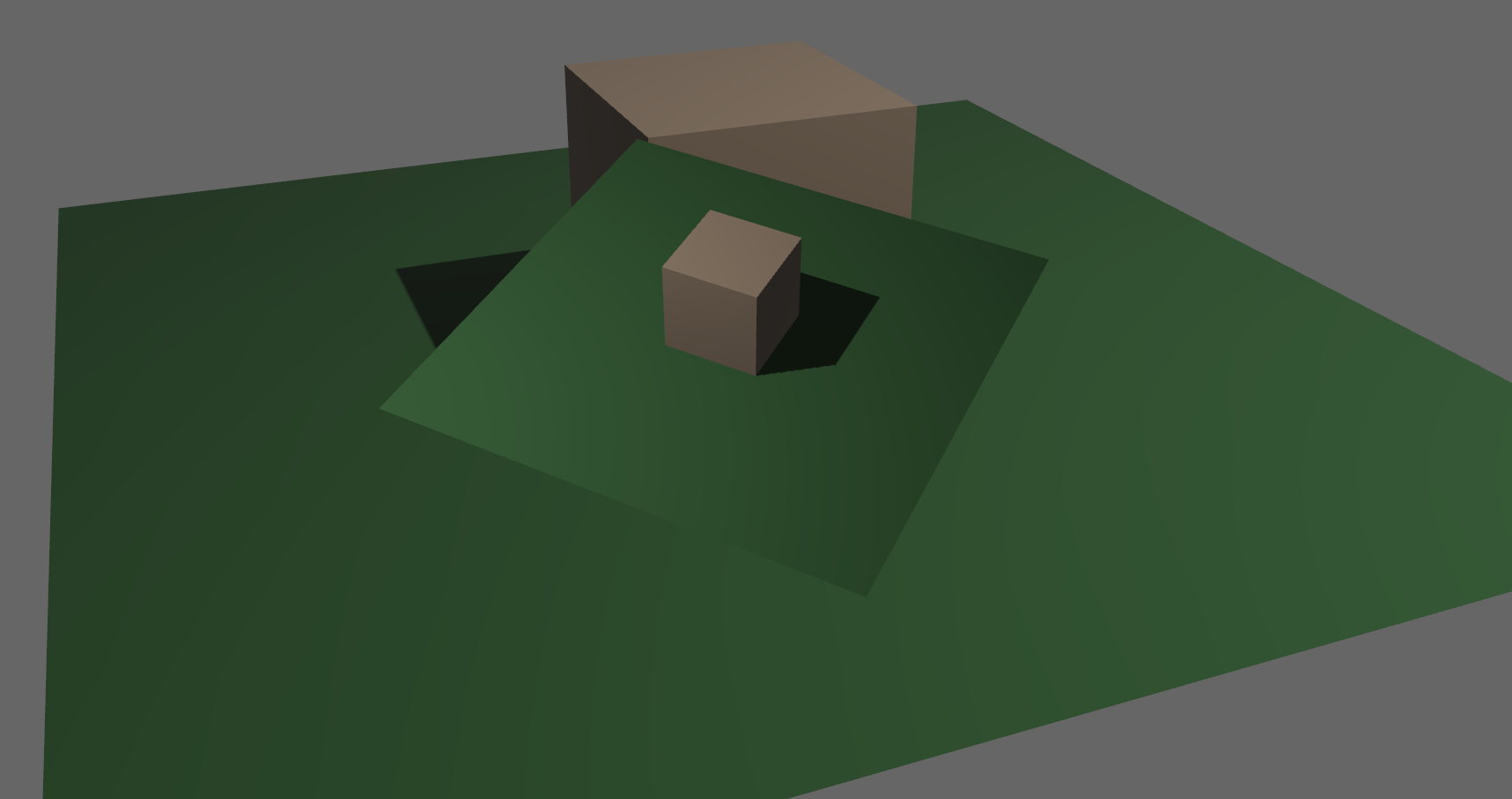
This PR fixes#5789, by enabling movable (and scalable) directional light shadow volumes.
## Solution
This PR changes `ExtractedDirectionalLight` to hold a copy of the `DirectionalLight` entity's `GlobalTransform`, instead of just a `direction` vector. This allows the shadow map volume (as defined by the light's `shadow_projection` field) to be transformed honoring translation _and_ scale transforms, and not just rotation.
It also augments the texel size calculation (used to determine the `shadow_normal_bias`) so that it now takes into account the upper bound of the x/y/z scale of the `GlobalTransform`.
This change makes the directional light extraction code more consistent with point and spot lights (that already use `transform`), and allows easily moving and scaling the shadow volume along with a player entity based on camera distance/angle, immediately enabling more real world use cases until we have a more sophisticated adaptive implementation, such as the one described in #3629.
**Note:** While it was previously possible to update the projection achieving a similar effect, depending on the light direction and distance to the origin, the fact that the shadow map camera was always positioned at the origin with a hardcoded `Vec3::Y` up value meant you would get sub-optimal or inconsistent/incorrect results.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- `DirectionalLight` shadow volumes now honor translation and scale transforms
## Migration Guide
- If your directional lights were positioned at the origin and not scaled (the default, most common scenario) no changes are needed on your part; it just works as before;
- If you previously had a system for dynamically updating directional light shadow projections, you might now be able to simplify your code by updating the directional light entity's transform instead;
- In the unlikely scenario that a scene with directional lights that previously rendered shadows correctly has missing shadows, make sure your directional lights are positioned at (0, 0, 0) and are not scaled to a size that's too large or too small.