Currently, we look up each `MeshInputUniform` index in a hash table that
maps the main entity ID to the index every frame. This is inefficient,
cache unfriendly, and unnecessary, as the `MeshInputUniform` index for
an entity remains the same from frame to frame (even if the input
uniform changes). This commit changes the `IndexSet` in the `RenderBin`
to an `IndexMap` that maps the `MainEntity` to `MeshInputUniformIndex`
(a new type that this patch adds for more type safety).
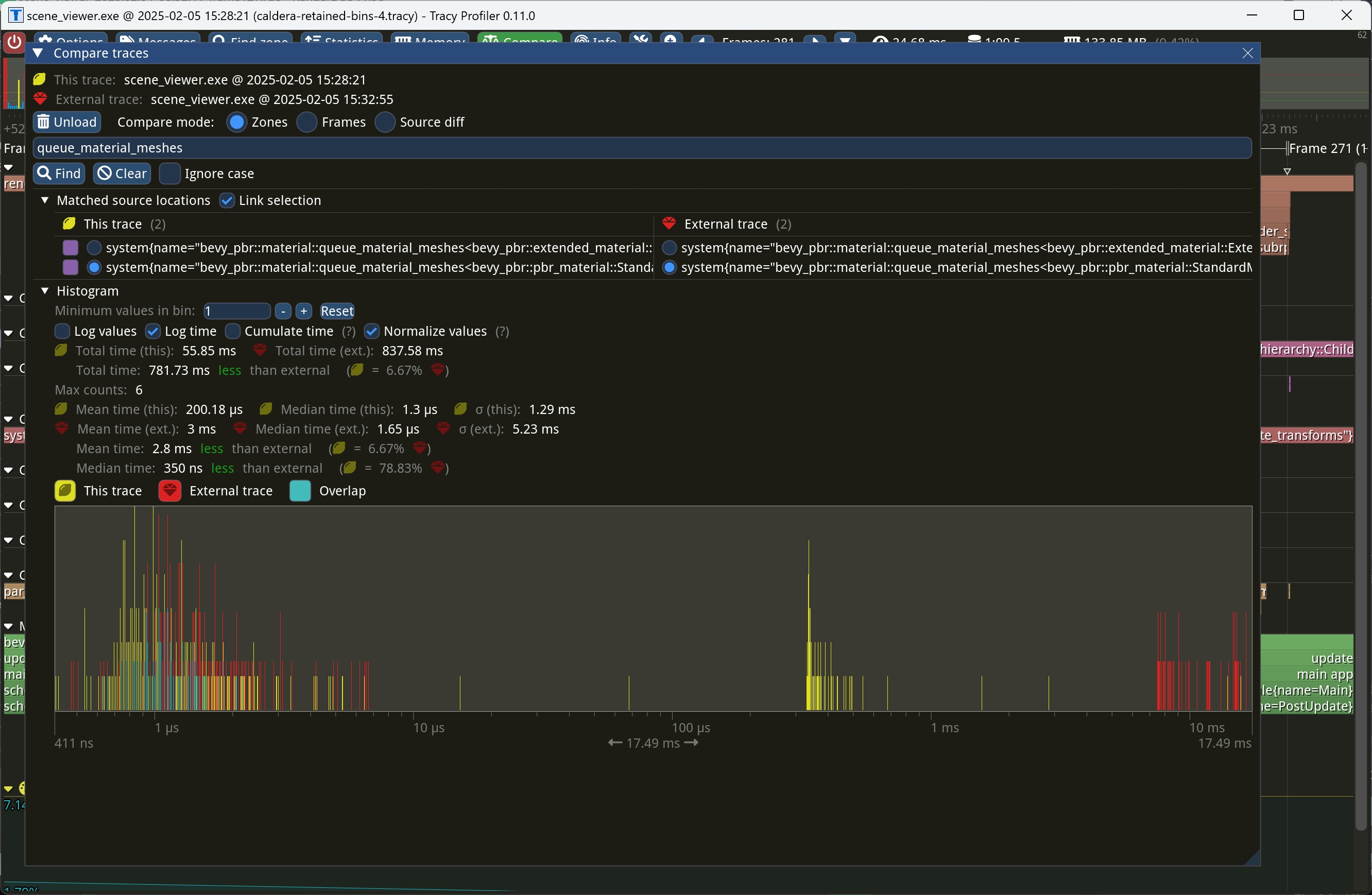
On Caldera with parallel `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`, this
patch improves that function from 3.18 ms to 2.42 ms, a 31% speedup.
This PR makes Bevy keep entities in bins from frame to frame if they
haven't changed. This reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes`
and related functions to near zero for static geometry. This patch uses
the same change tick technique that #17567 uses to detect when meshes
have changed in such a way as to require re-binning.
In order to quickly find the relevant bin for an entity when that entity
has changed, we introduce a new type of cache, the *bin key cache*. This
cache stores a mapping from main world entity ID to cached bin key, as
well as the tick of the most recent change to the entity. As we iterate
through the visible entities in `queue_material_meshes`, we check the
cache to see whether the entity needs to be re-binned. If it doesn't,
then we mark it as clean in the `valid_cached_entity_bin_keys` bit set.
If it does, then we insert it into the correct bin, and then mark the
entity as clean. At the end, all entities not marked as clean are
removed from the bins.
This patch has a dramatic effect on the rendering performance of most
benchmarks, as it effectively eliminates `queue_material_meshes` from
the profile. Note, however, that it generally simultaneously regresses
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` by a bit (not by enough to
outweigh the win, however). I believe that's because, before this patch,
`queue_material_meshes` put the bins in the CPU cache for
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` to use, while with this patch,
`batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase` must load the bins into the CPU
cache itself.
On Caldera, this reduces the time spent in `queue_material_meshes` from
5+ ms to 0.2ms-0.3ms. Note that benchmarking on that scene is very noisy
right now because of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/17535.
We won't be able to retain render phases from frame to frame if the keys
are unstable. It's not as simple as simply keying off the main world
entity, however, because some main world entities extract to multiple
render world entities. For example, directional lights extract to
multiple shadow cascades, and point lights extract to one view per
cubemap face. Therefore, we key off a new type, `RetainedViewEntity`,
which contains the main entity plus a *subview ID*.
This is part of the preparation for retained bins.
---------
Co-authored-by: ickshonpe <david.curthoys@googlemail.com>
Currently, our batchable binned items are stored in a hash table that
maps bin key, which includes the batch set key, to a list of entities.
Multidraw is handled by sorting the bin keys and accumulating adjacent
bins that can be multidrawn together (i.e. have the same batch set key)
into multidraw commands during `batch_and_prepare_binned_render_phase`.
This is reasonably efficient right now, but it will complicate future
work to retain indirect draw parameters from frame to frame. Consider
what must happen when we have retained indirect draw parameters and the
application adds a bin (i.e. a new mesh) that shares a batch set key
with some pre-existing meshes. (That is, the new mesh can be multidrawn
with the pre-existing meshes.) To be maximally efficient, our goal in
that scenario will be to update *only* the indirect draw parameters for
the batch set (i.e. multidraw command) containing the mesh that was
added, while leaving the others alone. That means that we have to
quickly locate all the bins that belong to the batch set being modified.
In the existing code, we would have to sort the list of bin keys so that
bins that can be multidrawn together become adjacent to one another in
the list. Then we would have to do a binary search through the sorted
list to find the location of the bin that was just added. Next, we would
have to widen our search to adjacent indexes that contain the same batch
set, doing expensive comparisons against the batch set key every time.
Finally, we would reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the
stored pointers to the indirect draw parameters that the bins store.
By contrast, it'd be dramatically simpler if we simply changed the way
bins are stored to first map from batch set key (i.e. multidraw command)
to the bins (i.e. meshes) within that batch set key, and then from each
individual bin to the mesh instances. That way, the scenario above in
which we add a new mesh will be simpler to handle. First, we will look
up the batch set key corresponding to that mesh in the outer map to find
an inner map corresponding to the single multidraw command that will
draw that batch set. We will know how many meshes the multidraw command
is going to draw by the size of that inner map. Then we simply need to
reallocate the indirect draw parameters and update the pointers to those
parameters within the bins as necessary. There will be no need to do any
binary search or expensive batch set key comparison: only a single hash
lookup and an iteration over the inner map to update the pointers.
This patch implements the above technique. Because we don't have
retained bins yet, this PR provides no performance benefits. However, it
opens the door to maximally efficient updates when only a small number
of meshes change from frame to frame.
The main churn that this patch causes is that the *batch set key* (which
uniquely specifies a multidraw command) and *bin key* (which uniquely
specifies a mesh *within* that multidraw command) are now separate,
instead of the batch set key being embedded *within* the bin key.
In order to isolate potential regressions, I think that at least #16890,
#16836, and #16825 should land before this PR does.
## Migration Guide
* The *batch set key* is now separate from the *bin key* in
`BinnedPhaseItem`. The batch set key is used to collect multidrawable
meshes together. If you aren't using the multidraw feature, you can
safely set the batch set key to `()`.
Currently, `check_visibility` is parameterized over a query filter that
specifies the type of potentially-visible object. This has the
unfortunate side effect that we need a separate system,
`mark_view_visibility_as_changed_if_necessary`, to trigger view
visibility change detection. That system is quite slow because it must
iterate sequentially over all entities in the scene.
This PR moves the query filter from `check_visibility` to a new
component, `VisibilityClass`. `VisibilityClass` stores a list of type
IDs, each corresponding to one of the query filters we used to use.
Because `check_visibility` is no longer specialized to the query filter
at the type level, Bevy now only needs to invoke it once, leading to
better performance as `check_visibility` can do change detection on the
fly rather than delegating it to a separate system.
This commit also has ergonomic improvements, as there's no need for
applications that want to add their own custom renderable components to
add specializations of the `check_visibility` system to the schedule.
Instead, they only need to ensure that the `ViewVisibility` component is
properly kept up to date. The recommended way to do this, and the way
that's demonstrated in the `custom_phase_item` and
`specialized_mesh_pipeline` examples, is to make `ViewVisibility` a
required component and to add the type ID to it in a component add hook.
This patch does this for `Mesh3d`, `Mesh2d`, `Sprite`, `Light`, and
`Node`, which means that most app code doesn't need to change at all.
Note that, although this patch has a large impact on the performance of
visibility determination, it doesn't actually improve the end-to-end
frame time of `many_cubes`. That's because the render world was already
effectively hiding the latency from
`mark_view_visibility_as_changed_if_necessary`. This patch is, however,
necessary for *further* improvements to `many_cubes` performance.
`many_cubes` trace before:

`many_cubes` trace after:

## Migration Guide
* `check_visibility` no longer takes a `QueryFilter`, and there's no
need to add it manually to your app schedule anymore for custom
rendering items. Instead, entities with custom renderable components
should add the appropriate type IDs to `VisibilityClass`. See
`custom_phase_item` for an example.
This commit allows Bevy to bind 16 lightmaps at a time, if the current
platform supports bindless textures. Naturally, if bindless textures
aren't supported, Bevy falls back to binding only a single lightmap at a
time. As lightmaps are usually heavily atlased, I doubt many scenes will
use more than 16 lightmap textures.
This has little performance impact now, but it's desirable for us to
reap the benefits of multidraw and bindless textures on scenes that use
lightmaps. Otherwise, we might have to break batches in order to switch
those lightmaps.
Additionally, this PR slightly reduces the cost of binning because it
makes the lightmap index in `Opaque3dBinKey` 32 bits instead of an
`AssetId`.
## Migration Guide
* The `Opaque3dBinKey::lightmap_image` field is now
`Opaque3dBinKey::lightmap_slab`, which is a lightweight identifier for
an entire binding array of lightmaps.
This commit adds support for *multidraw*, which is a feature that allows
multiple meshes to be drawn in a single drawcall. `wgpu` currently
implements multidraw on Vulkan, so this feature is only enabled there.
Multiple meshes can be drawn at once if they're in the same vertex and
index buffers and are otherwise placed in the same bin. (Thus, for
example, at present the materials and textures must be identical, but
see #16368.) Multidraw is a significant performance improvement during
the draw phase because it reduces the number of rebindings, as well as
the number of drawcalls.
This feature is currently only enabled when GPU culling is used: i.e.
when `GpuCulling` is present on a camera. Therefore, if you run for
example `scene_viewer`, you will not see any performance improvements,
because `scene_viewer` doesn't add the `GpuCulling` component to its
camera.
Additionally, the multidraw feature is only implemented for opaque 3D
meshes and not for shadows or 2D meshes. I plan to make GPU culling the
default and to extend the feature to shadows in the future. Also, in the
future I suspect that polyfilling multidraw on APIs that don't support
it will be fruitful, as even without driver-level support use of
multidraw allows us to avoid expensive `wgpu` rebindings.
This patch adds the infrastructure necessary for Bevy to support
*bindless resources*, by adding a new `#[bindless]` attribute to
`AsBindGroup`.
Classically, only a single texture (or sampler, or buffer) can be
attached to each shader binding. This means that switching materials
requires breaking a batch and issuing a new drawcall, even if the mesh
is otherwise identical. This adds significant overhead not only in the
driver but also in `wgpu`, as switching bind groups increases the amount
of validation work that `wgpu` must do.
*Bindless resources* are the typical solution to this problem. Instead
of switching bindings between each texture, the renderer instead
supplies a large *array* of all textures in the scene up front, and the
material contains an index into that array. This pattern is repeated for
buffers and samplers as well. The renderer now no longer needs to switch
binding descriptor sets while drawing the scene.
Unfortunately, as things currently stand, this approach won't quite work
for Bevy. Two aspects of `wgpu` conspire to make this ideal approach
unacceptably slow:
1. In the DX12 backend, all binding arrays (bindless resources) must
have a constant size declared in the shader, and all textures in an
array must be bound to actual textures. Changing the size requires a
recompile.
2. Changing even one texture incurs revalidation of all textures, a
process that takes time that's linear in the total size of the binding
array.
This means that declaring a large array of textures big enough to
encompass the entire scene is presently unacceptably slow. For example,
if you declare 4096 textures, then `wgpu` will have to revalidate all
4096 textures if even a single one changes. This process can take
multiple frames.
To work around this problem, this PR groups bindless resources into
small *slabs* and maintains a free list for each. The size of each slab
for the bindless arrays associated with a material is specified via the
`#[bindless(N)]` attribute. For instance, consider the following
declaration:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[bindless(16)]
struct MyMaterial {
#[buffer(0)]
color: Vec4,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
diffuse: Handle<Image>,
}
```
The `#[bindless(N)]` attribute specifies that, if bindless arrays are
supported on the current platform, each resource becomes a binding array
of N instances of that resource. So, for `MyMaterial` above, the `color`
attribute is exposed to the shader as `binding_array<vec4<f32>, 16>`,
the `diffuse` texture is exposed to the shader as
`binding_array<texture_2d<f32>, 16>`, and the `diffuse` sampler is
exposed to the shader as `binding_array<sampler, 16>`. Inside the
material's vertex and fragment shaders, the applicable index is
available via the `material_bind_group_slot` field of the `Mesh`
structure. So, for instance, you can access the current color like so:
```wgsl
// `uniform` binding arrays are a non-sequitur, so `uniform` is automatically promoted
// to `storage` in bindless mode.
@group(2) @binding(0) var<storage> material_color: binding_array<Color, 4>;
...
@fragment
fn fragment(in: VertexOutput) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
let color = material_color[mesh[in.instance_index].material_bind_group_slot];
...
}
```
Note that portable shader code can't guarantee that the current platform
supports bindless textures. Indeed, bindless mode is only available in
Vulkan and DX12. The `BINDLESS` shader definition is available for your
use to determine whether you're on a bindless platform or not. Thus a
portable version of the shader above would look like:
```wgsl
#ifdef BINDLESS
@group(2) @binding(0) var<storage> material_color: binding_array<Color, 4>;
#else // BINDLESS
@group(2) @binding(0) var<uniform> material_color: Color;
#endif // BINDLESS
...
@fragment
fn fragment(in: VertexOutput) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
#ifdef BINDLESS
let color = material_color[mesh[in.instance_index].material_bind_group_slot];
#else // BINDLESS
let color = material_color;
#endif // BINDLESS
...
}
```
Importantly, this PR *doesn't* update `StandardMaterial` to be bindless.
So, for example, `scene_viewer` will currently not run any faster. I
intend to update `StandardMaterial` to use bindless mode in a follow-up
patch.
A new example, `shaders/shader_material_bindless`, has been added to
demonstrate how to use this new feature.
Here's a Tracy profile of `submit_graph_commands` of this patch and an
additional patch (not submitted yet) that makes `StandardMaterial` use
bindless. Red is those patches; yellow is `main`. The scene was Bistro
Exterior with a hack that forces all textures to opaque. You can see a
1.47x mean speedup.

## Migration Guide
* `RenderAssets::prepare_asset` now takes an `AssetId` parameter.
* Bin keys now have Bevy-specific material bind group indices instead of
`wgpu` material bind group IDs, as part of the bindless change. Use the
new `MaterialBindGroupAllocator` to map from bind group index to bind
group ID.
# Objective
Glam has some common and useful types and helpers that are not in the
prelude of `bevy_math`. This includes shorthand constructors like
`vec3`, or even `Vec3A`, the aligned version of `Vec3`.
```rust
// The "normal" way to create a 3D vector
let vec = Vec3::new(2.0, 1.0, -3.0);
// Shorthand version
let vec = vec3(2.0, 1.0, -3.0);
```
## Solution
Add the following types and methods to the prelude:
- `vec2`, `vec3`, `vec3a`, `vec4`
- `uvec2`, `uvec3`, `uvec4`
- `ivec2`, `ivec3`, `ivec4`
- `bvec2`, `bvec3`, `bvec3a`, `bvec4`, `bvec4a`
- `mat2`, `mat3`, `mat3a`, `mat4`
- `quat` (not sure if anyone uses this, but for consistency)
- `Vec3A`
- `BVec3A`, `BVec4A`
- `Mat3A`
I did not add the u16, i16, or f64 variants like `dvec2`, since there
are currently no existing types like those in the prelude.
The shorthand constructors are currently used a lot in some places in
Bevy, and not at all in others. In a follow-up, we might want to
consider if we have a preference for the shorthand, and make a PR to
change the codebase to use it more consistently.
# Objective
Fixes#15940
## Solution
Remove the `pub use` and fix the compile errors.
Make `bevy_image` available as `bevy::image`.
## Testing
Feature Frenzy would be good here! Maybe I'll learn how to use it if I
have some time this weekend, or maybe a reviewer can use it.
## Migration Guide
Use `bevy_image` instead of `bevy_render::texture` items.
---------
Co-authored-by: chompaa <antony.m.3012@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- wgpu 0.20 made workgroup vars stop being zero-init by default. this
broke some applications (cough foresight cough) and now we workaround
it. wgpu exposes a compilation option that zero initializes workgroup
memory by default, but bevy does not expose it.
## Solution
- expose the compilation option wgpu gives us
## Testing
- ran examples: 3d_scene, compute_shader_game_of_life, gpu_readback,
lines, specialized_mesh_pipeline. they all work
- confirmed fix for our own problems
---
</details>
## Migration Guide
- add `zero_initialize_workgroup_memory: false,` to
`ComputePipelineDescriptor` or `RenderPipelineDescriptor` structs to
preserve 0.14 functionality, add `zero_initialize_workgroup_memory:
true,` to restore bevy 0.13 functionality.
# Objective
- Required components replace bundles, but `SpatialBundle` is yet to be
deprecated
## Solution
- Deprecate `SpatialBundle`
- Insert `Transform` and `Visibility` instead in examples using it
- In `spawn` or `insert` inserting a default `Transform` or `Visibility`
with component already requiring either, remove those components from
the tuple
## Testing
- Did you test these changes? If so, how?
Yes, I ran the examples I changed and tests
- Are there any parts that need more testing?
The `gamepad_viewer` and and `custom_shader_instancing` examples don't
work as intended due to entirely unrelated code, didn't check main.
- How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything
specific they need to know?
Run examples, or just check that all spawned values are identical
- If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are
there any important ones you can't test?
Linux, wayland trough x11 (cause that's the default feature)
---
## Migration Guide
`SpatialBundle` is now deprecated, insert `Transform` and `Visibility`
instead which will automatically insert all other components that were
in the bundle. If you do not specify these values and any other
components in your `spawn`/`insert` call already requires either of
these components you can leave that one out.
before:
```rust
commands.spawn(SpatialBundle::default());
```
after:
```rust
commands.spawn((Transform::default(), Visibility::default());
```
# Objective
In the Render World, there are a number of collections that are derived
from Main World entities and are used to drive rendering. The most
notable are:
- `VisibleEntities`, which is generated in the `check_visibility` system
and contains visible entities for a view.
- `ExtractedInstances`, which maps entity ids to asset ids.
In the old model, these collections were trivially kept in sync -- any
extracted phase item could look itself up because the render entity id
was guaranteed to always match the corresponding main world id.
After #15320, this became much more complicated, and was leading to a
number of subtle bugs in the Render World. The main rendering systems,
i.e. `queue_material_meshes` and `queue_material2d_meshes`, follow a
similar pattern:
```rust
for visible_entity in visible_entities.iter::<With<Mesh2d>>() {
let Some(mesh_instance) = render_mesh_instances.get_mut(visible_entity) else {
continue;
};
// Look some more stuff up and specialize the pipeline...
let bin_key = Opaque2dBinKey {
pipeline: pipeline_id,
draw_function: draw_opaque_2d,
asset_id: mesh_instance.mesh_asset_id.into(),
material_bind_group_id: material_2d.get_bind_group_id().0,
};
opaque_phase.add(
bin_key,
*visible_entity,
BinnedRenderPhaseType::mesh(mesh_instance.automatic_batching),
);
}
```
In this case, `visible_entities` and `render_mesh_instances` are both
collections that are created and keyed by Main World entity ids, and so
this lookup happens to work by coincidence. However, there is a major
unintentional bug here: namely, because `visible_entities` is a
collection of Main World ids, the phase item being queued is created
with a Main World id rather than its correct Render World id.
This happens to not break mesh rendering because the render commands
used for drawing meshes do not access the `ItemQuery` parameter, but
demonstrates the confusion that is now possible: our UI phase items are
correctly being queued with Render World ids while our meshes aren't.
Additionally, this makes it very easy and error prone to use the wrong
entity id to look up things like assets. For example, if instead we
ignored visibility checks and queued our meshes via a query, we'd have
to be extra careful to use `&MainEntity` instead of the natural
`Entity`.
## Solution
Make all collections that are derived from Main World data use
`MainEntity` as their key, to ensure type safety and avoid accidentally
looking up data with the wrong entity id:
```rust
pub type MainEntityHashMap<V> = hashbrown::HashMap<MainEntity, V, EntityHash>;
```
Additionally, we make all `PhaseItem` be able to provide both their Main
and Render World ids, to allow render phase implementors maximum
flexibility as to what id should be used to look up data.
You can think of this like tracking at the type level whether something
in the Render World should use it's "primary key", i.e. entity id, or
needs to use a foreign key, i.e. `MainEntity`.
## Testing
##### TODO:
This will require extensive testing to make sure things didn't break!
Additionally, some extraction logic has become more complicated and
needs to be checked for regressions.
## Migration Guide
With the advent of the retained render world, collections that contain
references to `Entity` that are extracted into the render world have
been changed to contain `MainEntity` in order to prevent errors where a
render world entity id is used to look up an item by accident. Custom
rendering code may need to be changed to query for `&MainEntity` in
order to look up the correct item from such a collection. Additionally,
users who implement their own extraction logic for collections of main
world entity should strongly consider extracting into a different
collection that uses `MainEntity` as a key.
Additionally, render phases now require specifying both the `Entity` and
`MainEntity` for a given `PhaseItem`. Custom render phases should ensure
`MainEntity` is available when queuing a phase item.
# Objective
Yet another PR for migrating stuff to required components. This time,
cameras!
## Solution
As per the [selected
proposal](https://hackmd.io/tsYID4CGRiWxzsgawzxG_g#Combined-Proposal-1-Selected),
deprecate `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` in favor of `Camera2d`
and `Camera3d`.
Adding a `Camera` without `Camera2d` or `Camera3d` now logs a warning,
as suggested by Cart [on
Discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1264881140007702558/1291506402832945273).
I would personally like cameras to work a bit differently and be split
into a few more components, to avoid some footguns and confusing
semantics, but that is more controversial, and shouldn't block this core
migration.
## Testing
I ran a few 2D and 3D examples, and tried cameras with and without
render graphs.
---
## Migration Guide
`Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` have been deprecated in favor of
`Camera2d` and `Camera3d`. Inserting them will now also insert the other
components required by them automatically.
# Objective
Fixes#14782
## Solution
Enable the lint and fix all upcoming hints (`--fix`). Also tried to
figure out the false-positive (see review comment). Maybe split this PR
up into multiple parts where only the last one enables the lint, so some
can already be merged resulting in less many files touched / less
potential for merge conflicts?
Currently, there are some cases where it might be easier to read the
code with the qualifier, so perhaps remove the import of it and adapt
its cases? In the current stage it's just a plain adoption of the
suggestions in order to have a base to discuss.
## Testing
`cargo clippy` and `cargo run -p ci` are happy.
Switches `Msaa` from being a globally configured resource to a per
camera view component.
Closes#7194
# Objective
Allow individual views to describe their own MSAA settings. For example,
when rendering to different windows or to different parts of the same
view.
## Solution
Make `Msaa` a component that is required on all camera bundles.
## Testing
Ran a variety of examples to ensure that nothing broke.
TODO:
- [ ] Make sure android still works per previous comment in
`extract_windows`.
---
## Migration Guide
`Msaa` is no longer configured as a global resource, and should be
specified on each spawned camera if a non-default setting is desired.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com>
As reported in #14004, many third-party plugins, such as Hanabi, enqueue
entities that don't have meshes into render phases. However, the
introduction of indirect mode added a dependency on mesh-specific data,
breaking this workflow. This is because GPU preprocessing requires that
the render phases manage indirect draw parameters, which don't apply to
objects that aren't meshes. The existing code skips over binned entities
that don't have indirect draw parameters, which causes the rendering to
be skipped for such objects.
To support this workflow, this commit adds a new field,
`non_mesh_items`, to `BinnedRenderPhase`. This field contains a simple
list of (bin key, entity) pairs. After drawing batchable and unbatchable
objects, the non-mesh items are drawn one after another. Bevy itself
doesn't enqueue any items into this list; it exists solely for the
application and/or plugins to use.
Additionally, this commit switches the asset ID in the standard bin keys
to be an untyped asset ID rather than that of a mesh. This allows more
flexibility, allowing bins to be keyed off any type of asset.
This patch adds a new example, `custom_phase_item`, which simultaneously
serves to demonstrate how to use this new feature and to act as a
regression test so this doesn't break again.
Fixes#14004.
## Changelog
### Added
* `BinnedRenderPhase` now contains a `non_mesh_items` field for plugins
to add custom items to.