2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
//! Animation for the game engine Bevy
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#![warn(missing_docs)]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
use std::ops::Deref;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
use bevy_app::{App, CoreStage, Plugin};
|
|
|
|
|
use bevy_asset::{AddAsset, Assets, Handle};
|
2022-05-26 00:27:18 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_core::Name;
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_ecs::{
|
|
|
|
|
change_detection::DetectChanges,
|
|
|
|
|
entity::Entity,
|
|
|
|
|
prelude::Component,
|
|
|
|
|
reflect::ReflectComponent,
|

Exclusive Systems Now Implement `System`. Flexible Exclusive System Params (#6083)
# Objective
The [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) involves allowing exclusive systems to be referenced and ordered relative to parallel systems. We've agreed that unifying systems under `System` is the right move.
This is an alternative to #4166 (see rationale in the comments I left there). Note that this builds on the learnings established there (and borrows some patterns).
## Solution
This unifies parallel and exclusive systems under the shared `System` trait, removing the old `ExclusiveSystem` trait / impls. This is accomplished by adding a new `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` impl similar to `FunctionSystem`. It is backed by `ExclusiveSystemParam`, which is similar to `SystemParam`. There is a new flattened out SystemContainer api (which cuts out a lot of trait and type complexity).
This means you can remove all cases of `exclusive_system()`:
```rust
// before
commands.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system());
// after
commands.add_system(some_system);
```
I've also implemented `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `&mut QueryState` and `&mut SystemState`, which makes this possible in exclusive systems:
```rust
fn some_exclusive_system(
world: &mut World,
transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>,
state: &mut SystemState<(Res<Time>, Query<&Player>)>,
) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
println!("{transform:?}");
}
let (time, players) = state.get(world);
for player in players.iter() {
println!("{player:?}");
}
}
```
Note that "exclusive function systems" assume `&mut World` is present (and the first param). I think this is a fair assumption, given that the presence of `&mut World` is what defines the need for an exclusive system.
I added some targeted SystemParam `static` constraints, which removed the need for this:
``` rust
fn some_exclusive_system(state: &mut SystemState<(Res<'static, Time>, Query<&'static Player>)>) {}
```
## Related
- #2923
- #3001
- #3946
## Changelog
- `ExclusiveSystem` trait (and implementations) has been removed in favor of sharing the `System` trait.
- `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveSystemParam` were added, enabling flexible exclusive function systems
- `&mut SystemState` and `&mut QueryState` now implement `ExclusiveSystemParam`
- Exclusive and parallel System configuration is now done via a unified `SystemDescriptor`, `IntoSystemDescriptor`, and `SystemContainer` api.
## Migration Guide
Calling `.exclusive_system()` is no longer required (or supported) for converting exclusive system functions to exclusive systems:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system.exclusive_system());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system);
```
Converting "normal" parallel systems to exclusive systems is done by calling the exclusive ordering apis:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system().at_end());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_system.at_end());
```
Query state in exclusive systems can now be cached via ExclusiveSystemParams, which should be preferred for clarity and performance reasons:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
fn some_system(world: &mut World) {
let mut transforms = world.query::<&Transform>();
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
// New (0.9)
fn some_system(world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
```
2022-09-26 23:57:07 +00:00
|
|
|
schedule::IntoSystemDescriptor,
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
system::{Query, Res},
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
2022-07-10 20:29:06 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_hierarchy::Children;
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_math::{Quat, Vec3};
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective
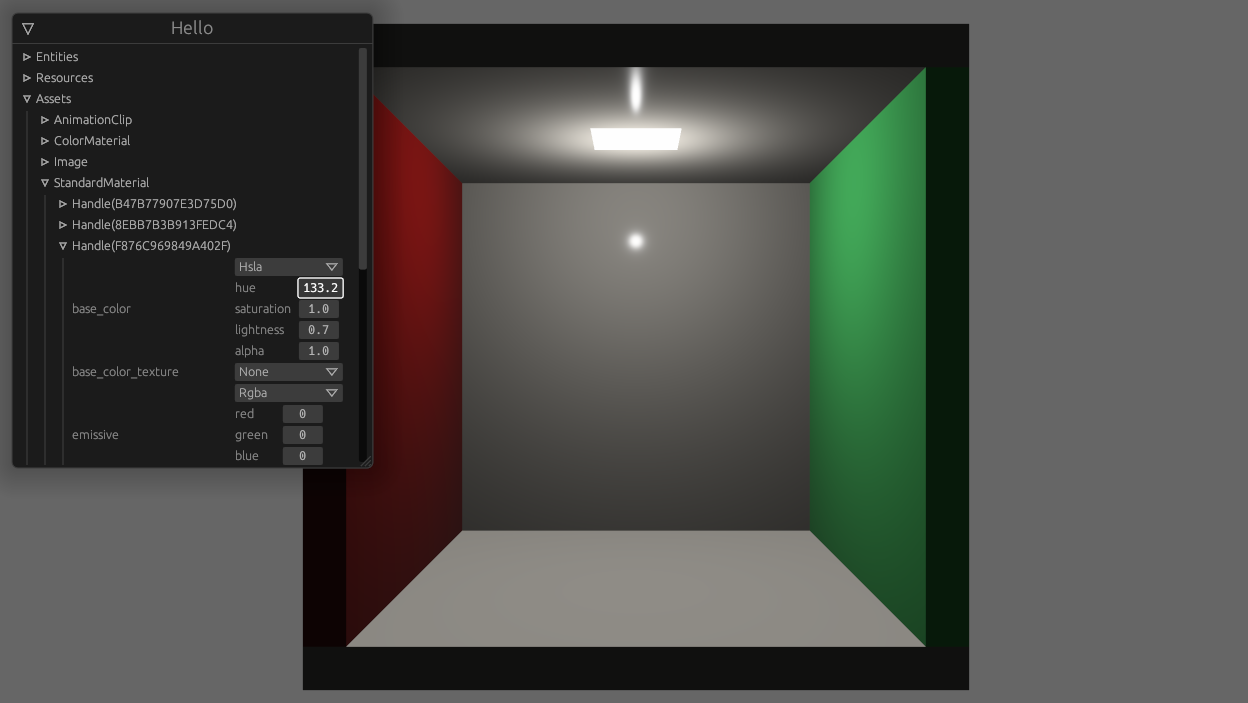
^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_reflect::{FromReflect, Reflect, TypeUuid};
|
2022-05-26 00:27:18 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_time::Time;
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_transform::{prelude::Transform, TransformSystem};
|
|
|
|
|
use bevy_utils::{tracing::warn, HashMap};
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[allow(missing_docs)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub mod prelude {
|
|
|
|
|
#[doc(hidden)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub use crate::{
|
|
|
|
|
AnimationClip, AnimationPlayer, AnimationPlugin, EntityPath, Keyframes, VariableCurve,
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// List of keyframes for one of the attribute of a [`Transform`].
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective

^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect, Clone, Debug)]
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
pub enum Keyframes {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Keyframes for rotation.
|
|
|
|
|
Rotation(Vec<Quat>),
|
|
|
|
|
/// Keyframes for translation.
|
|
|
|
|
Translation(Vec<Vec3>),
|
|
|
|
|
/// Keyframes for scale.
|
|
|
|
|
Scale(Vec<Vec3>),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Describes how an attribute of a [`Transform`] should be animated.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// `keyframe_timestamps` and `keyframes` should have the same length.
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective

^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect, Clone, Debug)]
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
pub struct VariableCurve {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Timestamp for each of the keyframes.
|
|
|
|
|
pub keyframe_timestamps: Vec<f32>,
|
|
|
|
|
/// List of the keyframes.
|
|
|
|
|
pub keyframes: Keyframes,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Path to an entity, with [`Name`]s. Each entity in a path must have a name.
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective

^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect, Clone, Debug, Hash, PartialEq, Eq, Default)]
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
pub struct EntityPath {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Parts of the path
|
|
|
|
|
pub parts: Vec<Name>,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// A list of [`VariableCurve`], and the [`EntityPath`] to which they apply.
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective

^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect, Clone, TypeUuid, Debug, Default)]
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
#[uuid = "d81b7179-0448-4eb0-89fe-c067222725bf"]
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct AnimationClip {
|
|
|
|
|
curves: HashMap<EntityPath, Vec<VariableCurve>>,
|
|
|
|
|
duration: f32,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl AnimationClip {
|
|
|
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
|
|
|
/// Hashmap of the [`VariableCurve`]s per [`EntityPath`].
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn curves(&self) -> &HashMap<EntityPath, Vec<VariableCurve>> {
|
|
|
|
|
&self.curves
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-04-27 17:37:30 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Duration of the clip, represented in seconds
|
2022-04-27 23:44:06 +00:00
|
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn duration(&self) -> f32 {
|
|
|
|
|
self.duration
|
2022-04-27 17:37:30 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Add a [`VariableCurve`] to an [`EntityPath`].
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn add_curve_to_path(&mut self, path: EntityPath, curve: VariableCurve) {
|
|
|
|
|
// Update the duration of the animation by this curve duration if it's longer
|
|
|
|
|
self.duration = self
|
|
|
|
|
.duration
|
|
|
|
|
.max(*curve.keyframe_timestamps.last().unwrap_or(&0.0));
|
|
|
|
|
self.curves.entry(path).or_default().push(curve);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Animation controls
|
|
|
|
|
#[derive(Component, Reflect)]
|
|
|
|
|
#[reflect(Component)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct AnimationPlayer {
|
|
|
|
|
paused: bool,
|
|
|
|
|
repeat: bool,
|
|
|
|
|
speed: f32,
|
|
|
|
|
elapsed: f32,
|
|
|
|
|
animation_clip: Handle<AnimationClip>,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl Default for AnimationPlayer {
|
|
|
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
paused: false,
|
|
|
|
|
repeat: false,
|
|
|
|
|
speed: 1.0,
|
|
|
|
|
elapsed: 0.0,
|
|
|
|
|
animation_clip: Default::default(),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl AnimationPlayer {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Start playing an animation, resetting state of the player
|
2022-10-24 21:01:09 +00:00
|
|
|
pub fn start(&mut self, handle: Handle<AnimationClip>) -> &mut Self {
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
*self = Self {
|
|
|
|
|
animation_clip: handle,
|
|
|
|
|
..Default::default()
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-10-24 21:01:09 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Start playing an animation, resetting state of the player, unless the requested animation is already playing.
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn play(&mut self, handle: Handle<AnimationClip>) -> &mut Self {
|
|
|
|
|
if self.animation_clip != handle || self.is_paused() {
|
|
|
|
|
self.start(handle);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Set the animation to repeat
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn repeat(&mut self) -> &mut Self {
|
|
|
|
|
self.repeat = true;
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Stop the animation from repeating
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn stop_repeating(&mut self) -> &mut Self {
|
|
|
|
|
self.repeat = false;
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Pause the animation
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn pause(&mut self) {
|
|
|
|
|
self.paused = true;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Unpause the animation
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn resume(&mut self) {
|
|
|
|
|
self.paused = false;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Is the animation paused
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn is_paused(&self) -> bool {
|
|
|
|
|
self.paused
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Speed of the animation playback
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn speed(&self) -> f32 {
|
|
|
|
|
self.speed
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Set the speed of the animation playback
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn set_speed(&mut self, speed: f32) -> &mut Self {
|
|
|
|
|
self.speed = speed;
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Time elapsed playing the animation
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn elapsed(&self) -> f32 {
|
|
|
|
|
self.elapsed
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Seek to a specific time in the animation
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn set_elapsed(&mut self, elapsed: f32) -> &mut Self {
|
|
|
|
|
self.elapsed = elapsed;
|
|
|
|
|
self
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// System that will play all animations, using any entity with a [`AnimationPlayer`]
|
|
|
|
|
/// and a [`Handle<AnimationClip>`] as an animation root
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn animation_player(
|
|
|
|
|
time: Res<Time>,
|
|
|
|
|
animations: Res<Assets<AnimationClip>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut animation_players: Query<(Entity, &mut AnimationPlayer)>,
|
|
|
|
|
names: Query<&Name>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut transforms: Query<&mut Transform>,
|
|
|
|
|
children: Query<&Children>,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
2022-07-11 15:28:50 +00:00
|
|
|
for (entity, mut player) in &mut animation_players {
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
if let Some(animation_clip) = animations.get(&player.animation_clip) {
|
|
|
|
|
// Continue if paused unless the `AnimationPlayer` was changed
|
|
|
|
|
// This allow the animation to still be updated if the player.elapsed field was manually updated in pause
|
|
|
|
|
if player.paused && !player.is_changed() {
|
|
|
|
|
continue;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
if !player.paused {
|
|
|
|
|
player.elapsed += time.delta_seconds() * player.speed;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
let mut elapsed = player.elapsed;
|
|
|
|
|
if player.repeat {
|
|
|
|
|
elapsed %= animation_clip.duration;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
if elapsed < 0.0 {
|
|
|
|
|
elapsed += animation_clip.duration;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
'entity: for (path, curves) in &animation_clip.curves {
|
|
|
|
|
// PERF: finding the target entity can be optimised
|
|
|
|
|
let mut current_entity = entity;
|
|
|
|
|
// Ignore the first name, it is the root node which we already have
|
|
|
|
|
for part in path.parts.iter().skip(1) {
|
|
|
|
|
let mut found = false;
|
|
|
|
|
if let Ok(children) = children.get(current_entity) {
|
|
|
|
|
for child in children.deref() {
|
|
|
|
|
if let Ok(name) = names.get(*child) {
|
|
|
|
|
if name == part {
|
|
|
|
|
// Found a children with the right name, continue to the next part
|
|
|
|
|
current_entity = *child;
|
|
|
|
|
found = true;
|
|
|
|
|
break;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
if !found {
|
|
|
|
|
warn!("Entity not found for path {:?} on part {:?}", path, part);
|
|
|
|
|
continue 'entity;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
if let Ok(mut transform) = transforms.get_mut(current_entity) {
|
|
|
|
|
for curve in curves {
|
2022-04-04 19:45:51 +00:00
|
|
|
// Some curves have only one keyframe used to set a transform
|
|
|
|
|
if curve.keyframe_timestamps.len() == 1 {
|
|
|
|
|
match &curve.keyframes {
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Rotation(keyframes) => transform.rotation = keyframes[0],
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Translation(keyframes) => {
|
2022-05-31 01:38:07 +00:00
|
|
|
transform.translation = keyframes[0];
|
2022-04-04 19:45:51 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Scale(keyframes) => transform.scale = keyframes[0],
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
continue;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
// Find the current keyframe
|
|
|
|
|
// PERF: finding the current keyframe can be optimised
|
|
|
|
|
let step_start = match curve
|
|
|
|
|
.keyframe_timestamps
|
|
|
|
|
.binary_search_by(|probe| probe.partial_cmp(&elapsed).unwrap())
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
2022-10-17 16:42:34 +00:00
|
|
|
Ok(n) if n >= curve.keyframe_timestamps.len() - 1 => continue, // this curve is finished
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
Ok(i) => i,
|
|
|
|
|
Err(0) => continue, // this curve isn't started yet
|
|
|
|
|
Err(n) if n > curve.keyframe_timestamps.len() - 1 => continue, // this curve is finished
|
|
|
|
|
Err(i) => i - 1,
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
let ts_start = curve.keyframe_timestamps[step_start];
|
|
|
|
|
let ts_end = curve.keyframe_timestamps[step_start + 1];
|
|
|
|
|
let lerp = (elapsed - ts_start) / (ts_end - ts_start);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Apply the keyframe
|
|
|
|
|
match &curve.keyframes {
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Rotation(keyframes) => {
|
|
|
|
|
let rot_start = keyframes[step_start];
|
|
|
|
|
let mut rot_end = keyframes[step_start + 1];
|
|
|
|
|
// Choose the smallest angle for the rotation
|
|
|
|
|
if rot_end.dot(rot_start) < 0.0 {
|
|
|
|
|
rot_end = -rot_end;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
// Rotations are using a spherical linear interpolation
|
2022-07-01 03:58:54 +00:00
|
|
|
transform.rotation =
|
|
|
|
|
rot_start.normalize().slerp(rot_end.normalize(), lerp);
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Translation(keyframes) => {
|
|
|
|
|
let translation_start = keyframes[step_start];
|
|
|
|
|
let translation_end = keyframes[step_start + 1];
|
|
|
|
|
let result = translation_start.lerp(translation_end, lerp);
|
|
|
|
|
transform.translation = result;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Keyframes::Scale(keyframes) => {
|
|
|
|
|
let scale_start = keyframes[step_start];
|
|
|
|
|
let scale_end = keyframes[step_start + 1];
|
|
|
|
|
let result = scale_start.lerp(scale_end, lerp);
|
|
|
|
|
transform.scale = result;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Adds animation support to an app
|
|
|
|
|
#[derive(Default)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct AnimationPlugin {}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl Plugin for AnimationPlugin {
|
|
|
|
|
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
|
|
|
|
|
app.add_asset::<AnimationClip>()
|

add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` (#5923)
# Objective

^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
2022-10-28 20:42:33 +00:00
|
|
|
.register_asset_reflect::<AnimationClip>()
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
.register_type::<AnimationPlayer>()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_system_to_stage(
|
|
|
|
|
CoreStage::PostUpdate,
|
2022-07-10 20:29:06 +00:00
|
|
|
animation_player.before(TransformSystem::TransformPropagate),
|
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|