
Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
mod as_bind_group;
|
2023-01-30 18:12:16 +00:00
|
|
|
mod extract_component;
|
2022-05-30 18:36:03 +00:00
|
|
|
mod extract_resource;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
use bevy_macro_utils::BevyManifest;
|
|
|
|
|
use proc_macro::TokenStream;
|

Derive AsBindGroup Improvements: Better errors, more options, update examples (#5364)
# Objective
- Provide better compile-time errors and diagnostics.
- Add more options to allow more textures types and sampler types.
- Update array_texture example to use upgraded AsBindGroup derive macro.
## Solution
Split out the parsing of the inner struct/field attributes (the inside part of a `#[foo(...)]` attribute) for better clarity
Parse the binding index for all inner attributes, as it is part of all attributes (`#[foo(0, ...)`), then allow each attribute implementer to parse the rest of the attribute metadata as needed. This should make it very trivial to extend/change if needed in the future.
Replaced invocations of `panic!` with the `syn::Error` type, providing fine-grained errors that retains span information. This provides much nicer compile-time errors, and even better IDE errors.
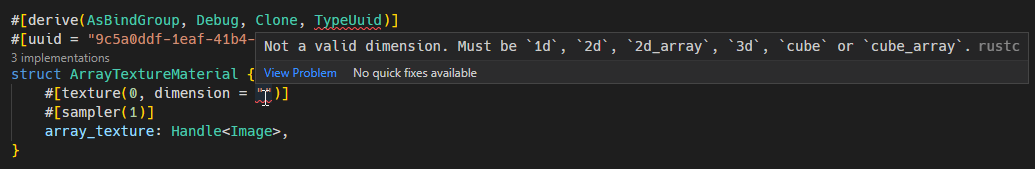
Updated the array_texture example to demonstrate the new changes.
## New AsBindGroup attribute options
### `#[texture(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|-------------- |---------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| dimension = "..." | `"1d"`, `"2d"`, `"2d_array"`, `"3d"`, `"cube"`, `"cube_array"` | `"2d"` |
| sample_type = "..." | `"float"`, `"depth"`, `"s_int"` or `"u_int"` | `"float"` |
| filterable = ... | `true`, `false` | `true` |
| multisampled = ... | `true`, `false` | `false` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[texture(0, dimension = "2d_array", visibility(vertex, fragment))]`
### `#[sampler(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|----------- |--------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| sampler_type = "..." | `"filtering"`, `"non_filtering"`, `"comparison"`. | `"filtering"` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[sampler(0, sampler_type = "filtering", visibility(vertex, fragment)]`
## Changelog
- Added more options to `#[texture(...)]` and `#[sampler(...)]` attributes, supporting more kinds of materials. See above for details.
- Upgraded IDE and compile-time error messages.
- Updated array_texture example using the new options.
2022-07-19 22:05:43 +00:00
|
|
|
use syn::{parse_macro_input, DeriveInput};
|
2022-05-30 18:36:03 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pub(crate) fn bevy_render_path() -> syn::Path {
|
|
|
|
|
BevyManifest::default()
|
|
|
|
|
.maybe_get_path("bevy_render")
|
|
|
|
|
// NOTE: If the derivation is within bevy_render, then we need to return 'crate'
|
|
|
|
|
.unwrap_or_else(|| BevyManifest::parse_str("crate"))
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[proc_macro_derive(ExtractResource)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn derive_extract_resource(input: TokenStream) -> TokenStream {
|
|
|
|
|
extract_resource::derive_extract_resource(input)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-01-30 18:12:16 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Implements `ExtractComponent` trait for a component.
|
|
|
|
|
/// The component must implement [`Clone`].
|
|
|
|
|
/// The component will be extracted into the render world via cloning.
|
|
|
|
|
/// Note that this only enables extraction of the component, it does not execute the extraction.
|
|
|
|
|
/// See `ExtractComponentPlugin` to actually perform the extraction.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// If you only want to extract a component conditionally, you may use the `extract_component_filter` attribute.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// # Example
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```no_compile
|
|
|
|
|
/// use bevy_ecs::component::Component;
|
|
|
|
|
/// use bevy_render_macros::ExtractComponent;
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[derive(Component, Clone, ExtractComponent)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[extract_component_filter(With<Camera>)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// pub struct Foo {
|
|
|
|
|
/// pub should_foo: bool,
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// // Without a filter (unconditional).
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[derive(Component, Clone, ExtractComponent)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// pub struct Bar {
|
|
|
|
|
/// pub should_bar: bool,
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```
|
|
|
|
|
#[proc_macro_derive(ExtractComponent, attributes(extract_component_filter))]
|
|
|
|
|
pub fn derive_extract_component(input: TokenStream) -> TokenStream {
|
|
|
|
|
extract_component::derive_extract_component(input)
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-01-09 18:50:55 +00:00
|
|
|
#[proc_macro_derive(
|
|
|
|
|
AsBindGroup,
|
2024-01-21 18:47:13 +00:00
|
|
|
attributes(uniform, storage_texture, texture, sampler, bind_group_data, storage)
|
2023-01-09 18:50:55 +00:00
|
|
|
)]
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
pub fn derive_as_bind_group(input: TokenStream) -> TokenStream {
|

Derive AsBindGroup Improvements: Better errors, more options, update examples (#5364)
# Objective
- Provide better compile-time errors and diagnostics.
- Add more options to allow more textures types and sampler types.
- Update array_texture example to use upgraded AsBindGroup derive macro.
## Solution
Split out the parsing of the inner struct/field attributes (the inside part of a `#[foo(...)]` attribute) for better clarity
Parse the binding index for all inner attributes, as it is part of all attributes (`#[foo(0, ...)`), then allow each attribute implementer to parse the rest of the attribute metadata as needed. This should make it very trivial to extend/change if needed in the future.
Replaced invocations of `panic!` with the `syn::Error` type, providing fine-grained errors that retains span information. This provides much nicer compile-time errors, and even better IDE errors.

Updated the array_texture example to demonstrate the new changes.
## New AsBindGroup attribute options
### `#[texture(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|-------------- |---------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| dimension = "..." | `"1d"`, `"2d"`, `"2d_array"`, `"3d"`, `"cube"`, `"cube_array"` | `"2d"` |
| sample_type = "..." | `"float"`, `"depth"`, `"s_int"` or `"u_int"` | `"float"` |
| filterable = ... | `true`, `false` | `true` |
| multisampled = ... | `true`, `false` | `false` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[texture(0, dimension = "2d_array", visibility(vertex, fragment))]`
### `#[sampler(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|----------- |--------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| sampler_type = "..." | `"filtering"`, `"non_filtering"`, `"comparison"`. | `"filtering"` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[sampler(0, sampler_type = "filtering", visibility(vertex, fragment)]`
## Changelog
- Added more options to `#[texture(...)]` and `#[sampler(...)]` attributes, supporting more kinds of materials. See above for details.
- Upgraded IDE and compile-time error messages.
- Updated array_texture example using the new options.
2022-07-19 22:05:43 +00:00
|
|
|
let input = parse_macro_input!(input as DeriveInput);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
as_bind_group::derive_as_bind_group(input).unwrap_or_else(|err| err.to_compile_error().into())
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|