2020-08-29 00:08:51 +00:00
|
|
|
[package]
|
|
|
|
|
name = "bevy_utils"
|
2023-07-10 21:19:27 +00:00
|
|
|
version = "0.12.0-dev"
|
2021-10-27 00:12:14 +00:00
|
|
|
edition = "2021"
|
2020-08-29 00:08:51 +00:00
|
|
|
description = "A collection of utils for Bevy Engine"
|
|
|
|
|
homepage = "https://bevyengine.org"
|
|
|
|
|
repository = "https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy"
|
2021-07-23 21:11:51 +00:00
|
|
|
license = "MIT OR Apache-2.0"
|
2020-08-29 00:08:51 +00:00
|
|
|
keywords = ["bevy"]
|
|
|
|
|
|

Introduce detailed_trace macro, use in TrackedRenderPass (#7639)
Profiles show that in extremely hot loops, like the draw loops in the renderer, invoking the trace! macro has noticeable overhead, even if the trace log level is not enabled.
Solve this by introduce a 'wrapper' detailed_trace macro around trace, that wraps the trace! log statement in a trivially false if statement unless a cargo feature is enabled
# Objective
- Eliminate significant overhead observed with trace-level logging in render hot loops, even when trace log level is not enabled.
- This is an alternative solution to the one proposed in #7223
## Solution
- Introduce a wrapper around the `trace!` macro called `detailed_trace!`. This macro wraps the `trace!` macro with an if statement that is conditional on a new cargo feature, `detailed_trace`. When the feature is not enabled (the default), then the if statement is trivially false and should be optimized away at compile time.
- Convert the observed hot occurrences of trace logging in `TrackedRenderPass` with this new macro.
Testing the results of
```
cargo run --profile stress-test --features bevy/trace_tracy --example many_cubes -- spheres
```
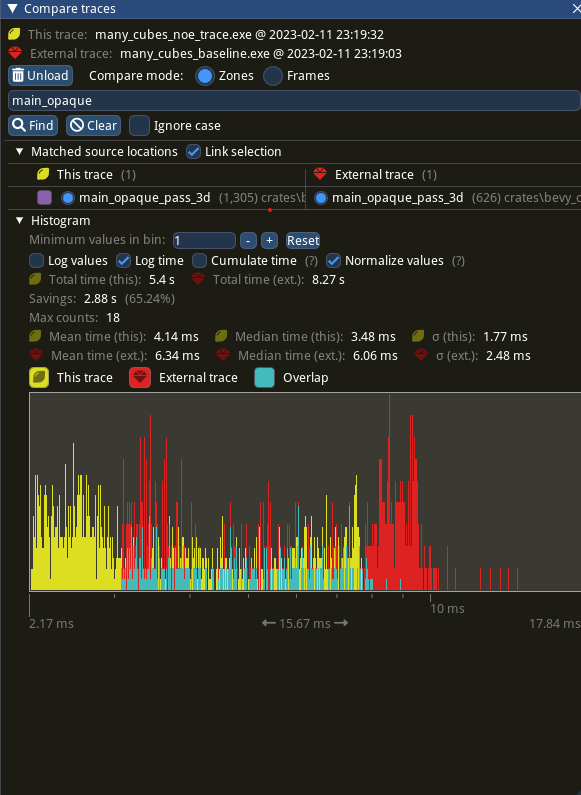
shows significant improvement of the `main_opaque_pass_3d` of the renderer, a median time decrease from 6.0ms to 3.5ms.
---
## Changelog
- For performance reasons, some detailed renderer trace logs now require the use of cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to setting the log level to `TRACE` in order to be shown.
## Migration Guide
- Some detailed bevy trace events now require the use of the cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to enabling `TRACE` level logging to view. Should you wish to see these logs, please compile your code with the bevy feature `detailed_trace`. Currently, the only logs that are affected are the renderer logs pertaining to `TrackedRenderPass` functions
2023-02-13 18:20:27 +00:00
|
|
|
[features]
|
|
|
|
|
detailed_trace = []
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-08-29 00:08:51 +00:00
|
|
|
[dependencies]
|
2023-05-23 02:17:07 +00:00
|
|
|
ahash = "0.8.3"
|
2022-04-27 19:08:11 +00:00
|
|
|
tracing = { version = "0.1", default-features = false, features = ["std"] }
|
2020-11-22 00:38:24 +00:00
|
|
|
instant = { version = "0.1", features = ["wasm-bindgen"] }
|
2022-05-30 17:26:23 +00:00
|
|
|
uuid = { version = "1.1", features = ["v4", "serde"] }
|
2023-06-21 13:04:44 +00:00
|
|
|
hashbrown = { version = "0.14", features = ["serde"] }
|
2023-10-25 19:20:17 +00:00
|
|
|
bevy_utils_proc_macros = { version = "0.12.0-dev", path = "macros" }
|
2023-01-17 01:39:17 +00:00
|
|
|
petgraph = "0.6"
|
|
|
|
|
thiserror = "1.0"
|

Automatic batching/instancing of draw commands (#9685)
# Objective
- Implement the foundations of automatic batching/instancing of draw
commands as the next step from #89
- NOTE: More performance improvements will come when more data is
managed and bound in ways that do not require rebinding such as mesh,
material, and texture data.
## Solution
- The core idea for batching of draw commands is to check whether any of
the information that has to be passed when encoding a draw command
changes between two things that are being drawn according to the sorted
render phase order. These should be things like the pipeline, bind
groups and their dynamic offsets, index/vertex buffers, and so on.
- The following assumptions have been made:
- Only entities with prepared assets (pipelines, materials, meshes) are
queued to phases
- View bindings are constant across a phase for a given draw function as
phases are per-view
- `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` is the only system that performs this
batching and has sole responsibility for preparing the per-object data.
As such the mesh binding and dynamic offsets are assumed to only vary as
a result of the `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` system, e.g. due to
having to split data across separate uniform bindings within the same
buffer due to the maximum uniform buffer binding size.
- Implement `GpuArrayBuffer` for `Mesh2dUniform` to store Mesh2dUniform
in arrays in GPU buffers rather than each one being at a dynamic offset
in a uniform buffer. This is the same optimisation that was made for 3D
not long ago.
- Change batch size for a range in `PhaseItem`, adding API for getting
or mutating the range. This is more flexible than a size as the length
of the range can be used in place of the size, but the start and end can
be otherwise whatever is needed.
- Add an optional mesh bind group dynamic offset to `PhaseItem`. This
avoids having to do a massive table move just to insert
`GpuArrayBufferIndex` components.
## Benchmarks
All tests have been run on an M1 Max on AC power. `bevymark` and
`many_cubes` were modified to use 1920x1080 with a scale factor of 1. I
run a script that runs a separate Tracy capture process, and then runs
the bevy example with `--features bevy_ci_testing,trace_tracy` and
`CI_TESTING_CONFIG=../benchmark.ron` with the contents of
`../benchmark.ron`:
```rust
(
exit_after: Some(1500)
)
```
...in order to run each test for 1500 frames.
The recent changes to `many_cubes` and `bevymark` added reproducible
random number generation so that with the same settings, the same rng
will occur. They also added benchmark modes that use a fixed delta time
for animations. Combined this means that the same frames should be
rendered both on main and on the branch.
The graphs compare main (yellow) to this PR (red).
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark`
<img width="1411" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 42 10"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/2088716a-c918-486c-8129-090b26fd2bc4">
The mesh and material are the same for all instances. This is basically
the best case for the initial batching implementation as it results in 1
draw for the ~11.7k visible meshes. It gives a ~30% reduction in median
frame time.
The 1000th frame is identical using the flip tool:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4615 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1404" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 45 18"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/5ee9c447-5bd2-45c6-9706-ac5ff8916daf">
This run uses 10 different materials by varying their textures. The
materials are randomly selected, and there is no sorting by material
bind group for opaque 3D so any batching is 'random'. The PR produces a
~5% reduction in median frame time. If we were to sort the opaque phase
by the material bind group, then this should be a lot faster. This
produces about 10.5k draws for the 11.7k visible entities. This makes
sense as randomly selecting from 10 materials gives a chance that two
adjacent entities randomly select the same material and can be batched.
The 1000th frame is identical in flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4537 seconds
```
### 3D Mesh `many_cubes --benchmark --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1394" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 48 44"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/f02a816b-a444-4c18-a96a-63b5436f3b7f">
This run varies the material data per instance by randomly-generating
its colour. This is the worst case for batching and that it performs
about the same as `main` is a good thing as it demonstrates that the
batching has minimal overhead when dealing with ~11k visible mesh
entities.
The 1000th frame is identical according to flip:

```
Mean: 0.000000
Weighted median: 0.000000
1st weighted quartile: 0.000000
3rd weighted quartile: 0.000000
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.000000
Evaluation time: 0.4568 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d`
<img width="1412" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 23 59 56"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/cb02ae07-237b-4646-ae9f-fda4dafcbad4">
This spawns 160 waves of 1000 quad meshes that are shaded with
ColorMaterial. Each wave has a different material so 160 waves currently
should result in 160 batches. This results in a 50% reduction in median
frame time.
Capturing a screenshot of the 1000th frame main vs PR gives:

```
Mean: 0.001222
Weighted median: 0.750432
1st weighted quartile: 0.453494
3rd weighted quartile: 0.969758
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.990296
Evaluation time: 0.4255 seconds
```
So they seem to produce the same results. I also double-checked the
number of draws. `main` does 160000 draws, and the PR does 160, as
expected.
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 09 22"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/4358da2e-ce32-4134-82df-3ab74c40849c">
This generates 10 textures and generates materials for each of those and
then selects one material per wave. The median frame time is reduced by
50%. Similar to the plain run above, this produces 160 draws on the PR
and 160000 on `main` and the 1000th frame is identical (ignoring the fps
counter text overlay).

```
Mean: 0.002877
Weighted median: 0.964980
1st weighted quartile: 0.668871
3rd weighted quartile: 0.982749
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.992377
Evaluation time: 0.4301 seconds
```
### 2D Mesh `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
mesh2d --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 00 13 53"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/b2198b18-3439-47ad-919a-cdabe190facb">
This creates unique materials per instance by randomly-generating the
material's colour. This is the worst case for 2D batching. Somehow, this
PR manages a 7% reduction in median frame time. Both main and this PR
issue 160000 draws.
The 1000th frame is the same:

```
Mean: 0.001214
Weighted median: 0.937499
1st weighted quartile: 0.635467
3rd weighted quartile: 0.979085
Min: 0.000000
Max: 0.988971
Evaluation time: 0.4462 seconds
```
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite`
<img width="1396" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 21 12"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/8b31e915-d6be-4cac-abf5-c6a4da9c3d43">
This just spawns 160 waves of 1000 sprites. There should be and is no
notable difference between main and the PR.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --material-texture-count 10`
<img width="1389" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 36 08"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/45fe8d6d-c901-4062-a349-3693dd044413">
This spawns the sprites selecting a texture at random per instance from
the 10 generated textures. This has no significant change vs main and
shouldn't.
### 2D Sprite `bevymark --benchmark --waves 160 --per-wave 1000 --mode
sprite --vary-per-instance`
<img width="1401" alt="Screenshot 2023-09-04 at 12 29 52"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/302146/762c5c60-352e-471f-8dbe-bbf10e24ebd6">
This sets the sprite colour as being unique per instance. This can still
all be drawn using one batch. There should be no difference but the PR
produces median frame times that are 4% higher. Investigation showed no
clear sources of cost, rather a mix of give and take that should not
happen. It seems like noise in the results.
### Summary
| Benchmark | % change in median frame time |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| many_cubes | 🟩 -30% |
| many_cubes 10 materials | 🟩 -5% |
| many_cubes unique materials | 🟩 ~0% |
| bevymark mesh2d | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d 10 materials | 🟩 -50% |
| bevymark mesh2d unique materials | 🟩 -7% |
| bevymark sprite | 🟥 2% |
| bevymark sprite 10 materials | 🟥 0.6% |
| bevymark sprite unique materials | 🟥 4.1% |
---
## Changelog
- Added: 2D and 3D mesh entities that share the same mesh and material
(same textures, same data) are now batched into the same draw command
for better performance.
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nico@nicopap.ch>
2023-09-21 22:12:34 +00:00
|
|
|
nonmax = "0.5"
|
2020-10-21 22:55:35 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[target.'cfg(target_arch = "wasm32")'.dependencies]
|
2023-10-25 19:20:17 +00:00
|
|
|
getrandom = { version = "0.2.0", features = ["js"] }
|