2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
#ifdef TONEMAP_IN_SHADER
|
|
|
|
|
#import bevy_core_pipeline::tonemapping
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
|

improve shader import model (#5703)
# Objective
operate on naga IR directly to improve handling of shader modules.
- give codespan reporting into imported modules
- allow glsl to be used from wgsl and vice-versa
the ultimate objective is to make it possible to
- provide user hooks for core shader functions (to modify light
behaviour within the standard pbr pipeline, for example)
- make automatic binding slot allocation possible
but ... since this is already big, adds some value and (i think) is at
feature parity with the existing code, i wanted to push this now.
## Solution
i made a crate called naga_oil (https://github.com/robtfm/naga_oil -
unpublished for now, could be part of bevy) which manages modules by
- building each module independantly to naga IR
- creating "header" files for each supported language, which are used to
build dependent modules/shaders
- make final shaders by combining the shader IR with the IR for imported
modules
then integrated this into bevy, replacing some of the existing shader
processing stuff. also reworked examples to reflect this.
## Migration Guide
shaders that don't use `#import` directives should work without changes.
the most notable user-facing difference is that imported
functions/variables/etc need to be qualified at point of use, and
there's no "leakage" of visible stuff into your shader scope from the
imports of your imports, so if you used things imported by your imports,
you now need to import them directly and qualify them.
the current strategy of including/'spreading' `mesh_vertex_output`
directly into a struct doesn't work any more, so these need to be
modified as per the examples (e.g. color_material.wgsl, or many others).
mesh data is assumed to be in bindgroup 2 by default, if mesh data is
bound into bindgroup 1 instead then the shader def `MESH_BINDGROUP_1`
needs to be added to the pipeline shader_defs.
2023-06-27 00:29:22 +00:00
|
|
|
#import bevy_render::view View
|
2023-02-11 17:55:18 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@group(0) @binding(0)
|
2021-10-08 19:55:24 +00:00
|
|
|
var<uniform> view: View;
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
struct VertexOutput {
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@location(0) uv: vec2<f32>,
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.
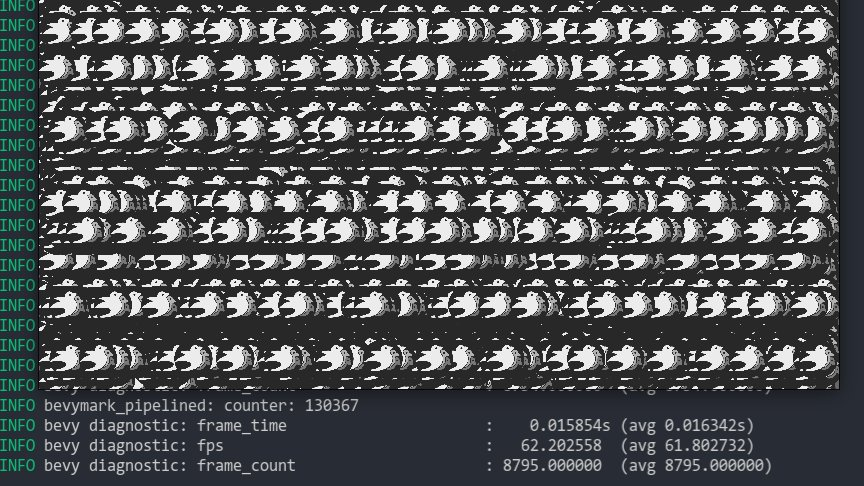
Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#ifdef COLORED
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@location(1) color: vec4<f32>,
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#endif
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@builtin(position) position: vec4<f32>,
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@vertex
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
fn vertex(
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@location(0) vertex_position: vec3<f32>,
|
|
|
|
|
@location(1) vertex_uv: vec2<f32>,
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#ifdef COLORED
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@location(2) vertex_color: vec4<f32>,
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#endif
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
) -> VertexOutput {
|
|
|
|
|
var out: VertexOutput;
|
|
|
|
|
out.uv = vertex_uv;
|
|
|
|
|
out.position = view.view_proj * vec4<f32>(vertex_position, 1.0);
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#ifdef COLORED
|
2022-03-30 19:38:24 +00:00
|
|
|
out.color = vertex_color;
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#endif
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
return out;
|
2022-06-14 00:32:33 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@group(1) @binding(0)
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
var sprite_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@group(1) @binding(1)
|
2021-06-28 22:36:50 +00:00
|
|
|
var sprite_sampler: sampler;
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
@fragment
|
|
|
|
|
fn fragment(in: VertexOutput) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
|
2022-06-14 00:32:33 +00:00
|
|
|
var color = textureSample(sprite_texture, sprite_sampler, in.uv);
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
#ifdef COLORED
|
|
|
|
|
color = in.color * color;
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#ifdef TONEMAP_IN_SHADER
|

improve shader import model (#5703)
# Objective
operate on naga IR directly to improve handling of shader modules.
- give codespan reporting into imported modules
- allow glsl to be used from wgsl and vice-versa
the ultimate objective is to make it possible to
- provide user hooks for core shader functions (to modify light
behaviour within the standard pbr pipeline, for example)
- make automatic binding slot allocation possible
but ... since this is already big, adds some value and (i think) is at
feature parity with the existing code, i wanted to push this now.
## Solution
i made a crate called naga_oil (https://github.com/robtfm/naga_oil -
unpublished for now, could be part of bevy) which manages modules by
- building each module independantly to naga IR
- creating "header" files for each supported language, which are used to
build dependent modules/shaders
- make final shaders by combining the shader IR with the IR for imported
modules
then integrated this into bevy, replacing some of the existing shader
processing stuff. also reworked examples to reflect this.
## Migration Guide
shaders that don't use `#import` directives should work without changes.
the most notable user-facing difference is that imported
functions/variables/etc need to be qualified at point of use, and
there's no "leakage" of visible stuff into your shader scope from the
imports of your imports, so if you used things imported by your imports,
you now need to import them directly and qualify them.
the current strategy of including/'spreading' `mesh_vertex_output`
directly into a struct doesn't work any more, so these need to be
modified as per the examples (e.g. color_material.wgsl, or many others).
mesh data is assumed to be in bindgroup 2 by default, if mesh data is
bound into bindgroup 1 instead then the shader def `MESH_BINDGROUP_1`
needs to be added to the pipeline shader_defs.
2023-06-27 00:29:22 +00:00
|
|
|
color = bevy_core_pipeline::tonemapping::tone_mapping(color, view.color_grading);
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
|

Sprite Batching (#3060)
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.

Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
2021-11-04 20:28:53 +00:00
|
|
|
return color;
|
2022-06-14 00:32:33 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|